Grapho-epitaxy dsa process with dimension control of template pattern
a grapho-epitaxy and template pattern technology, applied in the field of semiconductor processing, can solve the problems of high defect level, large resist feature size, and inability to form high-resolution mandrels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
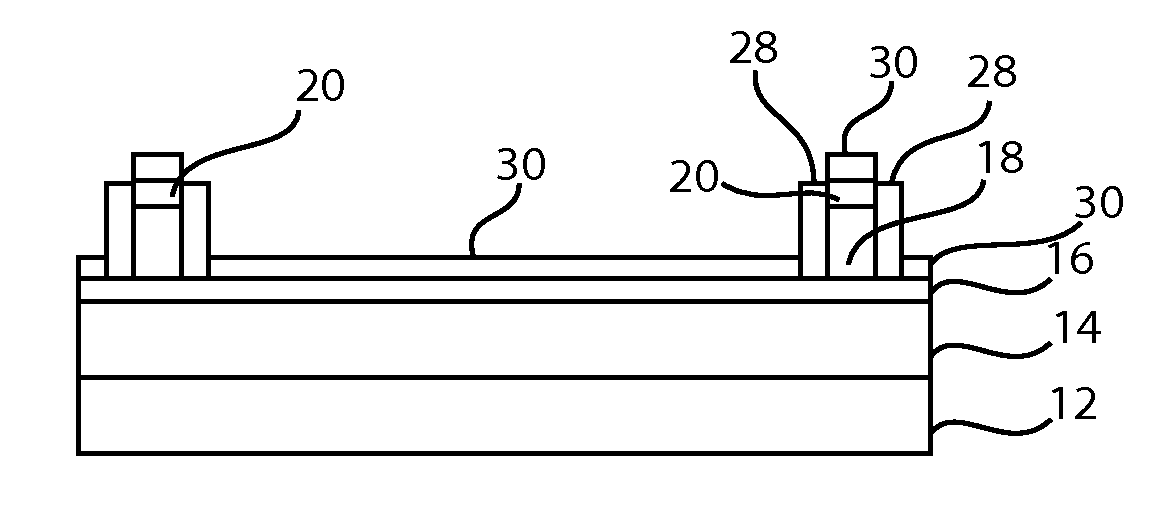
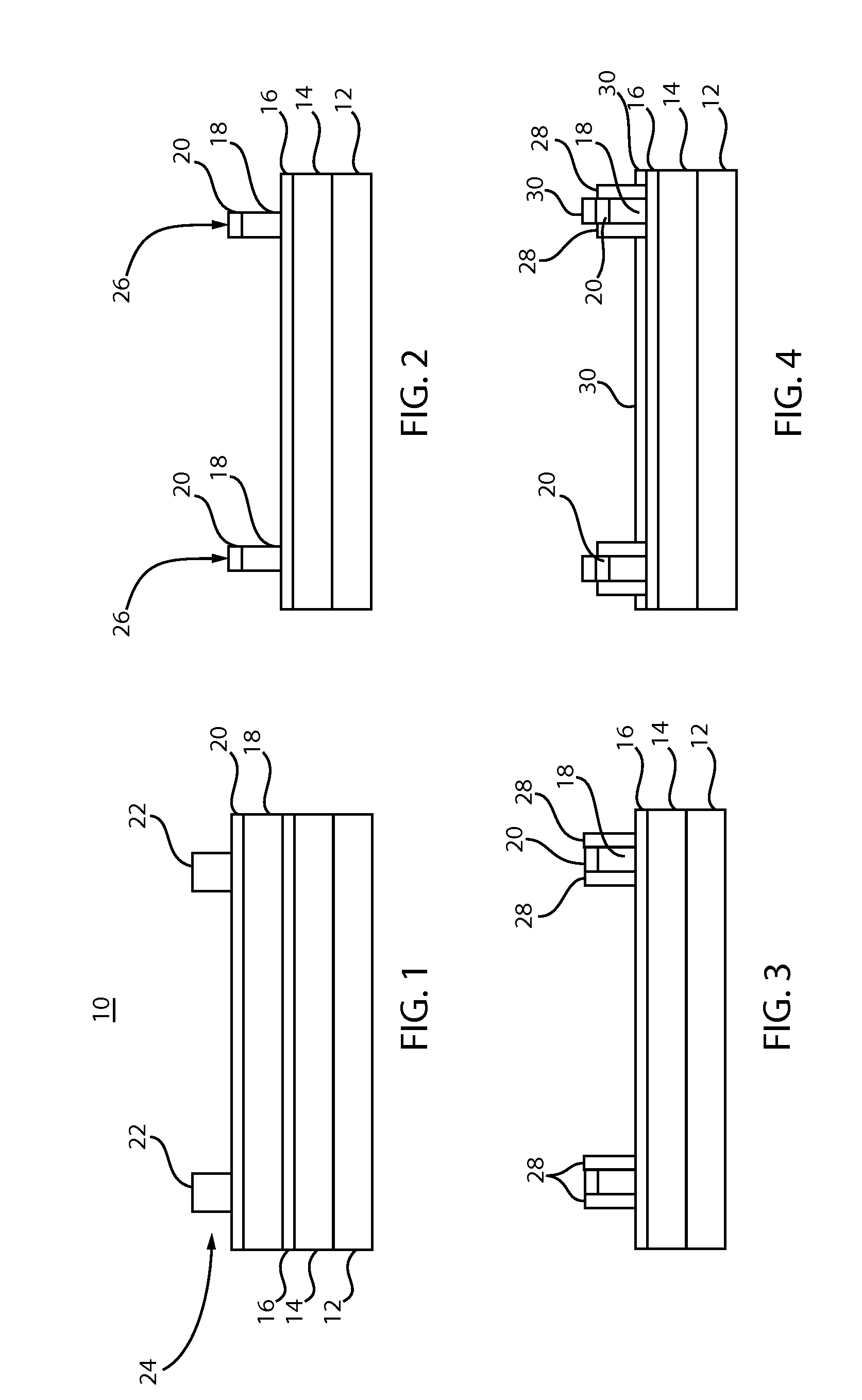
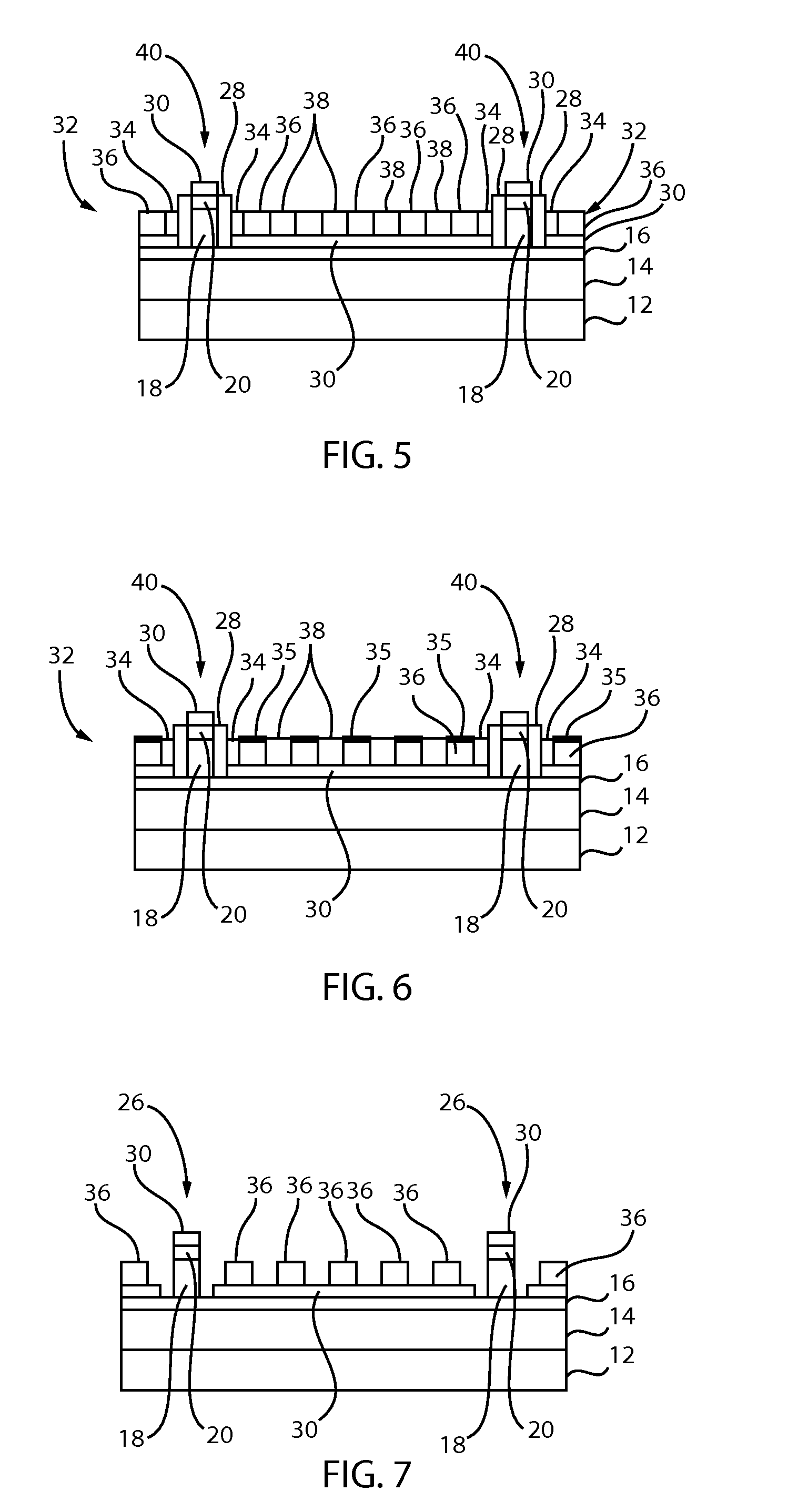
[0020]The present principles provide methods for forming templates with improved dimensional control. The templates may be provided for directed self-assembly (DSA) applications. In particularly useful embodiments, a dielectric stack is etched to form template lines. A substantially unreactive spacer is formed on sides of the template lines, which is employed to provide critical dimension control of the template line. DSA material is introduced between the spacers of the template lines and processed. A reactive ion etch (RIE) process may be employed to remove the spacers to provide an image reversed etch pattern for further etching, e.g., of a substrate or underlying layers.
[0021]In accordance with the present principles, an optical planarization layer (OPL) / silicon antireflection coating (ARC) stack may be patterned and combined with unreactive spacers (e.g., formed from a hydrophobic material with minimal hydroxyl groups) along sides of patterned stack. The patterned stack with sp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| feature sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com