Tailored recombinase for recombining asymmetric target sites in a plurality of retrovirus strains
a technology of retrovirus and target site, which is applied in the direction of transferases, peptide/protein ingredients, directed macromolecular evolution, etc., can solve the problems of restricted use of these enzymes and limited library screening in directed protein evolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identifying Asymmetric Target Sequences Present in a Plurality of Strains
[0185]The asymmetric target sequences were identified by a method divided in 3 steps: generation of a position weight matrix based on known recognition sites of a recombinase, provision of genomic sequences that are to be searched for recognition sites, and a binary search for potential target sites in the provided sequences and scoring of the resulting hits based on the initial position weight matrix, wherein the nucleotides are transformed into binary space.
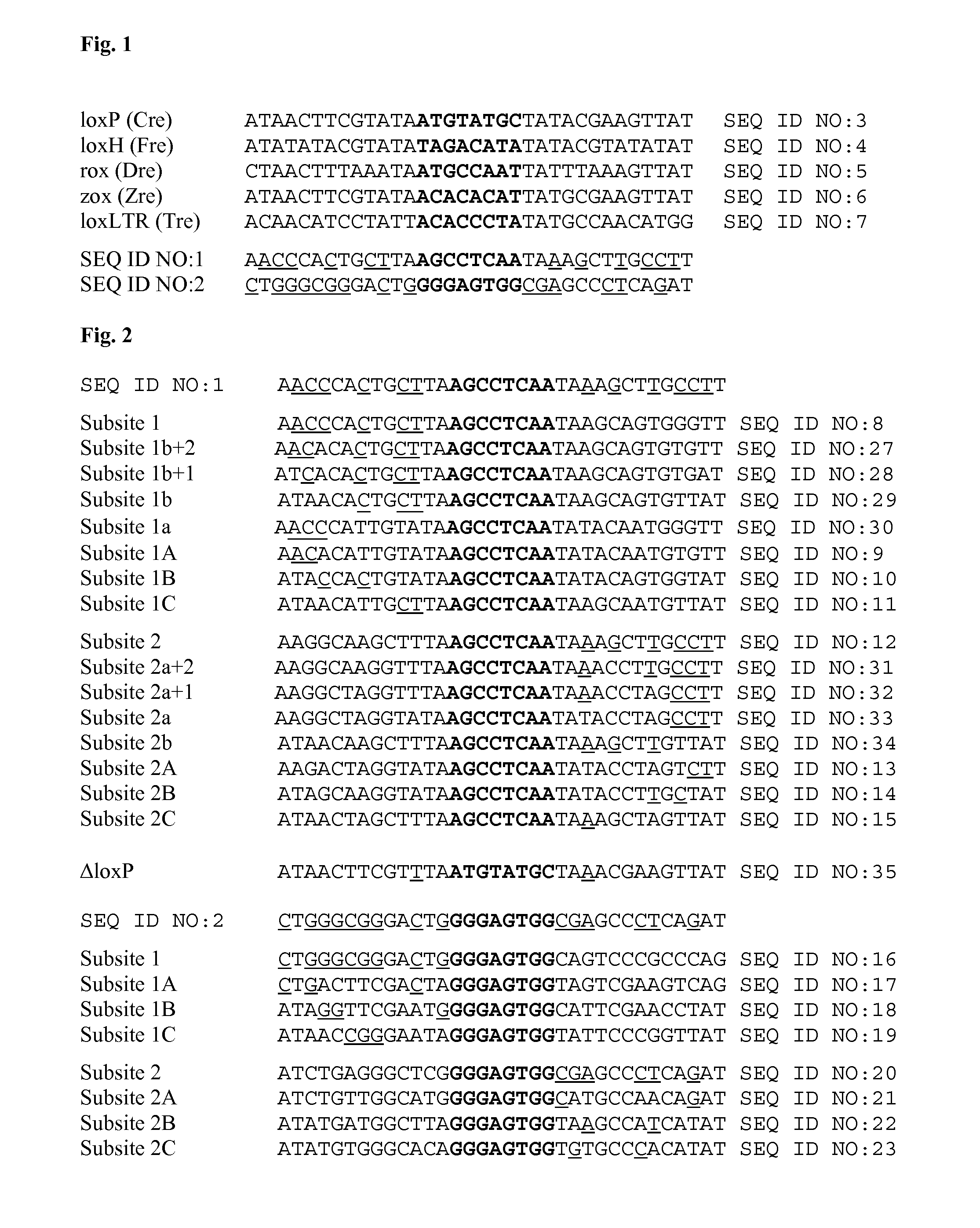
[0186]SEQ ID NO:1 was found to be present in 348 of 379 HIV-1 strains of subtype B. Furthermore, SEQ ID NO:1 was found to be present in 32 of 40 HIV-1 strains of subtype A. It is located in the R region of the LTR.
[0187]SEQ ID NO:2 was found to be present in 288 of 379 HIV-1 strains of subtype B. SEQ ID NO:2 was not found to be present in any of the searched 40 HIV-1 strains of subtype A. It is located in the U3 region of the LTR.
example 2
Generation of a Tailored Recombinase Recognising and Recombining an Asymmetric Target Sequence within the LTR of HIV-1
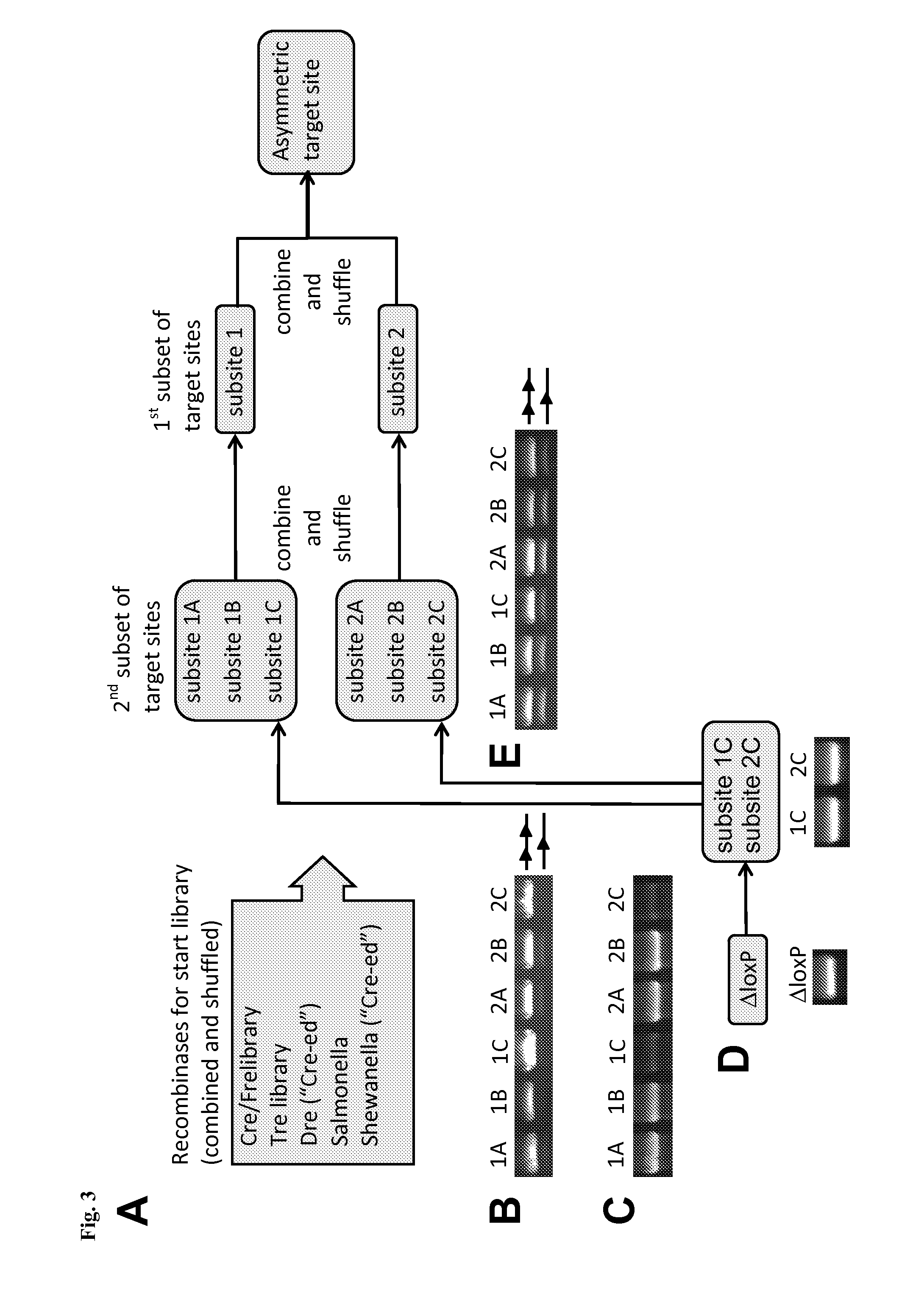
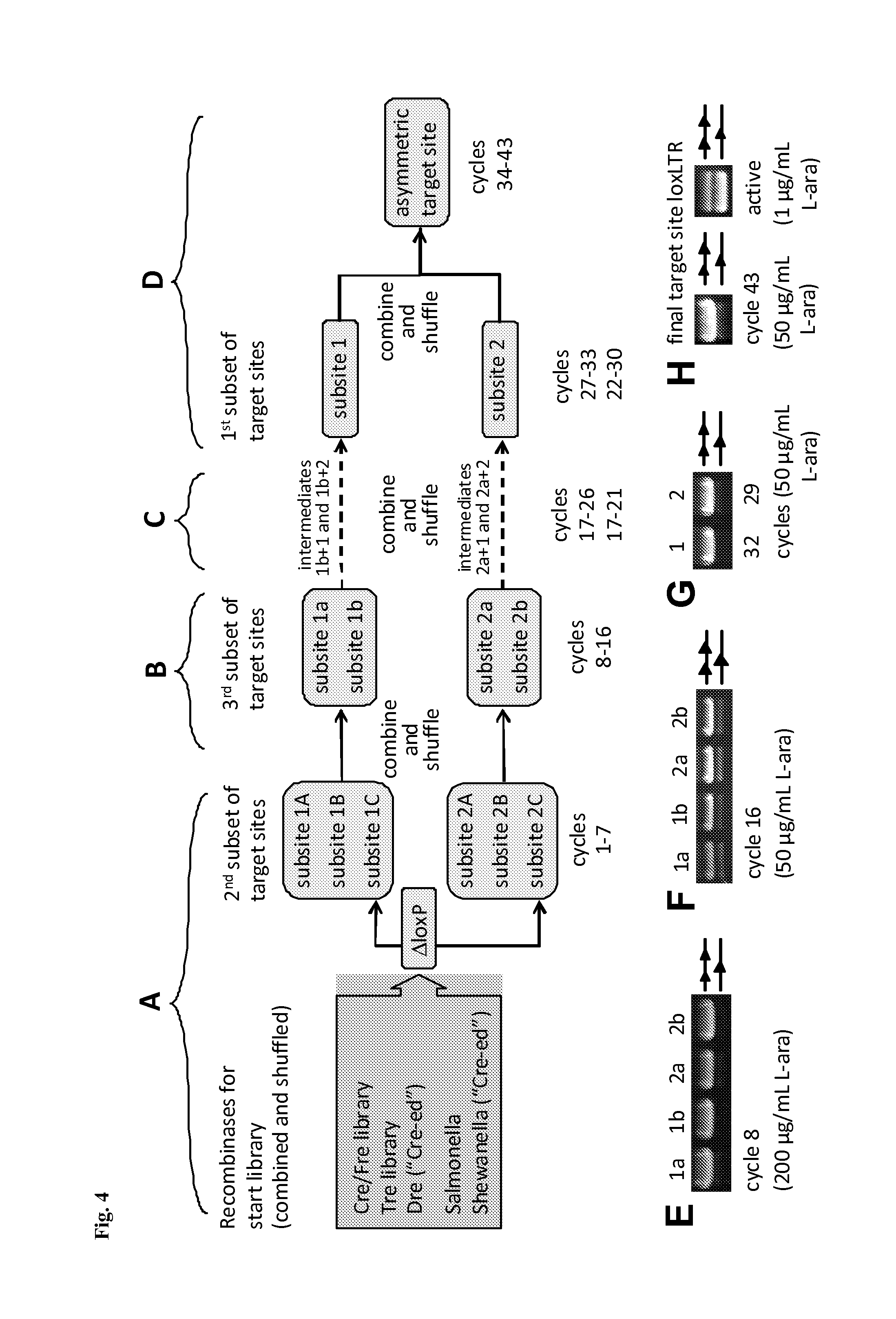
[0188]To start the evolution process, HIV-1 LTR sequences were selected which are highly conserved among HIV-1 strains. SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 were found to comply with these criteria and to represent asymmetric target sequences for which a tailored recombinase can be selected. In the following, the generation of a tailored recombinase recognizing SEQ ID NO:1 is described in detail.
[0189]A simplified outline of the evolution strategy and the progress made to date is outlined in FIG. 2. Overall, the evolution of a new Tre recombinase specifically recognizing the desired target sequence was conducted as disclosed in WO 2008 / 083931 and described by Sarkar et al. (Sarkar et al., Science 2007).
[0190]The start library of recombinases was generated by pooling and family shuffling Cre and several known Cre-like recombinases, namely a library of Cre mutants (Cre / Fre) (Bu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com