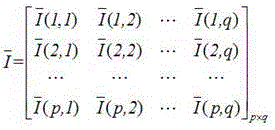Patents
Literature
33 results about "Model based segmentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
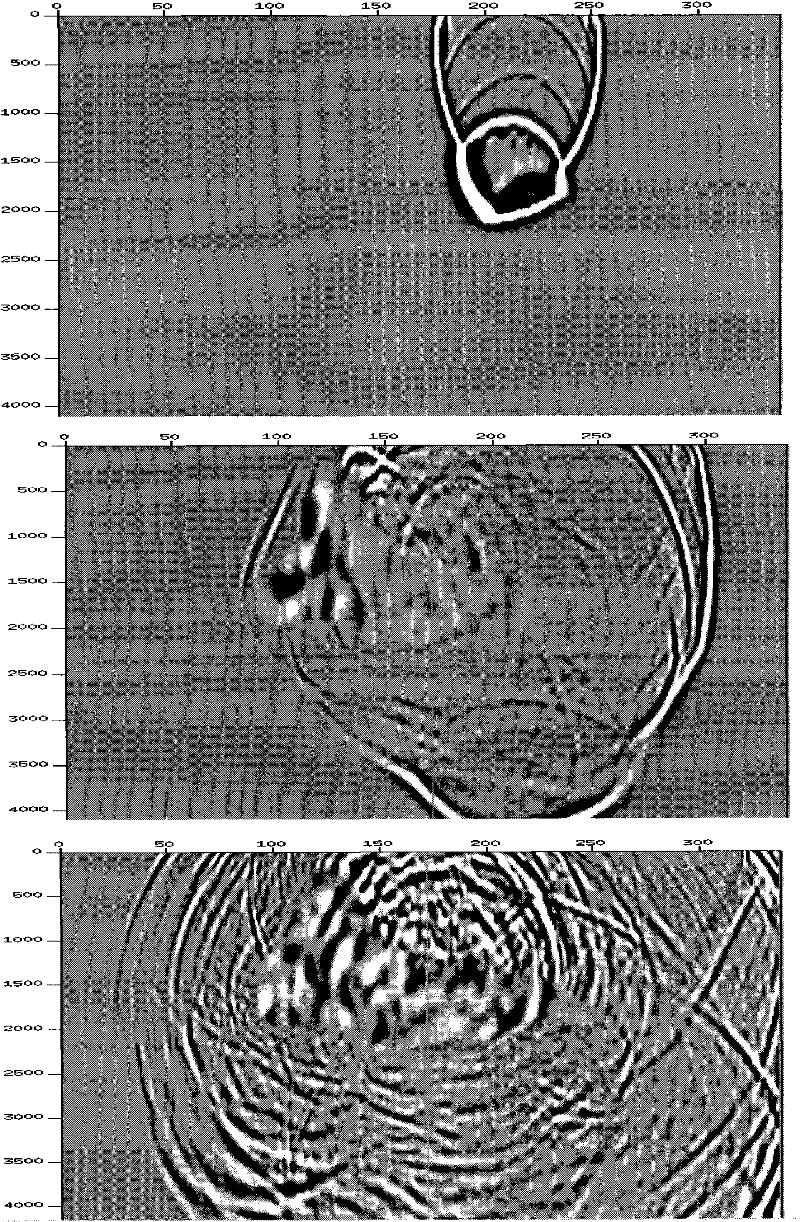
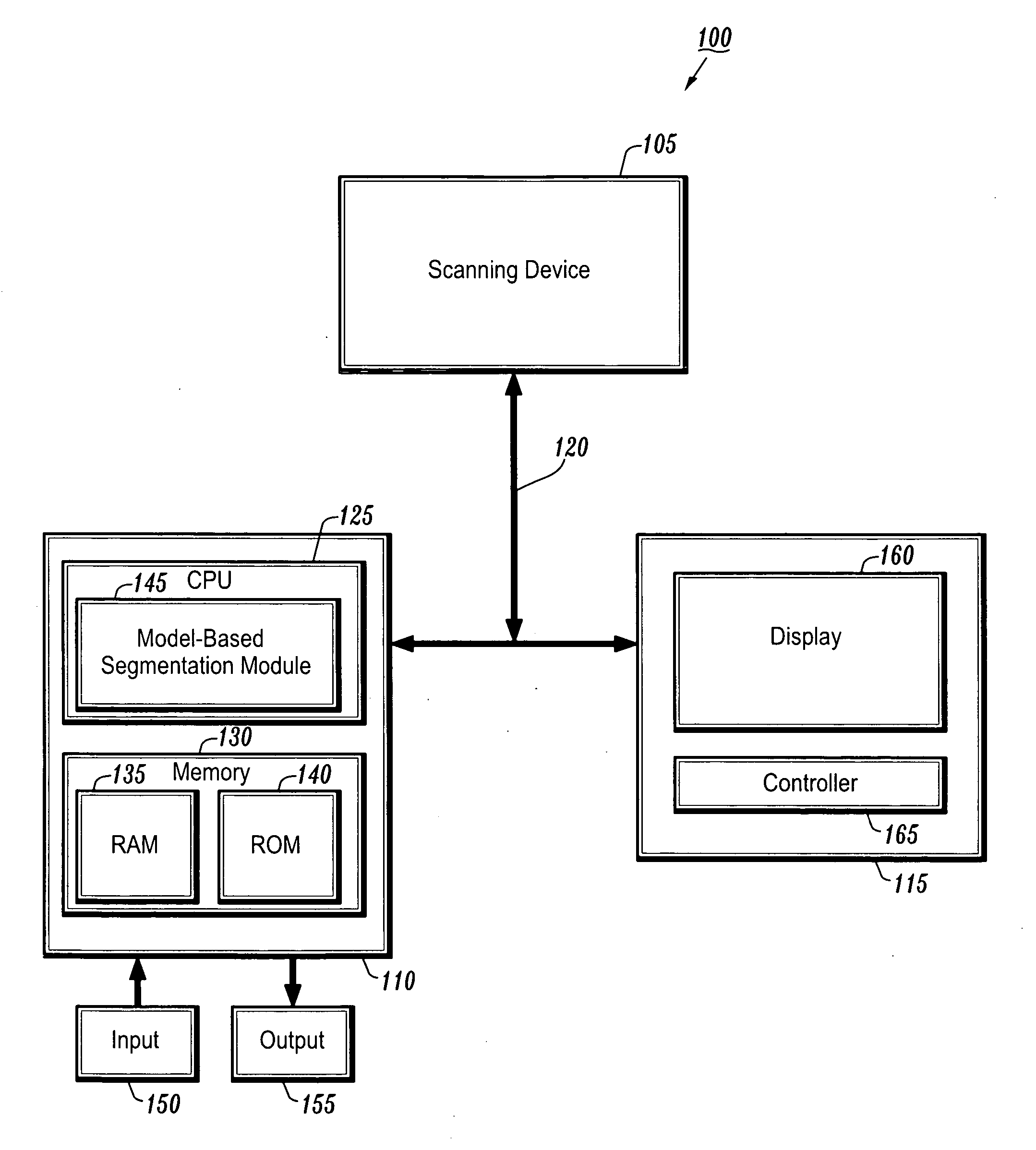
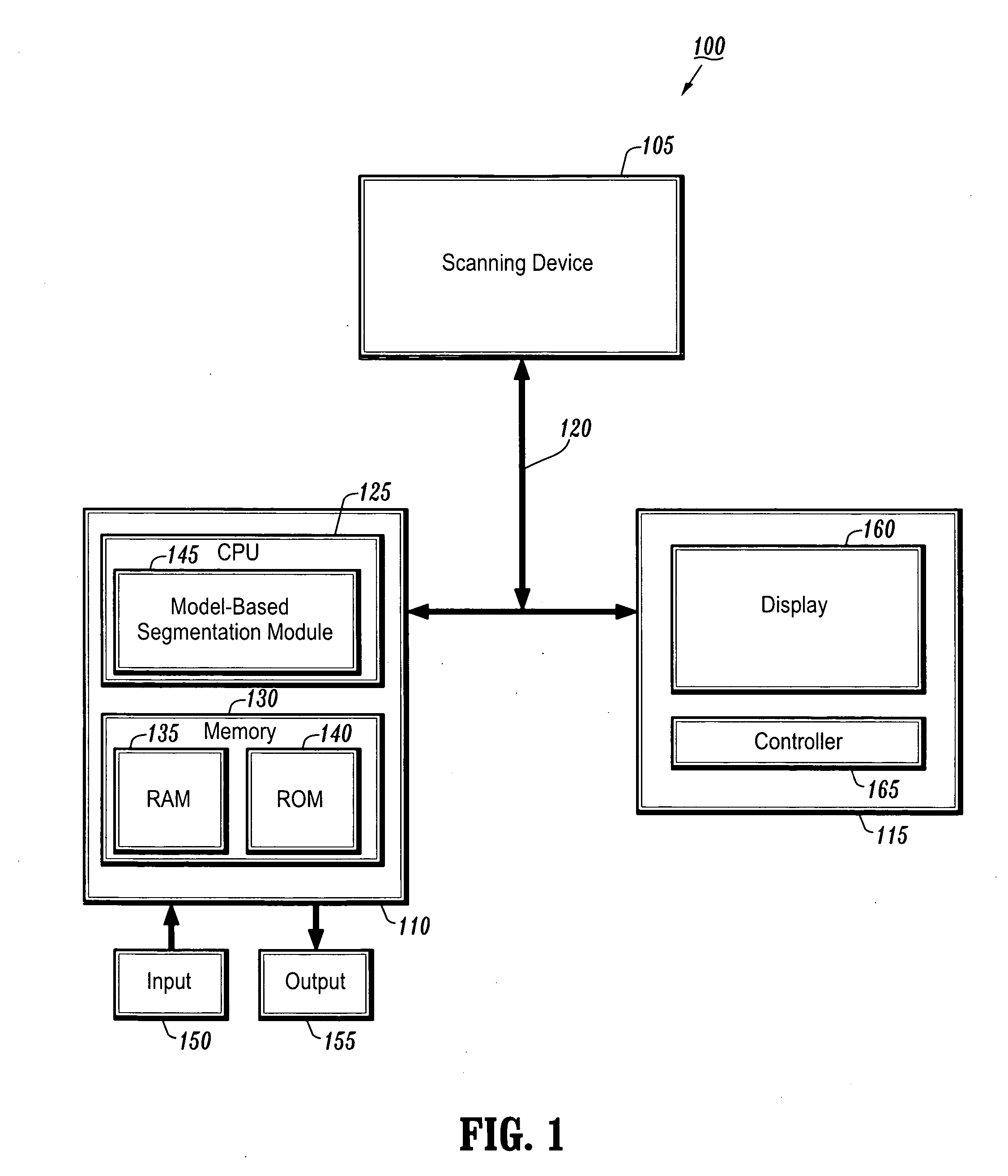
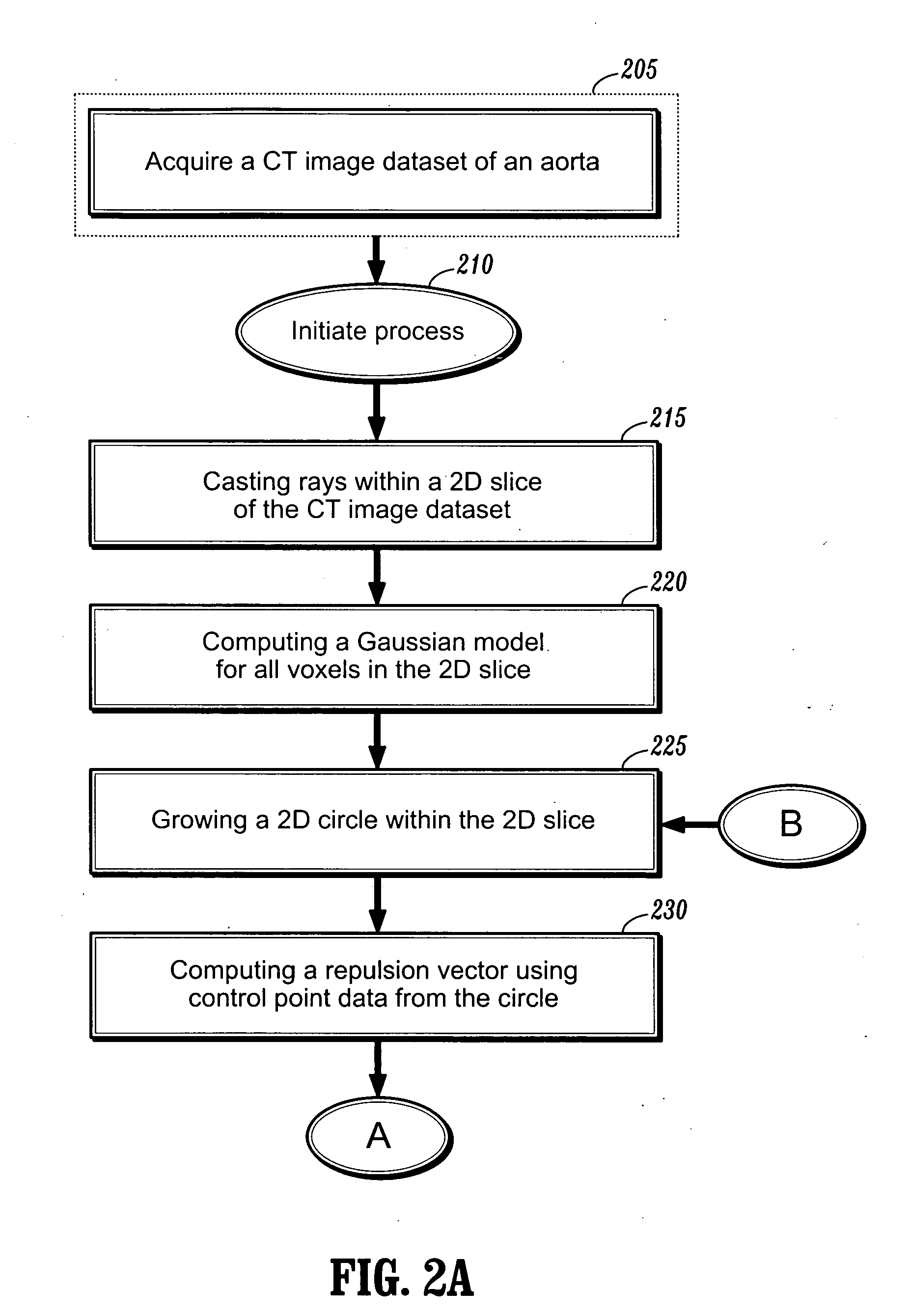
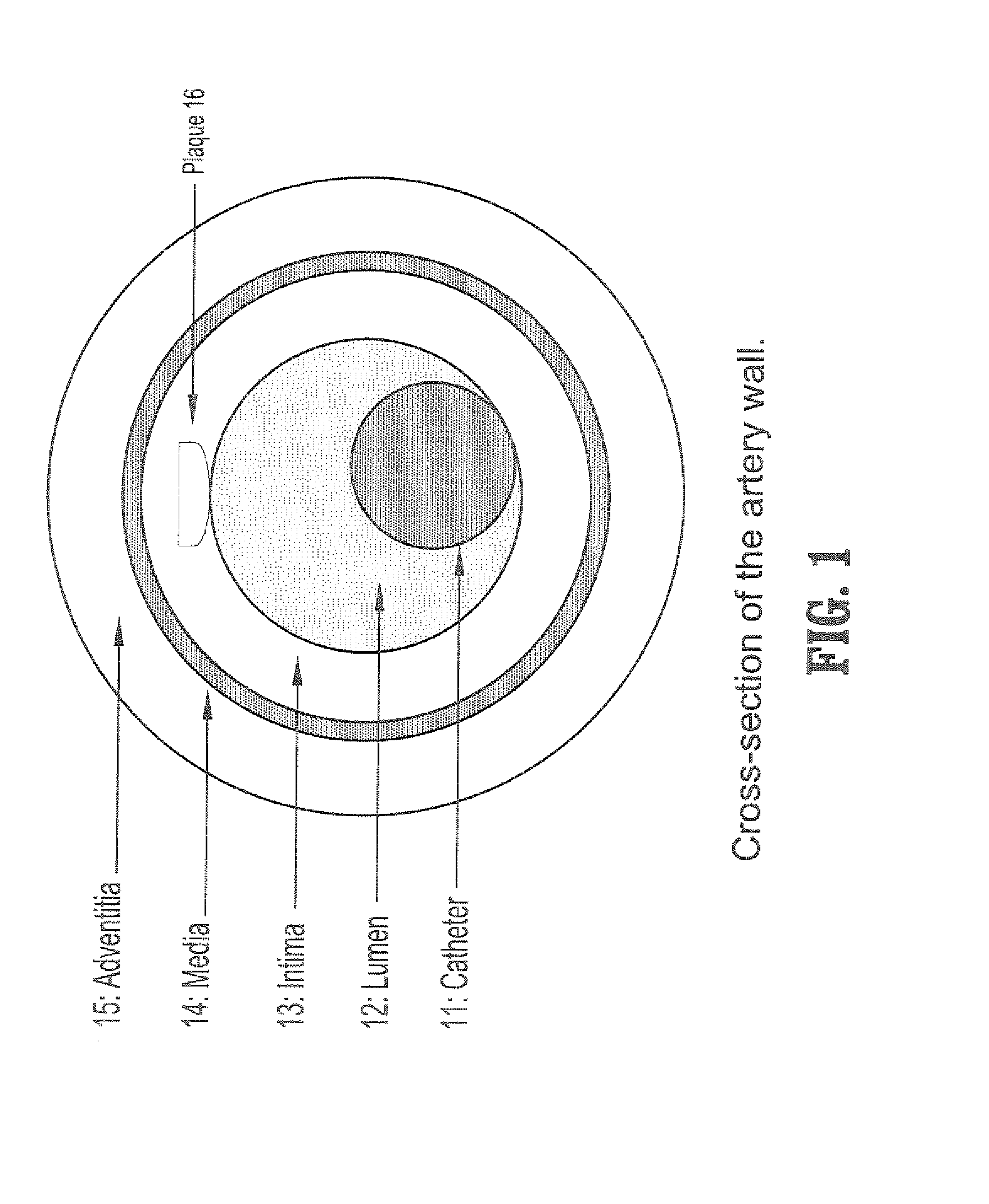
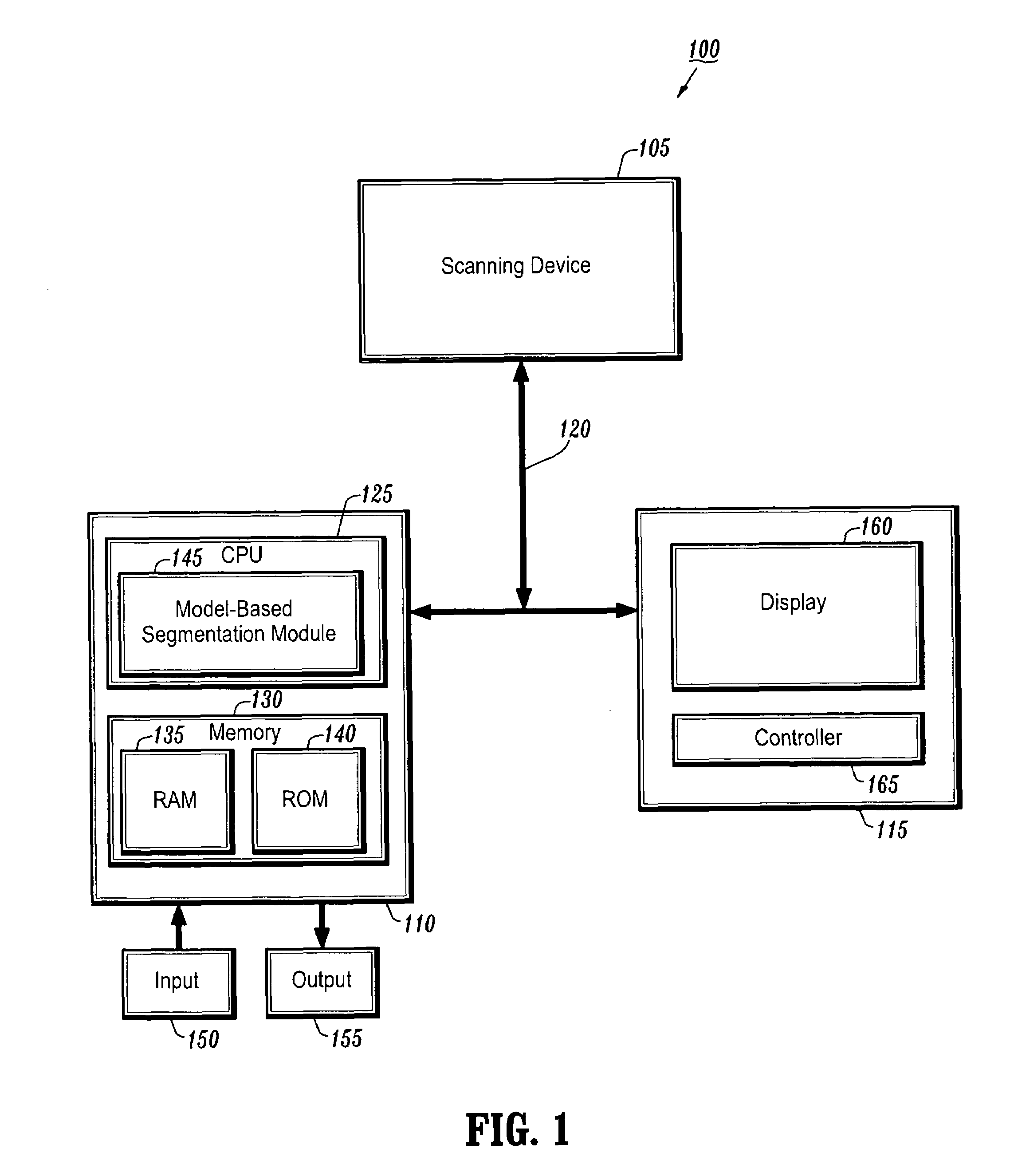
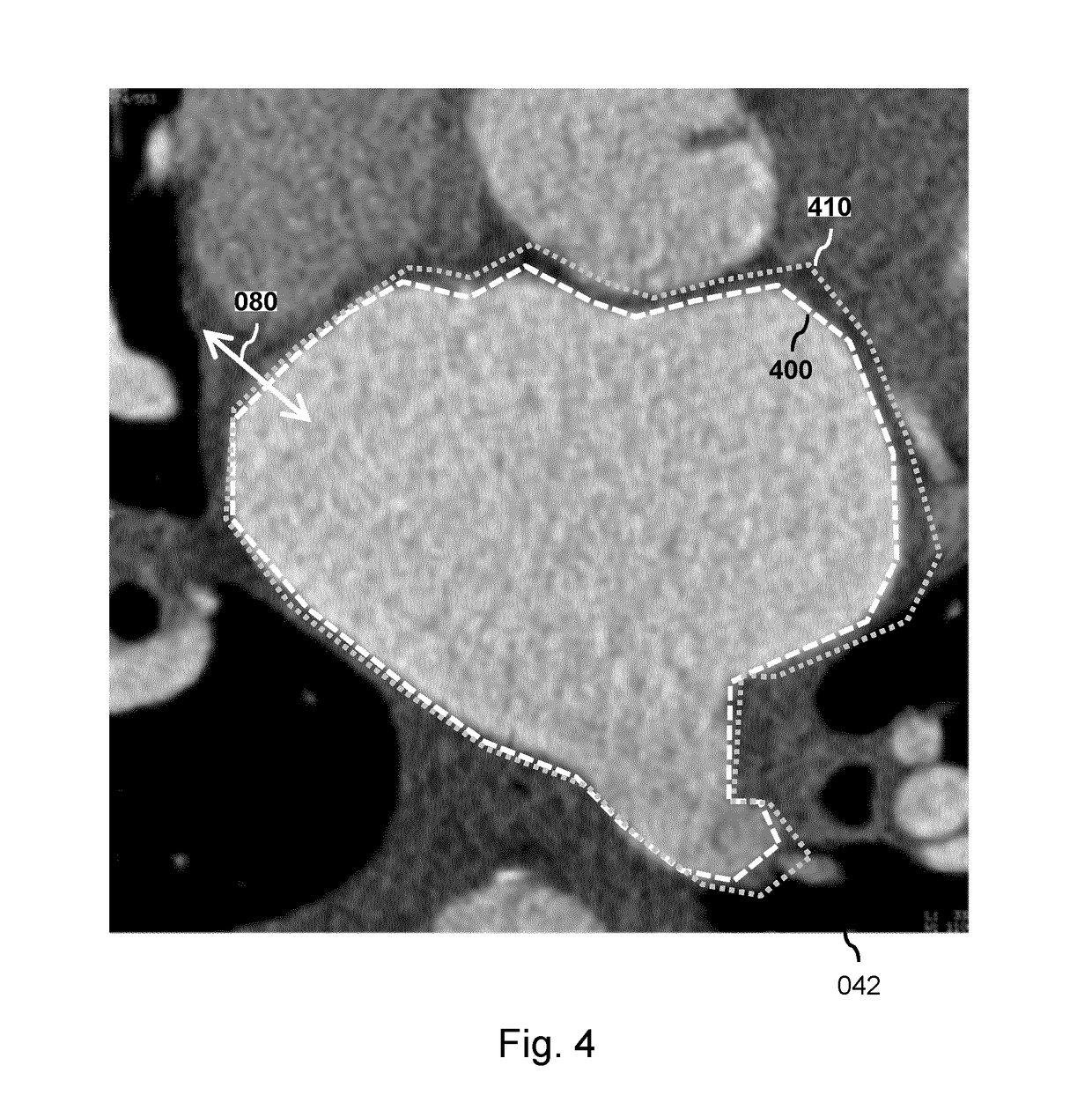
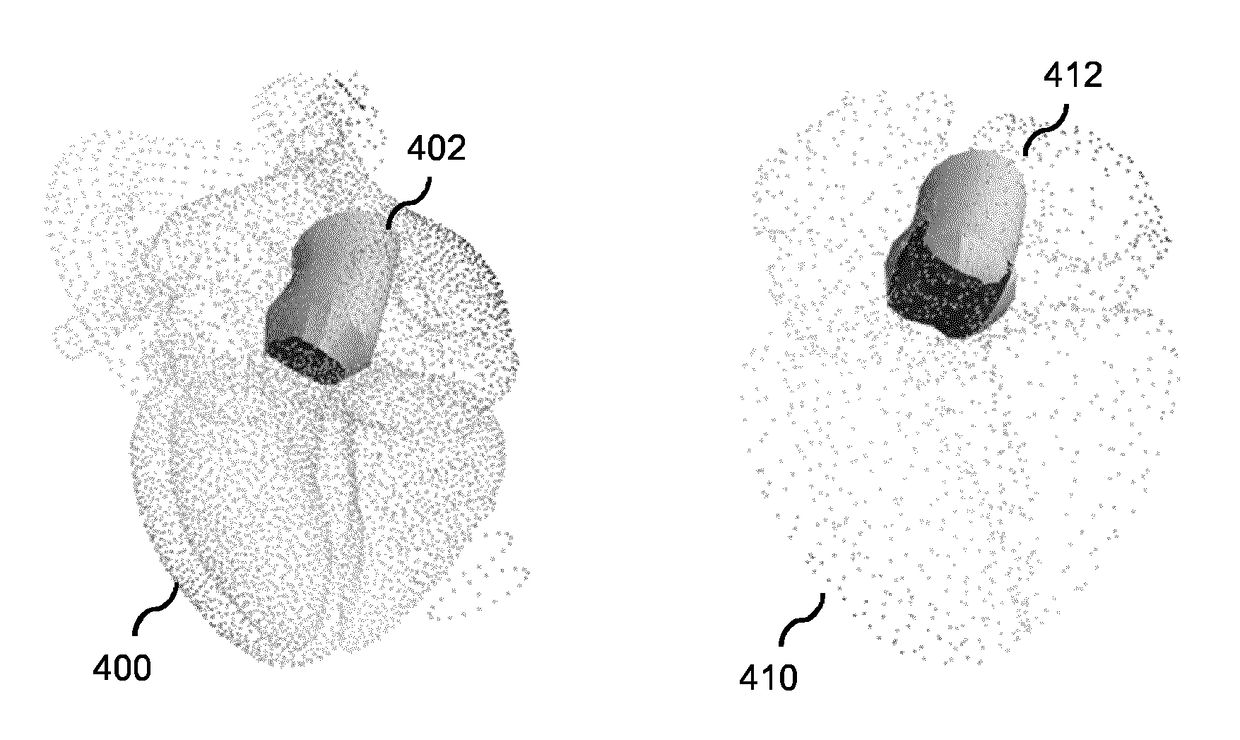
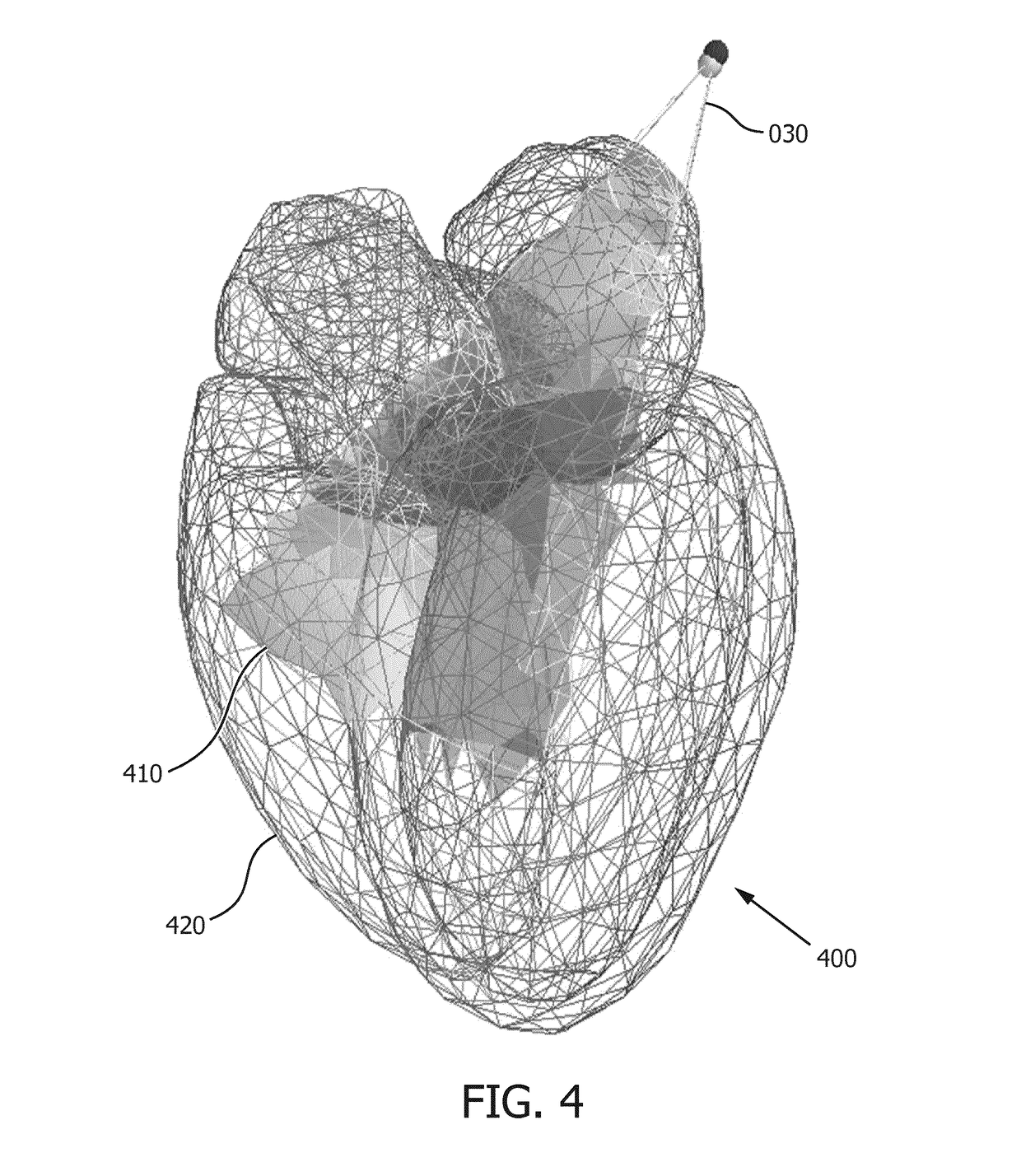
System and method for detecting the aortic valve using a model-based segmentation technique
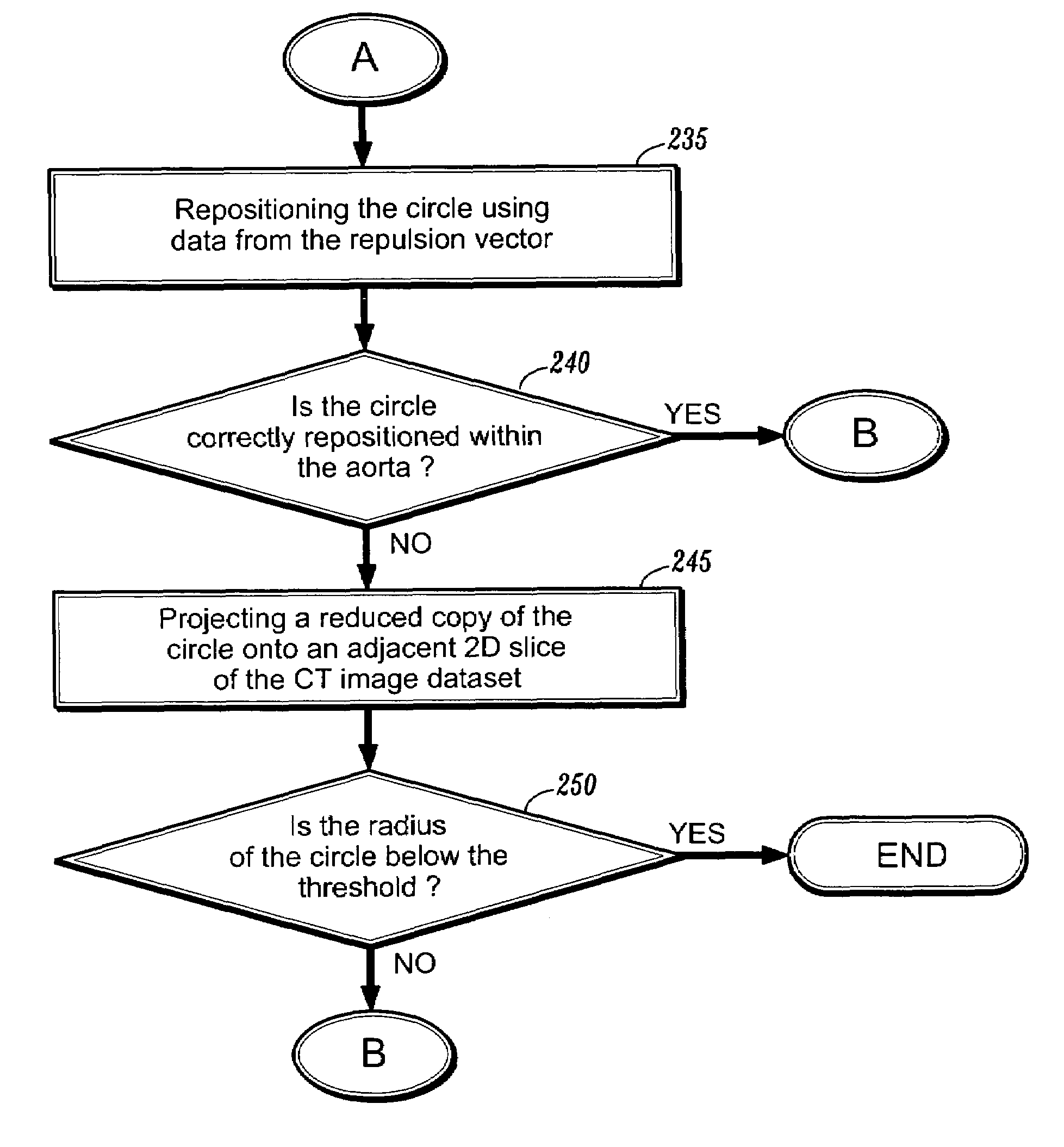
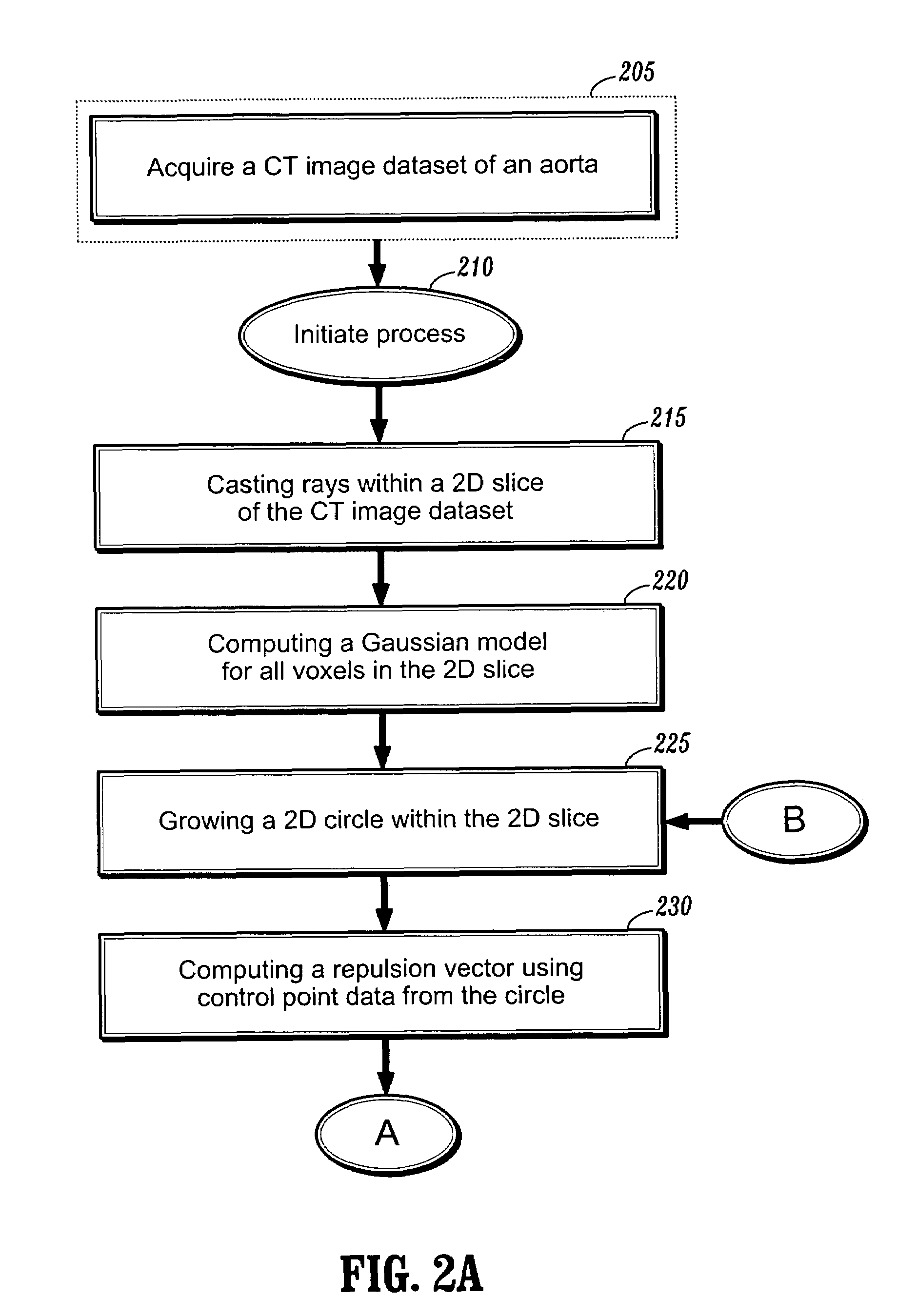
A system and method for detecting the aortic valve is provided. The method comprises: (a) casting rays on a slice of a computed tomography (CT) dataset of an aorta; (b) computing a Gaussian model for voxels on the slice, wherein the Gaussian model produces a threshold; (c) growing a circle from a point within the aorta until control points of the circle reach the threshold; (d) computing a repulsion vector for each control point reaching the threshold; (e) repositioning the circle according to an average of the repulsion vectors, wherein if the circle is within the aorta, repeating steps (c-e) until the circle is not within the aorta; (f) calculating a statistical value for the circle; (g) projecting a copy of the circle onto an adjacent slice; (h) reducing the radius of the copy of the circle; and (i) repeating steps (c-h) on remaining CT slices until the aortic valve is detected.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
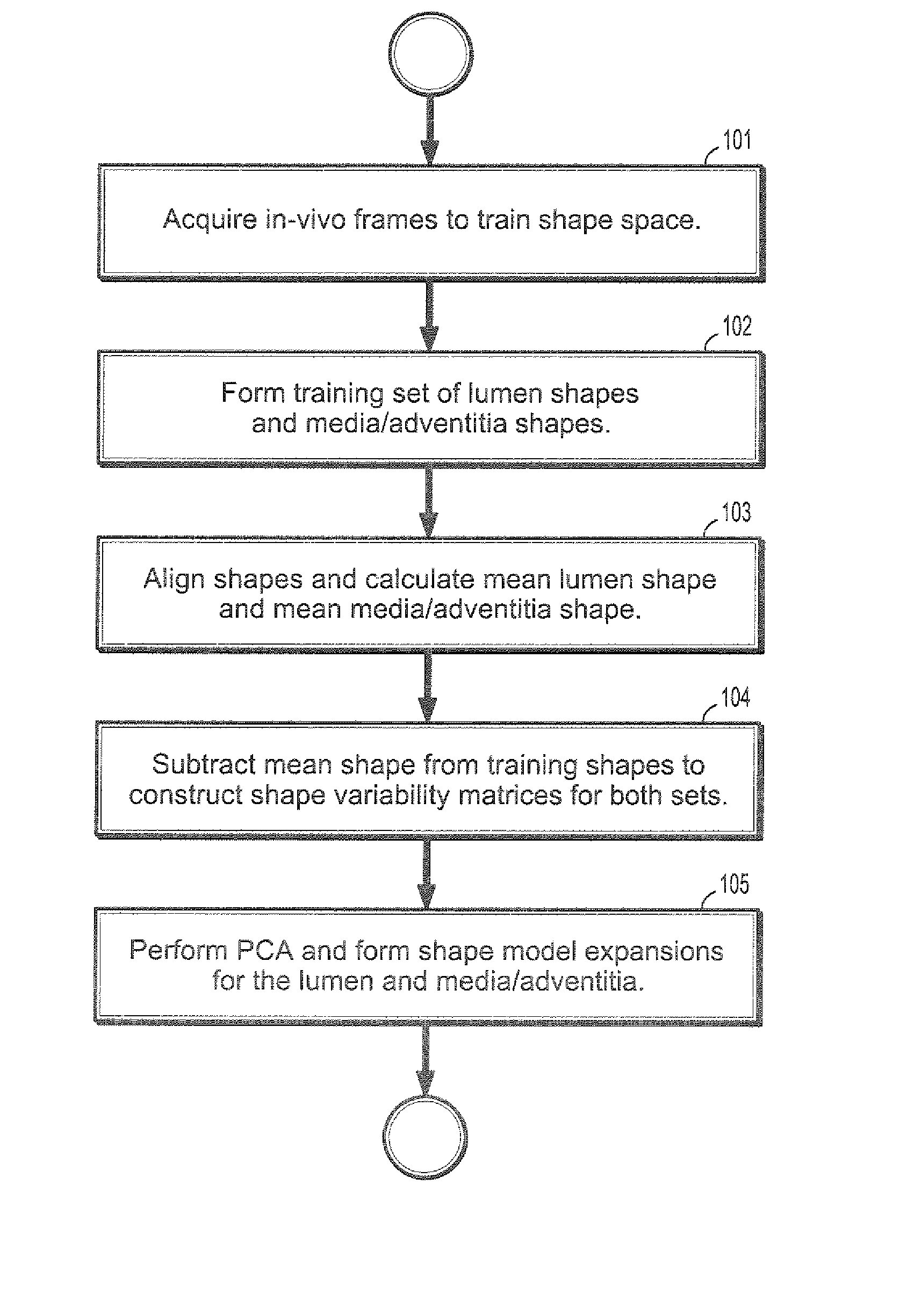
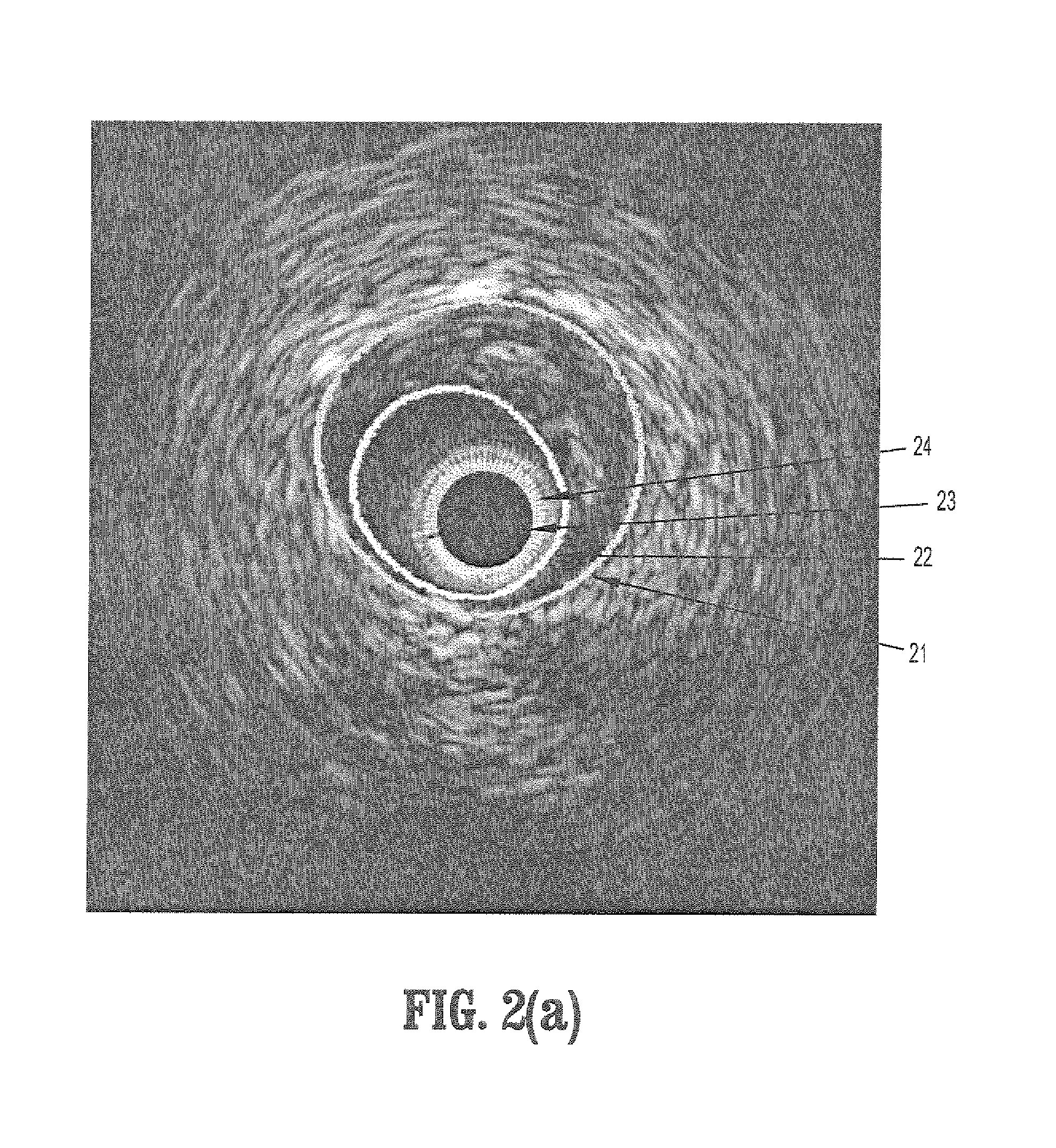
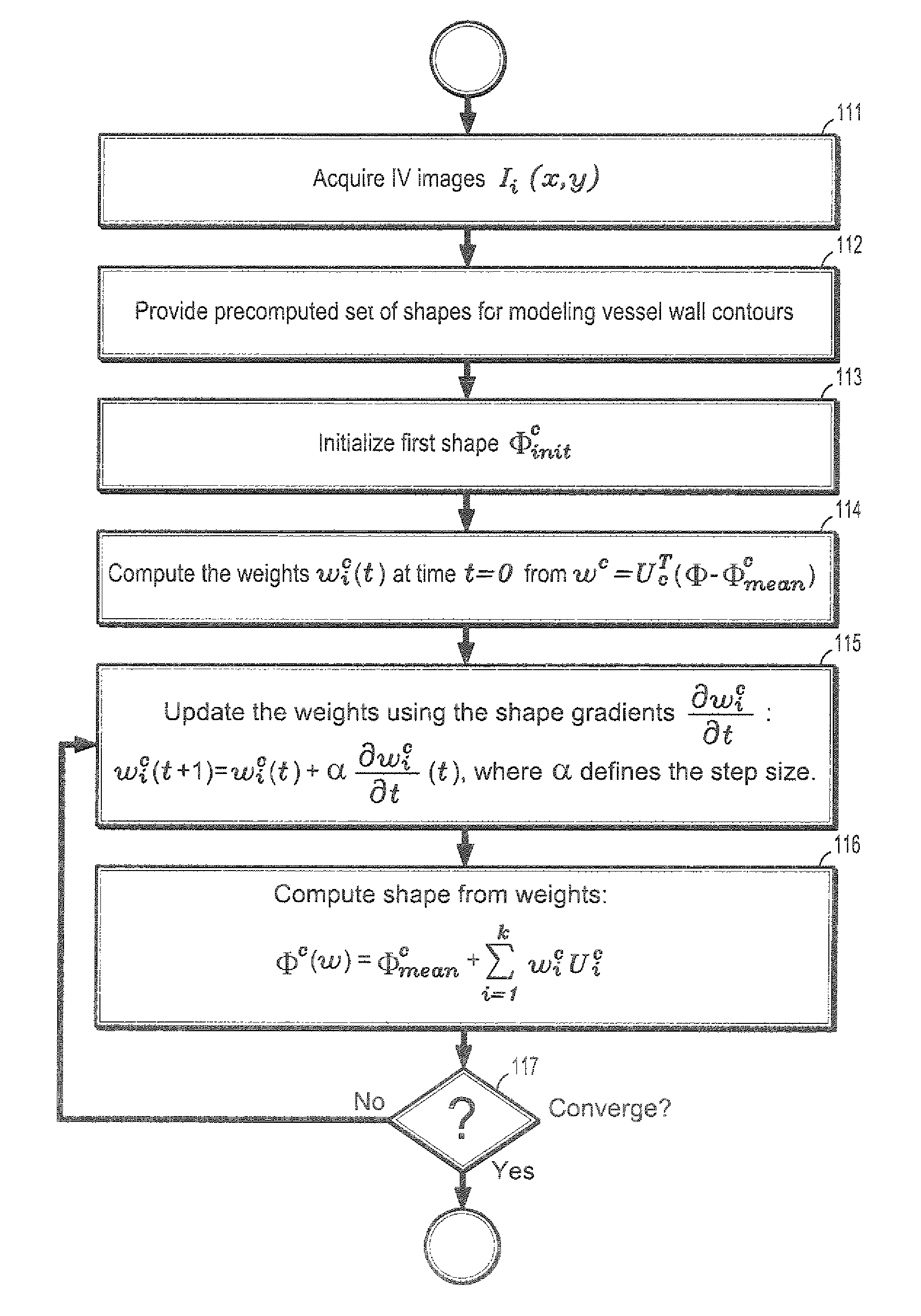
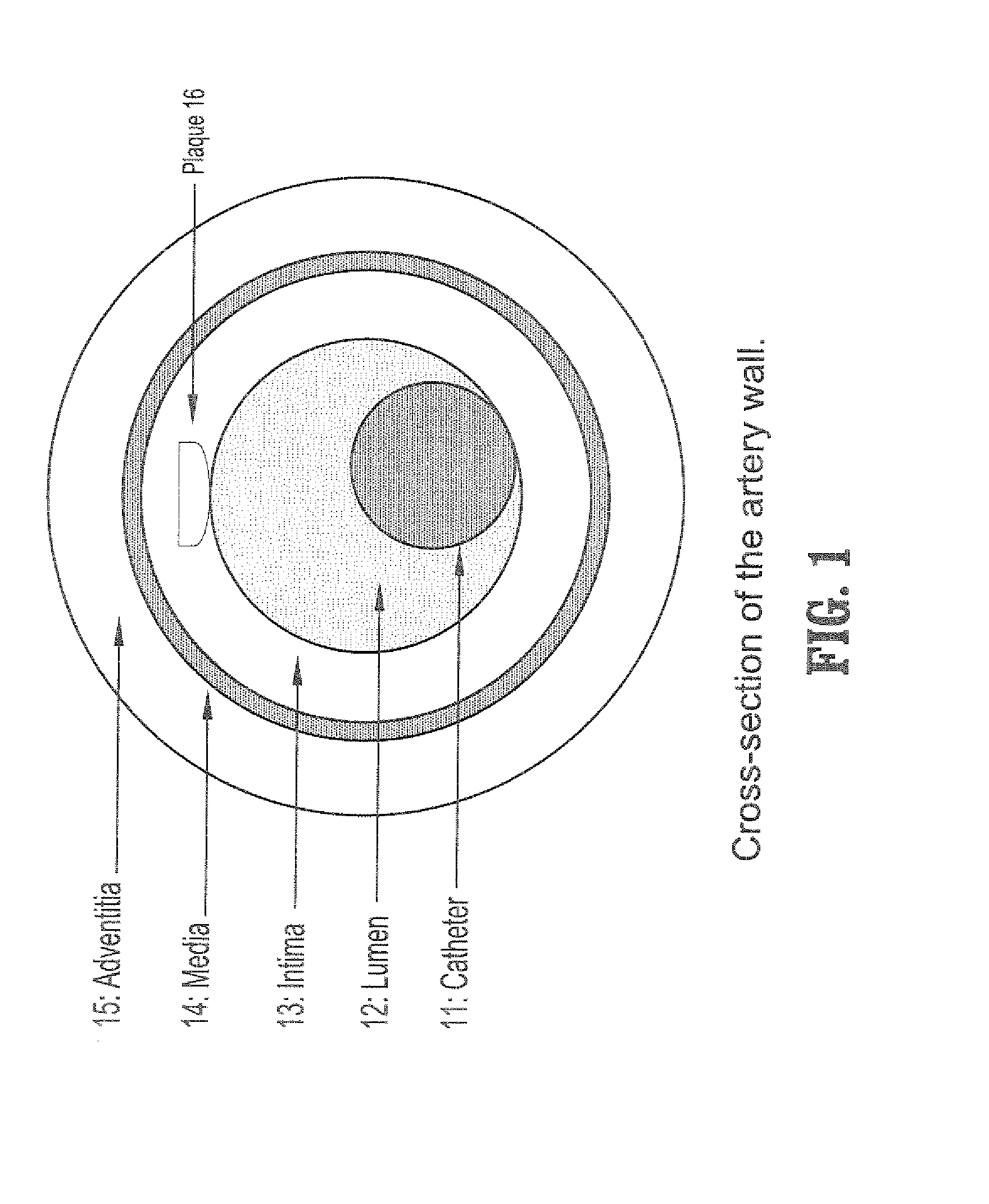
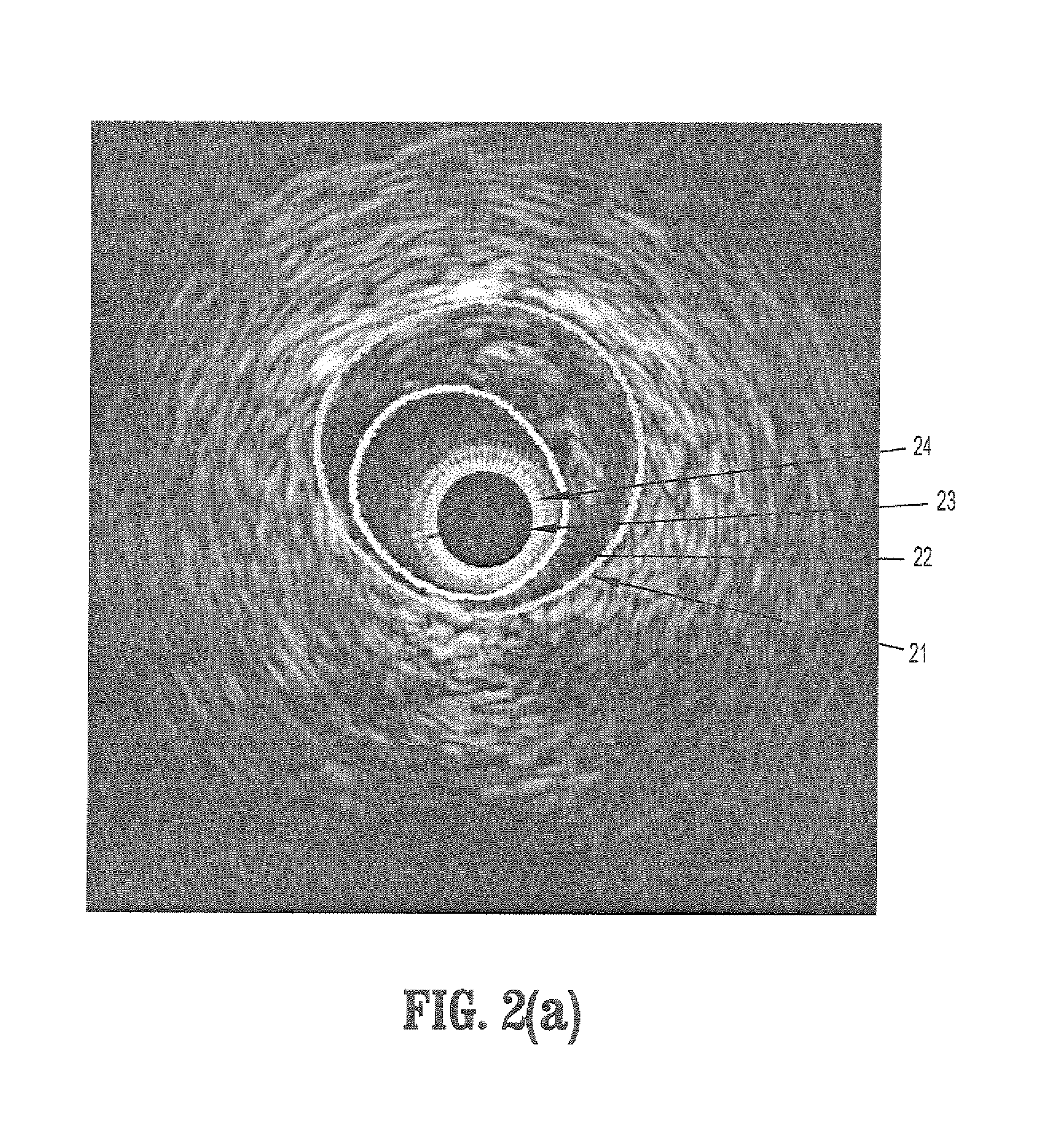
System and Method For Statistical Shape Model Based Segmentation of Intravascular Ultrasound and Optical Coherence Tomography Images
InactiveUS20080075375A1Improve segmentation qualitySufficient flexibilityImage enhancementImage analysisBoundary contourSonification
A method for segmenting intravascular images includes acquiring a series of digitized images acquired from inside a vessel, each said image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a 2-dimensional grid of pixels, providing a precomputed set of shapes for modeling contours of vessel wall boundaries, wherein a contour can be expressed as a sum of a mean shape and a inner product of shape modes and shape weights, initializing a boundary contour for one of said set of images, initializing said shape weights by projecting a contour into said shape modes, updating said shape weights from differential equations of said shape weights, and computing a contour by summing said mean shape and said inner product of shape modes and updated shape weights.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Hierarchical static shadow detection method
ActiveUS7366323B1Easy to handleEfficient identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsDependabilityLightness
There is provided a hierarchical shadow detection system for color aerial images. The system performs well with highly complex images as well as images having different brightness and illumination conditions. The system consists of two hierarchical levels of processing. The first level involves, pixel level classification, through modeling the image as a reliable lattice and then maximizing the lattice reliability using the EM algorithm. Next, region level verification, through further exploiting the domain knowledge is performed. Further analysis show that the MRF model based segmentation is a special case of the pixel level classification model. A quantitative comparison of the system and a state-of-the-art shadow detection algorithm clearly indicates that the new system is highly effective in detecting shadow regions in an image under different illumination and brightness conditions.
Owner:ZAMA INNOVATIONS LLC
System and method for statistical shape model based segmentation of intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography images
InactiveUS7831078B2Improve segmentation qualitySufficient flexibilityImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBoundary contourUltrasound angiography
A method for segmenting intravascular images includes acquiring a series of digitized images acquired from inside a vessel, each said image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a 2-dimensional grid of pixels, providing a precomputed set of shapes for modeling contours of vessel wall boundaries, wherein a contour can be expressed as a sum of a mean shape and a inner product of shape modes and shape weights, initializing a boundary contour for one of said set of images, initializing said shape weights by projecting a contour into said shape modes, updating said shape weights from differential equations of said shape weights, and computing a contour by summing said mean shape and said inner product of shape modes and updated shape weights.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods of utilizing image noise information
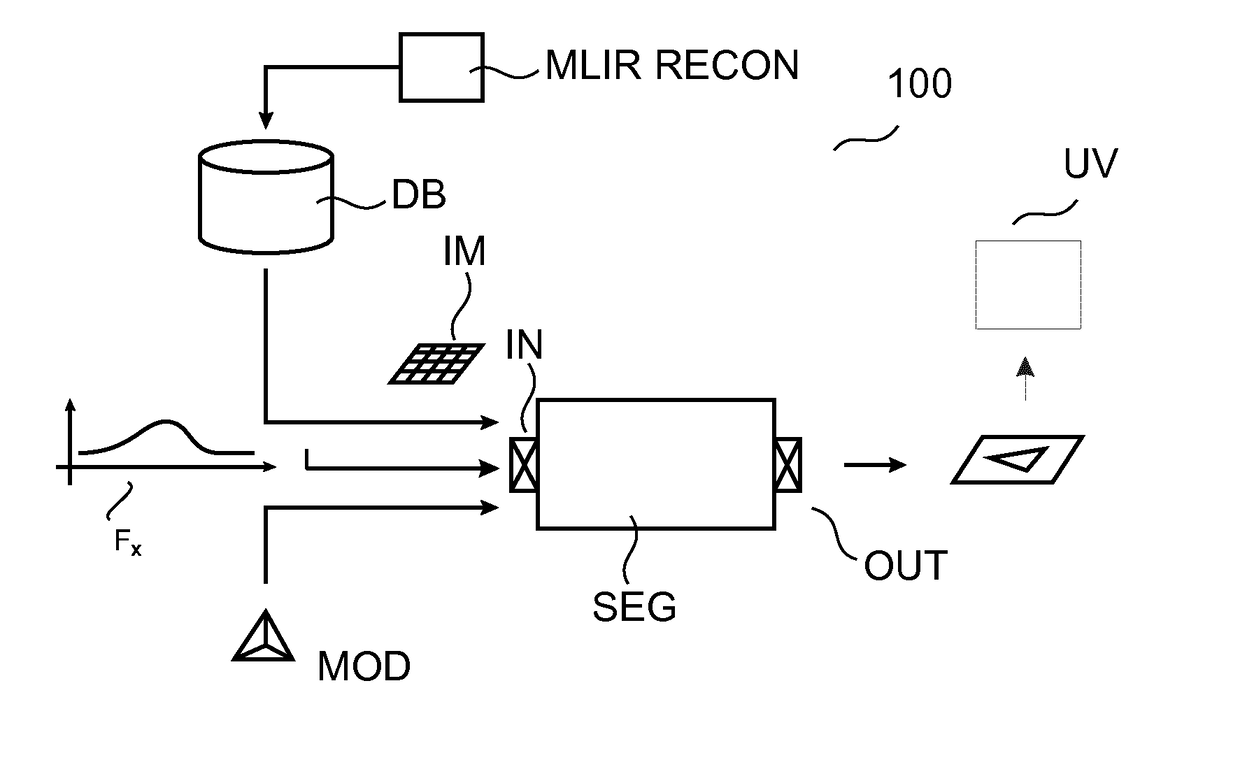
ActiveUS20160140725A1Increase uncertaintyIntuitive and convenientImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
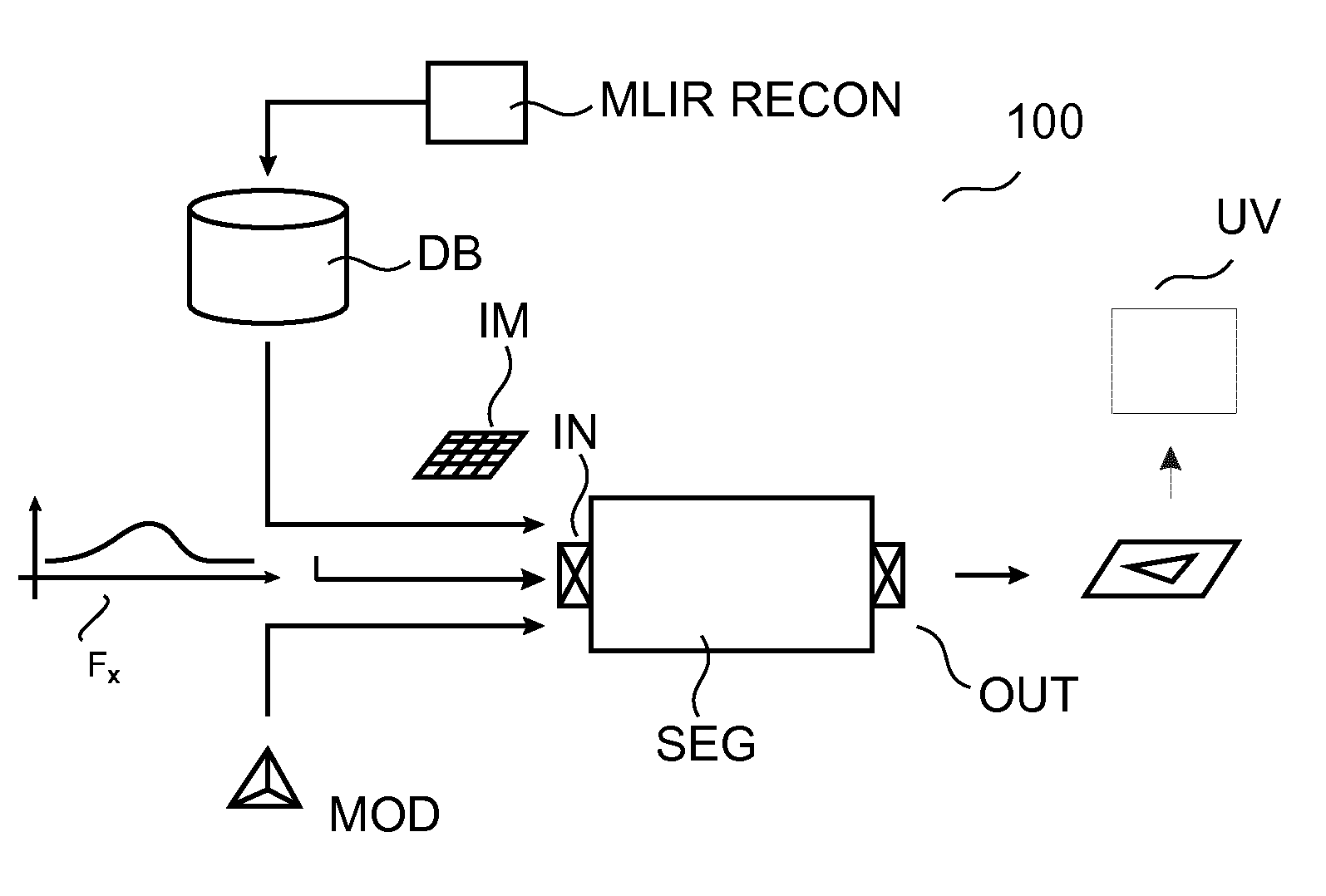
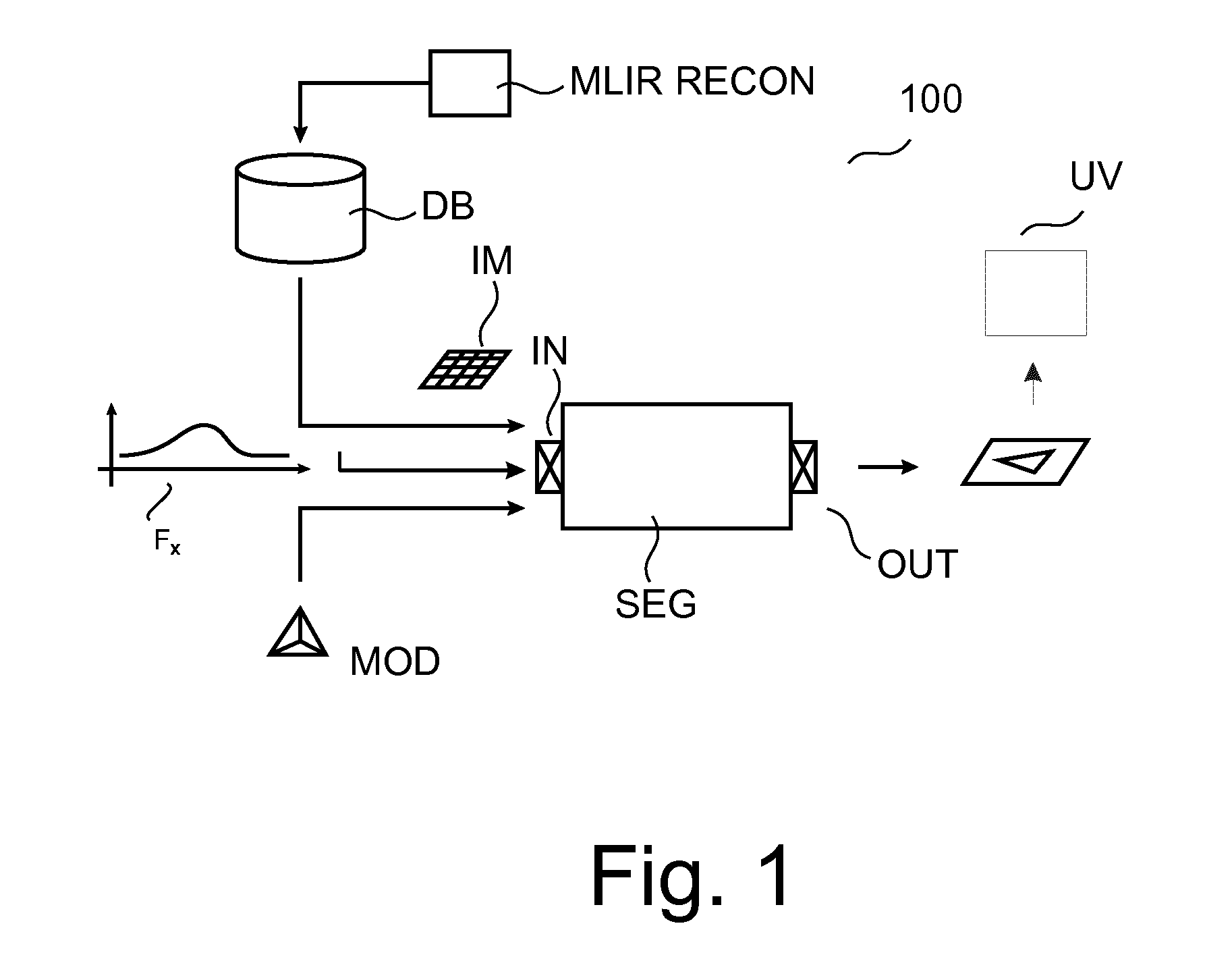
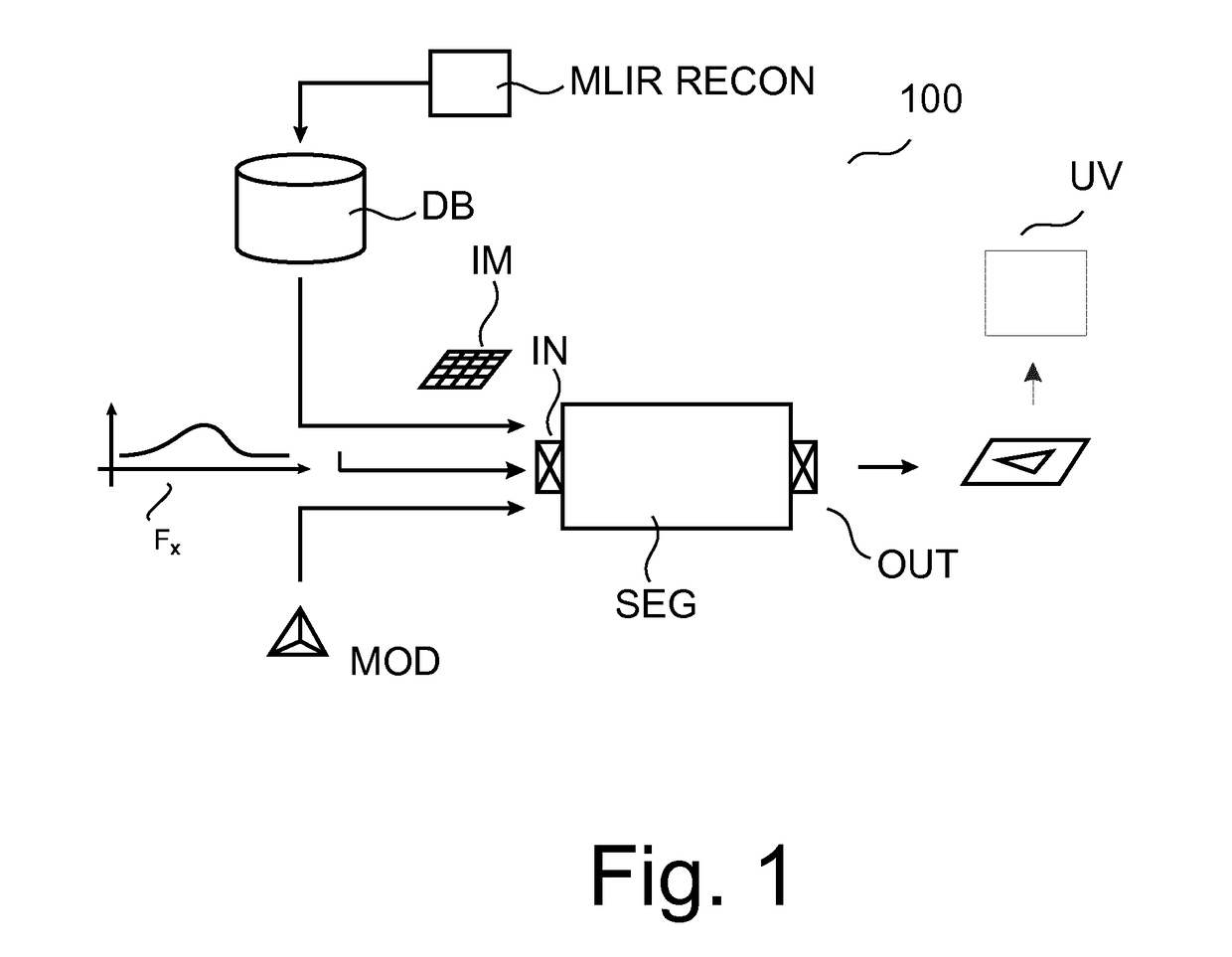
Image processing methods and related apparatuses (SEG,UV). The apparatuses (SEG,UV) operate to utilize noise signal information in images (IM). According to one aspect, apparatus (SEG) uses the noise information (FX) to control a model based segmentation. According to a further aspect, apparatus (UV) operates, based on the noise information (FX), to visualize the uncertainty of image information that resides at edge portions of the or an image (IM).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
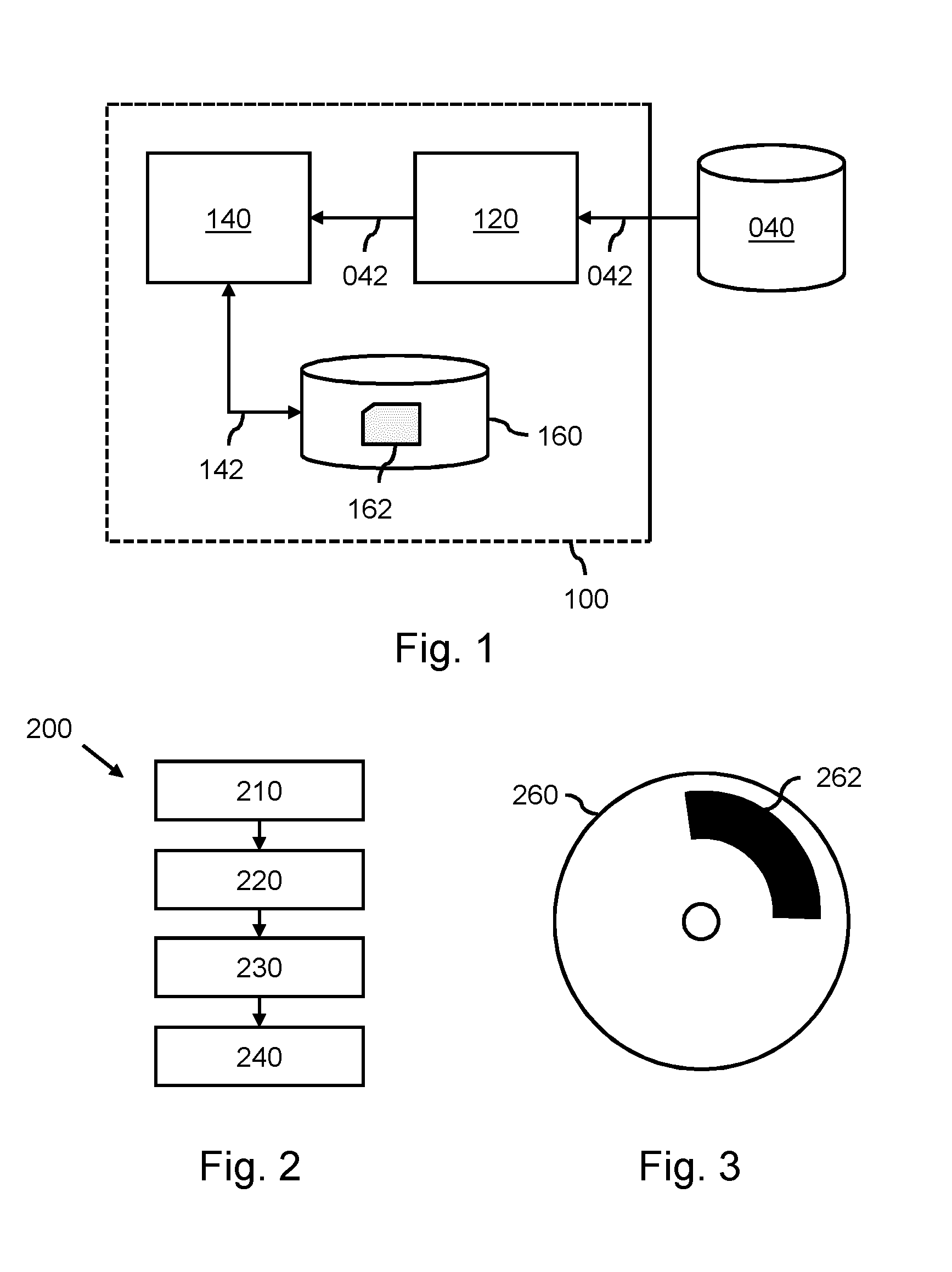
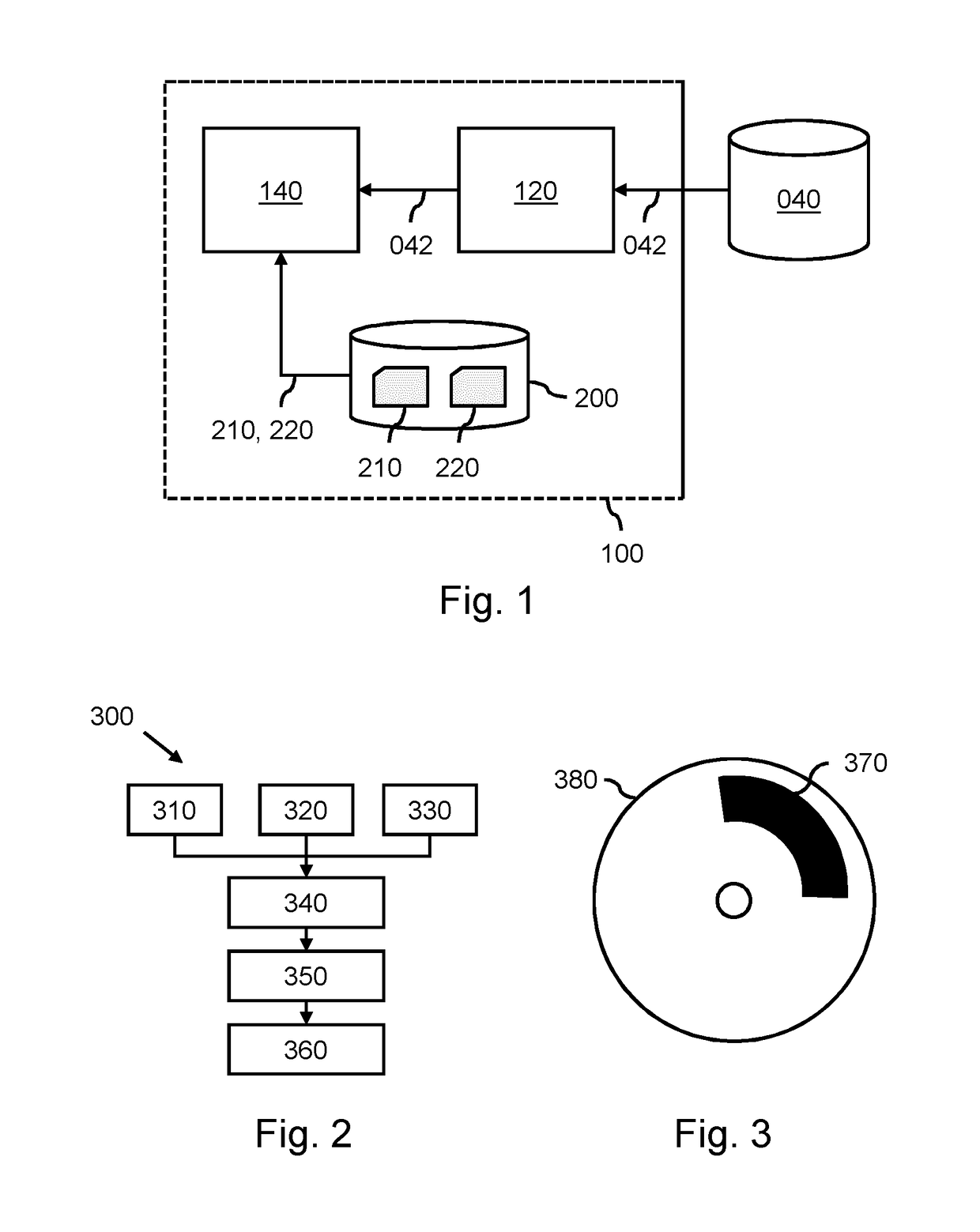
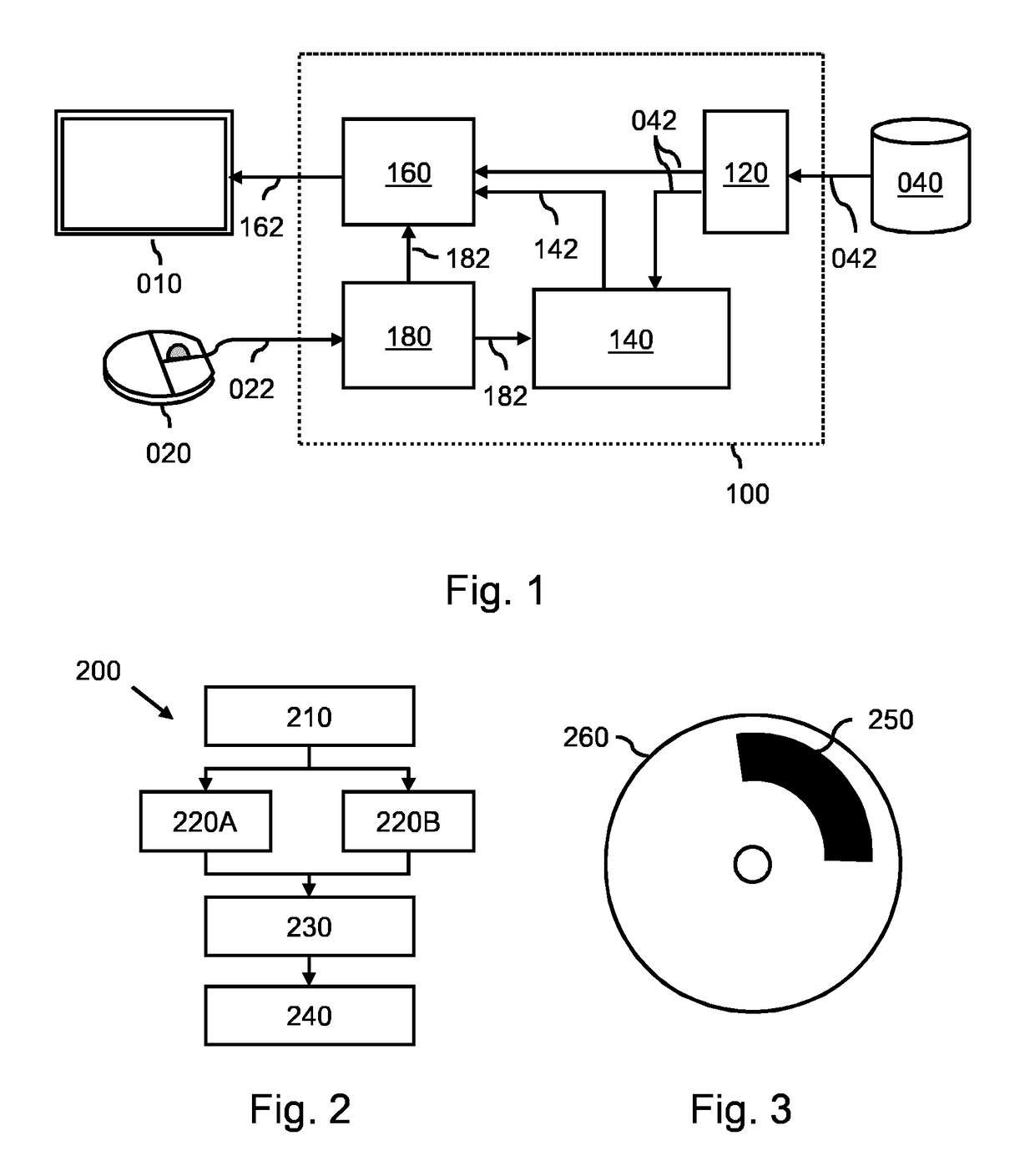
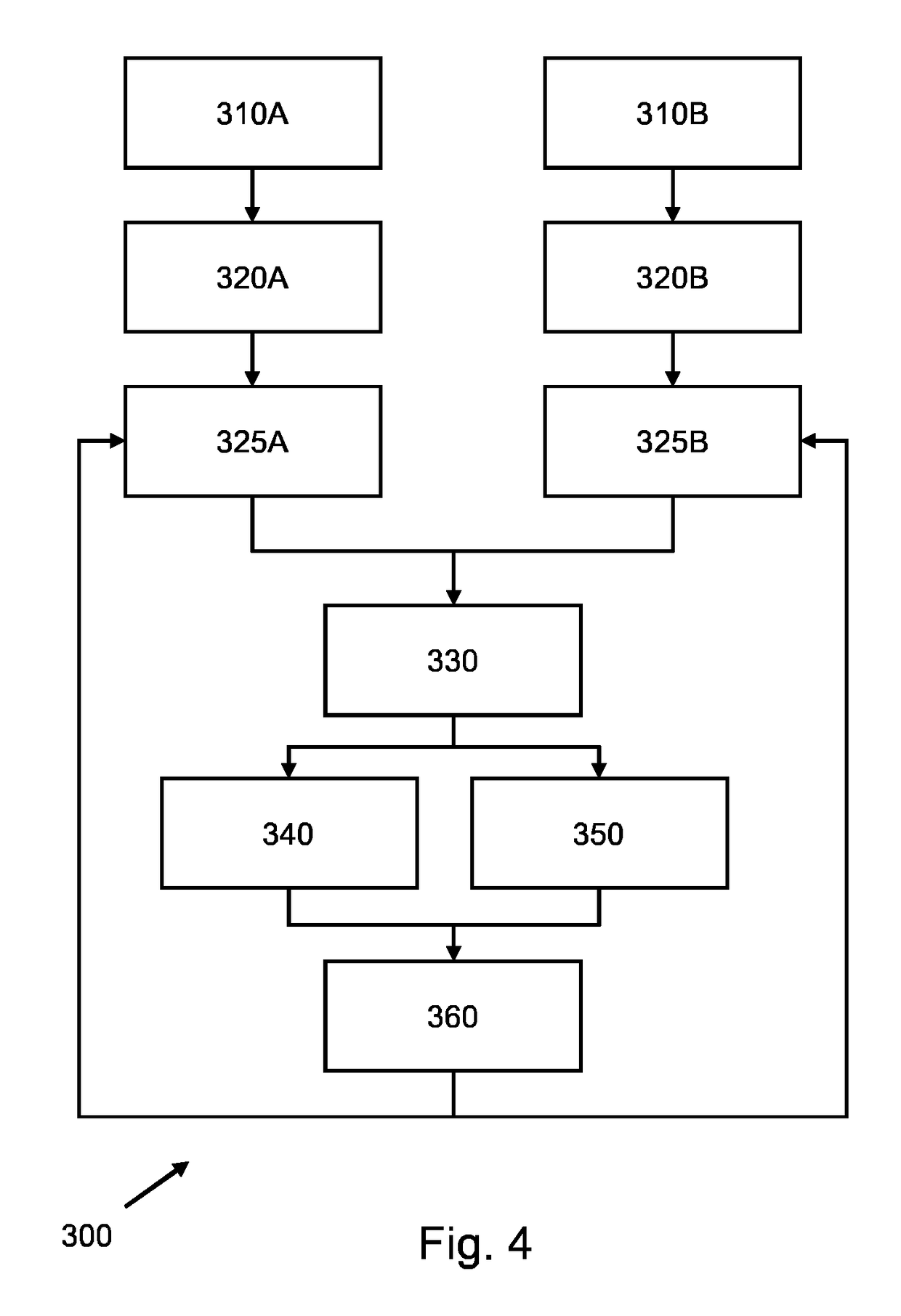
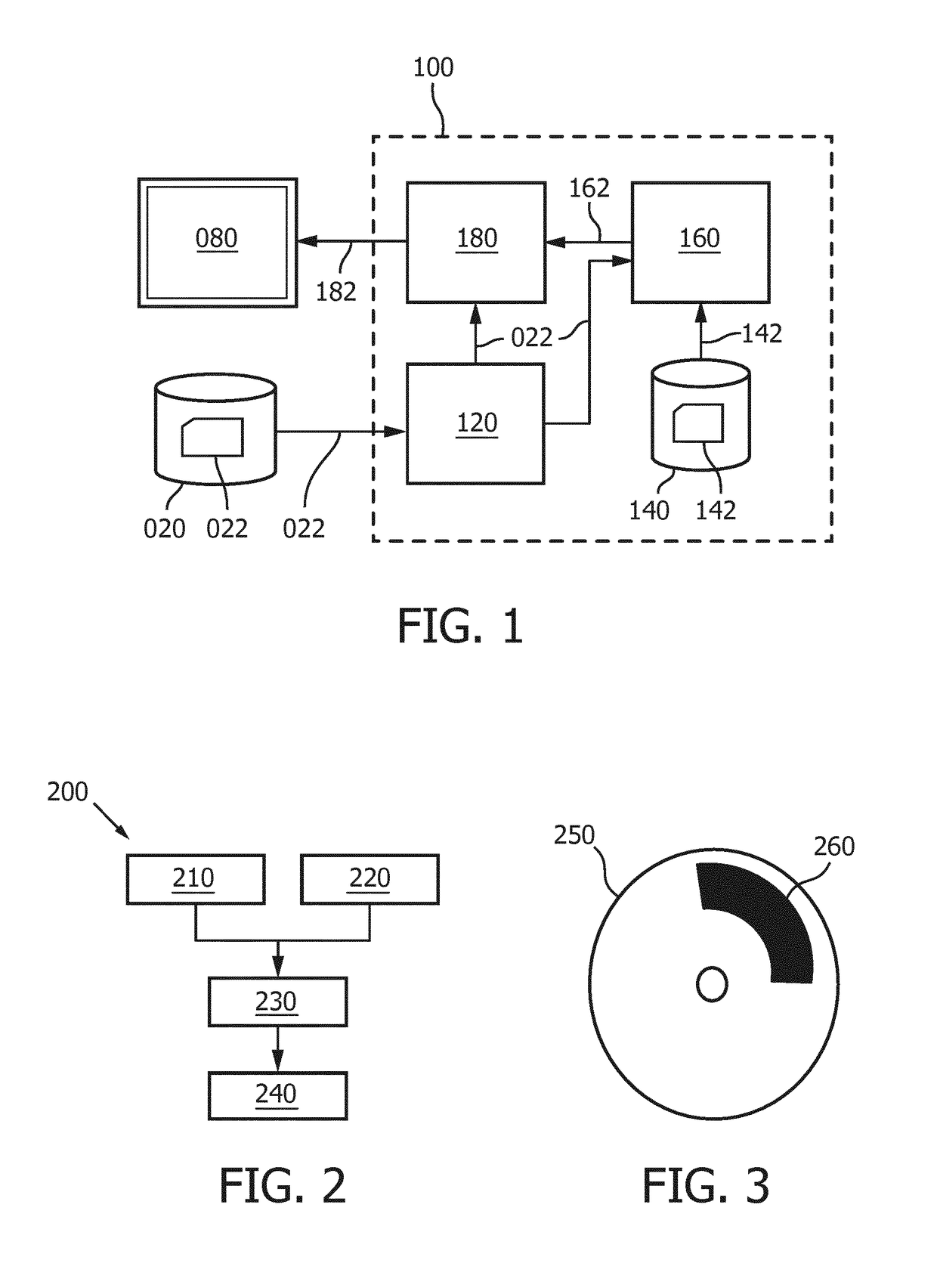
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS20160063726A1Cope wellImprove fitImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresPattern recognition
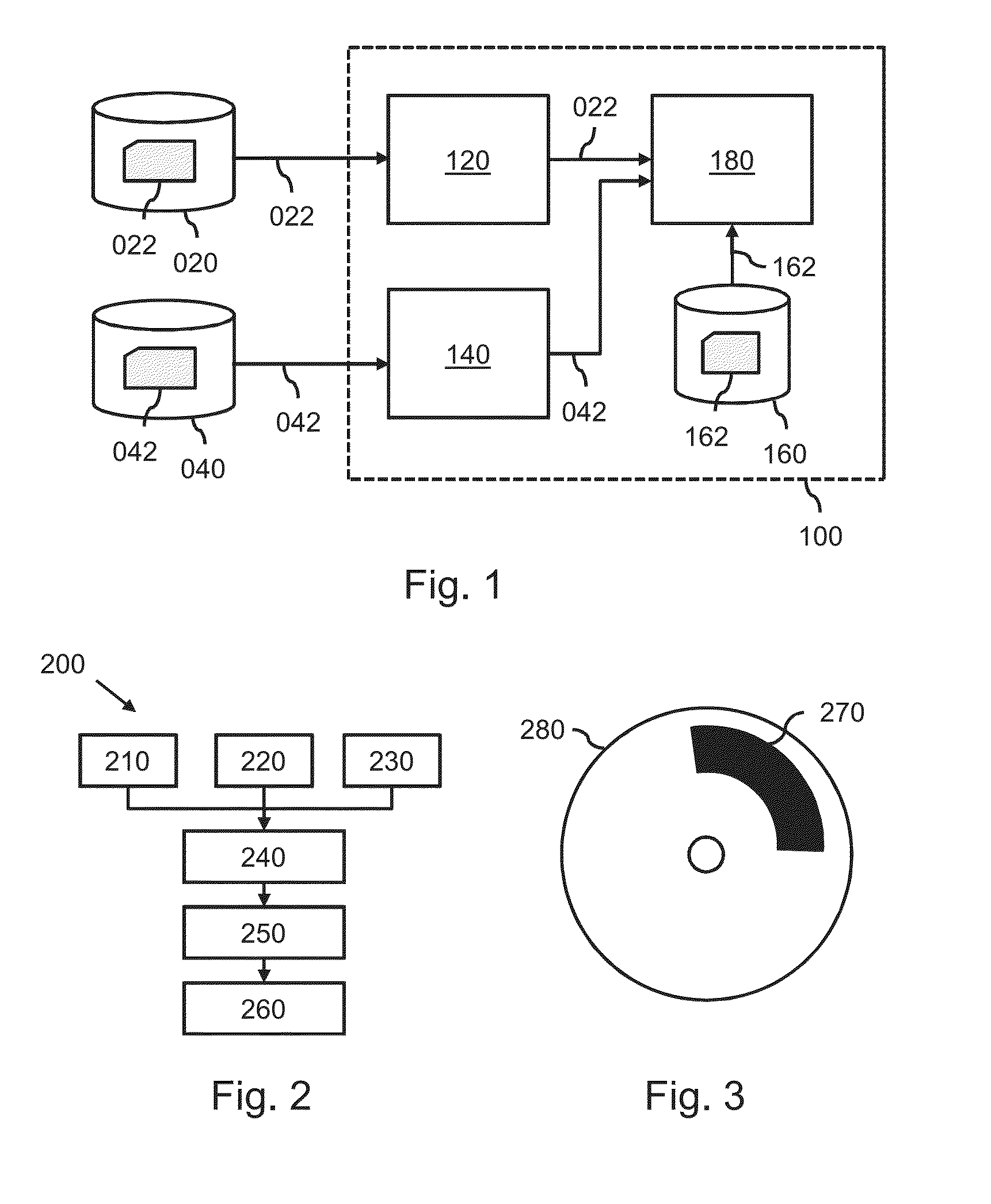
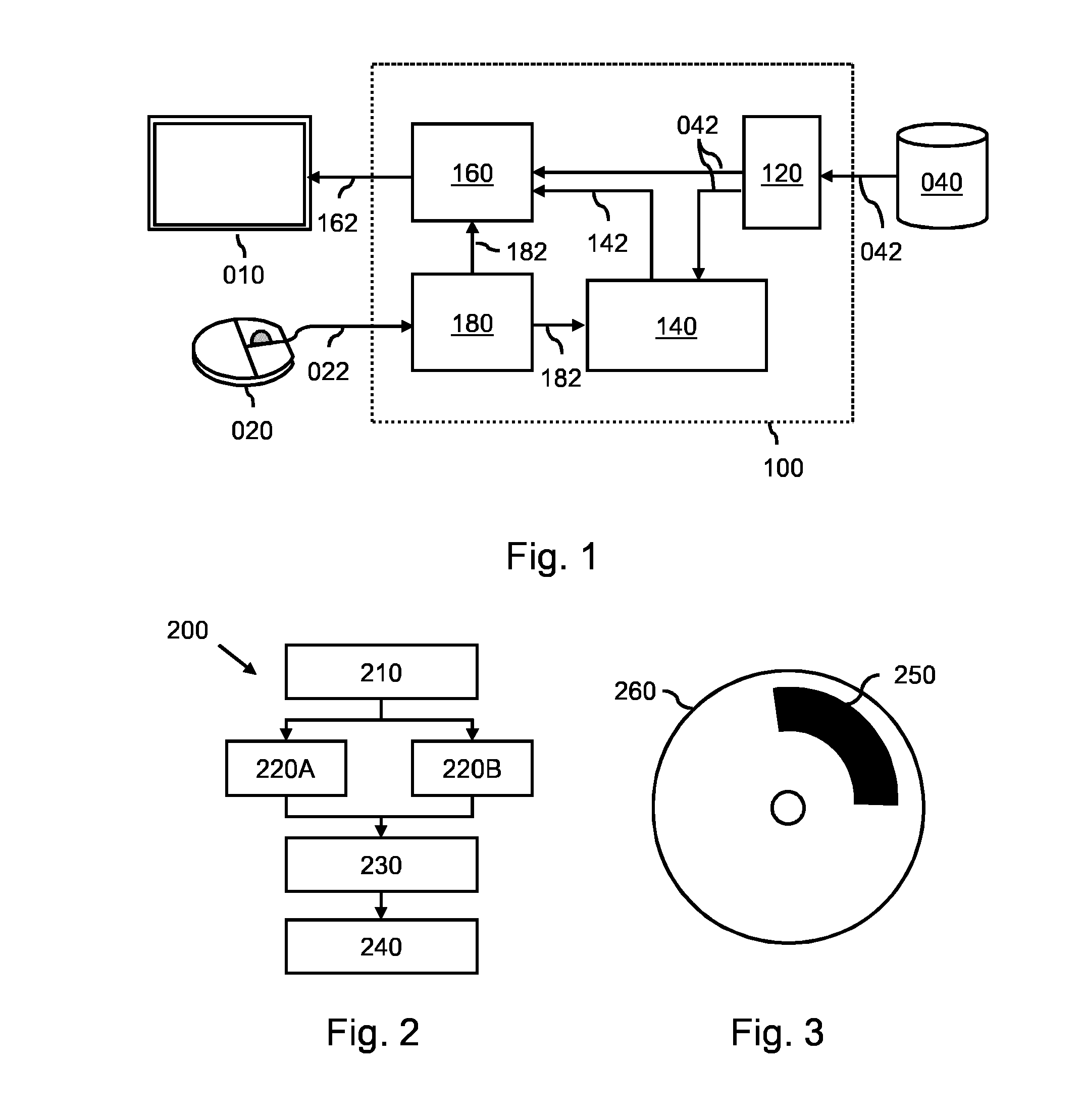
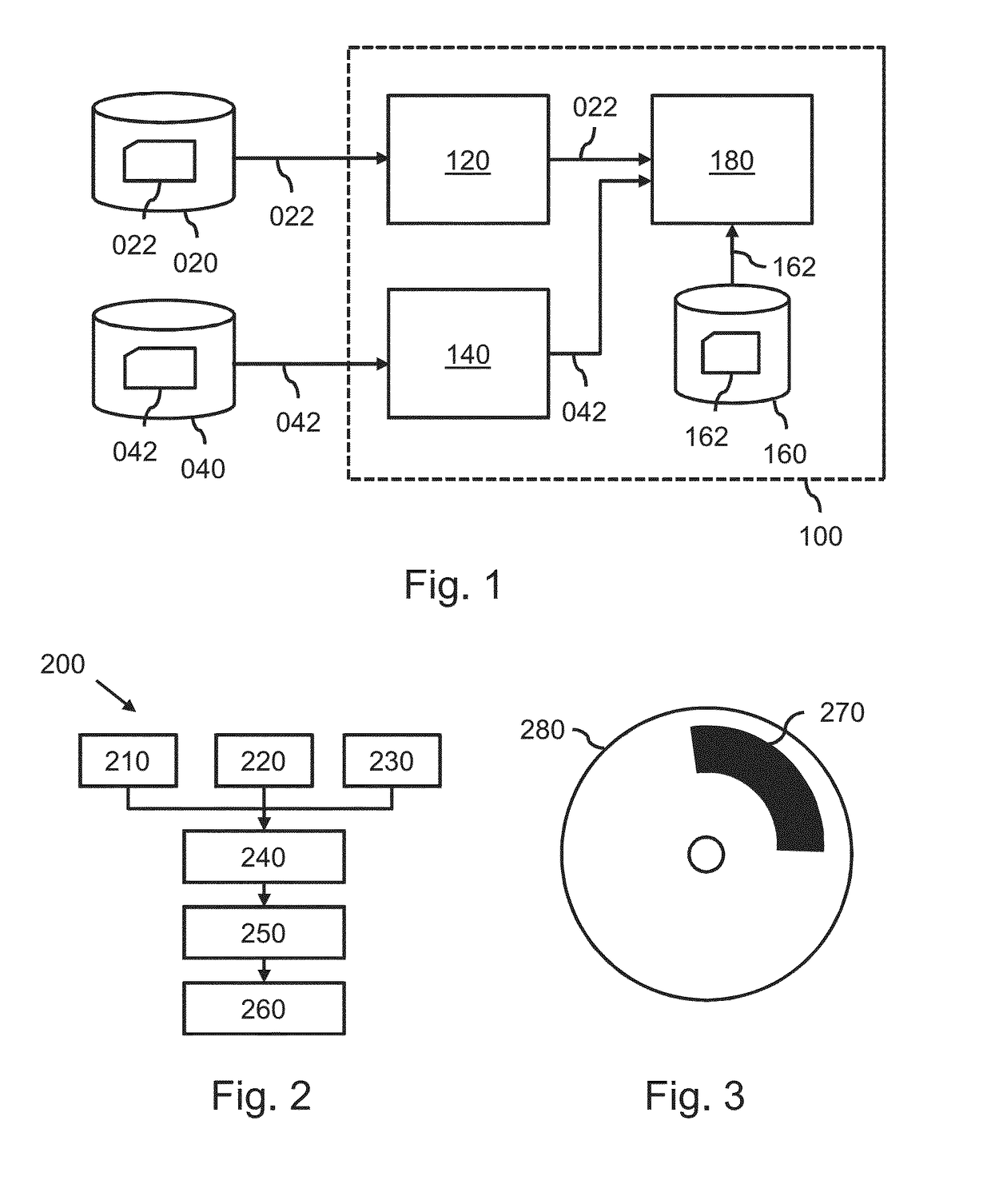
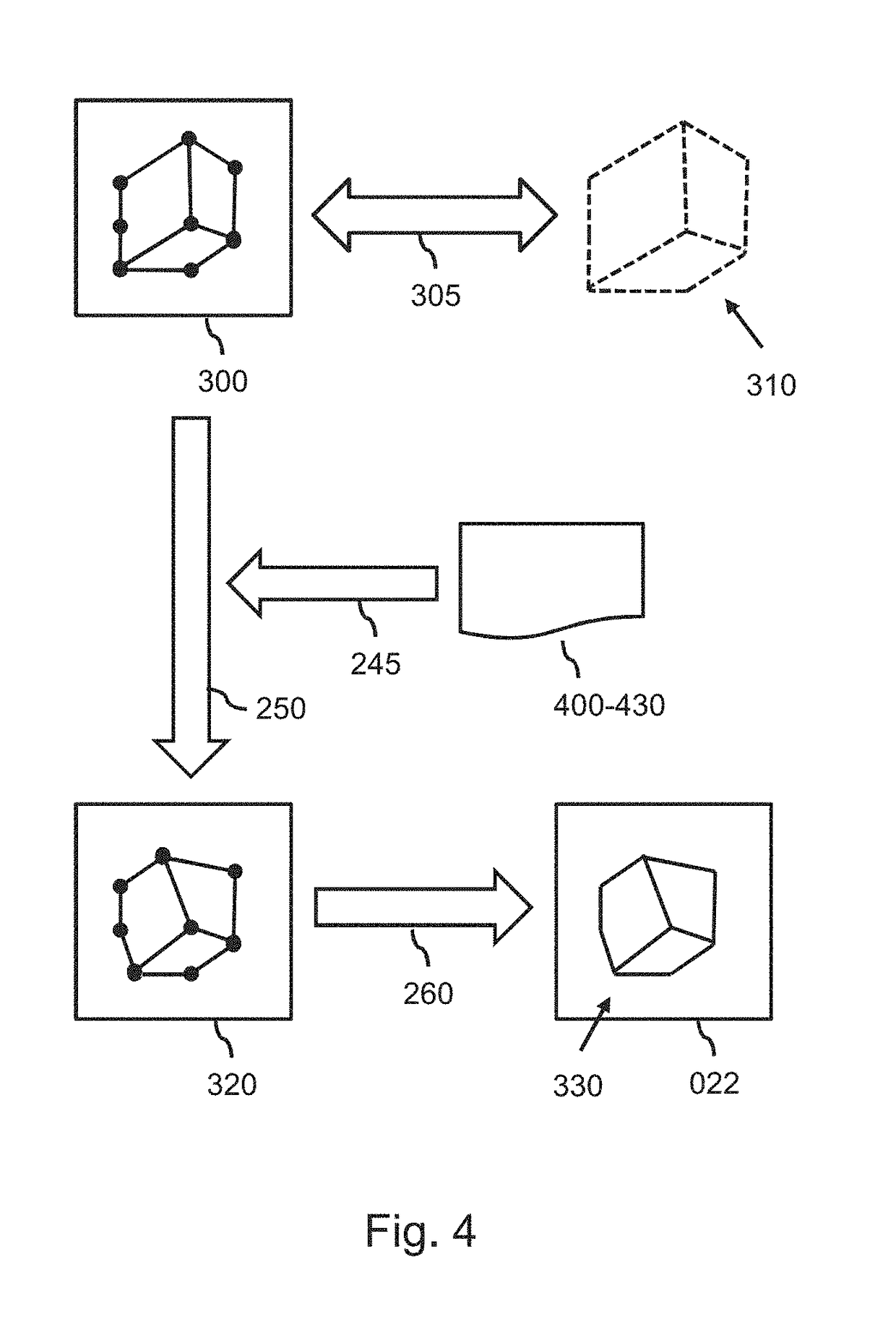
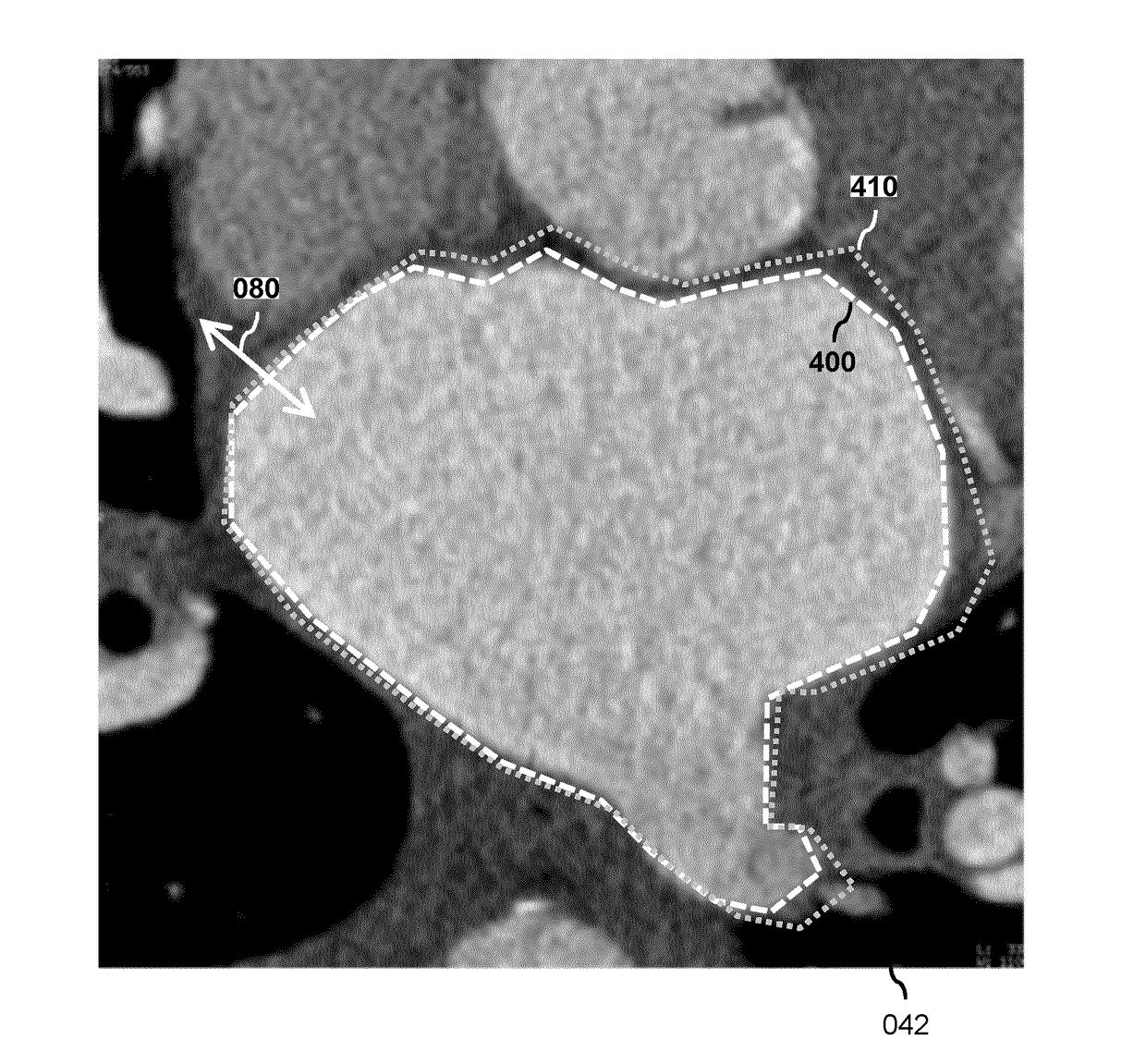
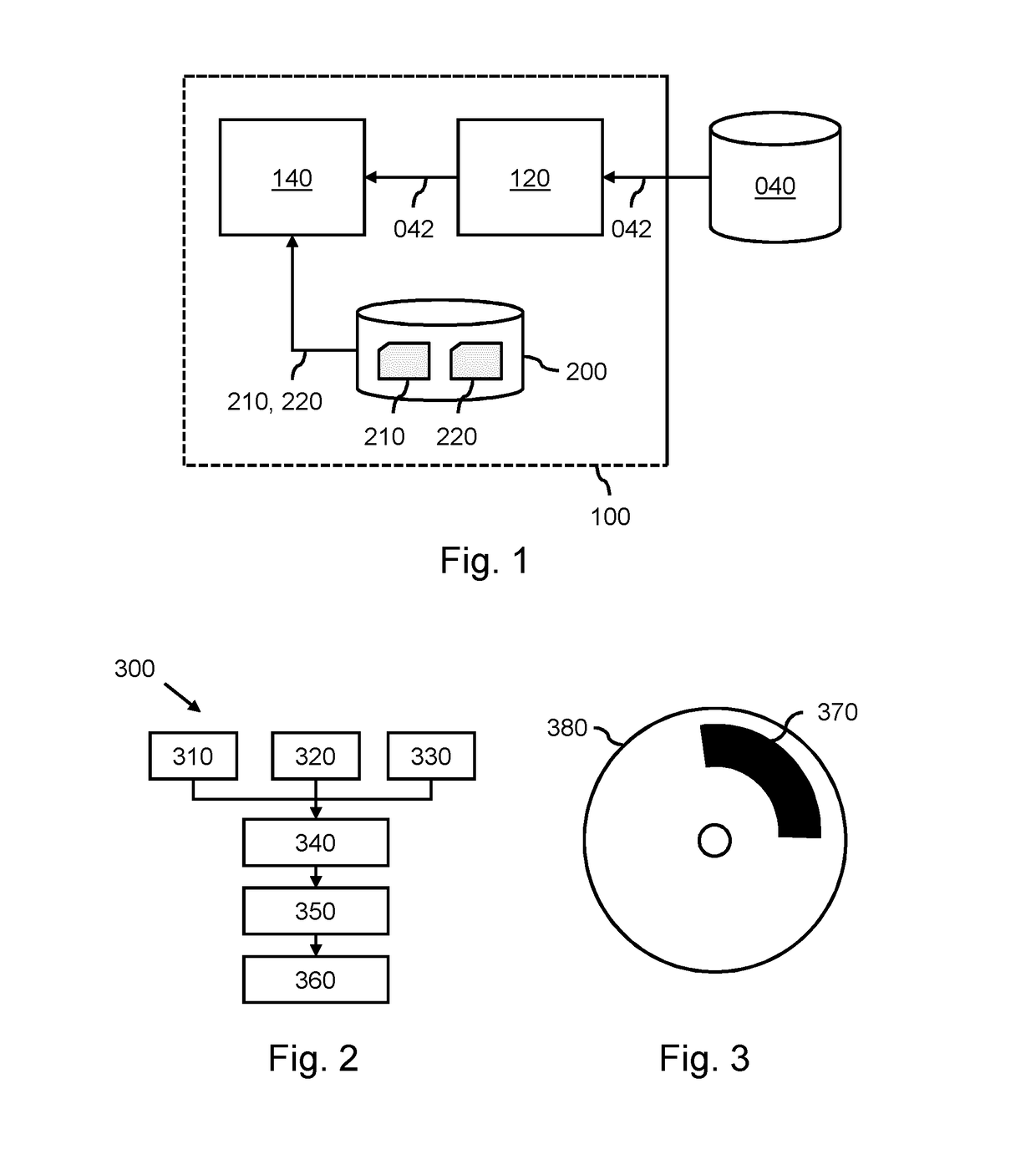
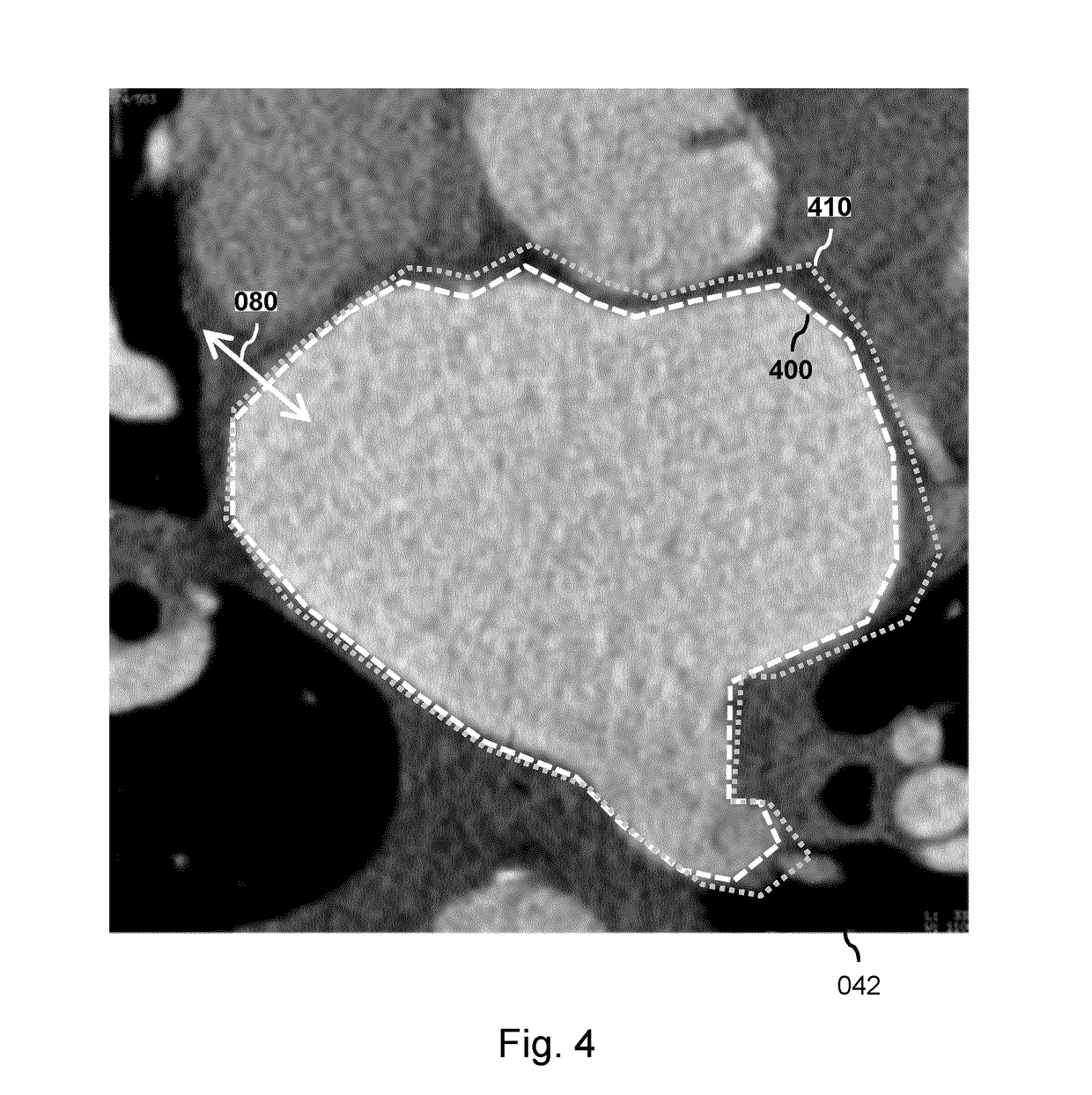
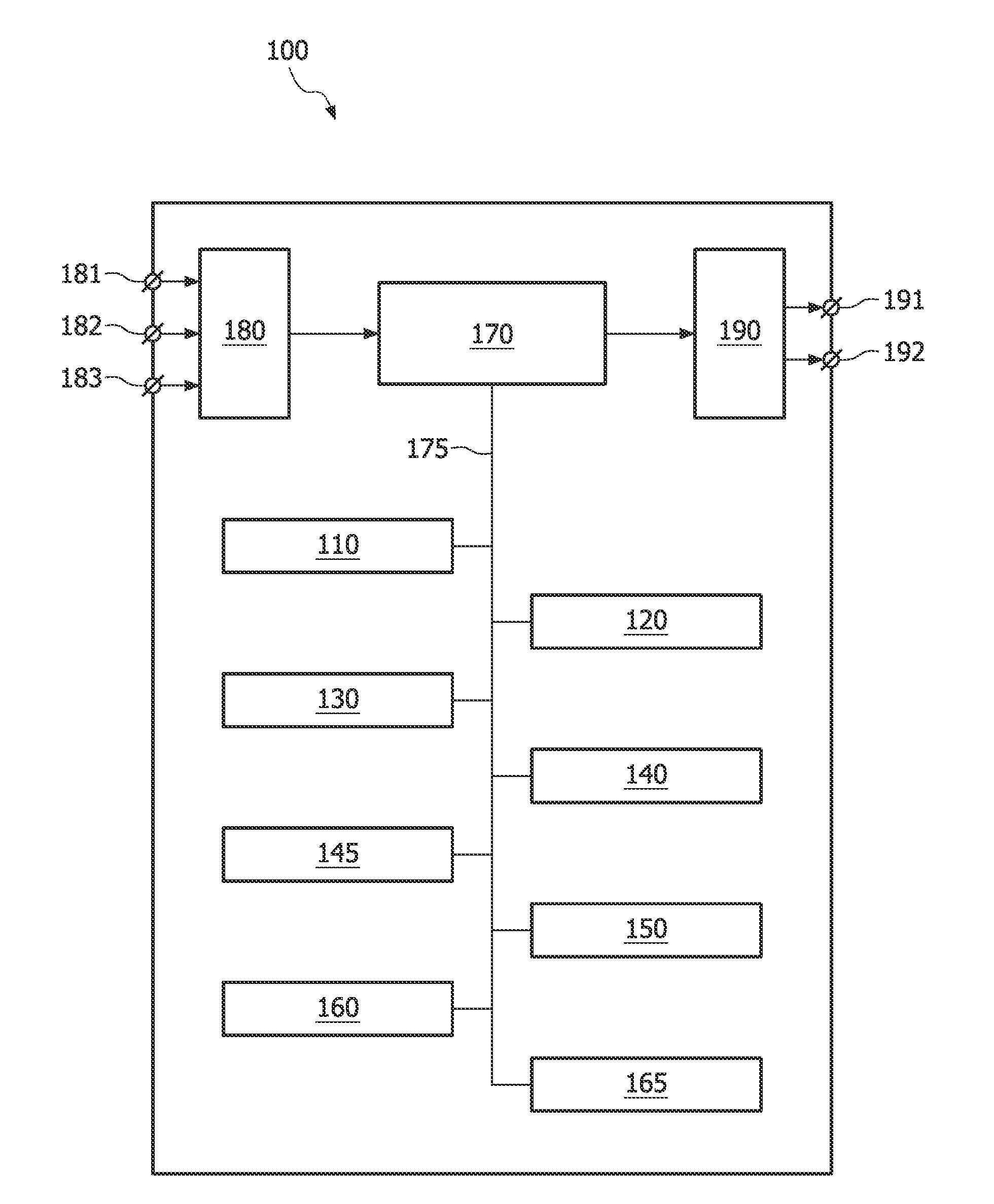
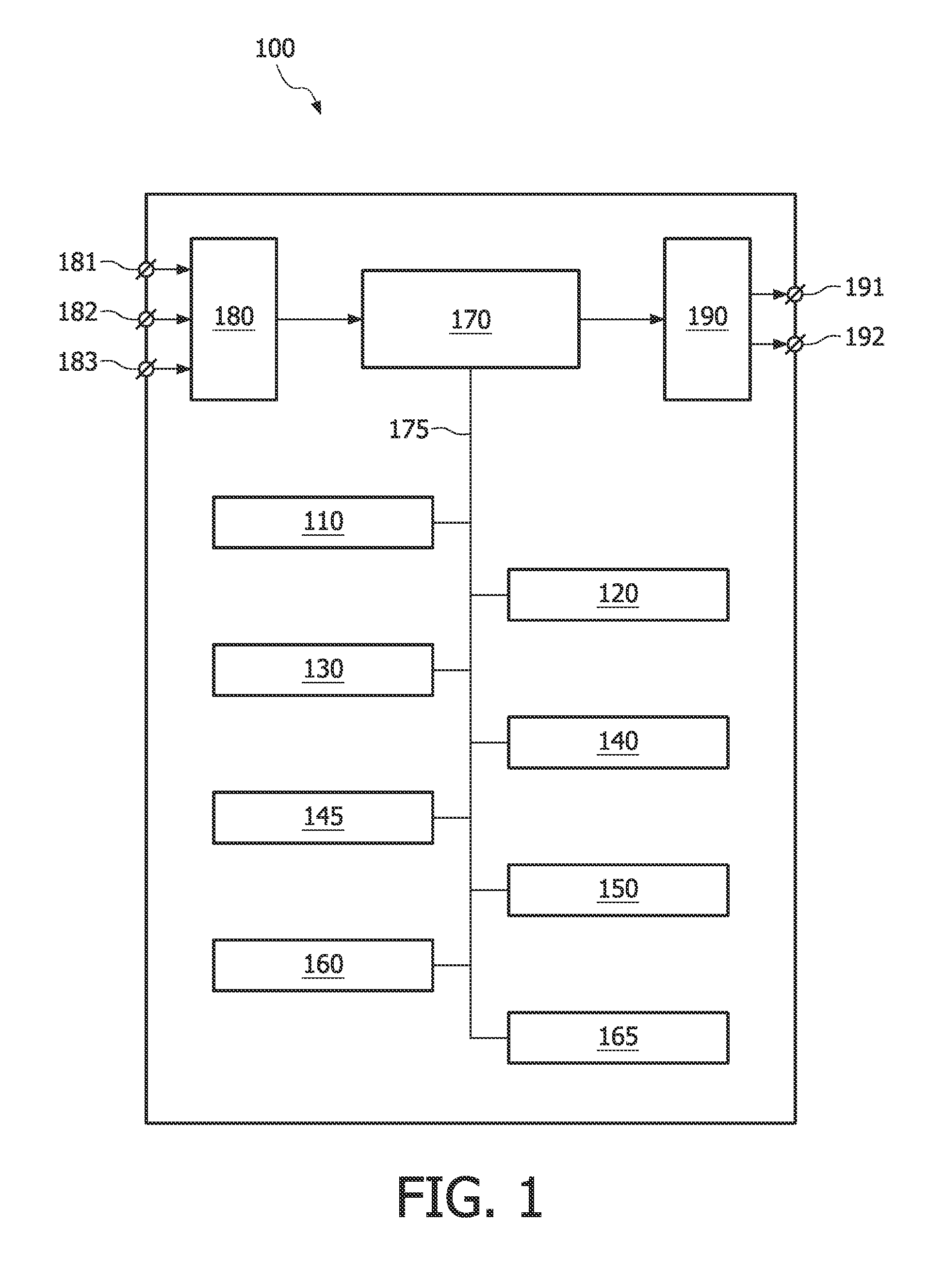
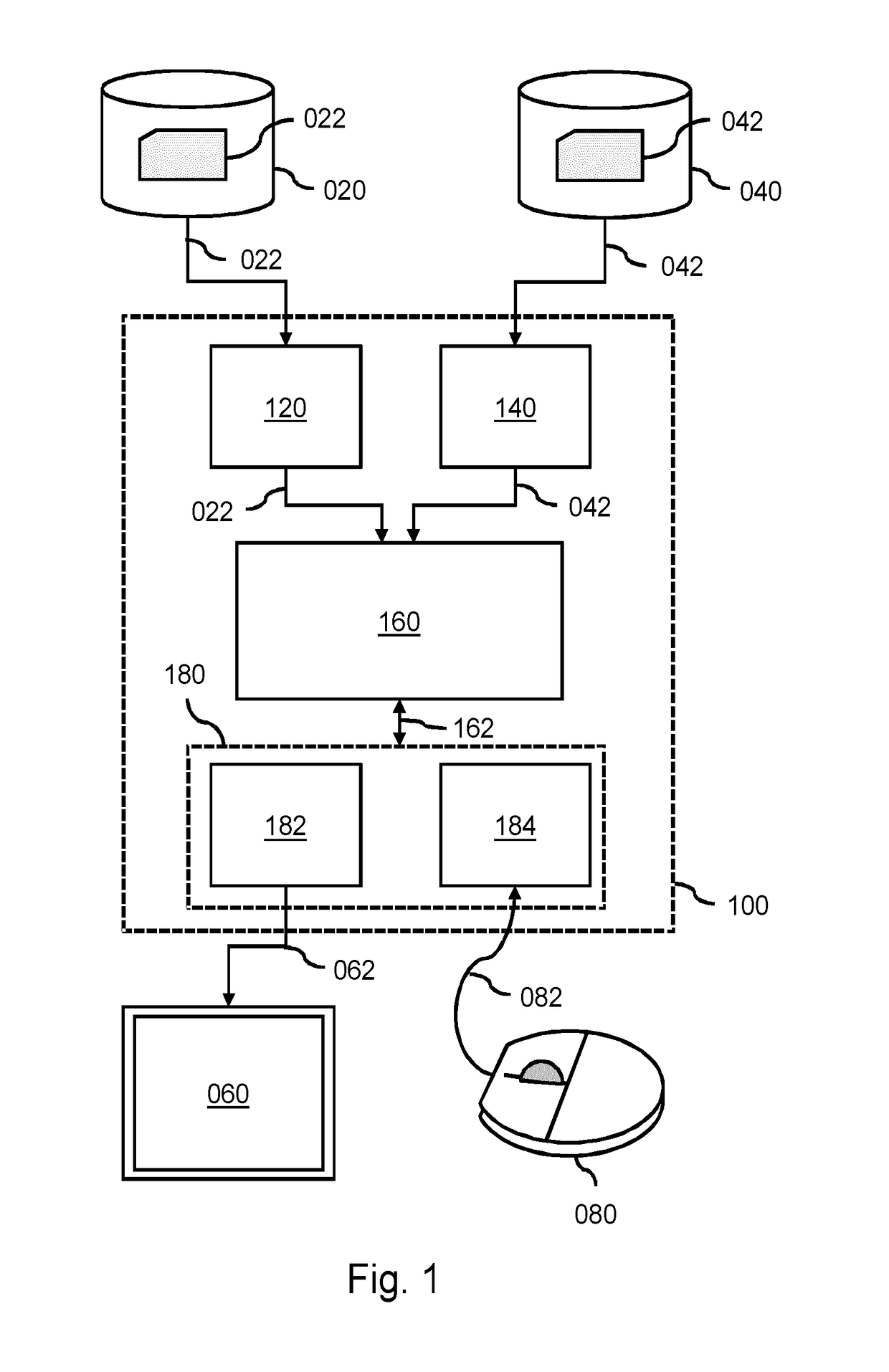
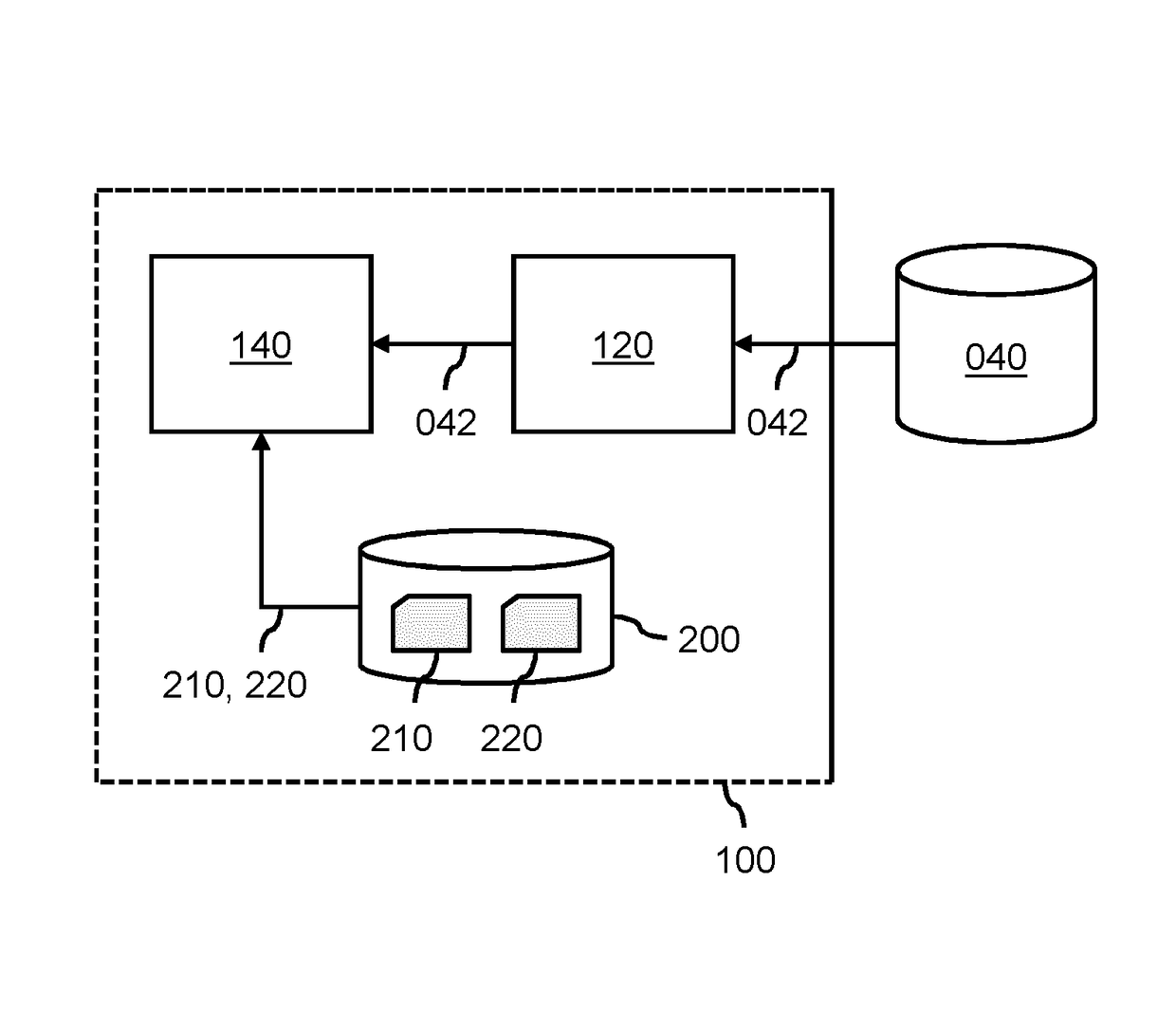
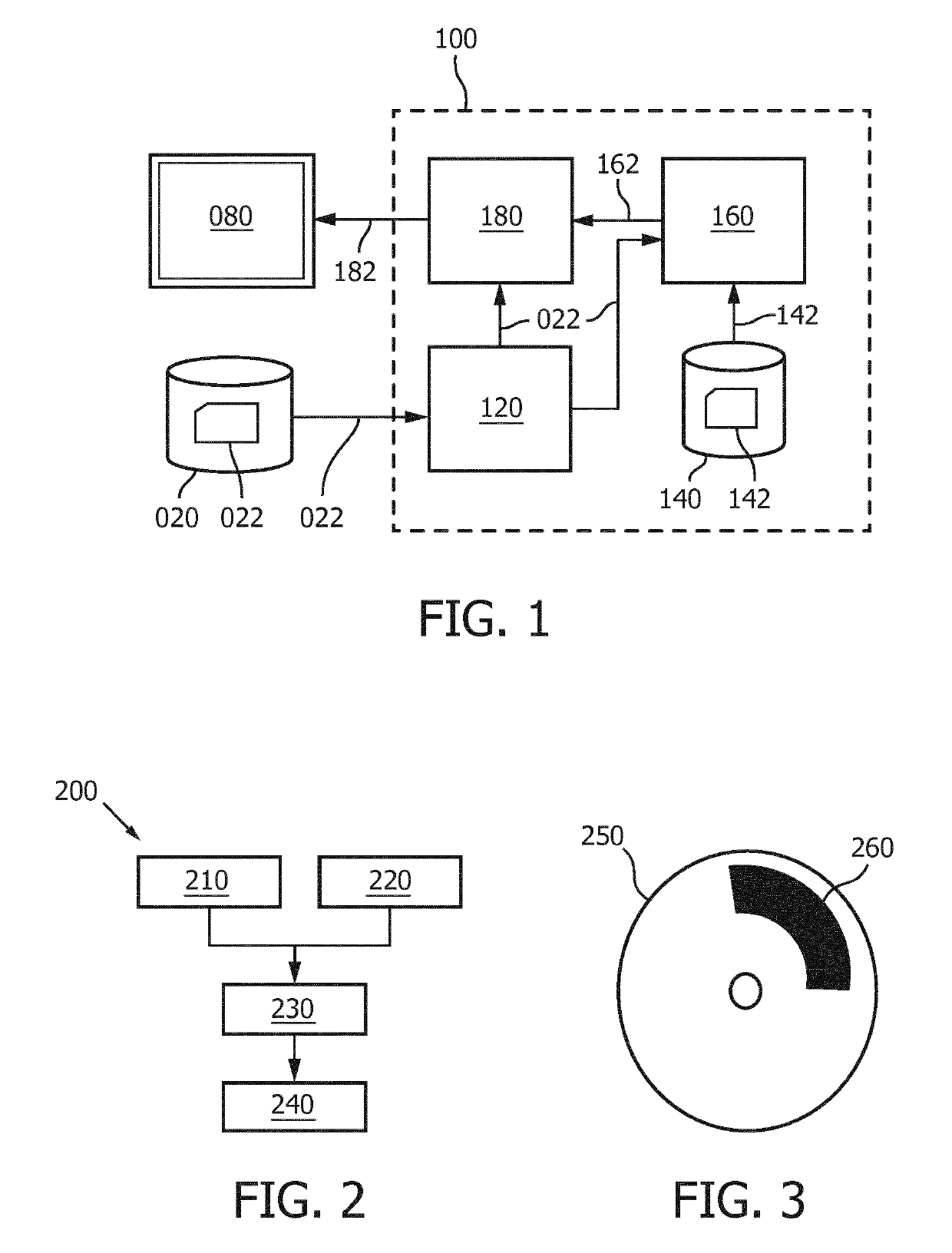
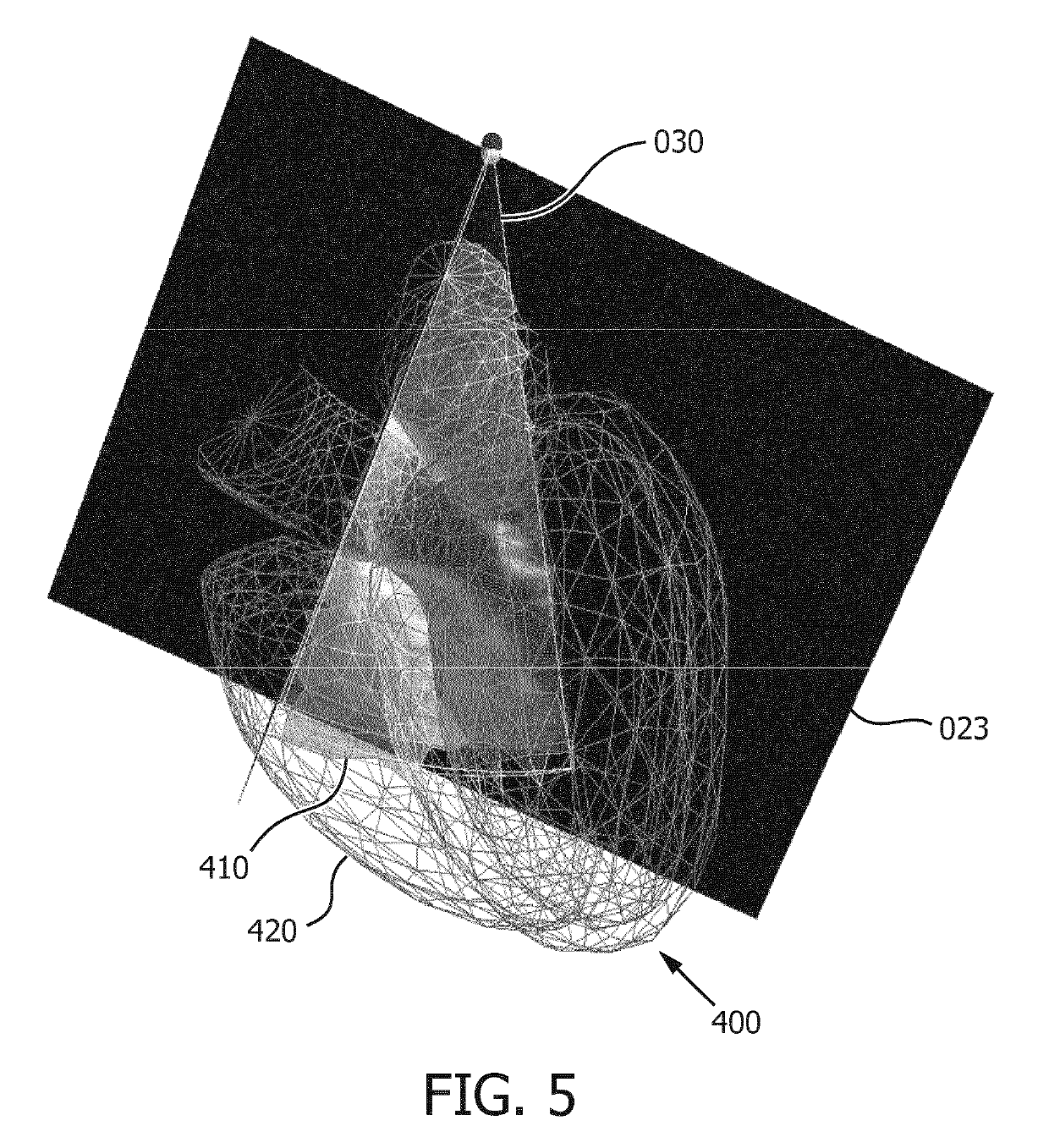
A system (100) and method is provided for performing a model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure in a medical image of a patient. The medical image (022) is accessed. Moreover, model data (162) is provided which defines a deformable model for segmenting the type of anatomical structure. The model-based segmentation of the anatomical structure is performed by adapting the deformable model to the anatomical structure in the medical image using an adaptation technique. In accordance with the present invention, performing the model based segmentation further comprises determining from patient data (042) medical information which is predictive of an appearance of the anatomical structure in the medical image, and adjusting or setting a segmentation parameter based on the medical information so as to adjust the model-based segmentation to said predicted appearance of the anatomical structure in the medical image, the segmentation parameter being a parameter of i) the deformable model or ii) the adaptation technique. Advantageously, the system and method are enabled to better cope with the inter-patient and inter-disease-stage variability in the appearance of anatomical structures.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Adaptive prior shape-based image segmentation method
InactiveCN101964112ASolve the problem of manually adjusting the weight coefficientImage analysisImaging processingWeight coefficient
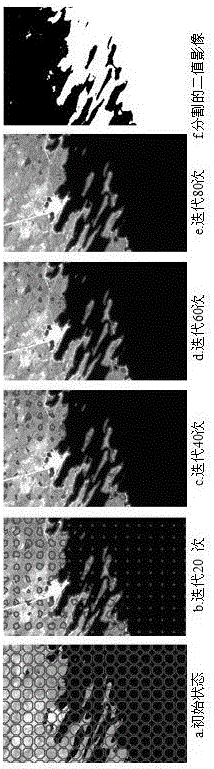
The invention relates to an adaptive prior shape-based image segmentation method in the technical field of image processing. The influence of noise interference on image segmentation is eliminated by an integer sign function; a constraint variation model is provided for the weight coefficient of a prior shape model and the conventional active contour model needs to be manually adjusted, so that the weight coefficient can be adaptively converged to a stable value; meanwhile, identification-based shape template selection is used for determining a certain prior shape template during segmentation, so that the problem that a prior shape model-based segmentation result cannot be obtained in the prior art is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS20160307331A1Reduce cognitive loadComprehensive understandingImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
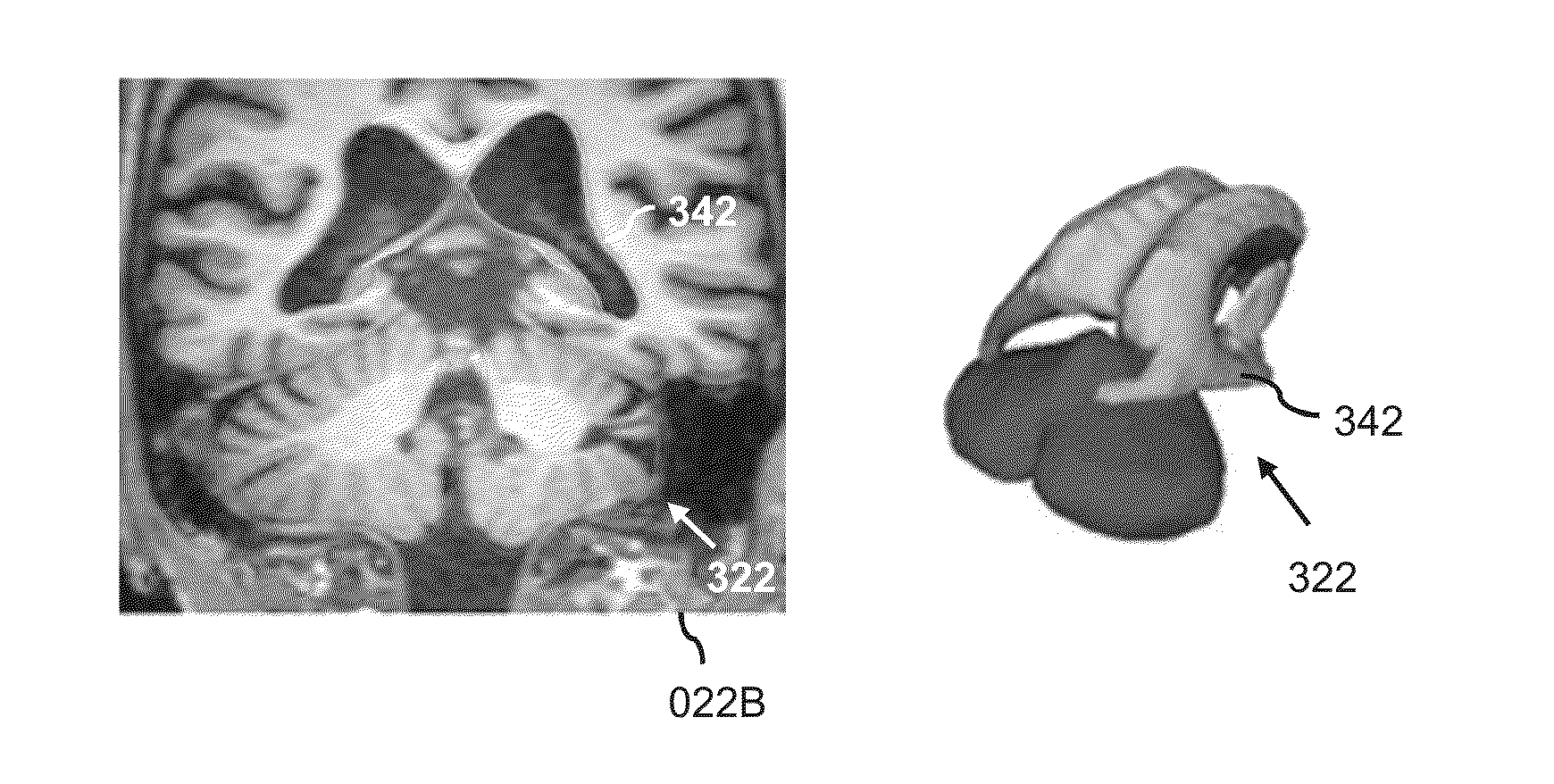
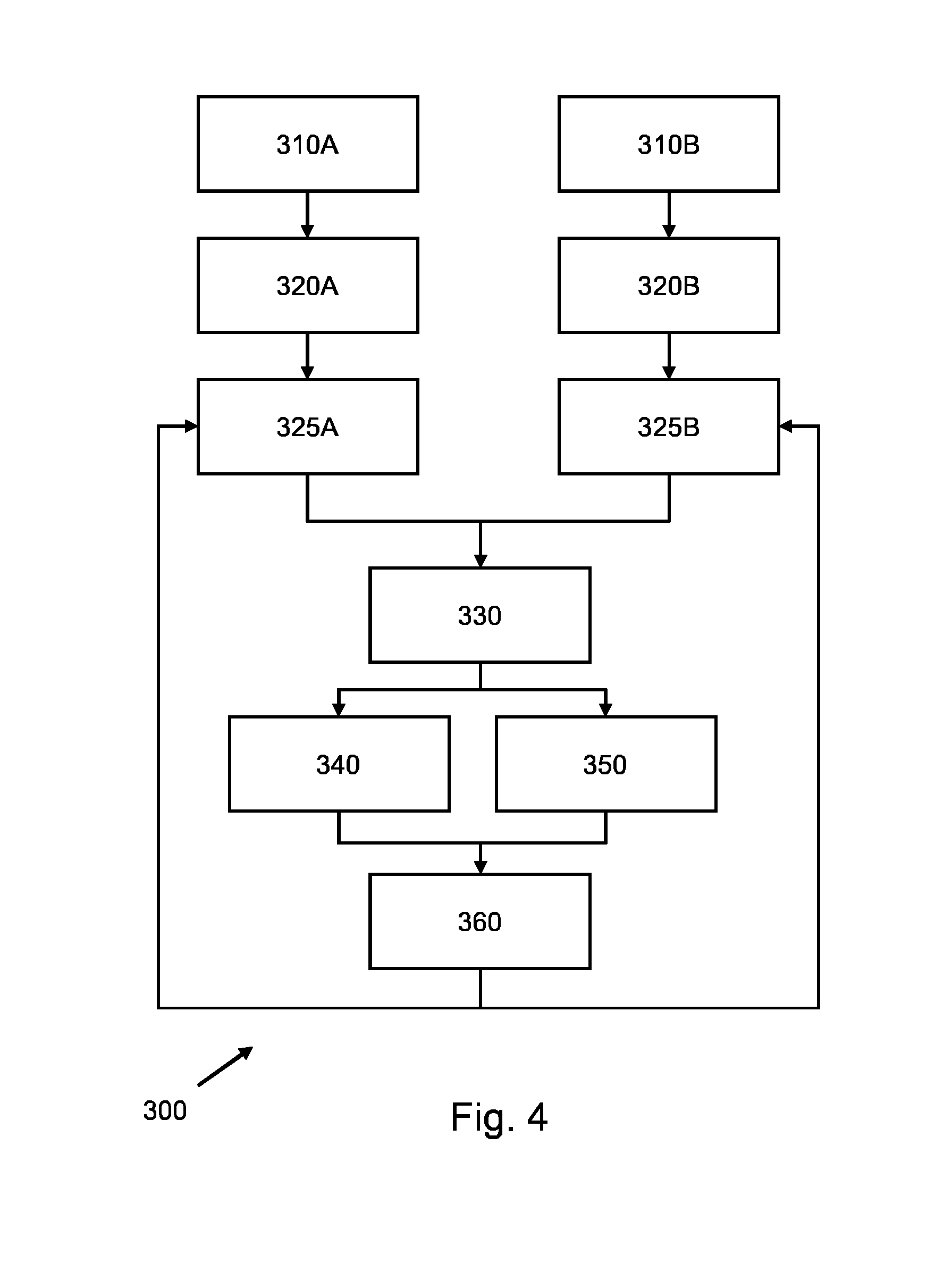
A system and method is provided which obtains different medical images (210) showing an anatomical structure of a patient and having been acquired by different medical imaging modalities and / or different medical imaging protocols. The system is configured for fitting a first deformable model to the anatomical structure in the first medical image (220A), fitting a second deformable model to the anatomical structure in the second medical image (220B), mutually aligning the first fitted model and the second fitted model (230), and subsequently fusing the first fitted model and the second fitted model to obtain a fused model (240) by augmenting the first fitted model with a part of the second fitted model which is missing in the first fitted model; or adjusting or replacing a part of the first fitted model based on a corresponding part of the second fitted model having obtained a better fit. The fused model represents a multimodal / multi-protocol segmentation of the anatomical structure, and provides a user with a more comprehensive understanding of the anatomical structure than known models.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method for detecting the aortic valve using a model-based segmentation technique
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Hierarchical static shadow detection method
InactiveUS7826640B1Easy to handleEfficient identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsDependabilityLightness
Owner:ZAMA INNOVATIONS LLC
A Wavefield Reconstruction Method Based on Model Segmentation
InactiveCN102269823AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingGeophoneReconstruction method
The invention relates to a wave field reconstruction method for determining the distribution of underground oil and gas reservoirs by petroleum geophysical prospecting. The wave field values at each discrete grid point at each moment are reconstructed by using the superimposed and offset profiles collected in the field and the discrete stratigraphic attribute model, and the wave field values at each moment are reconstructed. The wave field at the location of the detection point is used as the wave field reconstruction record at this moment, and the superposition and migration profiles of the wave field reconstruction are obtained by processing. The distribution of underground oil and gas reservoirs is determined by comparison. The invention is suitable for complex structural wave field reconstruction, has high precision, high efficiency and low frequency dispersion, and is an important basis for determining underground oil and gas reservoirs.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
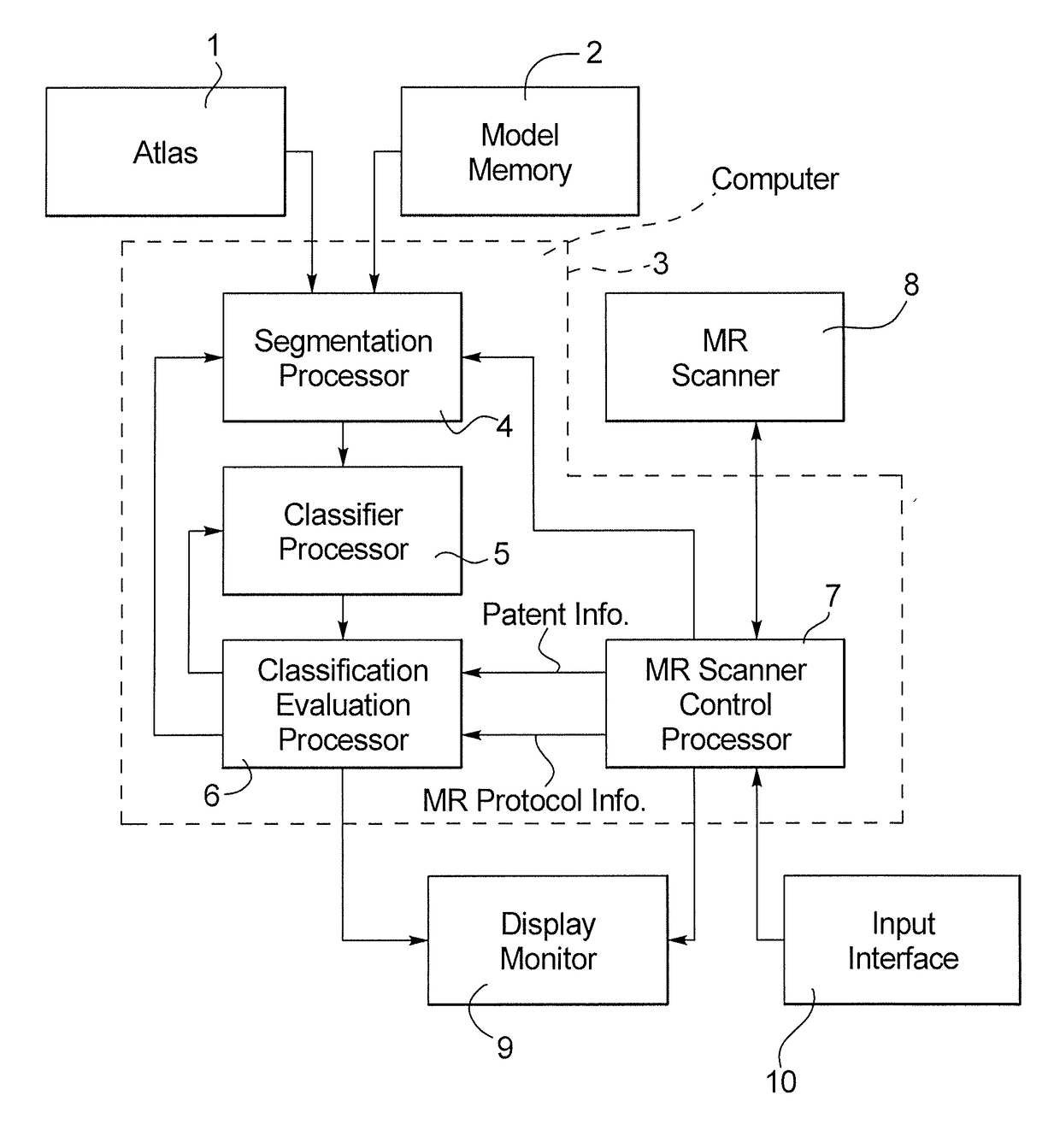
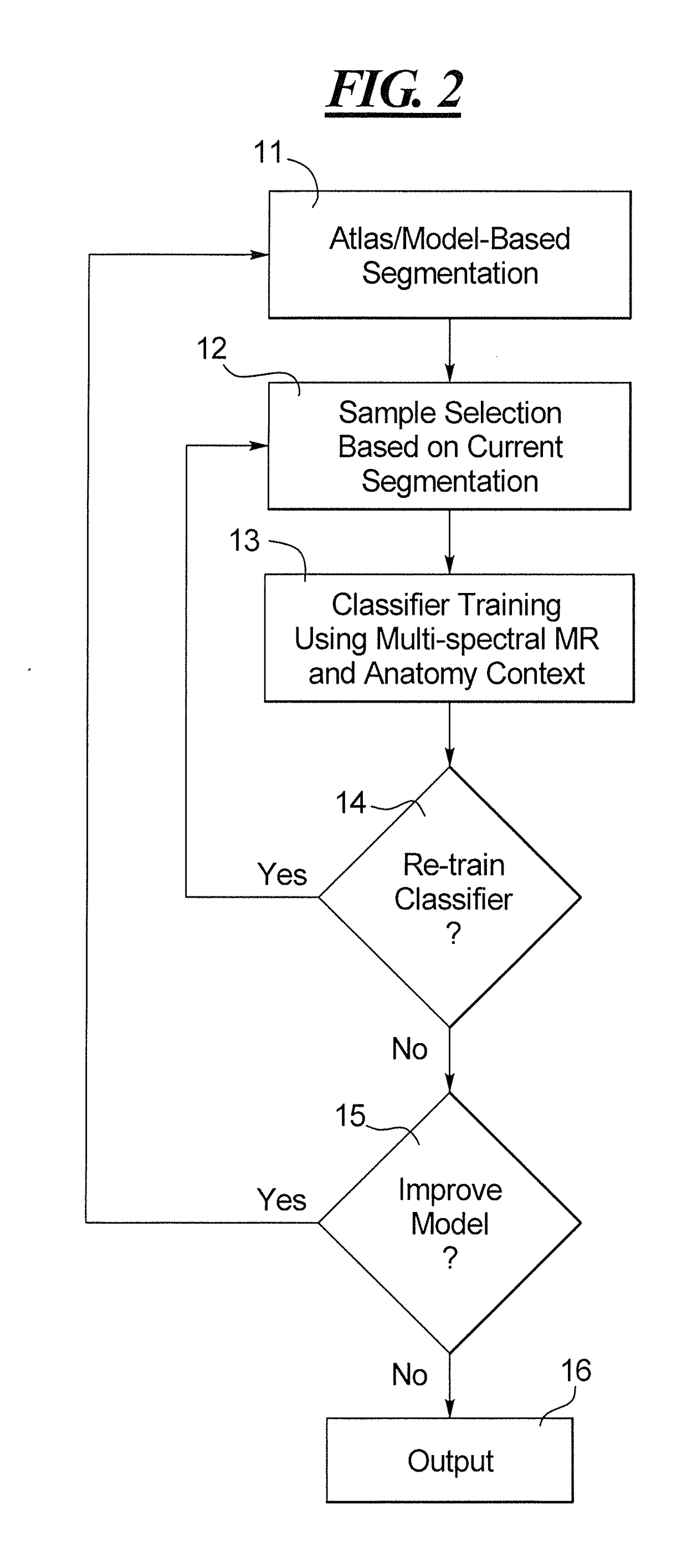
Method and apparatus for atlas/model-based segmentation of magnetic resonance images with weakly supervised examination-dependent learning
ActiveUS20170323444A1Avoiding and minimizingUseful for clinical practiceImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setResonance
In a magnetic resonance (MR) apparatus and segmentation method, a region in an MR image, acquired from a scan of a patient with an MR scanner of the apparatus, is provided to a computer for segmentation of the region from the overall image dataset. The segmentation takes place based on a classification of image elements of the image dataset, and the classification is iteratively re-trained in a weakly supervised learning algorithm based on examination-specific information provided to the computer.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for automatic or semi-automatic segmentation of a 3D image data set
ActiveUS9384413B2Avoid disadvantagesMethod implementationImage enhancementImage analysisData set3d image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods of utilizing image noise information
ActiveUS9761006B2Increase uncertaintyIntuitive and convenientImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
Image processing methods and related apparatuses (SEG,UV). The apparatuses (SEG,UV) operate to utilize noise signal information in images (IM). According to one aspect, apparatus (SEG) uses the noise information (FX) to control a model based segmentation. According to a further aspect, apparatus (UV) operates, based on the noise information (FX), to visualize the uncertainty of image information that resides at edge portions of the or an image (IM).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS9824457B2Cope wellImprove fitImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresPattern recognition
A system (100) and method is provided for performing a model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure in a medical image of a patient. The medical image (022) is accessed. Moreover, model data (162) is provided which defines a deformable model for segmenting the type of anatomical structure. The model-based segmentation of the anatomical structure is performed by adapting the deformable model to the anatomical structure in the medical image using an adaptation technique. In accordance with the present invention, performing the model based segmentation further comprises determining from patient data (042) medical information which is predictive of an appearance of the anatomical structure in the medical image, and adjusting or setting a segmentation parameter based on the medical information so as to adjust the model-based segmentation to said predicted appearance of the anatomical structure in the medical image, the segmentation parameter being a parameter of i) the deformable model or ii) the adaptation technique. Advantageously, the system and method are enabled to better cope with the inter-patient and inter-disease-stage variability in the appearance of anatomical structures.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Hierarchical static shadow detection method
InactiveUS7970168B1Easy to handleEfficient identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsDependabilityBrightness perception
Owner:ZAMA INNOVATIONS LLC
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS20170213338A1Increase awarenessImprove fitImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresGeometric relations
A system (100) is provided for performing a model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure in a medical image. The system comprises a processor (140) configured for performing a model-based segmentation of the anatomical structure by applying a deformable model to image data (042). Moreover, definition data (220) is provided which defines a geometric relation between a first part and a second part of the deformable model of which a corresponding first part of the anatomical structure is presumed to be better visible in the image data than a corresponding second part of the anatomical structure. The definition data is then used to adjust a fit of the second part of the deformable model. As a result, a better fit of the second part of the deformable model to the second part of the anatomical structure is obtained despite said part being relatively poorly visible in the image data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
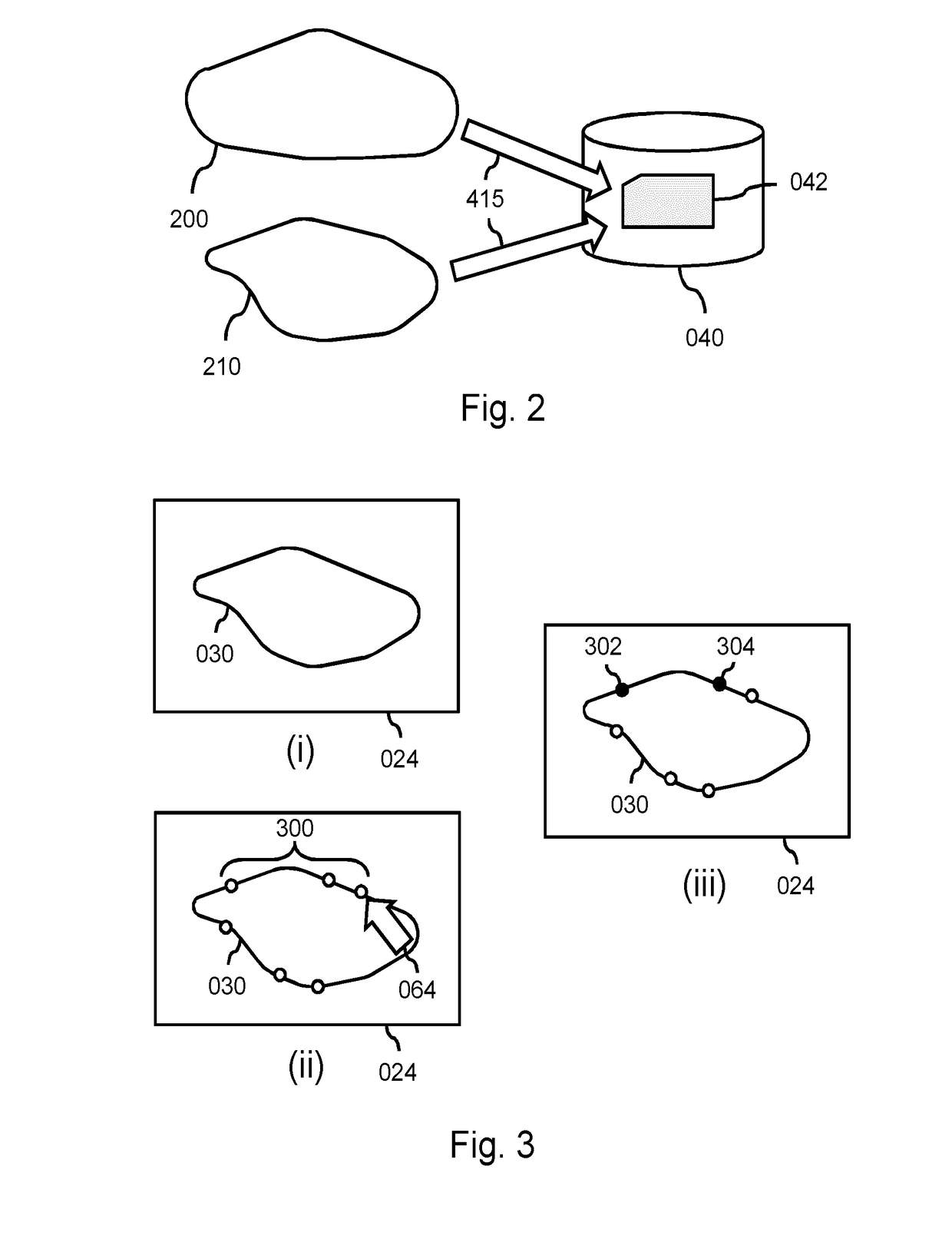
Simultaneous model-based segmentation of objects satisfying pre-defined spatial relationships
ActiveUS20110058061A1Minimize the possibilityHigh energyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionReference configuration
The invention relates to a system (100) for segmenting a plurality of objects in image data using simultaneous model-based image segmentation. A surface mesh is adapted to each object to be segmented. To avoid or reduce the possibility of mesh collision, a plurality of connecting edges for connecting two proximal meshes are used. A connection energy defined for the plurality of connecting edges allows controlling the spatial relationship between the first and second mesh. This is achieved by including in the connection energy expression terms that will increase the connection energy when the lengths of edges of the plurality of connecting edges connecting the first and second mesh decrease. Using the reference configuration of the plurality of connecting edges defined based on the pre-positioned first and second mesh allows taking into account prior knowledge about a typical spatial relationship between the first and second object of the plurality of objects.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
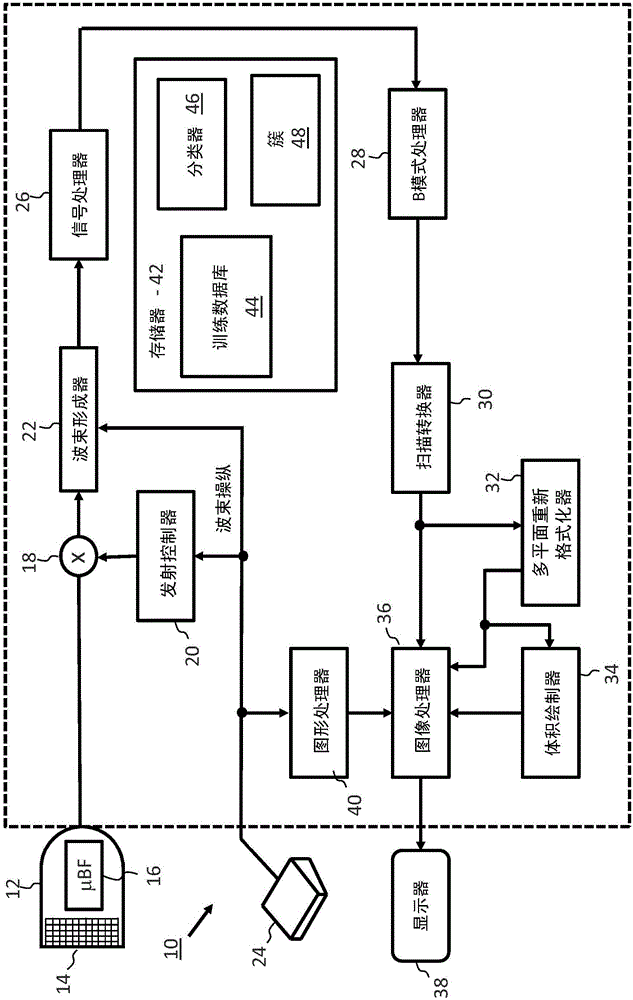
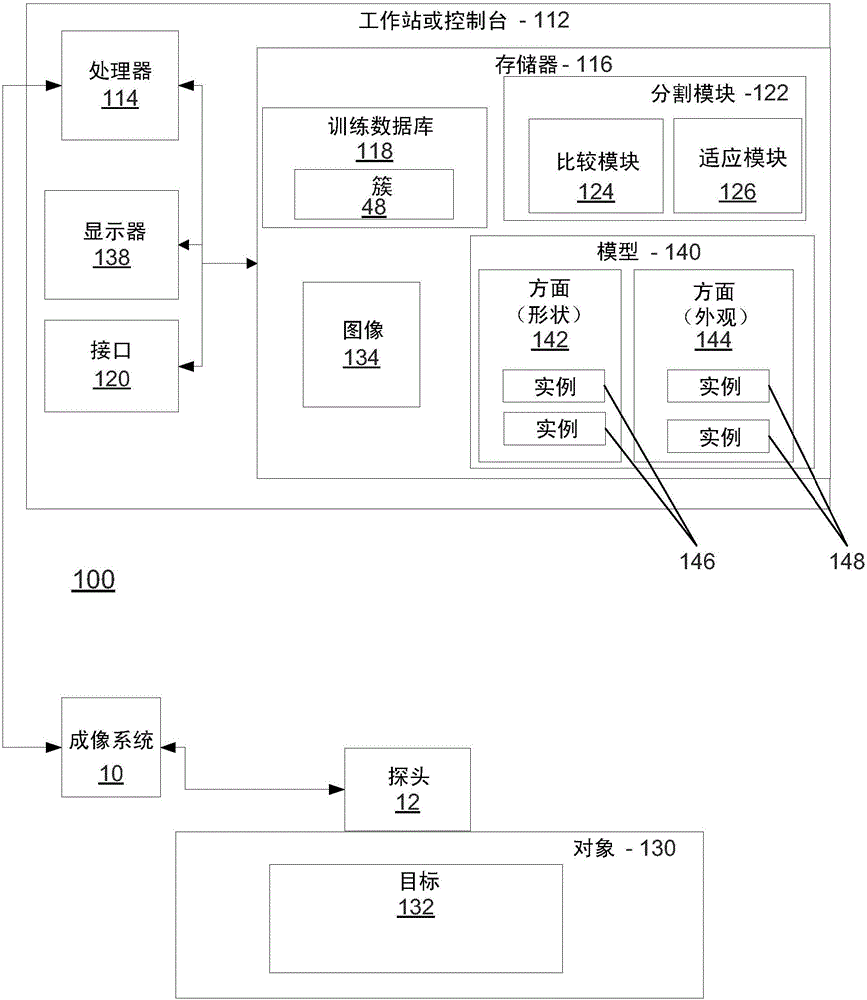
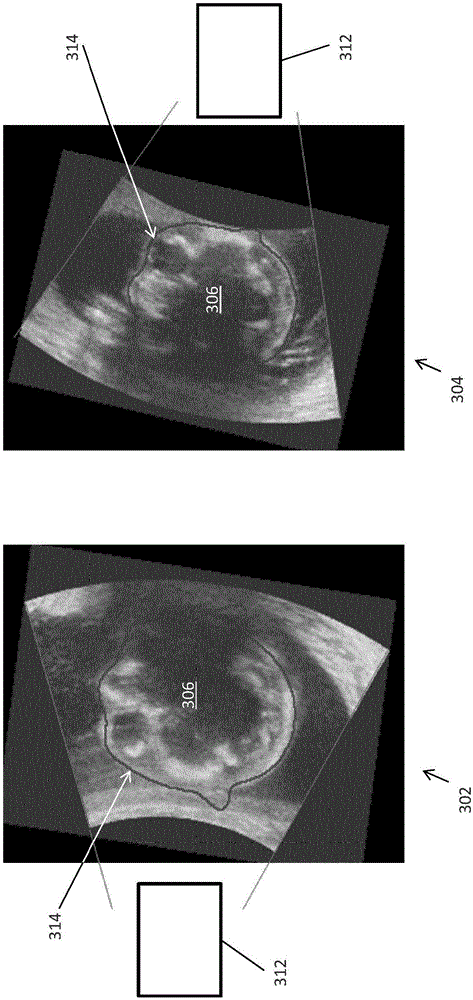
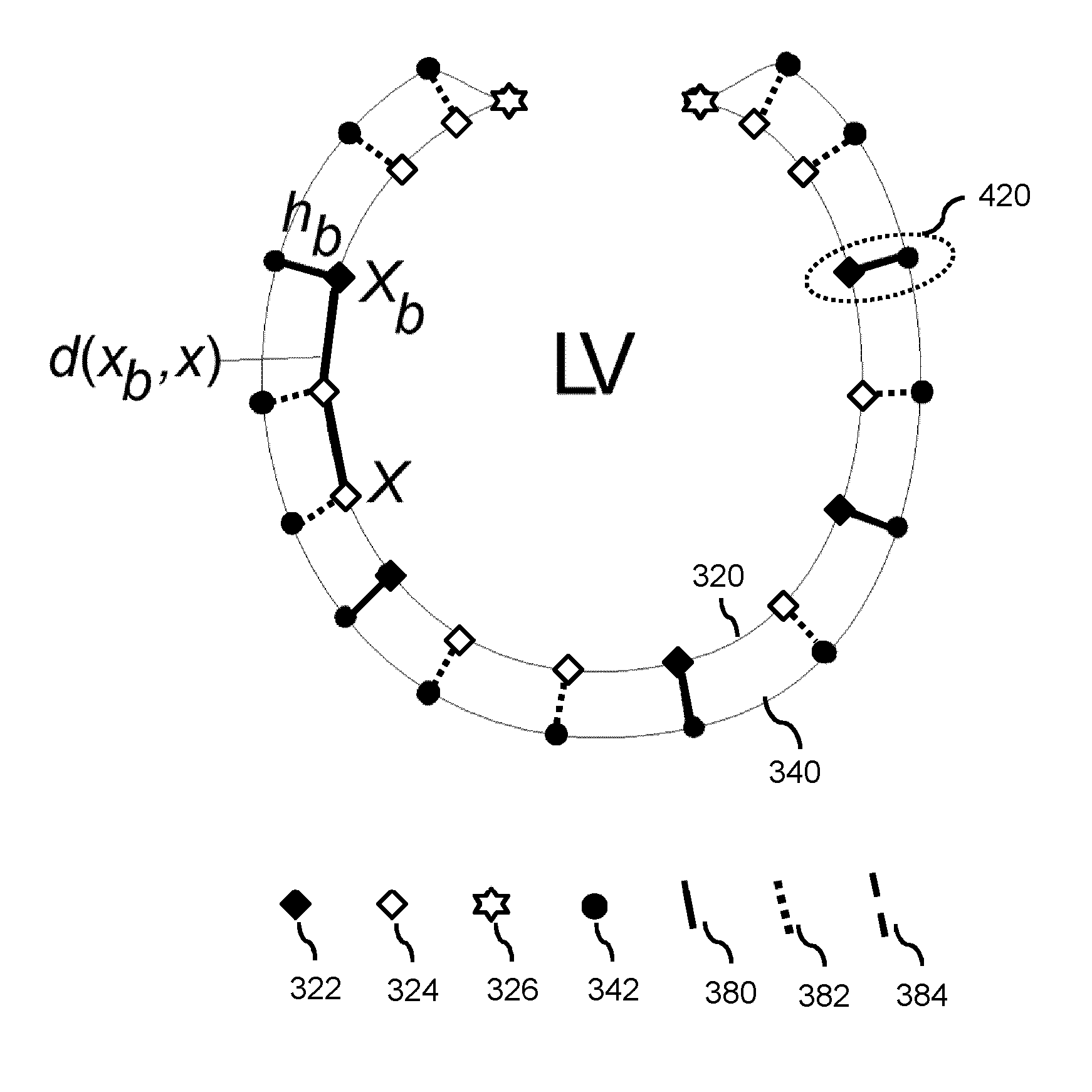
Acquisition-orientation-dependent features for model-based segmentation of ultrasound images
A model-based segmentation system includes a plurality of clusters (48), each cluster being formed to represent an orientation of a target to be segmented. One or more models (140) are associated with each cluster. The one or more models include an aspect associated with the orientation of the cluster, for example, the appearance of the target to be segmented. A comparison unit (124), configured in memory storage media, is configured to compare an ultrasound image to the clusters to determine a closest matching orientation and is configured to select the one or more models based upon the cluster with the closest matching orientation. A model adaptation module (126) is configured to adapt the one or more models to the ultrasound image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
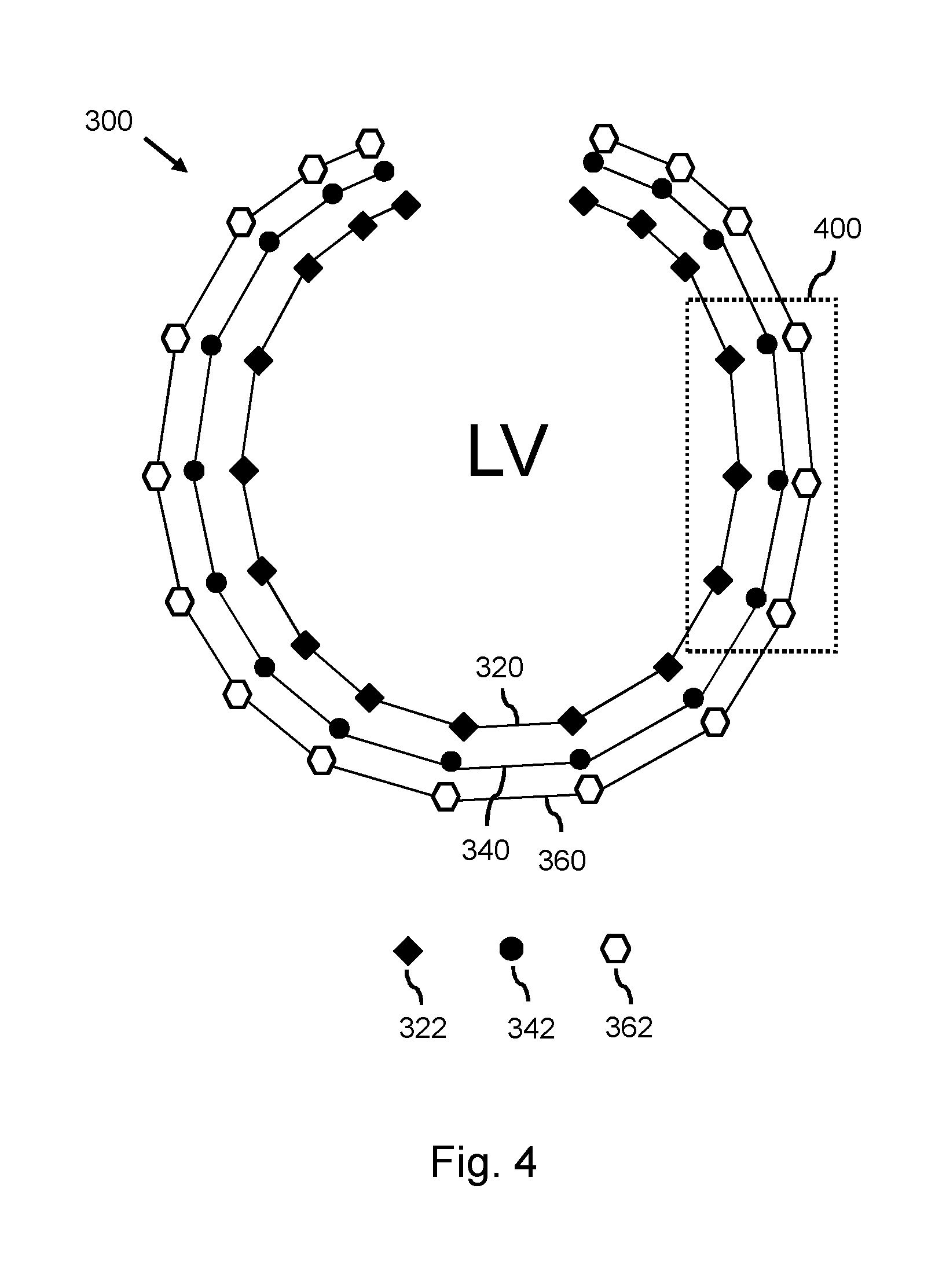
ActiveUS20160379372A1Depth accurateImprove spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresSurface layer
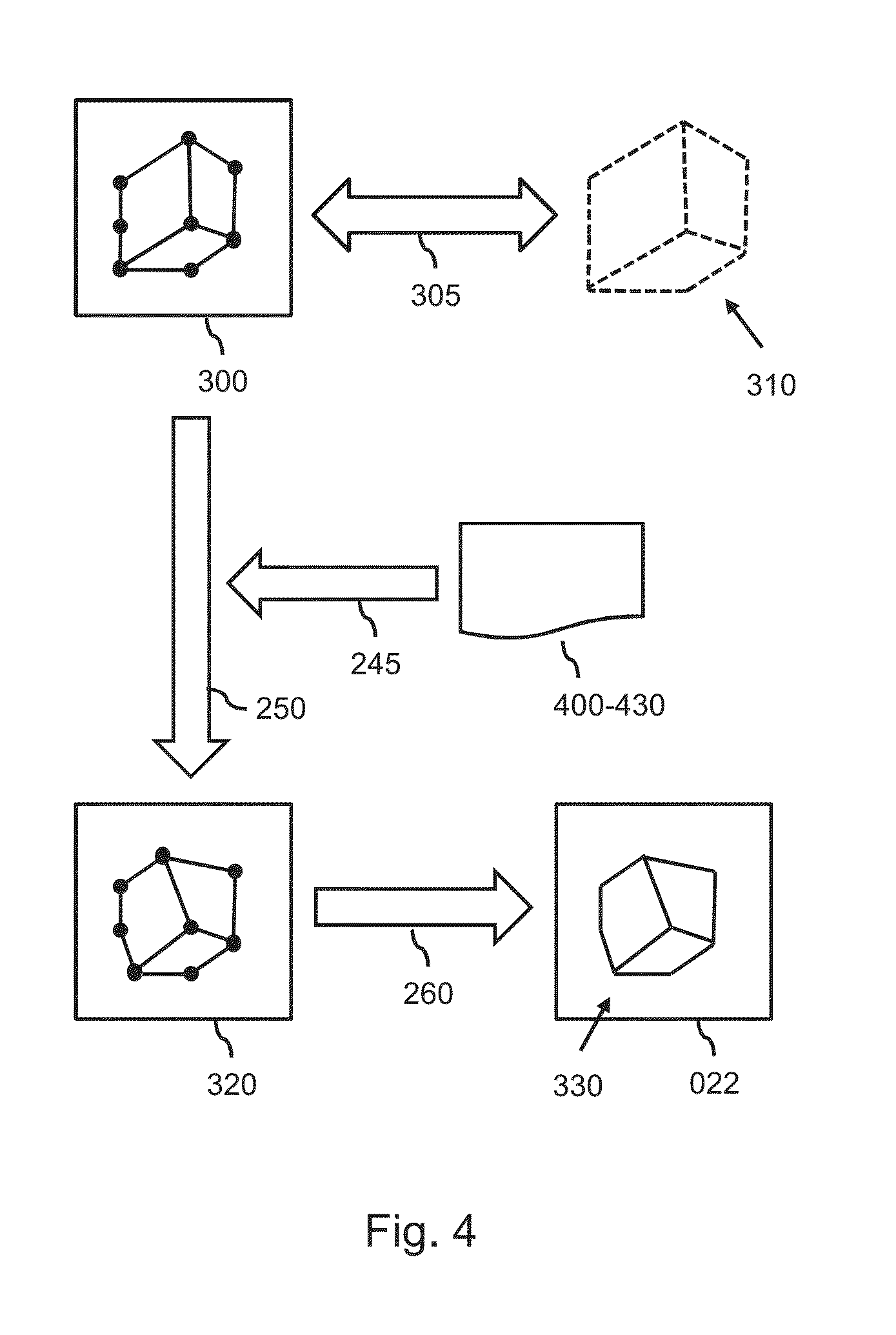
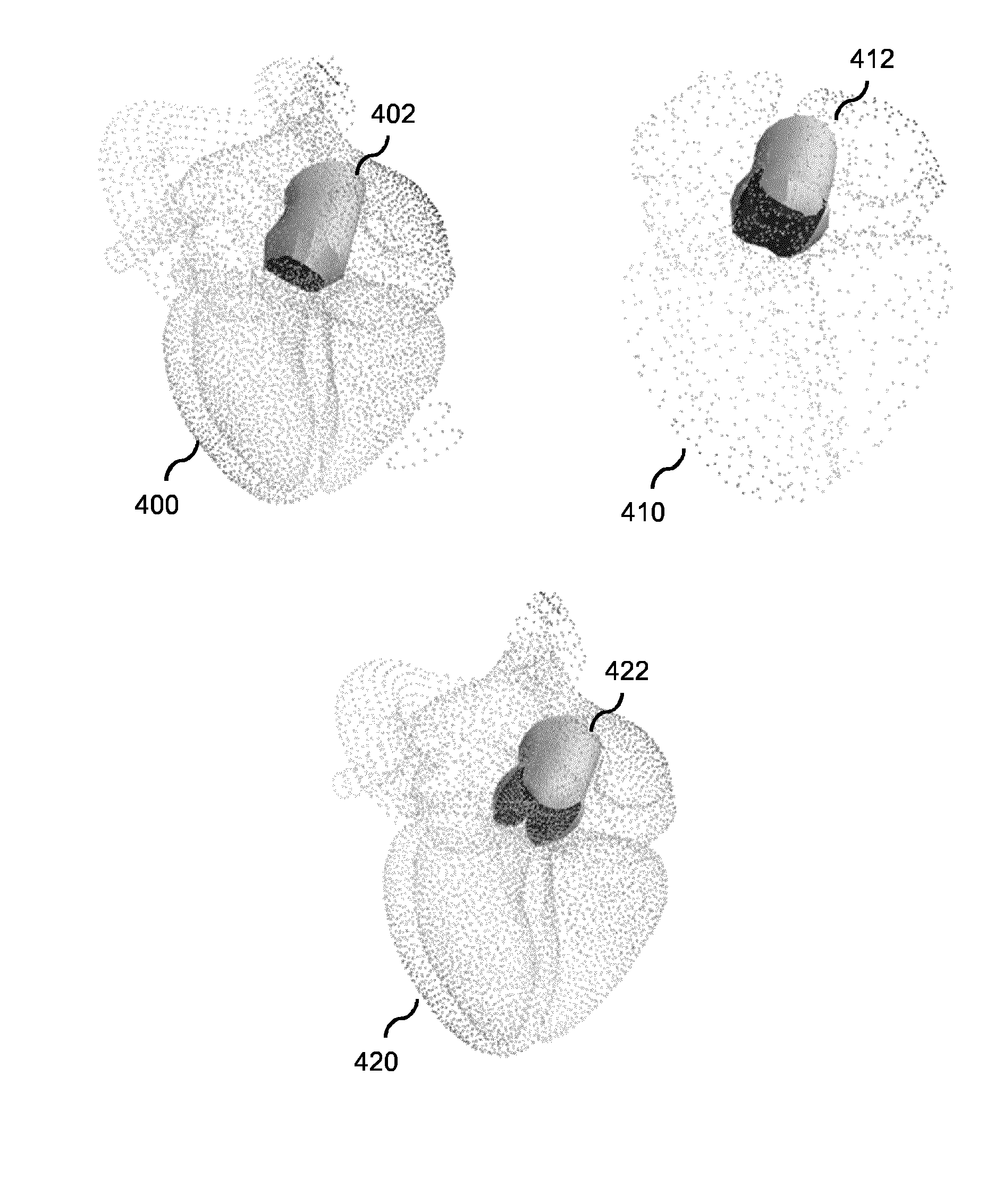
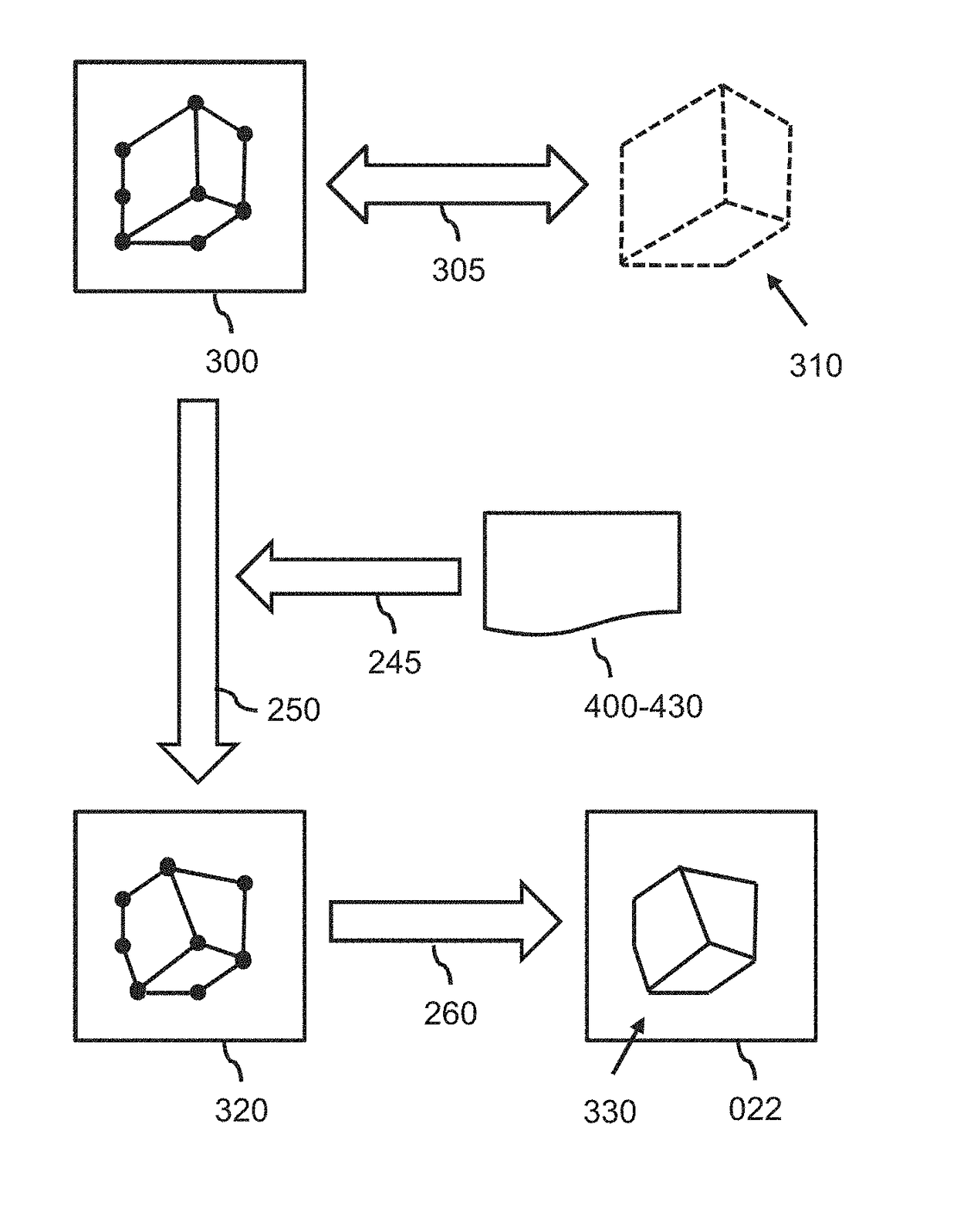
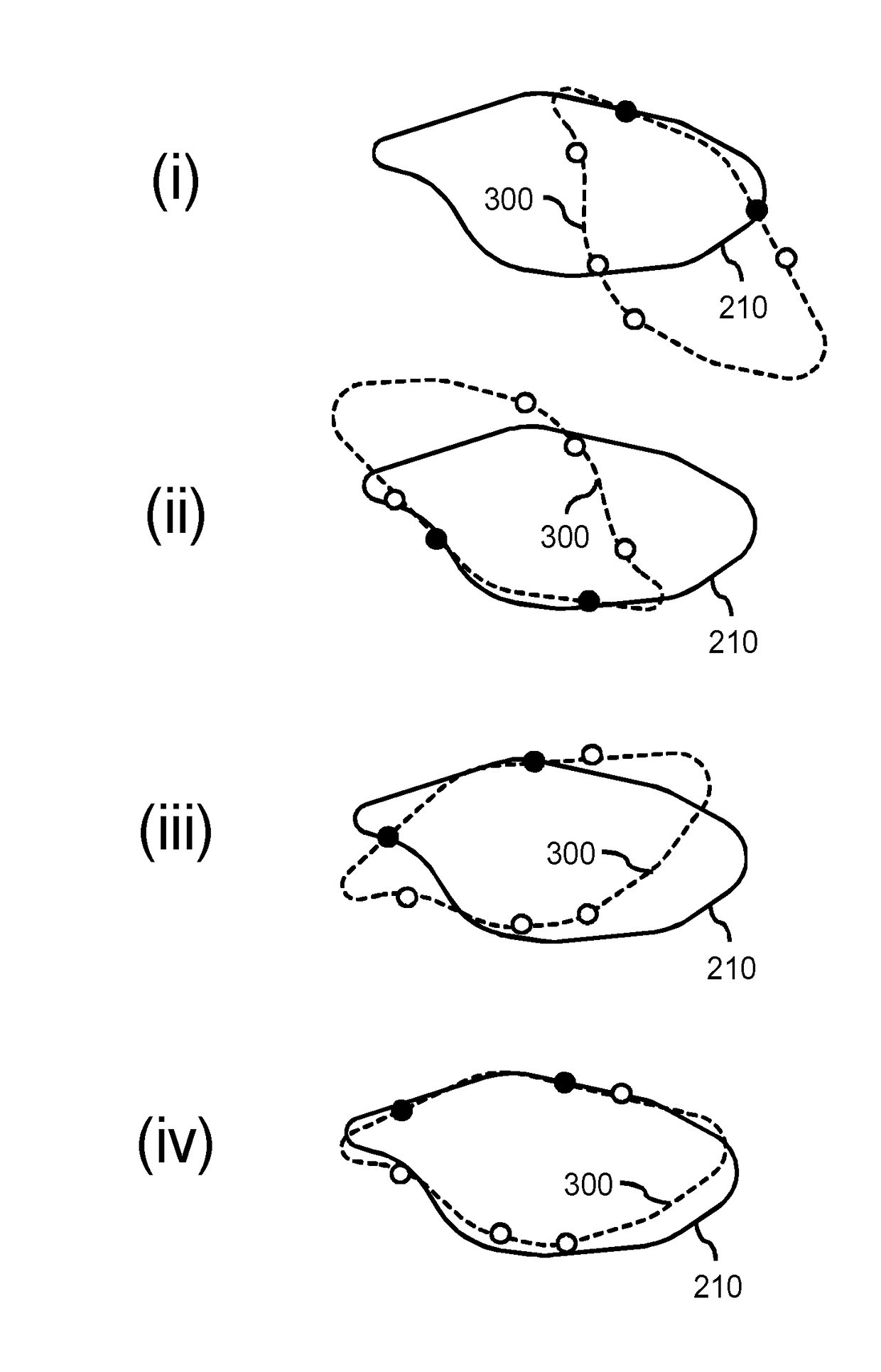
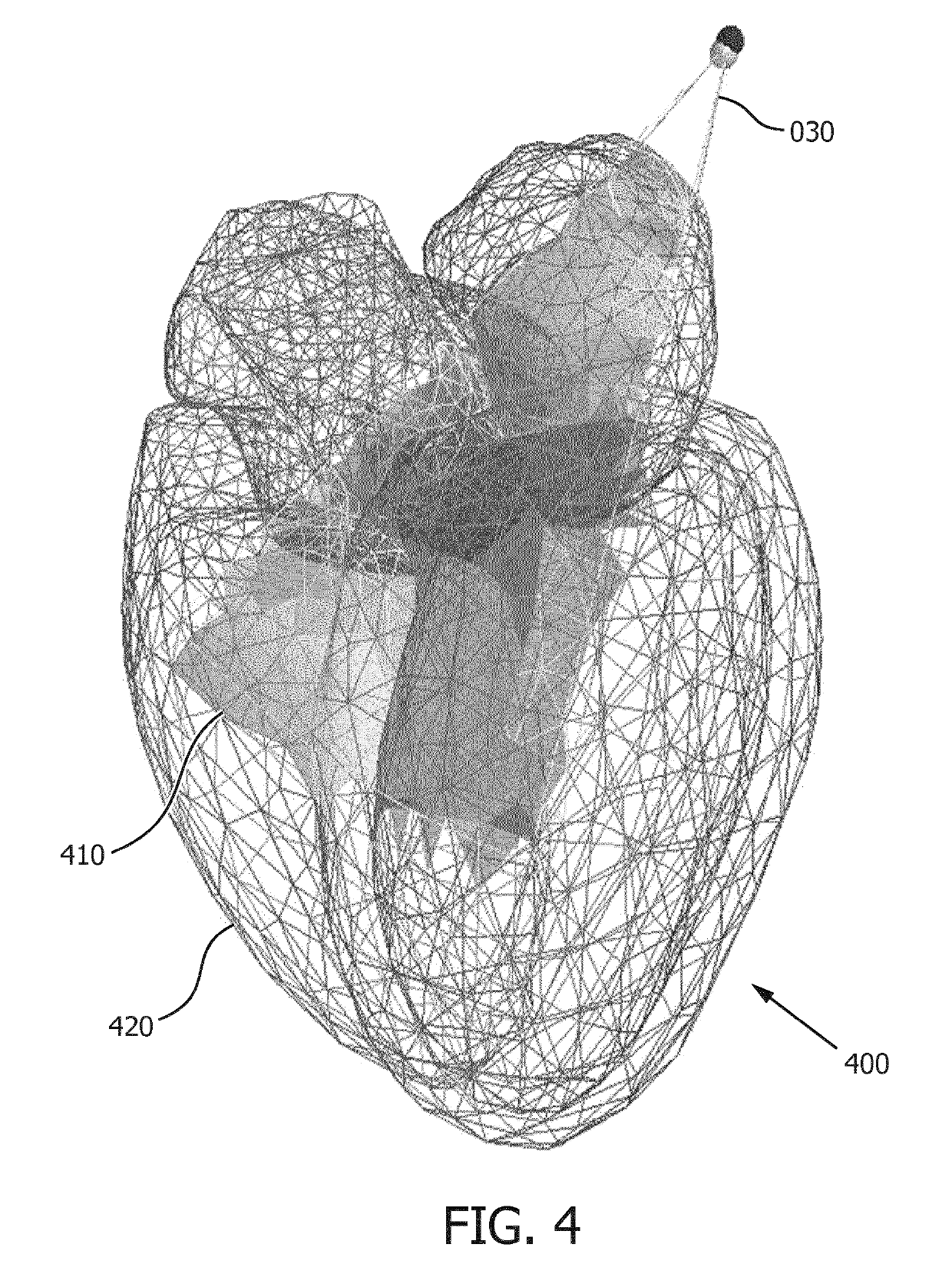
A method is provided for generating a deformable model (300) for segmenting an anatomical structure in a medical image. The anatomical structure comprises a wall. The deformable model (300) is generated such that it comprises, in addition to two surface meshes (320, 360), an intermediate layer mesh (340) for being applied in-between a first surface layer of the wall and a second surface layer of the wall. In generating the intermediate layer mesh (340), the mesh topology of at least part (400) of the intermediate layer mesh is matched to the mesh topology of one of the surface meshes (320, 360), thereby establishing matching mesh topologies. The deformable model (300), as generated, better matches the composition of such walls, thereby providing a more accurate segmentation.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Simultaneous model-based segmentation of objects satisfying pre-defined spatial relationships
The present invention relates to a system (100) for segmenting a plurality of objects in image data using simultaneous model-based image segmentation. A surface mesh is adapted to each object to be segmented. To avoid or reduce the possibility of mesh collision,a plurality of connecting edges for connecting two proximal meshes are used. A connection energy defined for the plurality of connecting edges allows controlling the spatial relationship between the first and second mesh. This is achieved by including in the connection energy expression terms that will increase the connection energy when the lengths of edges of the plurality of connecting edges connecting the first and second mesh decrease. Using the reference configuration of the plurality of connecting edges defined based on the pre- positioned first and second mesh allows taking into account prior knowledge about a typical spatial relationship between the first and second object of the plurality of objects.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus for adaptive contouring of a body part
ActiveUS20190251693A1Simple technologyShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionBody region
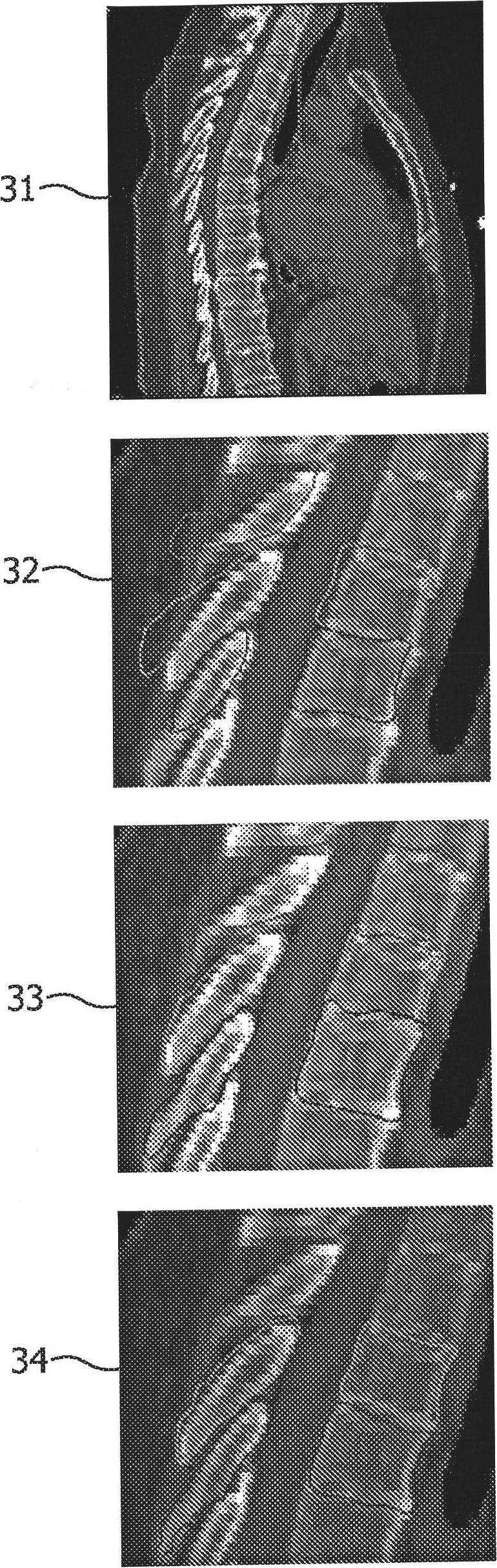
The present invention relates to an apparatus for adaptive contouring of a body part. It is described to provide (210) at least one image; wherein, the at least one image comprises a first image comprising image data of a body part. An initial automatic model based segmentation of image data of the body part in the first image is determined (220). Final segmentation data of the body part is determined (230) in response to a modification of the initial automatic model based segmentation. An updated model based segmentation can be applied (240) on the basis of the initial automatic model based segmentation and the final segmentation data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS20180137626A1Less time-consumingInvolvement is limitedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresGoodness of fit
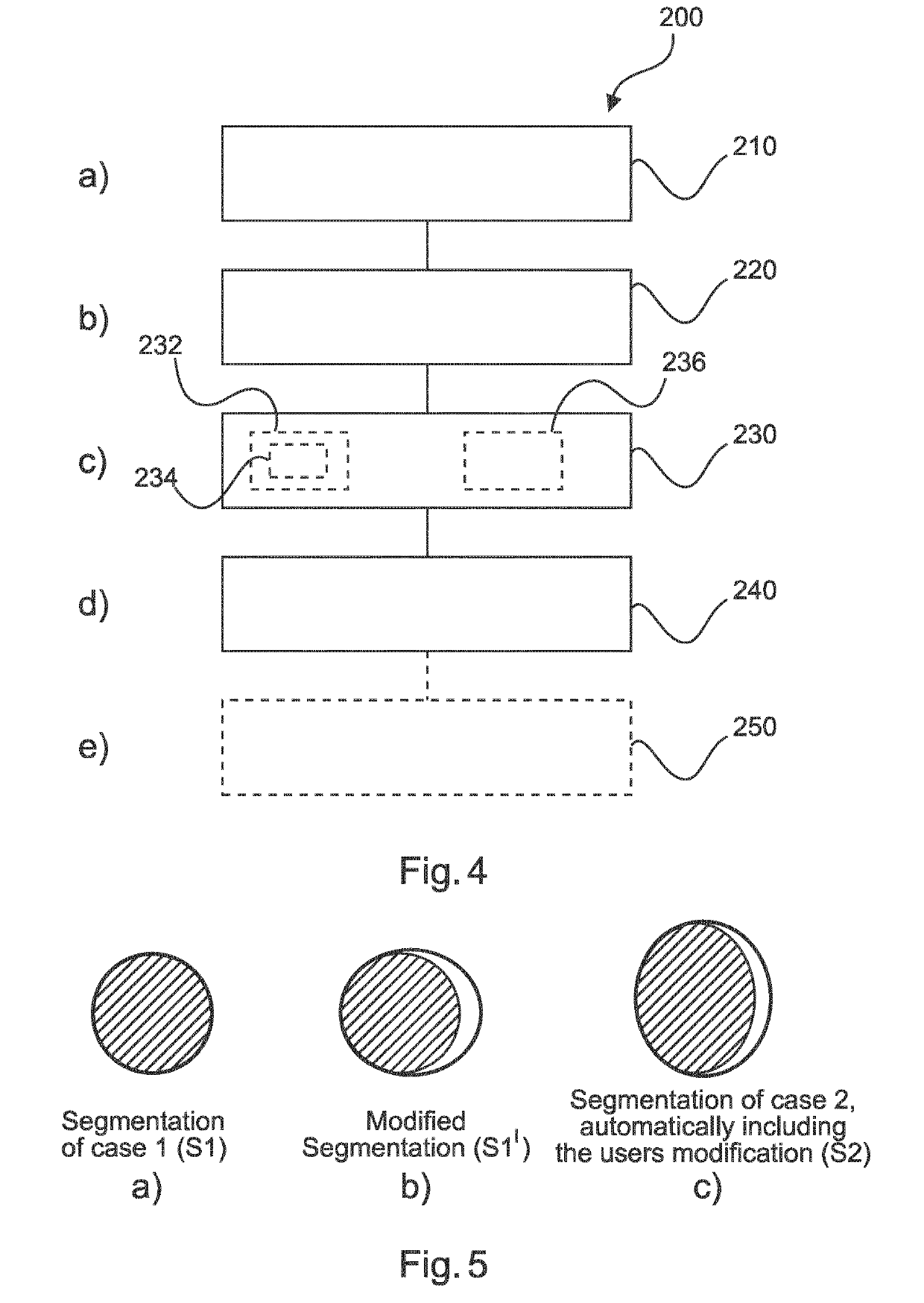
A system and method are provided for segmentation of an anatomical structure in which a user may interactively specify a limited set of boundary points of the anatomical structure in a view of a medical image. The set of boundary points may, on its own, be considered an insufficient segmentation of the anatomical structure in the medical image, but is rather used to select a segmentation model from a plurality of different segmentation models. The selection is based on a goodness-of-fit measure between the boundary points and each of the segmentation models. For example, a best-fitting model may be selected and used for segmentation of the anatomical structure. It is therefore not needed for the user to delineate the entire anatomical structure, which would be time consuming and ultimately error prone, nor is it needed for a segmentation algorithm to autonomously have to select a segmentation model, which may yield an erroneous selection.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS10002420B2Improve fitIncrease awarenessImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresGeometric relations
A system (100) is provided for performing a model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure in a medical image. The system comprises a processor (140) configured for performing a model-based segmentation of the anatomical structure by applying a deformable model to image data (042). Moreover, definition data (220) is provided which defines a geometric relation between a first part and a second part of the deformable model of which a corresponding first part of the anatomical structure is presumed to be better visible in the image data than a corresponding second part of the anatomical structure. The definition data is then used to adjust a fit of the second part of the deformable model. As a result, a better fit of the second part of the deformable model to the second part of the anatomical structure is obtained despite said part being relatively poorly visible in the image data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS9953429B2Comprehensive understandingReduce cognitive loadImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
A system and method is provided which obtains different medical images (210) showing an anatomical structure of a patient and having been acquired by different medical imaging modalities and / or different medical imaging protocols. The system is configured for fitting a first deformable model to the anatomical structure in the first medical image (220A), fitting a second deformable model to the anatomical structure in the second medical image (220B), mutually aligning the first fitted model and the second fitted model (230), and subsequently fusing the first fitted model and the second fitted model to obtain a fused model (240) by augmenting the first fitted model with a part of the second fitted model which is missing in the first fitted model; or adjusting or replacing a part of the first fitted model based on a corresponding part of the second fitted model having obtained a better fit. The fused model represents a multimodal / multi-protocol segmentation of the anatomical structure, and provides a user with a more comprehensive understanding of the anatomical structure than known models.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS20170337680A1Further processing of adaptedFor further processingImage enhancementImage analysisPersonalizationAnatomical structures
A system and method is provided for performing a model-based segmentation of a medical image which only partially shows an anatomical structure. In accordance therewith, a model is applied to the image data of the medical image, the model-based segmentation providing an adapted model having a first model part having been adapted to the first part of the anatomical structure in the medical image of the patient, and a second model part representing the second part of the anatomical structure not having been adapted to a corresponding part of the medical image. Metadata is generated which identifies the first model part to enable the first model part to be distinguished from the second model part in a further processing of the adapted model. Advantageously, the metadata can be used to generate an output image which visually indicates to the user which part of the model has been personalized and which part of the model has not been personalized. Other advantageous uses of the metadata in the further processing of the adapted model have also been conceived.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
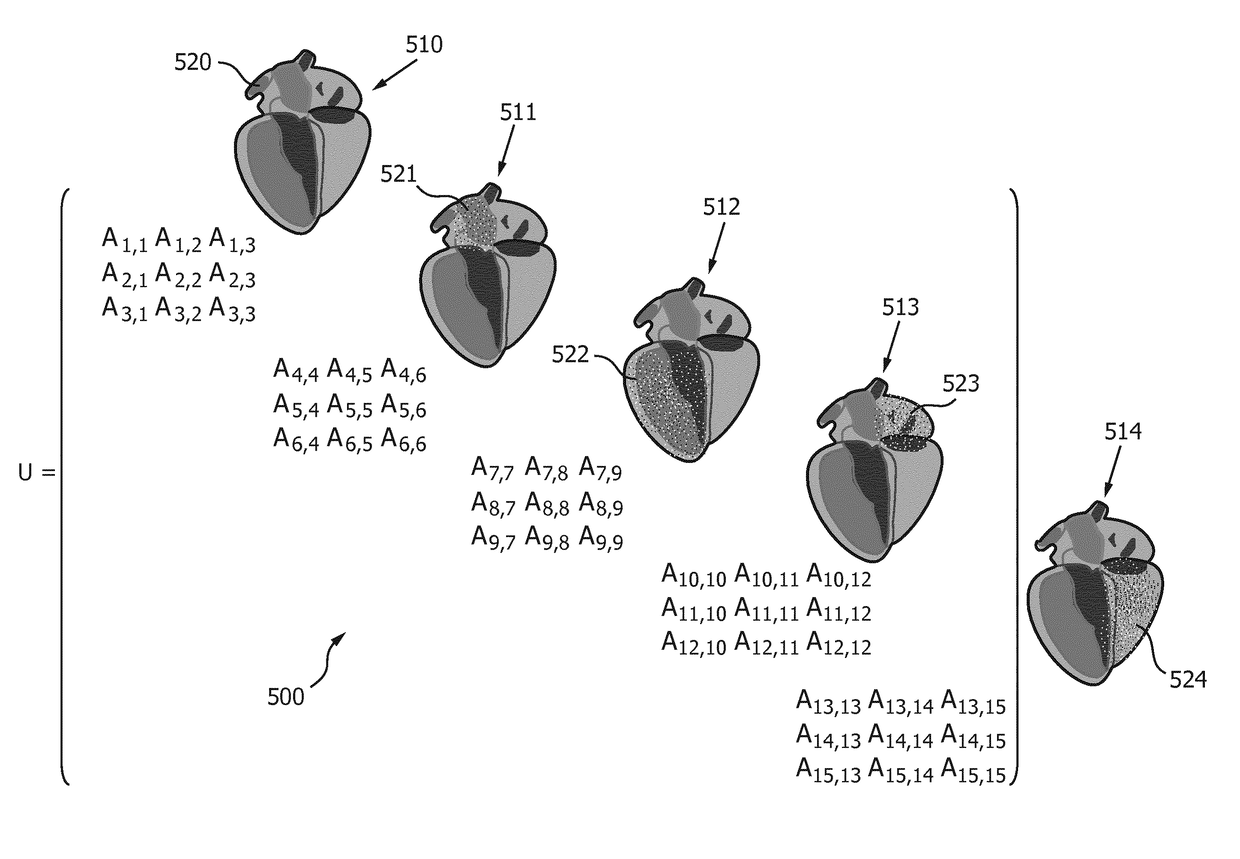
Probabilistic Refinement for Model-Based Segmentation
ActiveCN102947862BAccurate segmentationReliable Segmentation ResultsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVoxel
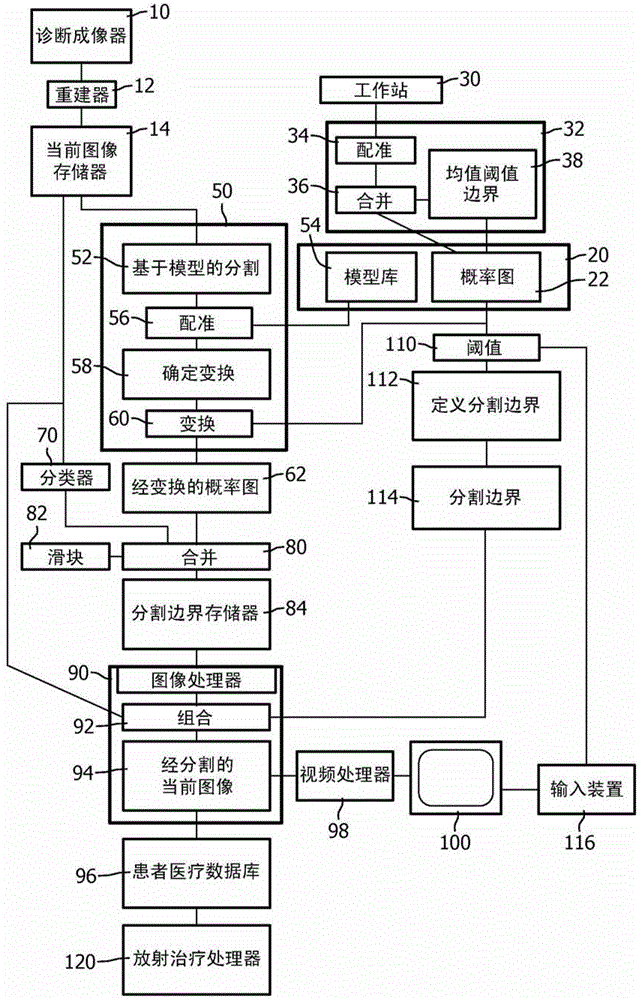
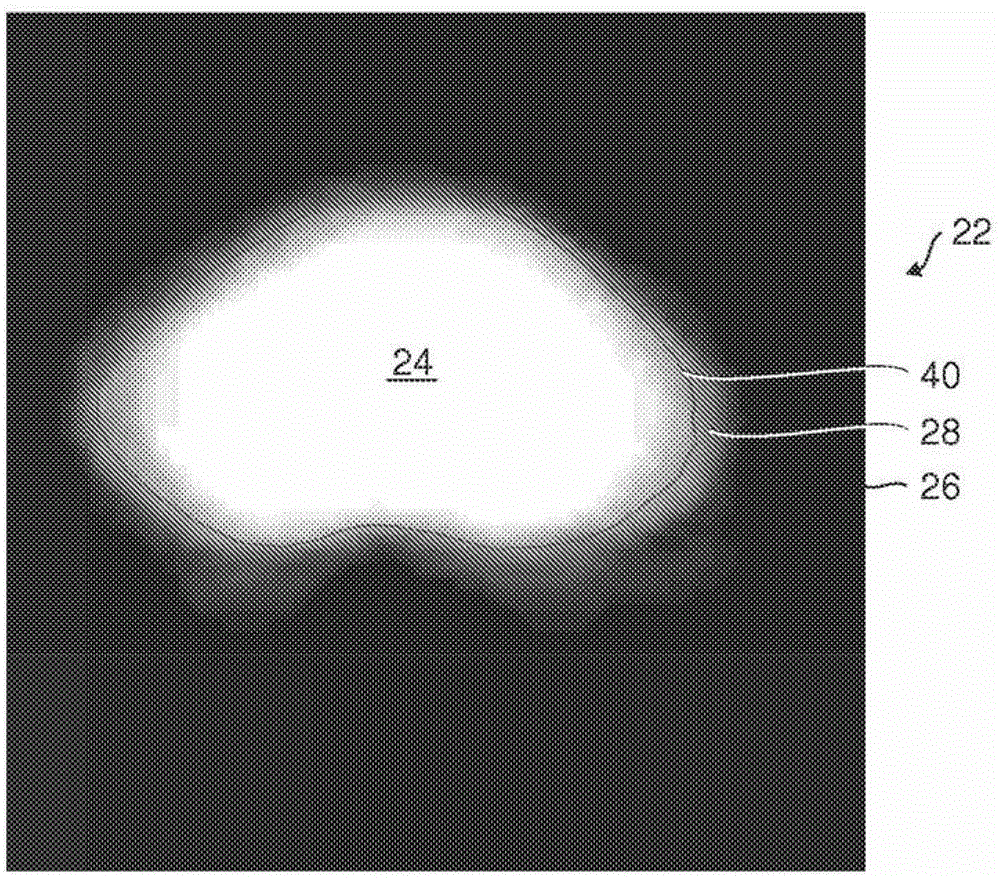
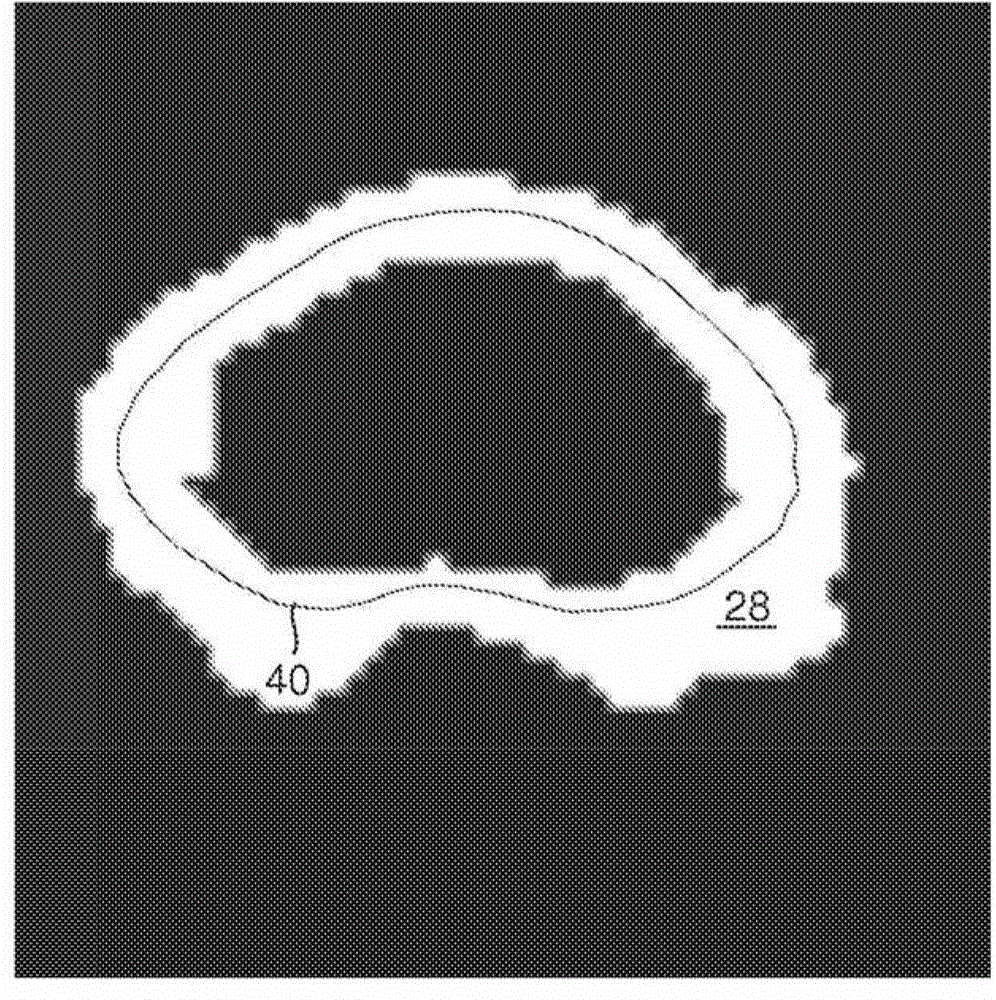
A system for segmenting current diagnostic images includes a workstation (30) which segments a volume of interest in previously generated diagnostic images of a selected volume of interest generated from a plurality of patients. One or more processors (32) are programmed to register the segmented previously generated images and merge the segmented previously generated images into a probability map that depicts a probability that each voxel represents the volume of interest (24) or background (26) and a mean segmentation boundary (40). A segmentation processor (50) registers the probability map with a current diagnostic image (14) to generate a transformed probability map (62). A previously-trained classifier (70) classifies voxels of the diagnostic image with a probability that each voxel depicts the volume of interest or the background. A merge processor (80) merges the probabilities from the classifier and the transformed probability map. A segmentation boundary processor (84) determines the segmentation boundary for the volume of interest based on the current image based on the merge probabilities.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Vector C-V Model Segmentation Method of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image Based on Band Selection
ActiveCN103854281BImprove Segmentation AccuracySplitting speed is fastImage analysisSpectral curveComputer vision
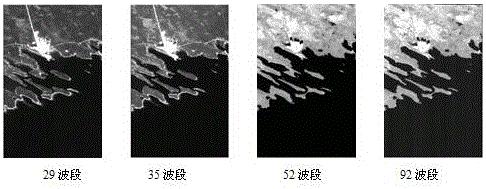
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image vector C-V model segmentation method based on wave band selection. Firstly, according to a spectral curve, wave bands high in contrast ratio between a target and the background are selected, further, according to relevant coefficients of the wave bands, the wave bands high in relevancy are removed so that a new wave band combination can be formed, and therefore according to the determined wave band assembly, a hyperspectral image vector matrix is established; on the basis, a vector C-V segmentation model based on the vector matrix is constructed, the edge guiding function based on gradient is introduced into the model, on the basis that a traditional C-V model is reserved to perform image segmentation based on area information, the capacity for capturing the target boundary in heterogeneous areas and under complex background conditions is enhanced through edge detail information of images, segmentation precision of the hyperspectral remote sensing images is improved, segmentation speed of the hyperspectral remote sensing images is increased.
Owner:清影医疗科技(深圳)有限公司
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS10402970B2For further processingStrong regularizationImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresRadiology
A system and method is provided for performing a model-based segmentation of a medical image which only partially shows an anatomical structure. In accordance therewith, a model is applied to the image data of the medical image, the model-based segmentation providing an adapted model having a first model part having been adapted to the first part of the anatomical structure in the medical image of the patient, and a second model part representing the second part of the anatomical structure not having been adapted to a corresponding part of the medical image. Metadata is generated which identifies the first model part to enable the first model part to be distinguished from the second model part in a further processing of the adapted model. Advantageously, the metadata can be used to generate an output image which visually indicates to the user which part of the model has been personalized and which part of the model has not been personalized. Other advantageous uses of the metadata in the further processing of the adapted model have also been conceived.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com