Tubular fiber structure and fiber reinforced composite material
a technology of tubular fiber which is applied in the field of tubular fiber structure and fiber reinforced composite material, can solve the problems of reducing the strength, reducing slit cracks, so as to reduce the energy absorption efficiency, reduce the strength, and simplify the coupling structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
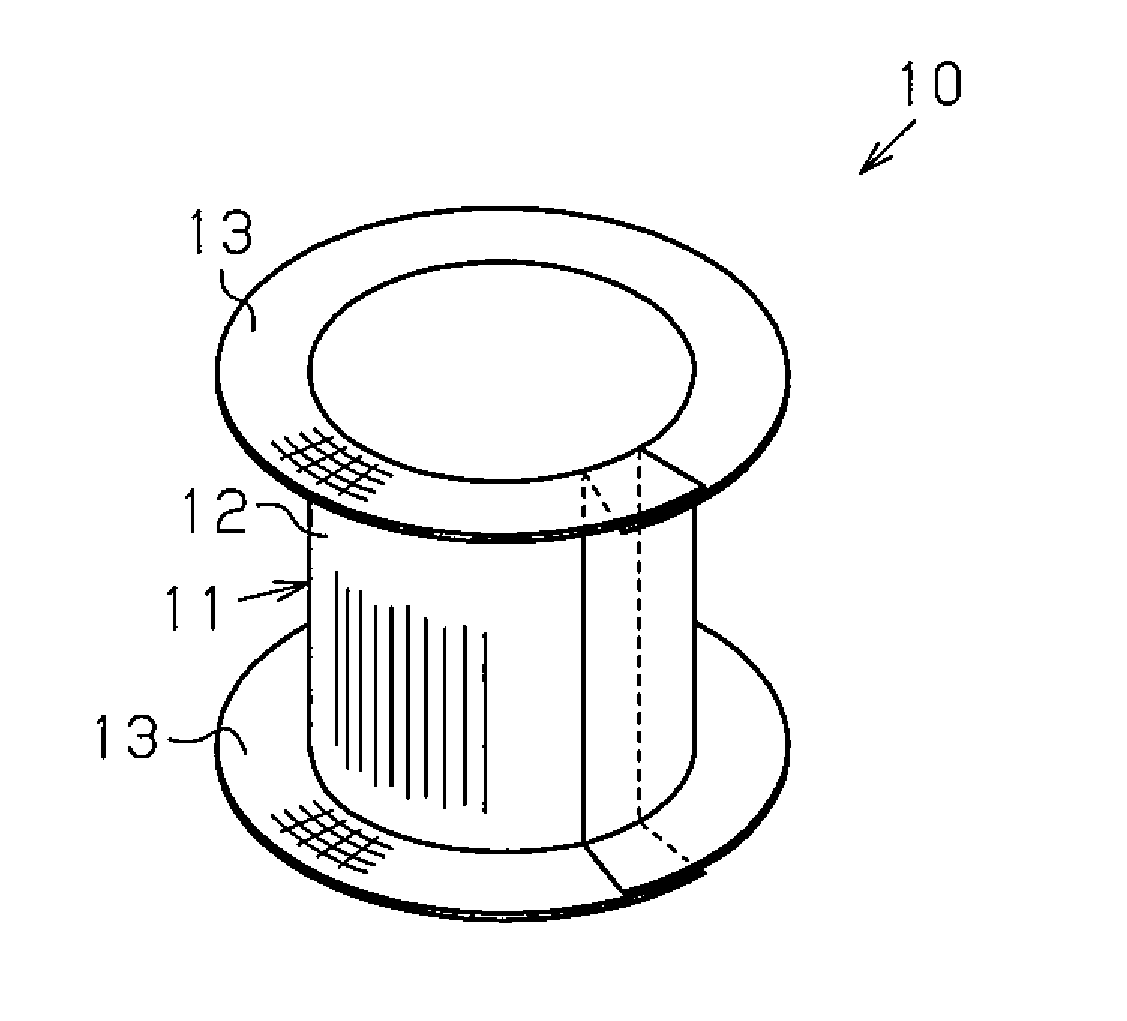
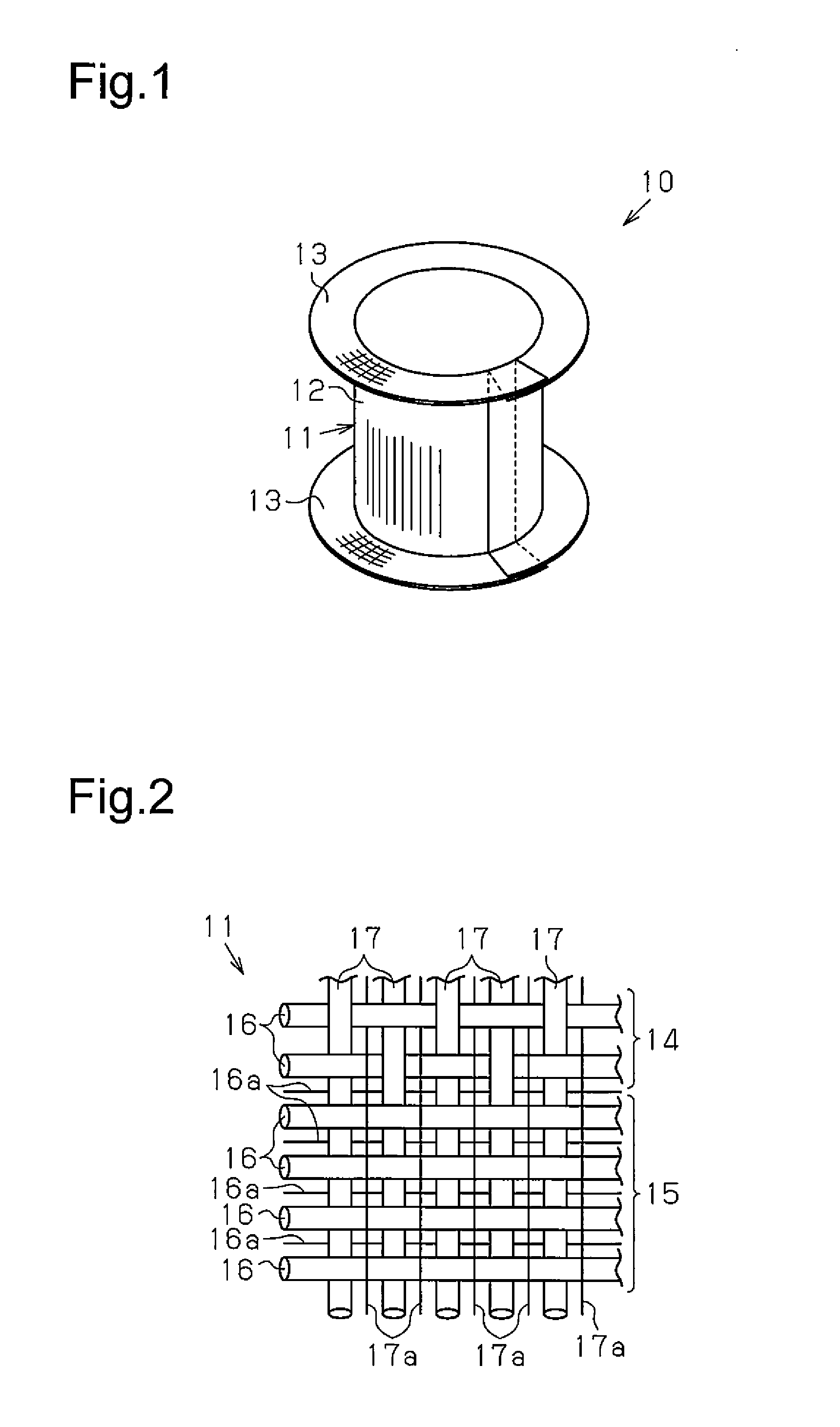
[0043]A first embodiment of a tubular fiber structure will now be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 4.
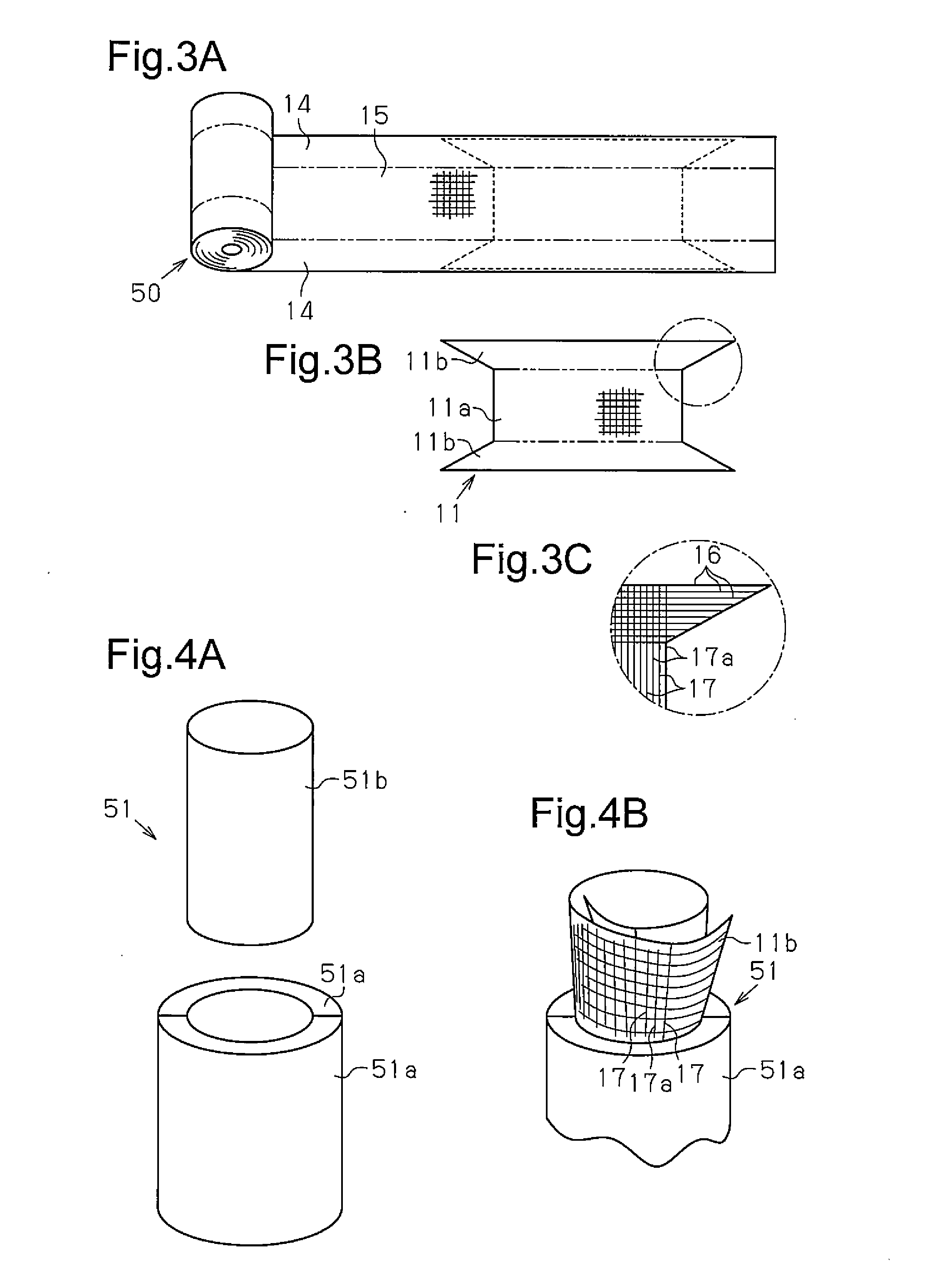
[0044]Referring to FIG. 1, a tubular fiber structure 10 is formed by rolling a sheet of a fabric base material 11 and shaping the rolled fabric base material 11. The tubular fiber structure 10 includes a tube 12 and a flange 13, which is located on at least one side (i.e., one axial end) of the tube 12. In this embodiment, the tube 12, which is tubular and has a circular cross-section, includes the flange 13 at two sides (two axial ends). The “fabric base material” is formed by threads laid out to extend in at least two directions and includes at least a portion that is woven from threads (interweaved portion).
[0045]Referring to FIG. 2, the fabric base material 11 includes a woven texture 14 and a non-woven texture 15. As shown in FIG. 3A, the fabric base material 11 of this embodiment includes the woven texture 14 at the two widthwise sides of the fabric base material 11 and t...
second embodiment
[0061]A second embodiment will now be described with reference to FIGS. 5 to 7. This embodiment differs from the tubular fiber structure 10 of the first embodiment in that a reinforcement portion 18 formed by a fabric base material 21 is arranged at the inner side of the tube 12. Otherwise, the structure is basically the same as the tubular fiber structure 10 of the first embodiment. Same reference numerals are given to those components that are the same as the corresponding components of the first embodiment. Such components will not be described in detail.
[0062]As shown in FIG. 5, the fabric base material 21 of the reinforcement portion 18 is continuous with a rolled inner end 11d of the tube-corresponding portion 11a, which corresponds to the tube 12, in the fabric base material 11 forming the tube 12 and the flanges 13. The fabric base material 21 is arranged so as to extend in the radial direction of the tube 12. The fabric base material 21 includes a fixed portion 21a, which i...
third embodiment
[0070]A third embodiment will now be described with reference to FIGS. 8 to 10. This embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that multiple layers of the fabric base material 11 are stacked and sewn together with stitching threads 22 so that the tube 12 is three-dimensional. Same reference numerals are given to those components that are the same as the corresponding components of the first embodiment. Such components will not be described in detail.
[0071]As shown in FIGS. 8 and 9, the overlapping layers of the fabric base material 11 at the tube 12 are lock-stitched with the stitching threads 22 so that the tubular fiber structure 10 is three-dimensional. As shown in FIG. 9, the stitching threads 22 include a piercing thread 22a, which is pierced through and returned from portions where the fabric base material 11 is overlapped in layers, and a locking thread 22b, which locks the piercing thread 22a to the fabric base material 11 at portions of the fabric base material 11 whe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angles | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angles | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angles | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com