Low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) driving circuit
a driving circuit and low voltage technology, applied in logic circuit coupling/interface arrangement, logic circuit coupling/interface using field-effect transistors, pulse techniques, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient head room of current sources and very limited output range of differential signaling circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049]In order to illustrate the purposes, features and advantages of the invention, the embodiments and figures of the invention are described in detail as follows.
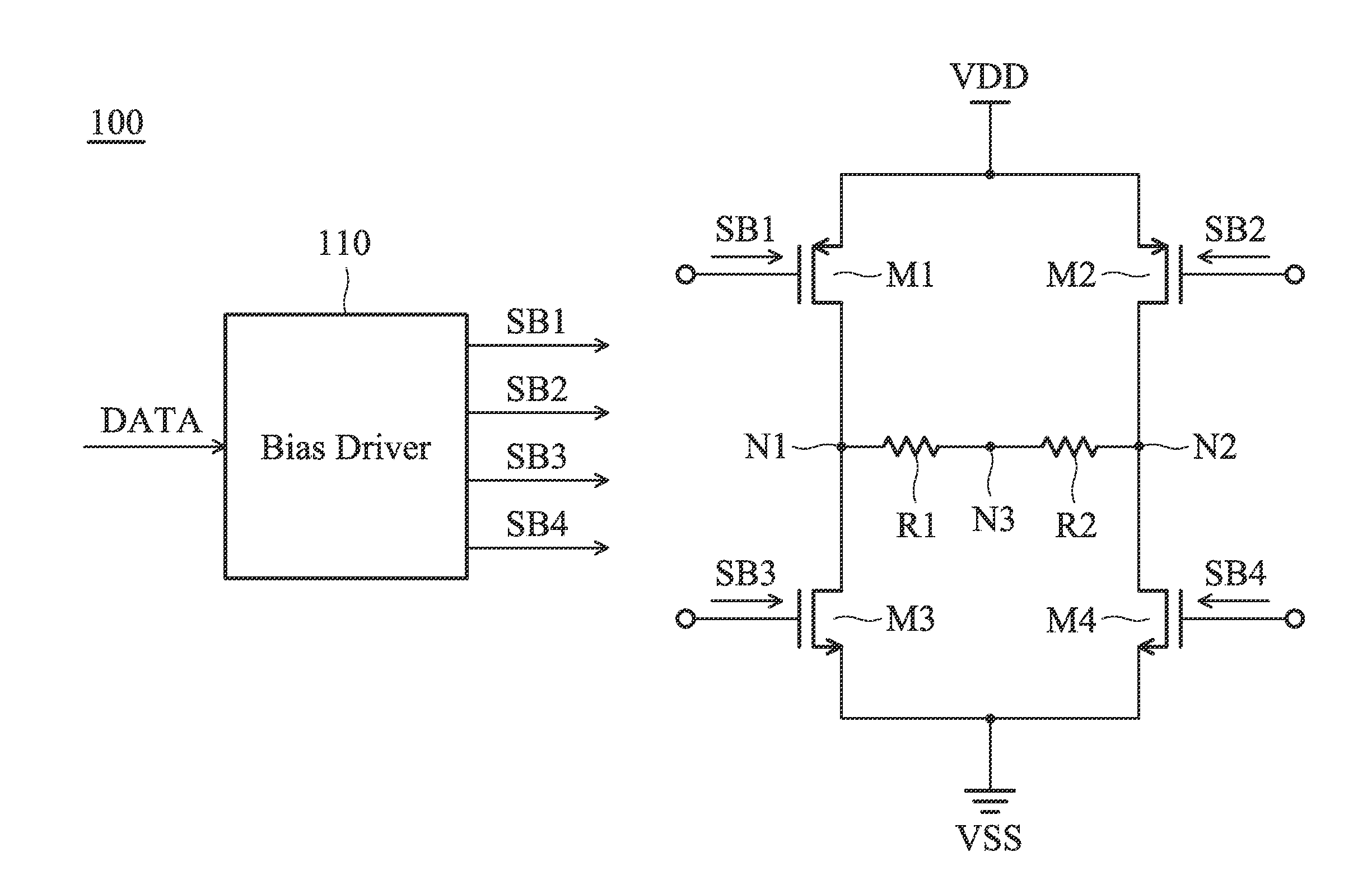
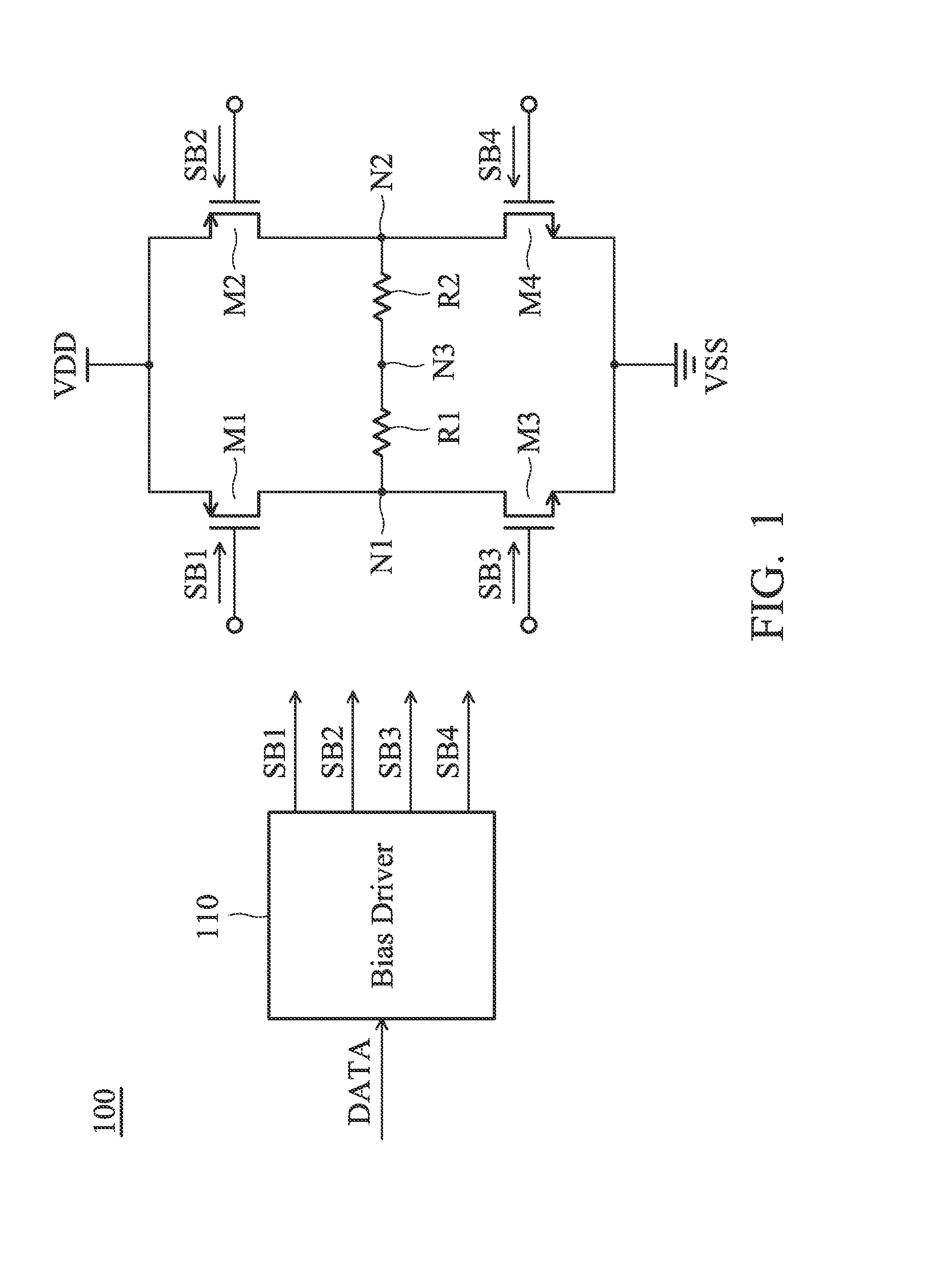
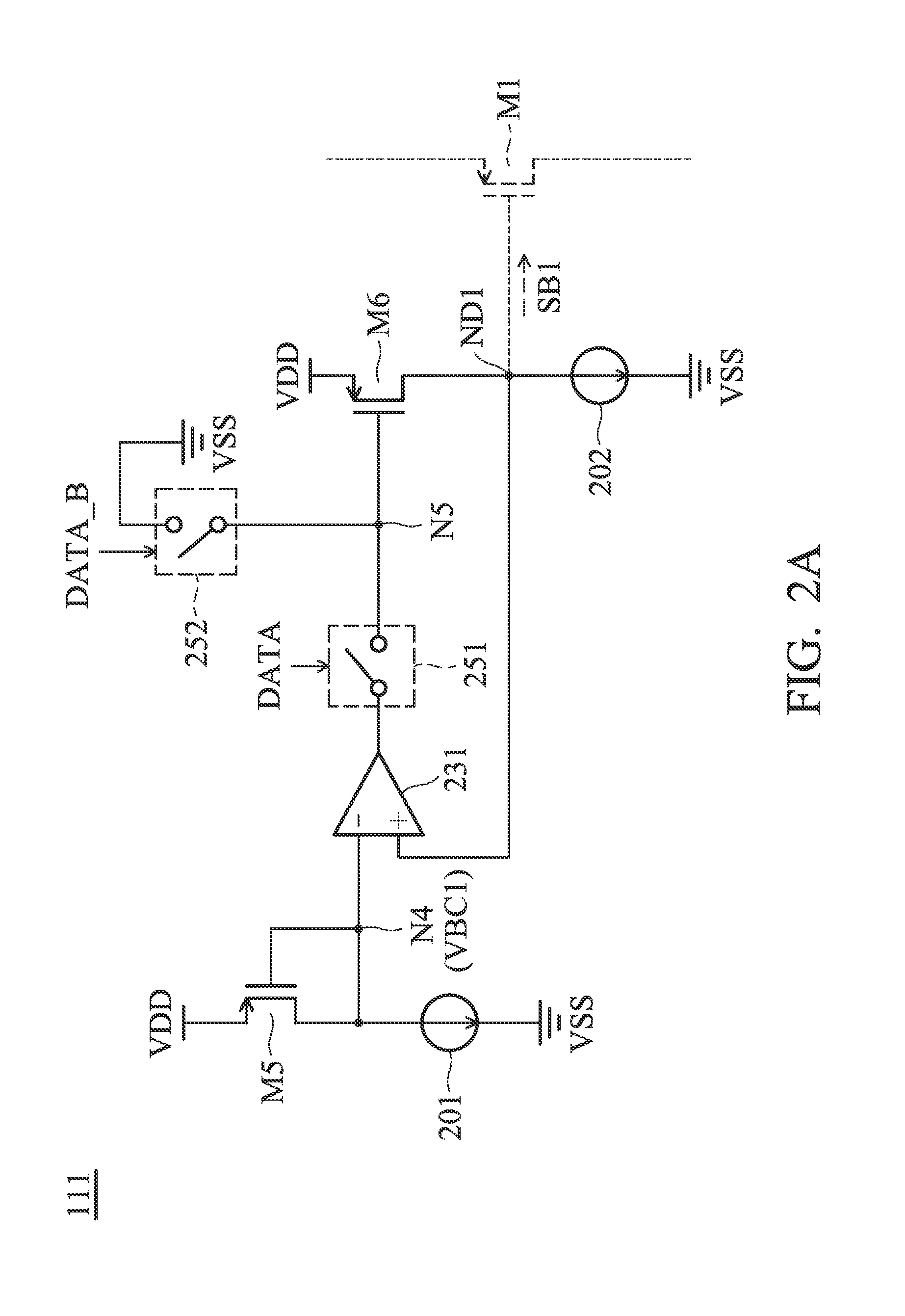
[0050]FIG. 1 is a diagram of an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) driving circuit 100 according to an embodiment of the invention. The LVDS driving circuit 100 includes a first transistor M1, a second transistor M2, a third transistor M3, a fourth transistor M4, a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2, and a bias driver 110. The bias driver 110 generates a first bias signal SB1, a second bias signal SB2, a third bias signal SB3, and a fourth bias signal SB4 for controlling the first transistor M1, the second transistor M2, the third transistor M3, and the fourth transistor M4, respectively, according to a data signal DATA. The data signal DATA may be a digital signal. In some embodiments, the first transistor M1 and the second transistor M2 are PMOS transistors (P-type Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com