Wound covering apparatus
a wound covering and bandage technology, applied in the field of wound covering equipment, can solve the problems of more damage, touch and potentially damage to the wound, lack of oxygenation for the burn/wound, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing the speed of the healing process, increasing the injury to the wound, and safe removal and reapplying of ointmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
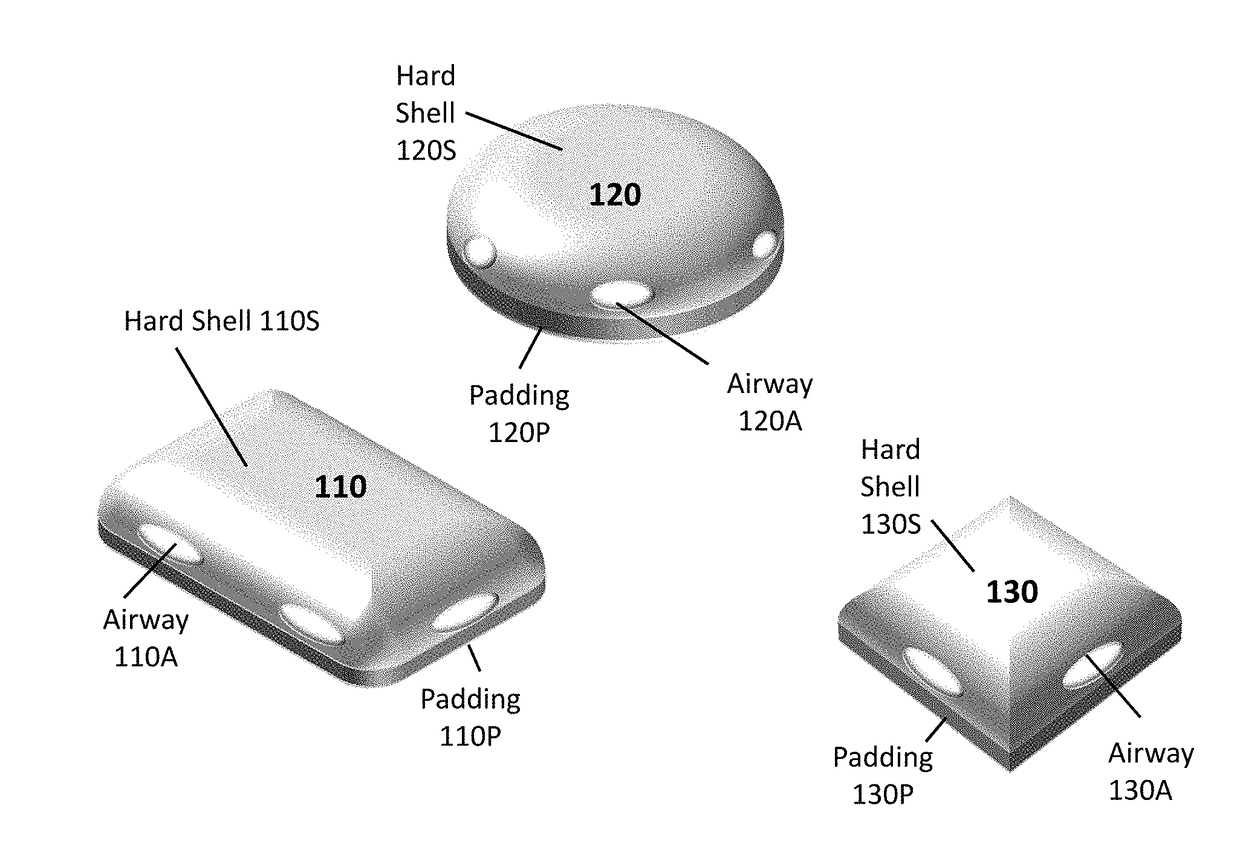
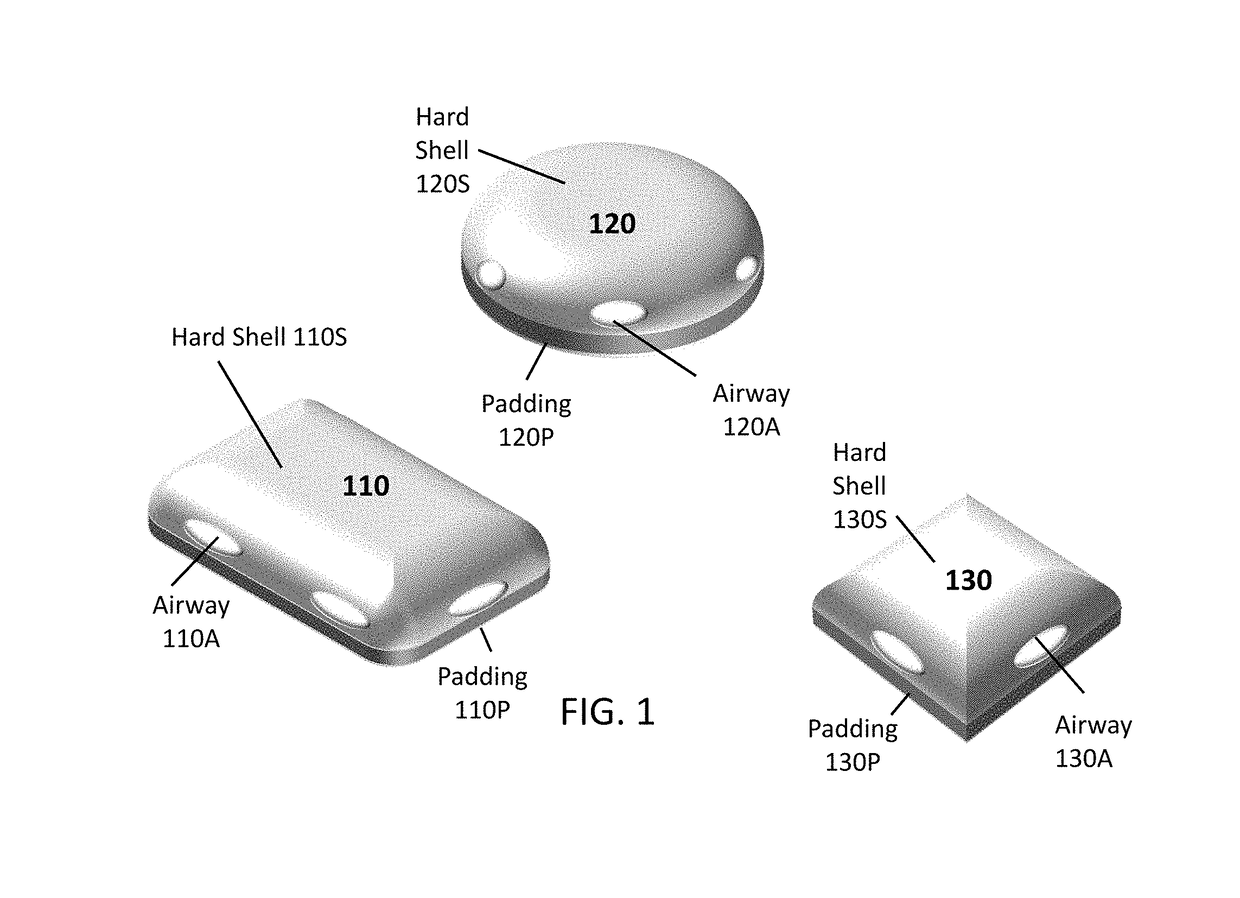
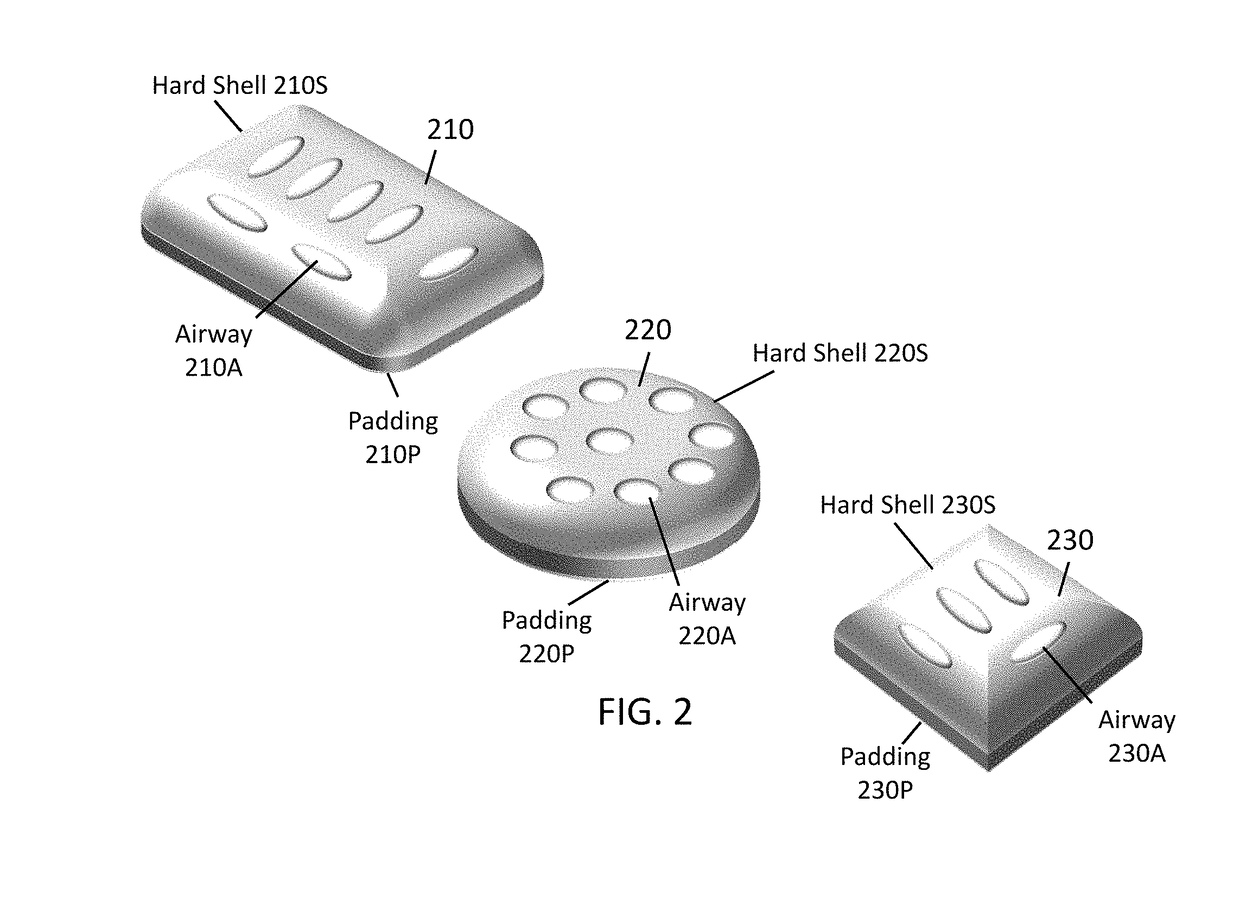
[0030]The present disclosure relates to apparatus for covering a burn or other wound in ways that prevent or limit touching the wound. The present disclosure describes Burn Bandages that may include domes or structures that bridge over a wide range of a burn or wound size. The apparatus may be a dome structure manufactured from a clear or transparent plastic like material to allow the patient to physically see the wound through the dome covering. The dome covering may also be constructed from any and all transparent materials that are used for their transparency in optics and in the decorative arts such as but not limited to: borosilicate glass, germanium dioxide, polycarbonate, any form of polyethylene, so-gel and any other appropriate transparent material know in the art. The dome covering may also be manufactured from any material that protects the wound from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun that may increase further injury to the wound. Such as, ultraviolet A (UVA) whi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com