Method and apparatus for atlas/model-based segmentation of magnetic resonance images with weakly supervised examination-dependent learning
a magnetic resonance image and model-based technology, applied in image enhancement, instruments, recognition of medical/anatomical patterns, etc., can solve the problems of difficult, or almost impossible, to distinguish between bone and air or lung tissue, and difficulty in bone segmentation,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
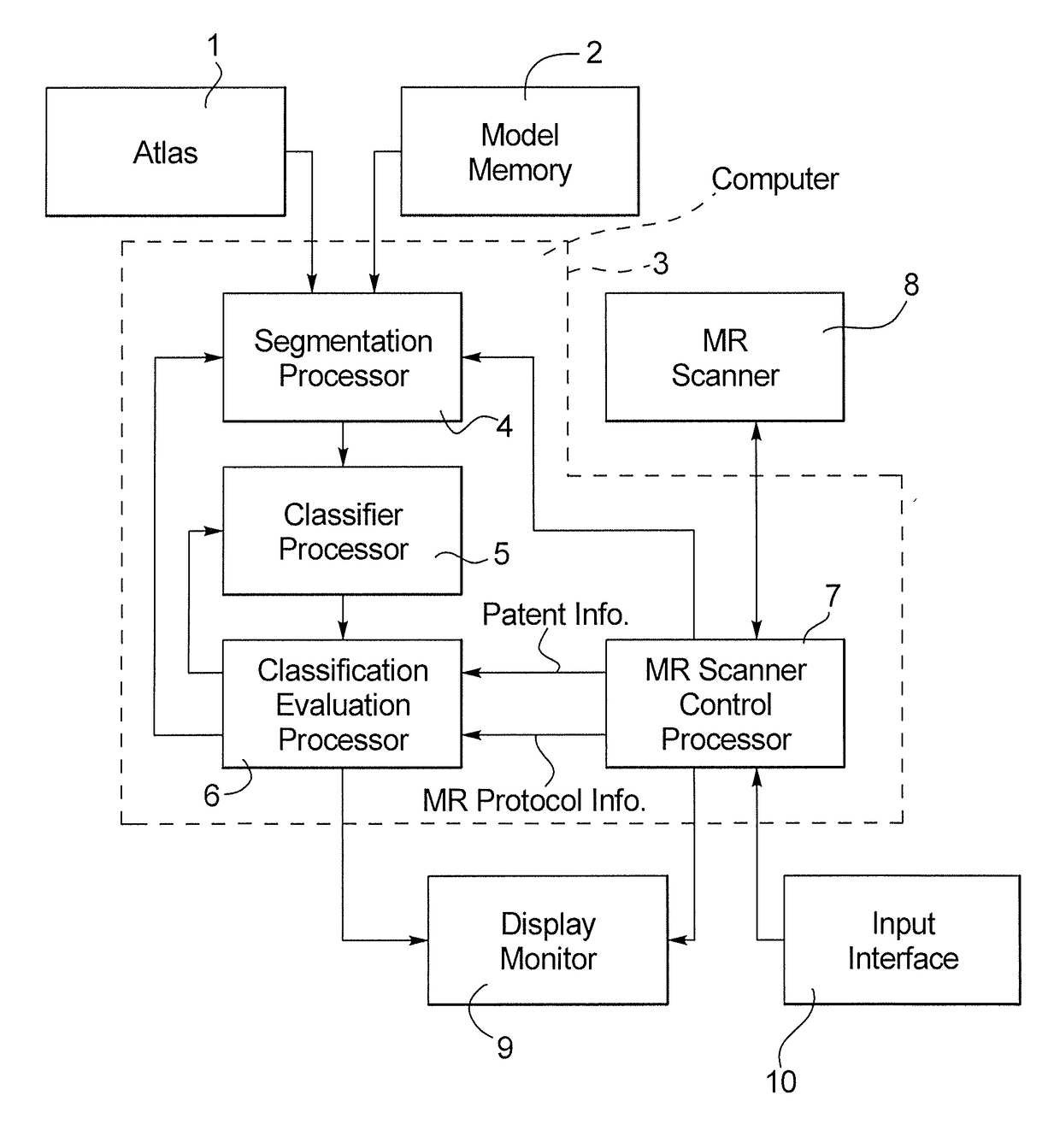
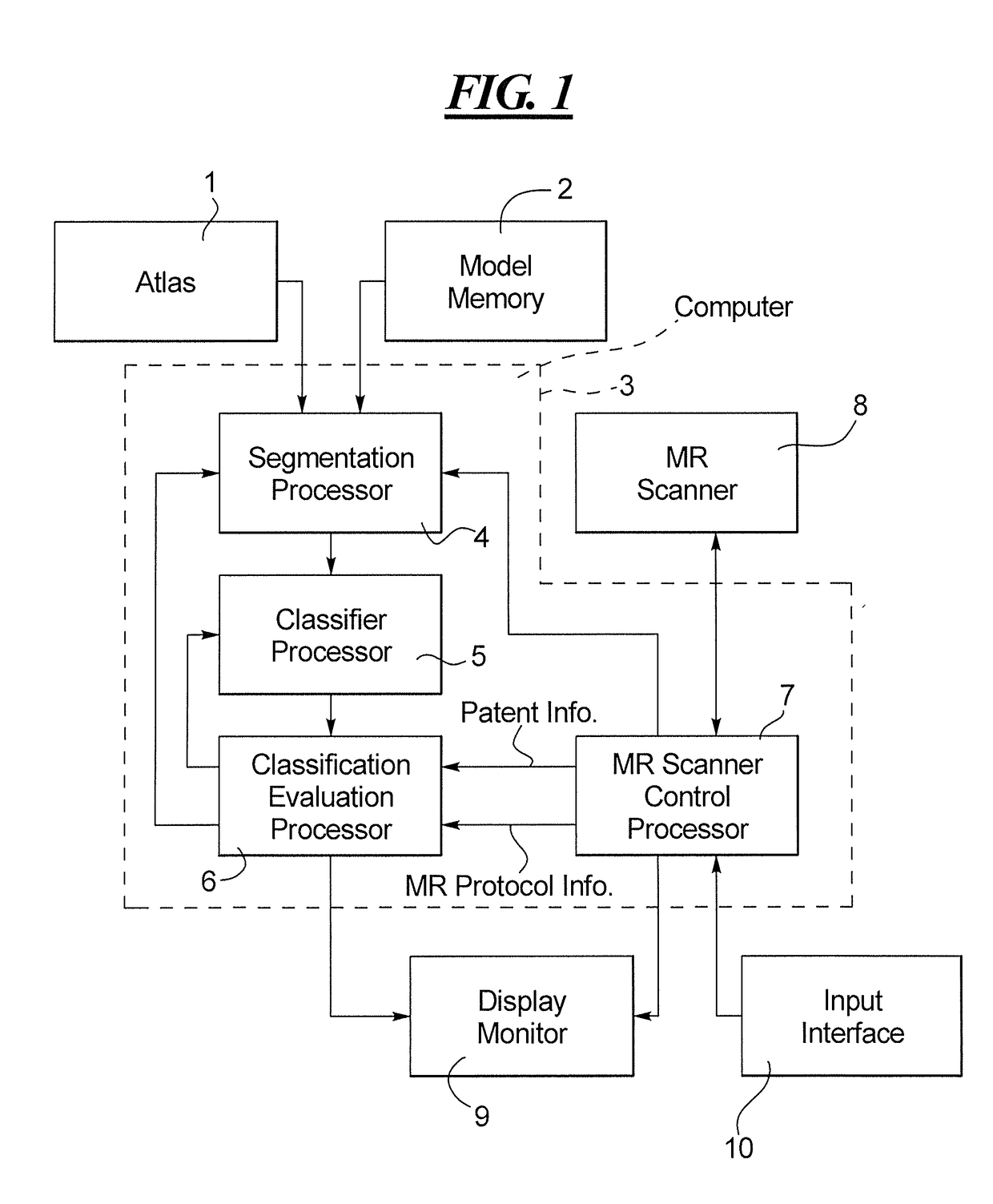
[0023]As shown in FIG. 1, the apparatus according to the invention makes use of an atlas 1 and / or a model memory 2 that provide a data file or model to a computer 3, specifically to a segmentation processor 4 of the computer 3. The segmentation processor 4 is also provided with a data file representing an MR image of a region of a patient, acquired by operation of an MR scanner 8. The MR image data file is provided from an MR scanner control processor 7 that operates the MR scanner 8 and generates image information from the acquired MR data in a known manner.
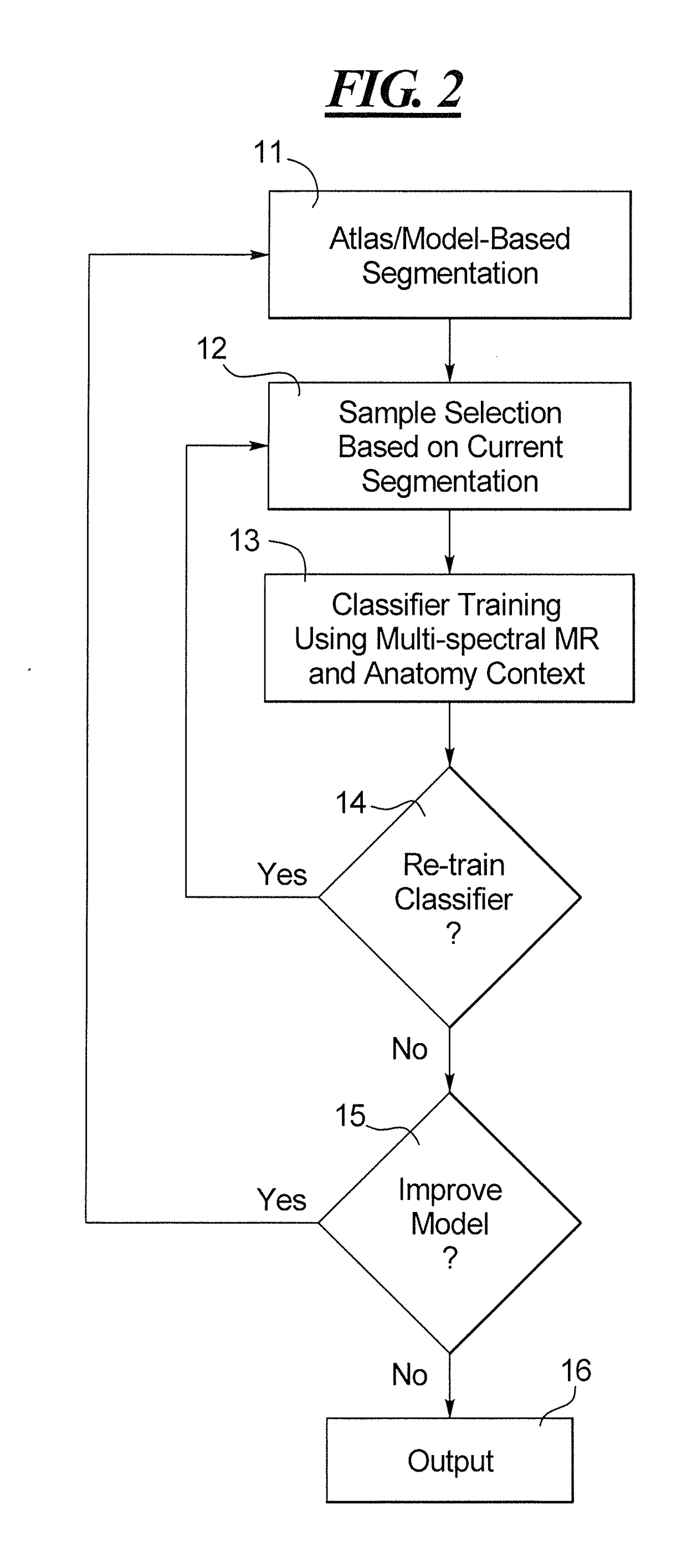
[0024]The acquired MR data represent image elements (pixels in the case of a 2D image, and voxels in the case of a 3D image), that each has different attributes or characteristics, such as intensity. The segmentation processor 4 operates in combination with a classifier processor 5 in order to classify the image elements of the provided MR image, in order to identify and extract image elements therefrom that have the image eleme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com