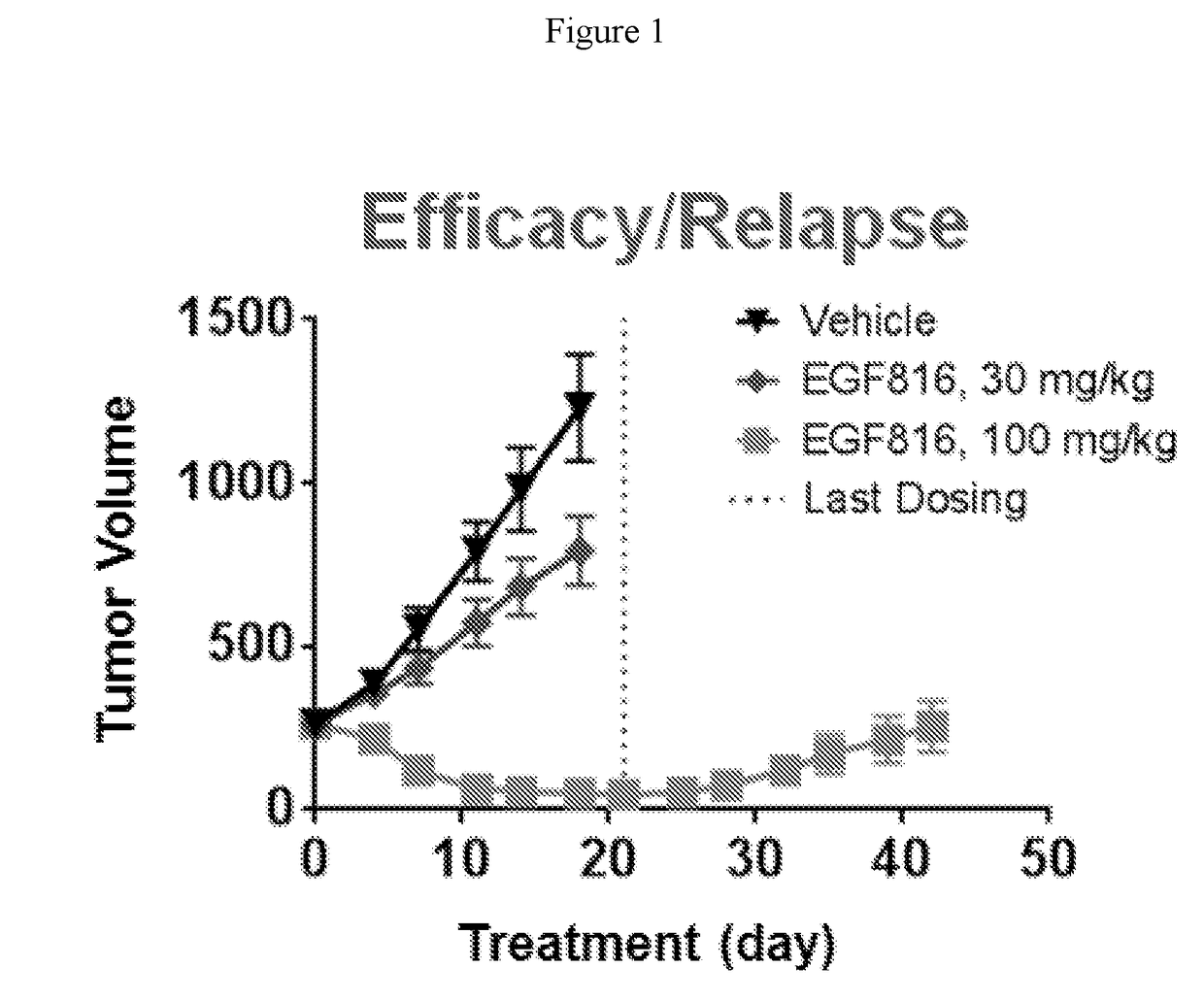
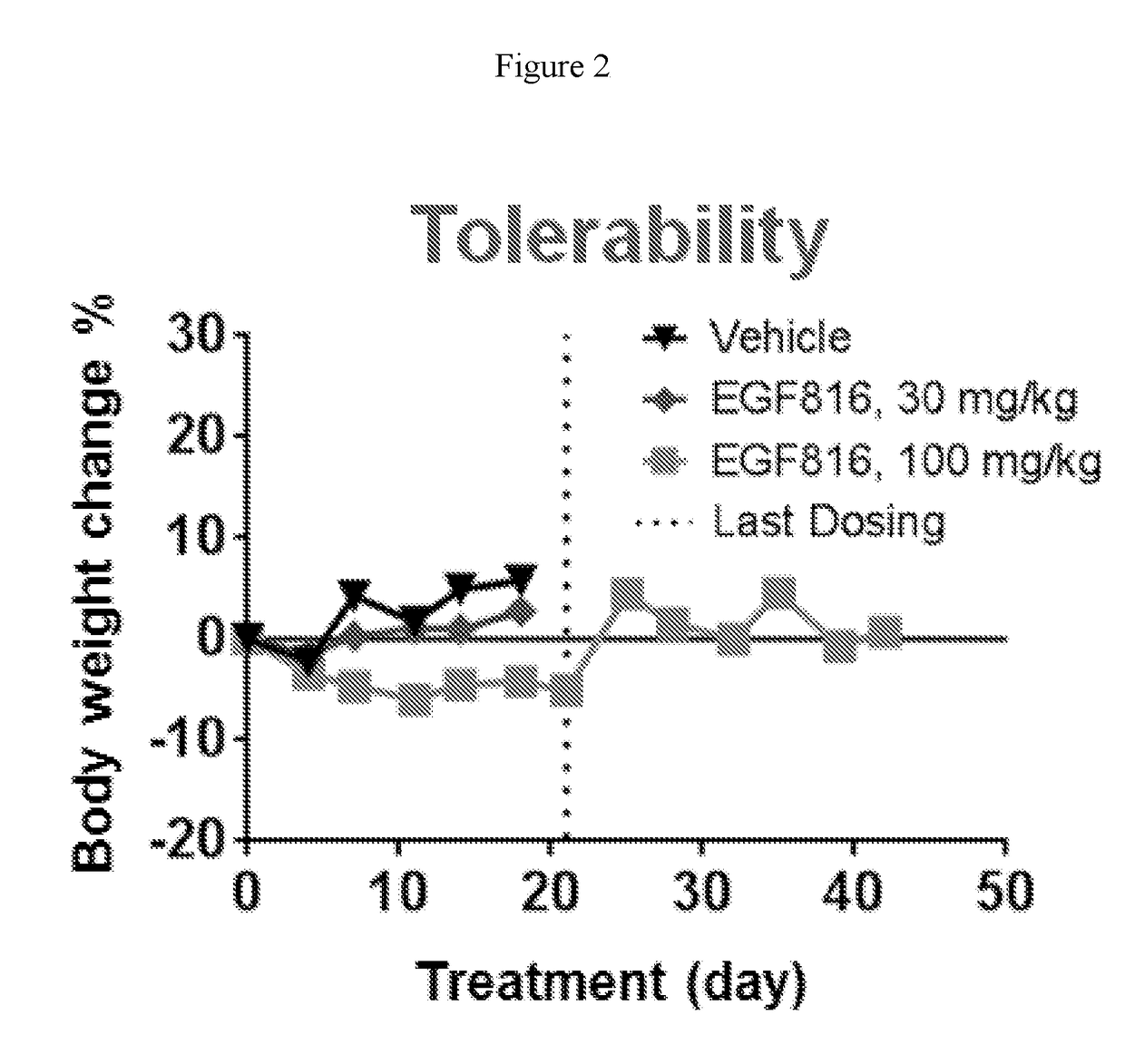
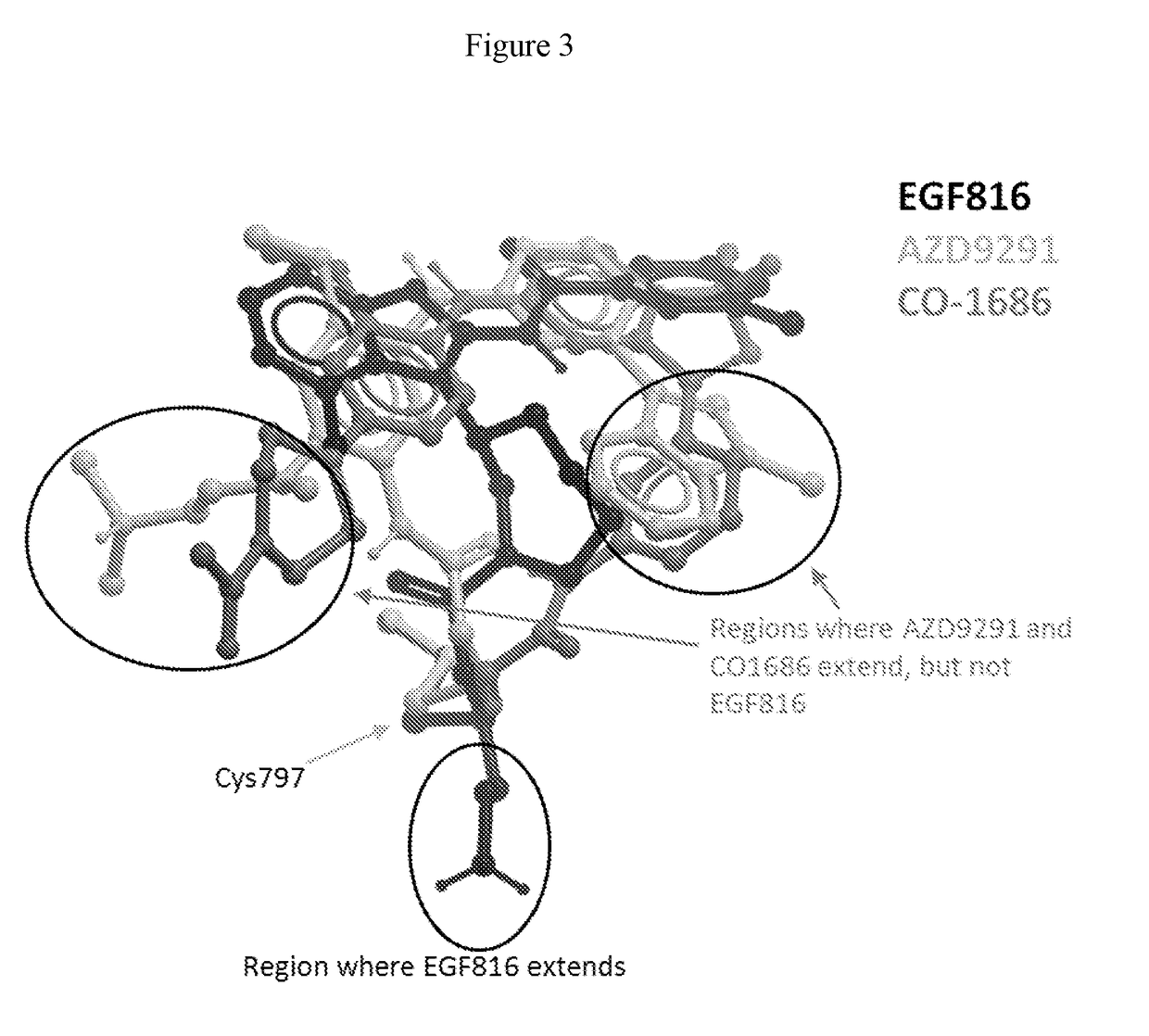
Methods for treating EGFR mutant cancers
a technology for egfr mutant cancer and treatment methods, applied in the direction of drug compositions, heterocyclic compound active ingredients, anti-cancer agents, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective treatment of egfr inhibitors, limited clinical efficacy, and inability to definitively translate into prolonged overall survival
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
7-chloro-1-(1-(4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enoyl)azepan-3-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-2-methylisonicotinamide (EGFRi) Biochemical Assays
[0108]IC50 Determinations.
[0109]All EGFR biochemical assays were carried out as described in WO2013 / 184757.
[0110]Biological Results
[0111]IC50 determinations for Compound A obtained from a EGFR biochemical assay as described above from EGFR (L858R / T790M) without and with 90-minute pre-incubation were 0.008 μM and <0.001 μM, respectively.
[0112]Compound A shows an inhibition IC50 determinations obtained from EGFR target modulation in engineered NIH / 3T3 cell lines for L858R / T790M and L858R, 0.011 μM and 0.015 μM, respectively. For WT the value was 0.259 μM.
[0113]The IC50 determinations obtained from EGFR target modulation in H1975 (EGFR L858 / T790M), H3255 (EGFR L858R), and HEKn (EGFR WT) cell lines were 0.013 μM, 0.030 μM and 1.180 μM respectively.
example 2
Salt and Mesylate Form B (Mesylate Trihydrate Form) of Compound A
[0114](R,E)-N-(7-chloro-1-(1-(4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enoyl)azepan-3-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-2-methylisonicotinamide as obtained in Example 5 of WO2013 / 184757 (1.0 g) was dissolved in acetone (30 mL) by heating to 55° C. to form a solution. Methanesulfonic acid (325 μL) was added to acetone (50 mL), and the methanesulfonic acid / acetone (22.2 mL) was added to the solution at 0.05 ml / min. Following precipitation, the resulting suspension was cooled to room temperature at 0.5° C. / min, and crystals were collected by filtration, and dried for 4 hours at 40° C. under vacuum. The collected crystals (300 mg) were suspended in acetone / H2O (6 mL; v / v=95 / 5) by heating to 50° C. The suspension was kept slurrying for 16 hours, and cooled to room temperature at 0.5° C. / min. The crystal was collected by filtration and dried for 4 hours at 40° C. under vacuum.
[0115]The structure of (R,E)-N-(7-chloro-1-(1-(4-(dimethylamino)but-2-e...
example 3
Compound A (EGF816) on EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Models in in Vitro Cell Assays
[0117]3.1 Cell Lines
[0118]NIH-3T3 Ex20_D770_N771insNPG cells (obtained from DFCI) were maintained in 10% FBS / DMEM P / S media supplemented with 2 μg / mL puromycin. Engineered BaF3 cells were maintained in 10% FBS / RMPI P / S media supplemented with 2 μg / mL puromycin. All cells were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37° C. with 5% CO2.
[0119]Full-length, wild-type EGFR cDNA was sub-cloned into the cloning vector pCR4 (LifeTech) and used as a template to create Ex20ins mutants D770_N771insSVD and V769_D770insASV with a site-directed mutagenesis kit (Agilent). Sequence-verified clones were double-digested with endonucleases XhoI and HpaI and ligated to similarly digested pMSCVpuroLuc expression vector (in-house). HEK293T cells were co-transfected with mutant EGFR pMSCVpuroLuc vector and pEcoPak viral packaging vector. Supernatants containing viral vectors were subsequently used to infect IL-3 dependent BaF3 cell...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com