Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and non-transitory storage medium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
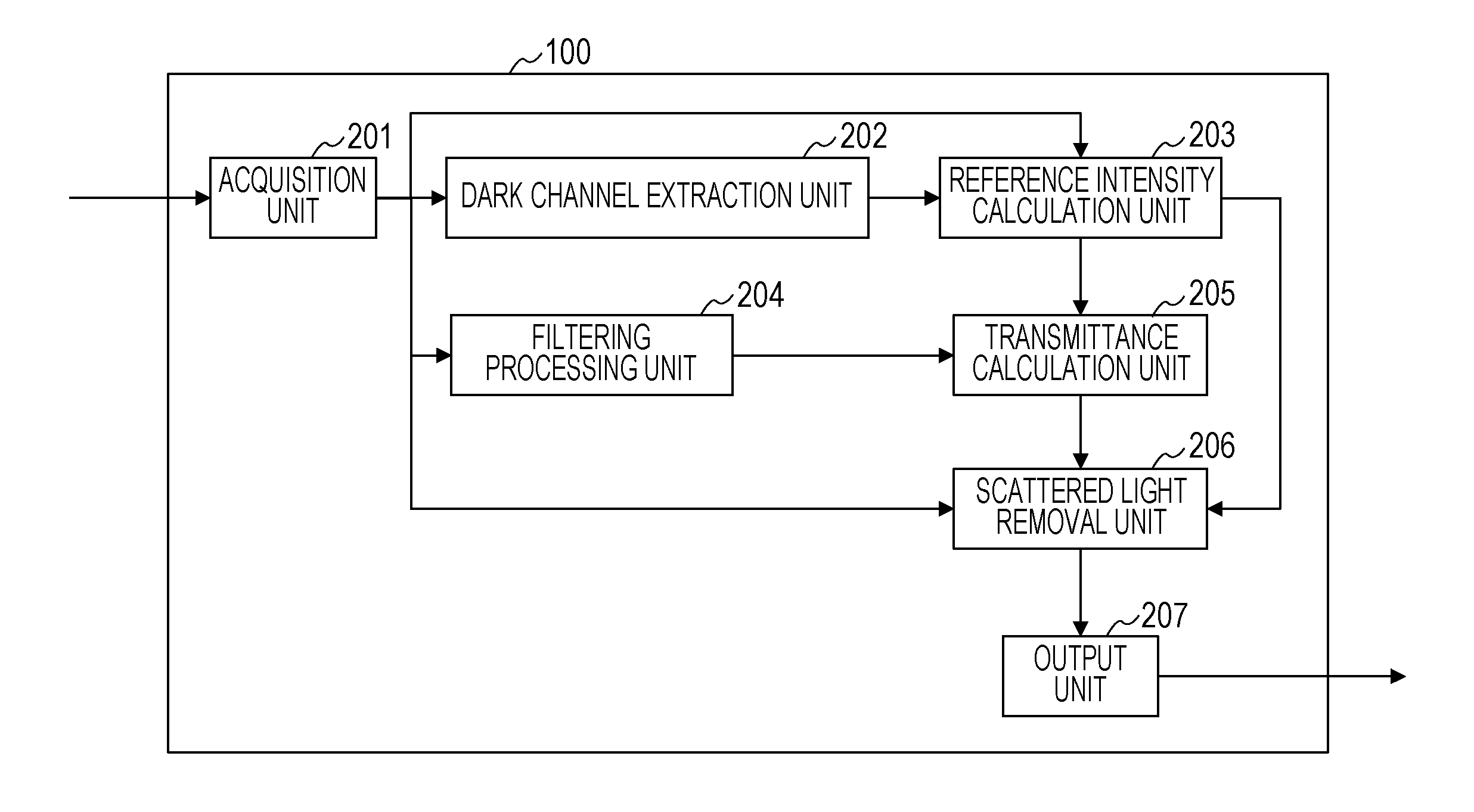
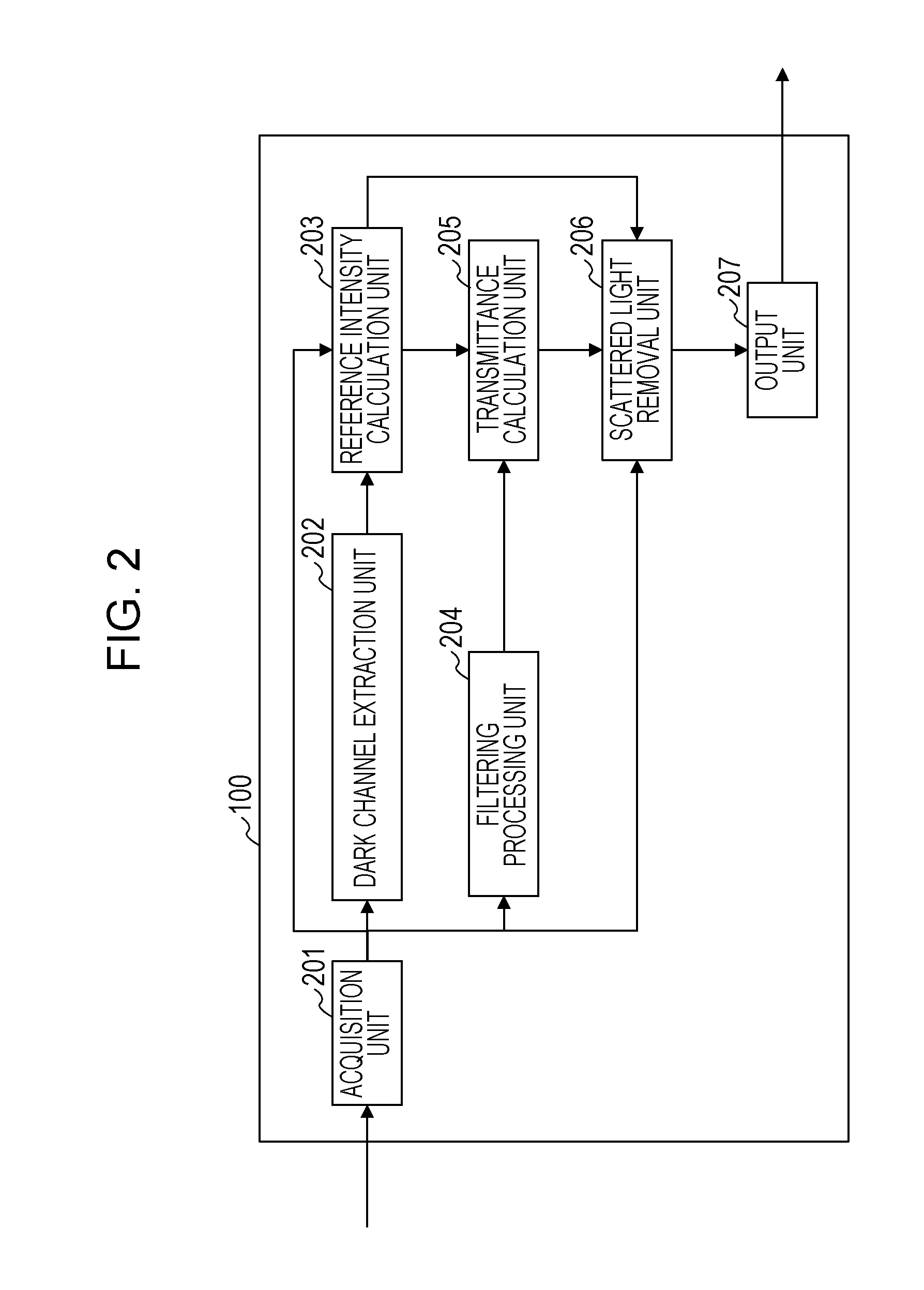
[0023]In a first embodiment, for each of R, G, and B channels, detection of scattered light is performed, and thus not only a reduction in contrast due to Mie scattering but also coloring due to Rayleigh scattering is corrected. The configuration of this embodiment will be described below.
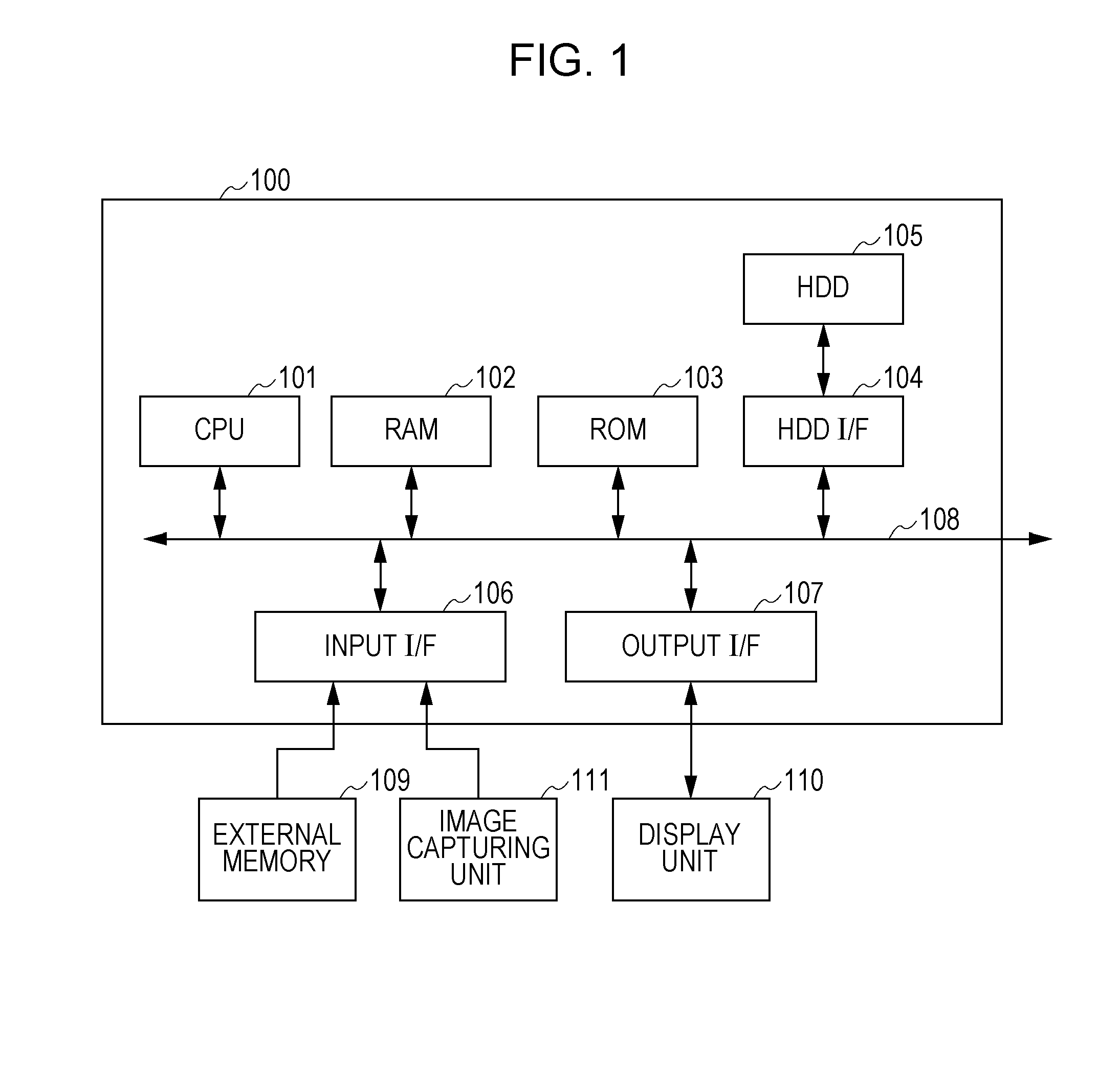
[0024]FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating the configuration of an image processing apparatus 100 according to this embodiment. The image processing apparatus 100 according to this embodiment includes a central processing unit (CPU) 101, a random access memory (RAM) 102, a read only memory (ROM) 103, a hard disk drive (HDD) interface (I / F) 104, an HDD 105, an input I / F 106, an output I / F 107, and a system bus 108. The CPU 101 is a processor that performs centralized control of components to be described below. The RAM 102 is a memory functioning as a main memory of the CPU 101 and a work area, and the ROM 103 is a memory storing a program for performing processes in the image processing apparatus...
second embodiment
[0056]The method according to the first embodiment enables an image in which both a component corresponding to Mie scattering (hereinafter referred to as a Mie scattering component) and a component corresponding to Rayleigh scattering (hereinafter referred to as a Rayleigh scattering component) are removed to be obtained. However, it is known that, in an actual image, even if there is no fog, mist, or the like, scattering due to Rayleigh scattering occurs. That is, when the degree of removal of Rayleigh scattering is kept to such an extent that an intensity of Rayleigh scattering is adjusted, a more natural image will be obtained. Thus, in a second embodiment, a more natural scattered-light-removed image is obtained by adding a Rayleigh scattering component whose intensity is corrected to the image which is obtained in the first embodiment and in which both a Mie scattering component and a Rayleigh scattering component are removed. A Mie scattering component is defined as a pixel va...
third embodiment
[0074]In the second embodiment, there has been described a method in which a more natural scattered-light-removed image is obtained by adding a Rayleigh scattering component whose intensity is corrected to an image in which both a Mie scattering component and a Rayleigh scattering component are removed. However, in some places where an image is captured, even in an image captured in clear weather, a small amount of scattering due to Mie scattering may occur. In an image captured in such a place, if the degree of removal of Mie scattering is excessively strong, an unnatural image may be generated. Thus, in a third embodiment, natural scattered-light-removed images appropriate to various scenes are obtained by adding not only a Rayleigh scattering component whose intensity is corrected but also a Mie scattering component whose intensity is corrected to an image in which both a Mie scattering component and a Rayleigh scattering component are removed.
[0075]A process performed in an imag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com