Method of manufacture a sliding bearing
a technology of sliding bearings and sliding plates, which is applied in the direction of refractive reflectors, mechanical devices, optical elements, etc., can solve the problems of high hard particulate concentration, difficult production of composite layers with such high concentration, and significant wear during the start-up phas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
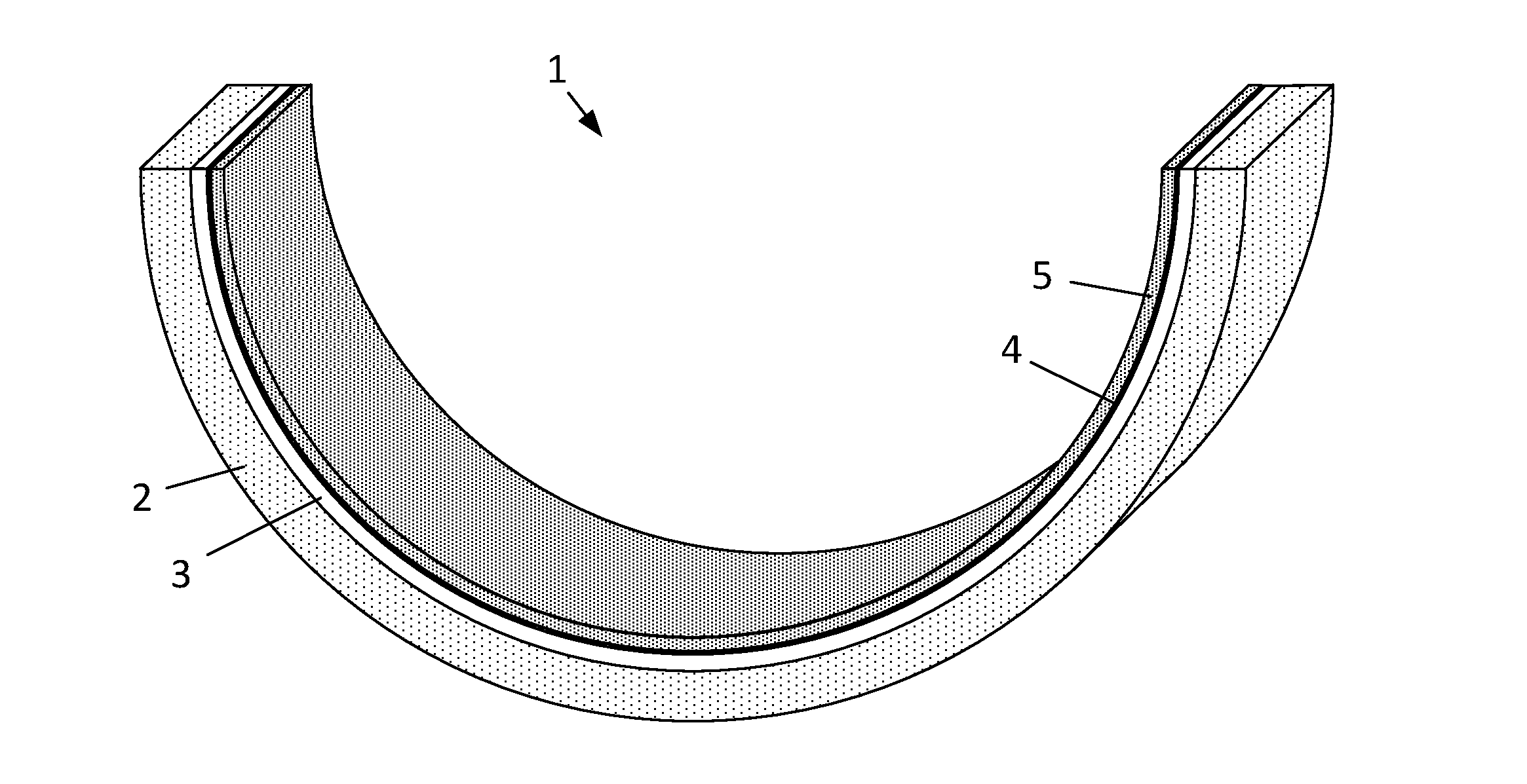
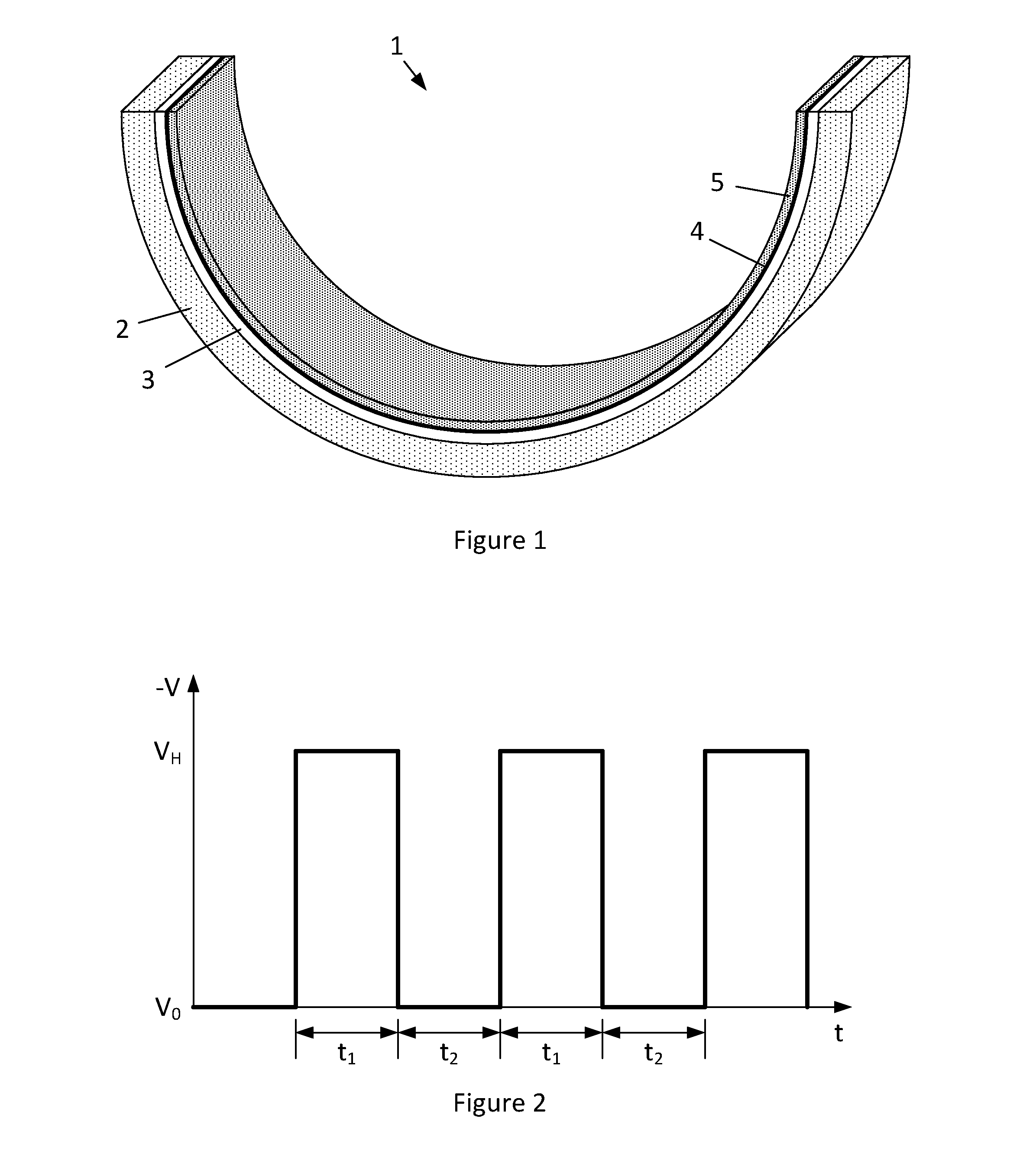
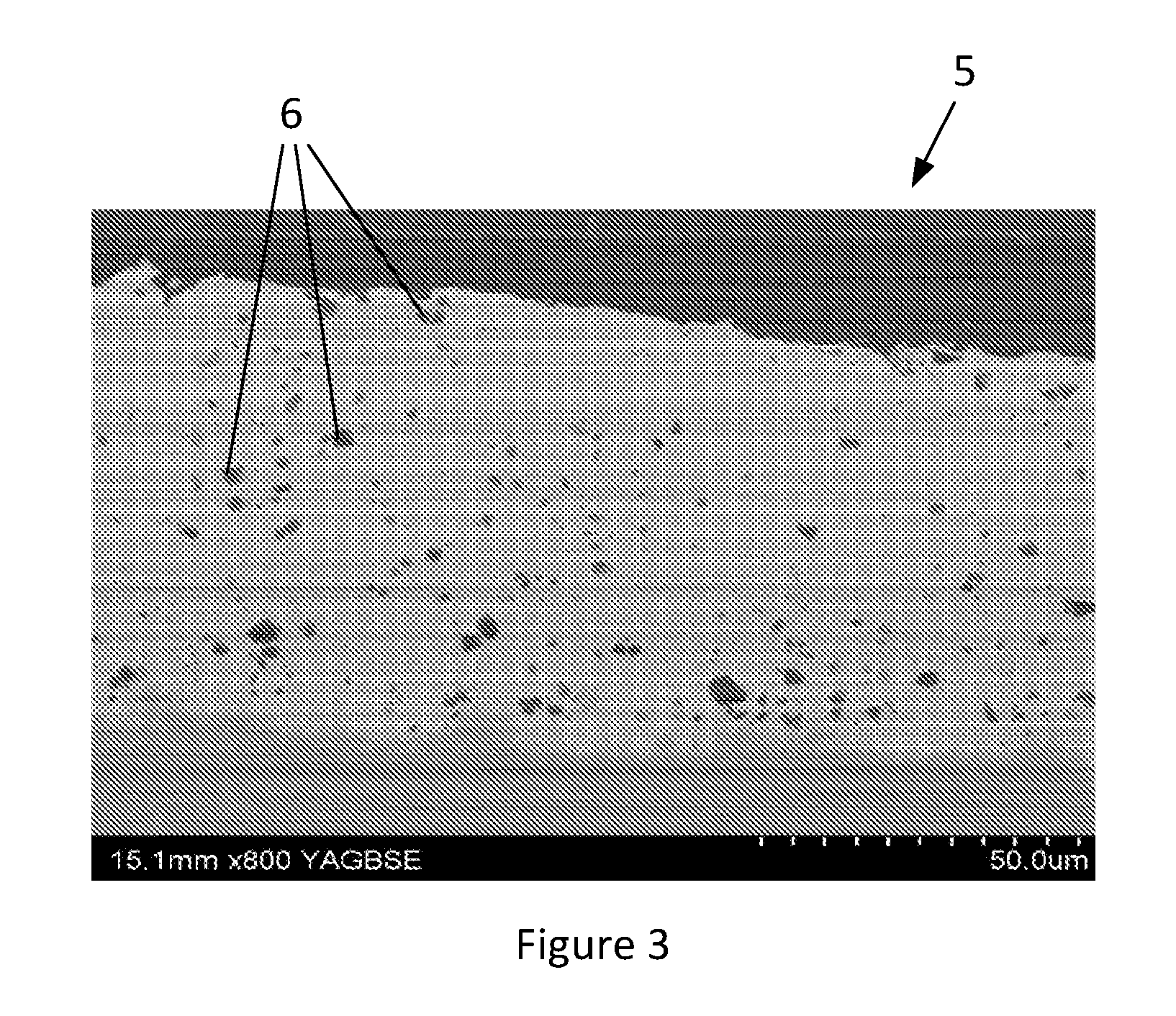
[0035]FIG. 1 illustrates a hollow generally semi-cylindrical bearing shell 1 having a steel backing layer 2, a copper-based alloy lining layer 3, a nickel or cobalt diffusion barrier 4, and a composite overlay layer 5 of hard particulate incorporated into a Sn matrix.
[0036]The bearing shell onto which the composite layer is deposited is provided as a cathode in a bath containing a suspension of hard particulate in an electroplating electrolyte, with an anode formed of a material corresponding to the metallic matrix, e.g. a high purity tin anode.
[0037]The electrolyte is a lead-free, tin methanesulfonic acid (MSA) electrolyte (tin ions in methanesulfonic acid), which may comprise performance enhancing additives, such as brightener and anti-foaming agent. For example the electrolyte may be the Bright Tin GBF 30 acidic electrolyte system from Schlötter® Galvanotechnik, which uses a recipe of Schlötter's ingredients consisting of 13.0 litres Tin Concentrate FS 20 (which contains 310 g / l ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| peak current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cathodic current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com