Self learning radio frequency monitoring system for identifying and locating faults in electrical distribution systems
a radio frequency monitoring and fault detection technology, applied in automated test systems, testing circuits, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of small electrical fault arcs that jump across cracks, rfm does not determine the location of equipment, rf emission activity, etc., and achieve the effect of high power plant reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
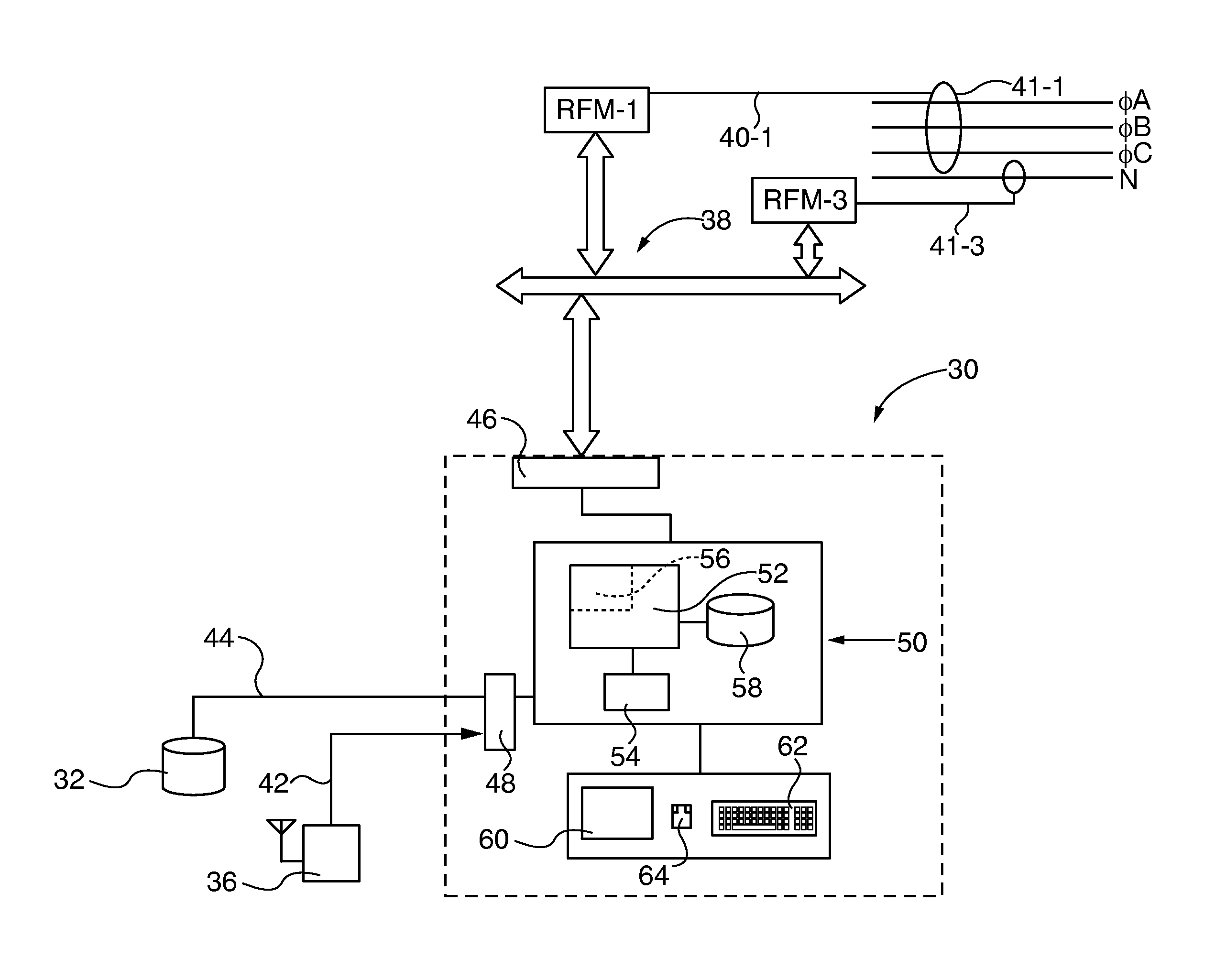
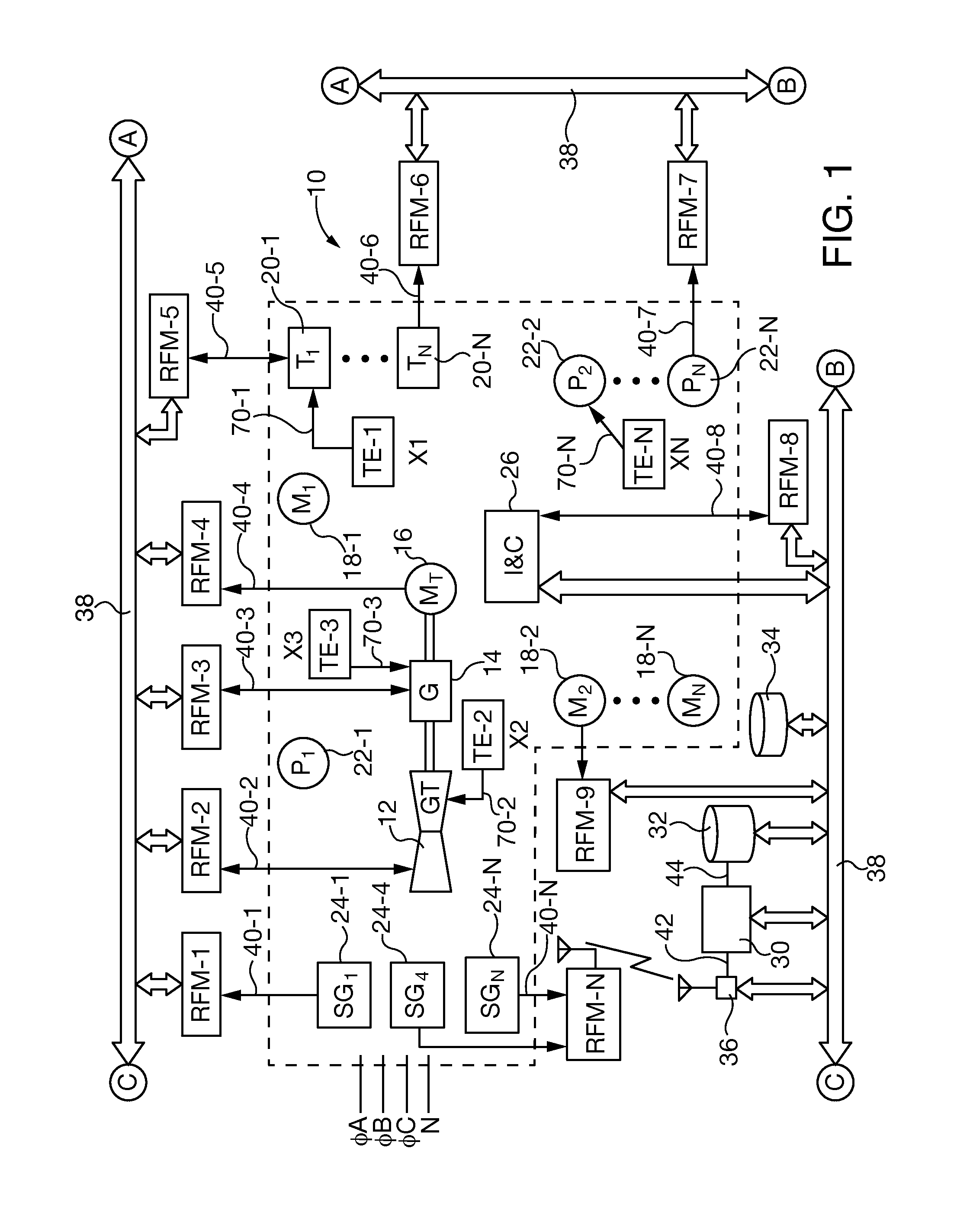
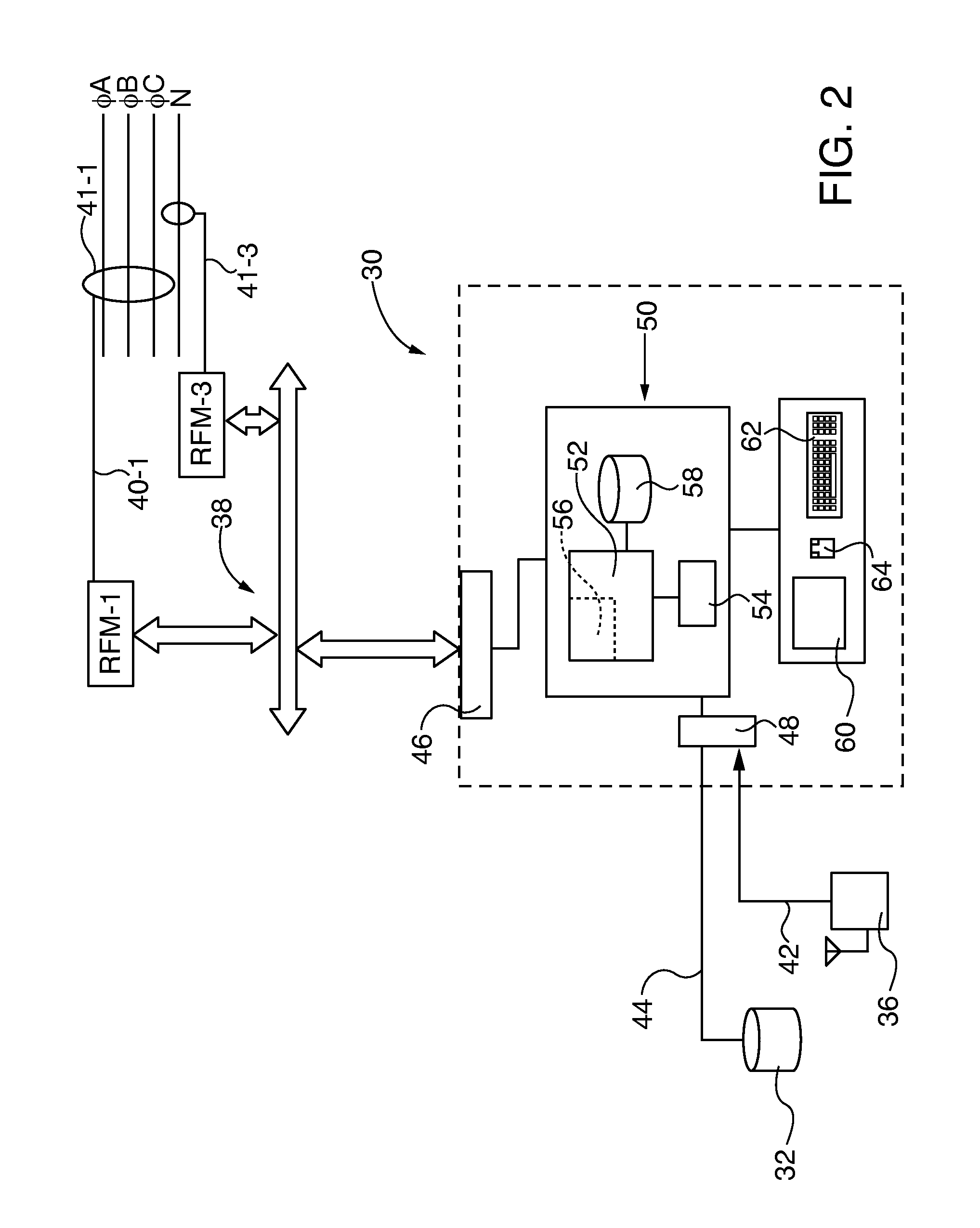
[0025]After considering the following description, those skilled in the art will realize that the by the teachings of the present invention electrical faults are detected in electrical distribution systems (EDS) by detection and location of radio frequency (RF) emissions generated by the fault with multiple time synchronized radio frequency monitors (RFM) distributed about the EDS. In embodiments of the invention the RFM location is reconfigurable to accommodate changes in the EDS configuration and / or component hardware. The RFMs are coupled to a self-learning, electrical fault monitor (EFM) that characterizes and / or locates electrical faults based on operating state (OS) patterns learned from transmission of test signals generated within the in the distributions system and / or that are preloaded into an EFM accessible base of stored knowledge. RF emissions data samples are characterized as safe operation (SO) states or potential electrical faults by accessing a base of stored knowle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com