Optical fiber splice element
a technology of optical fiber and splice element, which is applied in the field of optical fiber splice element, can solve the problems of slack storage, high optical loss 0.2 db-0.3 db, and slack storage, and leave unsightly and bulky excess fiber coils
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
[0294]Various embodiments are provided.
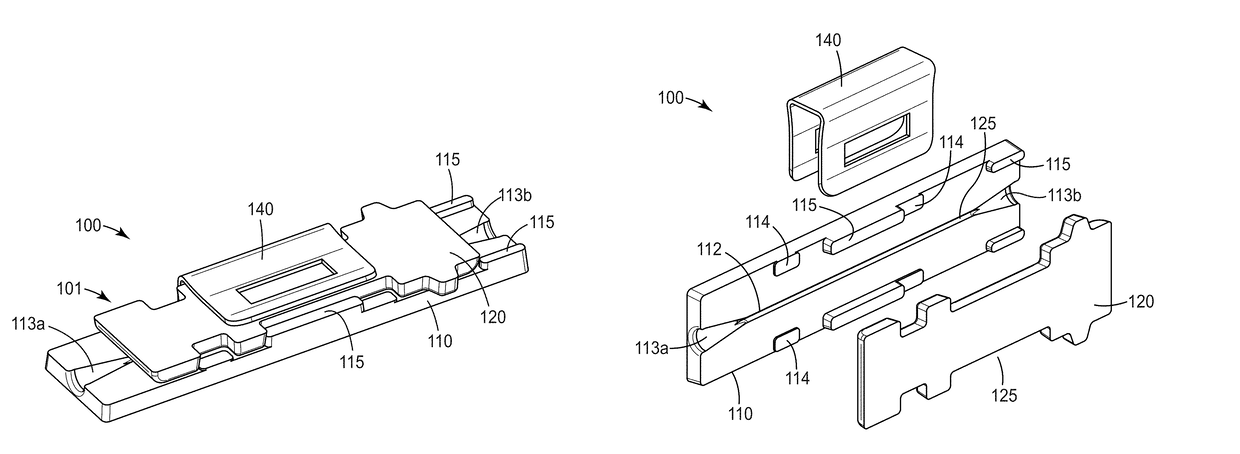
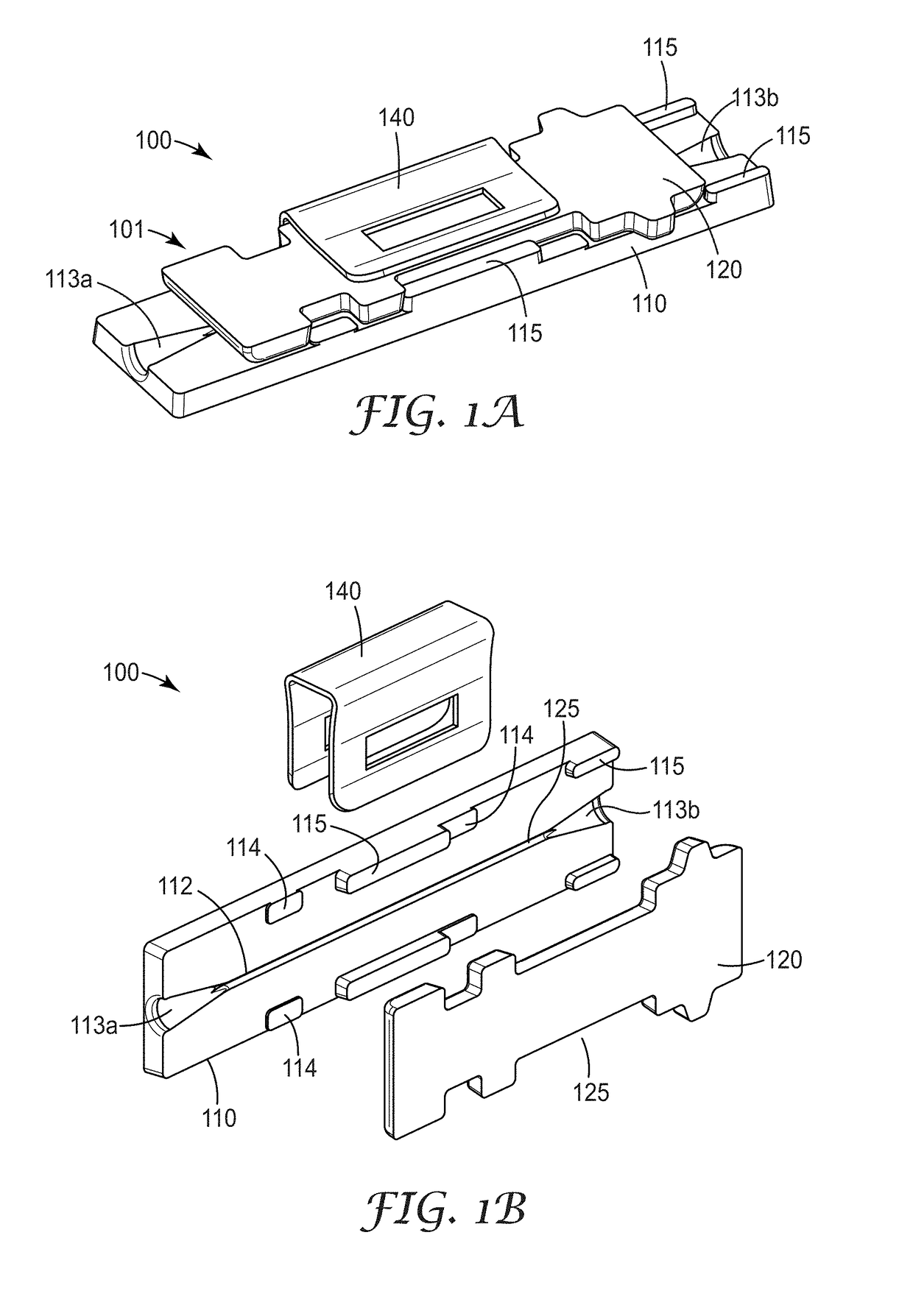
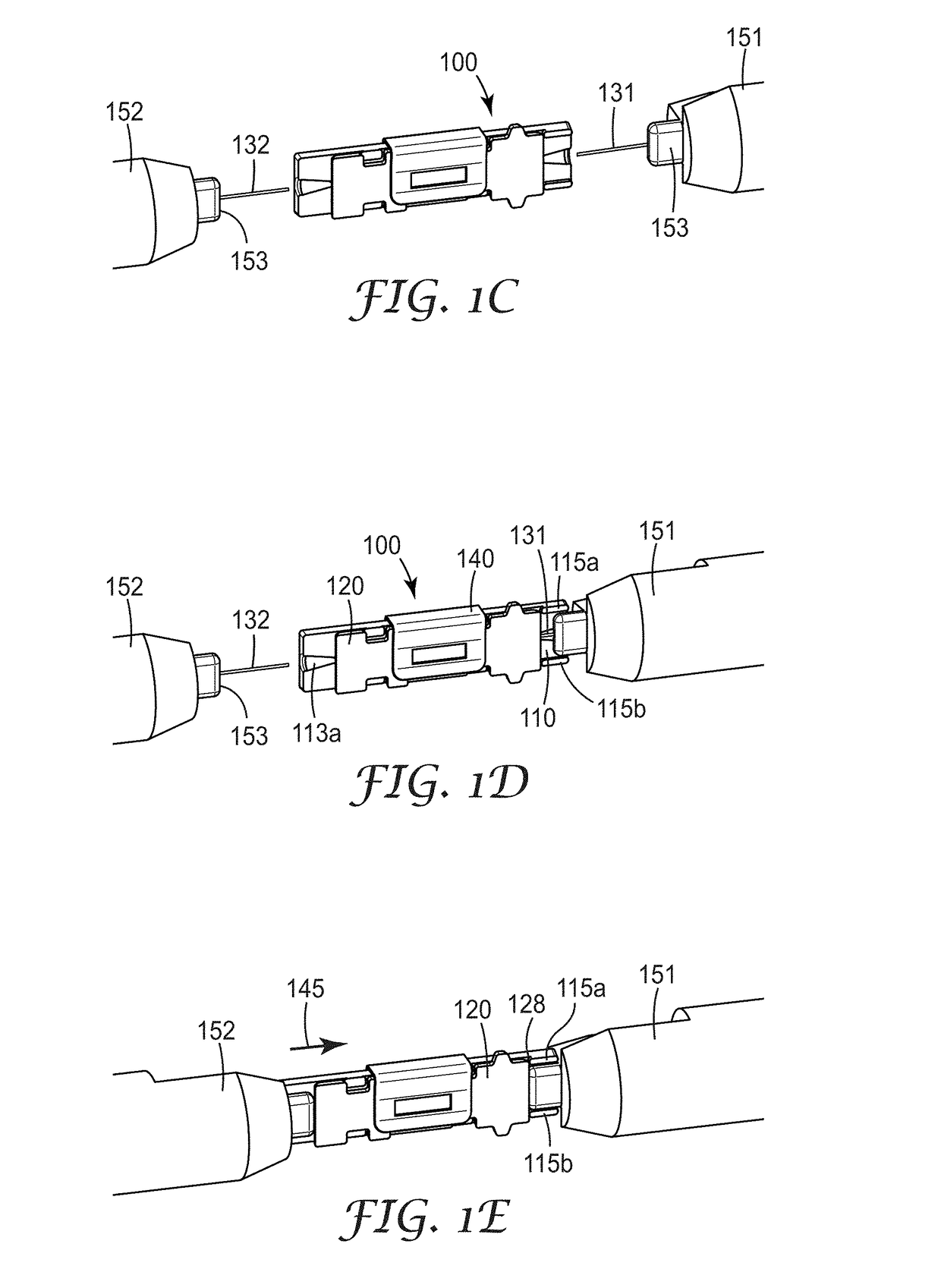
[0295]Embodiment 1A is a splice element for splicing a first and a second optical fiber, comprising an alignment mechanism having a base plate and a clamp plate, at least one of the base plate and clamp plate being formed from a silica material, and at least one of the base plate and clamp plate having an alignment groove configured to receive the first and second optical fibers in an end-to-end manner; and an optical adhesive disposed in at least a portion of the alignment groove, wherein the optical adhesive is curable via actinic radiation.
[0296]Embodiment 2A is the splice element of embodiment 1A, wherein the optical adhesive is blue light curable.
[0297]Embodiment 3A is the splice element of any preceding embodiment, wherein the optical adhesive comprises an adhesive composition containing non-aggregated, surface-modified silica nano-particles dispersed in an epoxy resin.
[0298]Embodiment 4A is the splice element of any preceding embodiment,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com