Methods for detection of plasma cell dyscrasia
a plasma cell and detection method technology, applied in the field of plasma cell dyscrasia detection, can solve the problems of low progression-free survival rate of patients, poor overall survival, and difficulty in cytogenetic approaches, and achieve high sensitivity and specificity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Derivation of a 32-Marker Gene Panel
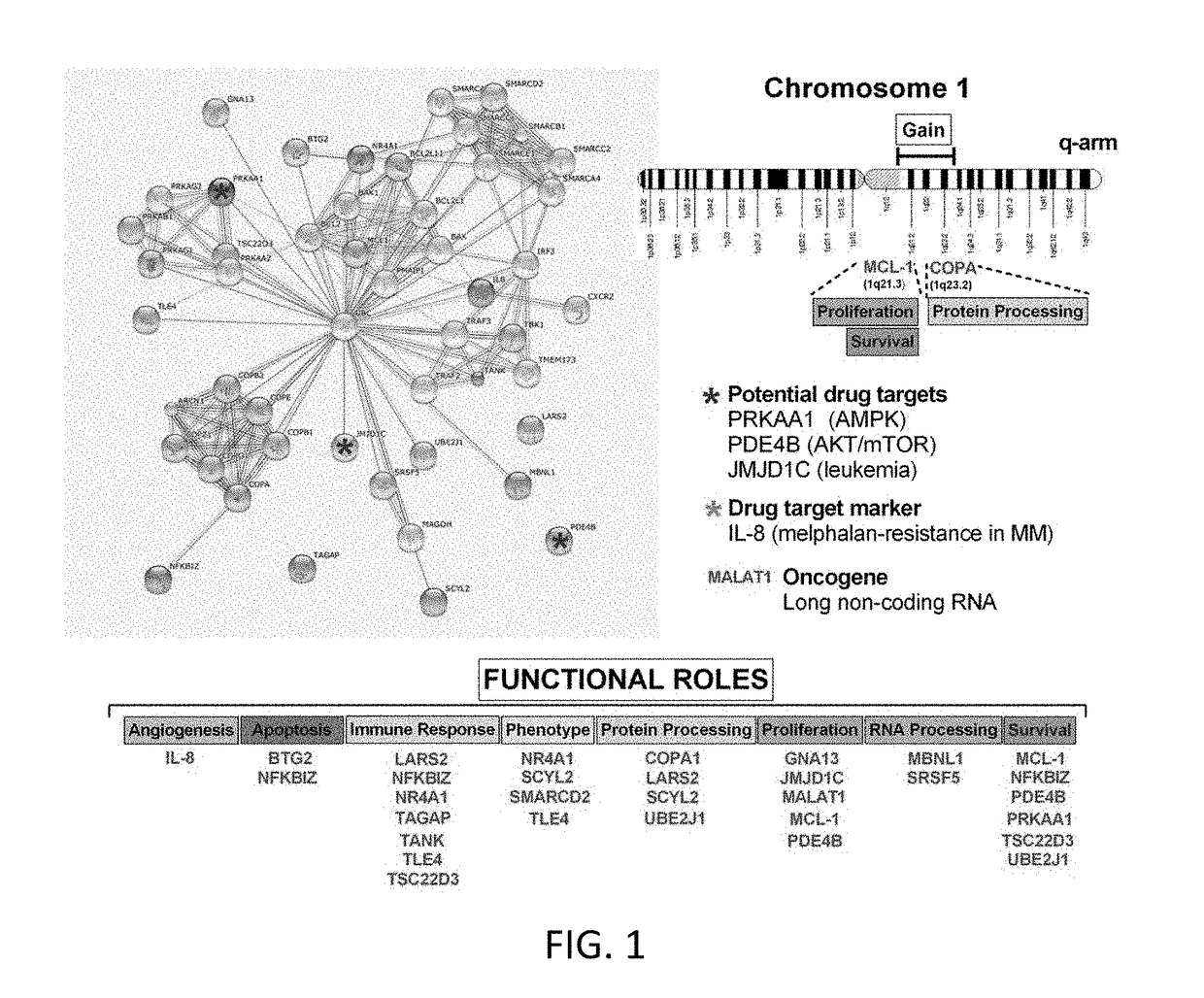
[0086]Raw probe intensities (n=1,354,896 features) from n=15 peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples were used to identify genes that best discriminated between controls and multiple myeloma using the transcriptional profile of GSE7116. Following removal of outliers, a total of 31 target transcripts (26 genes, 5 splice variants) and one house-keeping gene was identified in an unbiased manner as potential markers of myeloma (Table 2; FIG. 1). These genes were demonstrated to be expressed in multiple myeloma cell lines, IM-9 (normal diploid karyotype) and MM1R (dexamethasone-resistant), identifying they are produced by transformed B-lymphoblasts.
[0087]Then an artificial intelligence model of myeloma disease dynamics was built using normalized gene expression of these 31 markers (normalized to the housekeeping gene, TPT1) in whole blood from Controls (n=45), Responders / Stable (n=24: stable disease), and Newly Diagnosed / Relapsed (n=66: progressive d...
example 2
Diagnosis: Identification of Samples as Myeloma
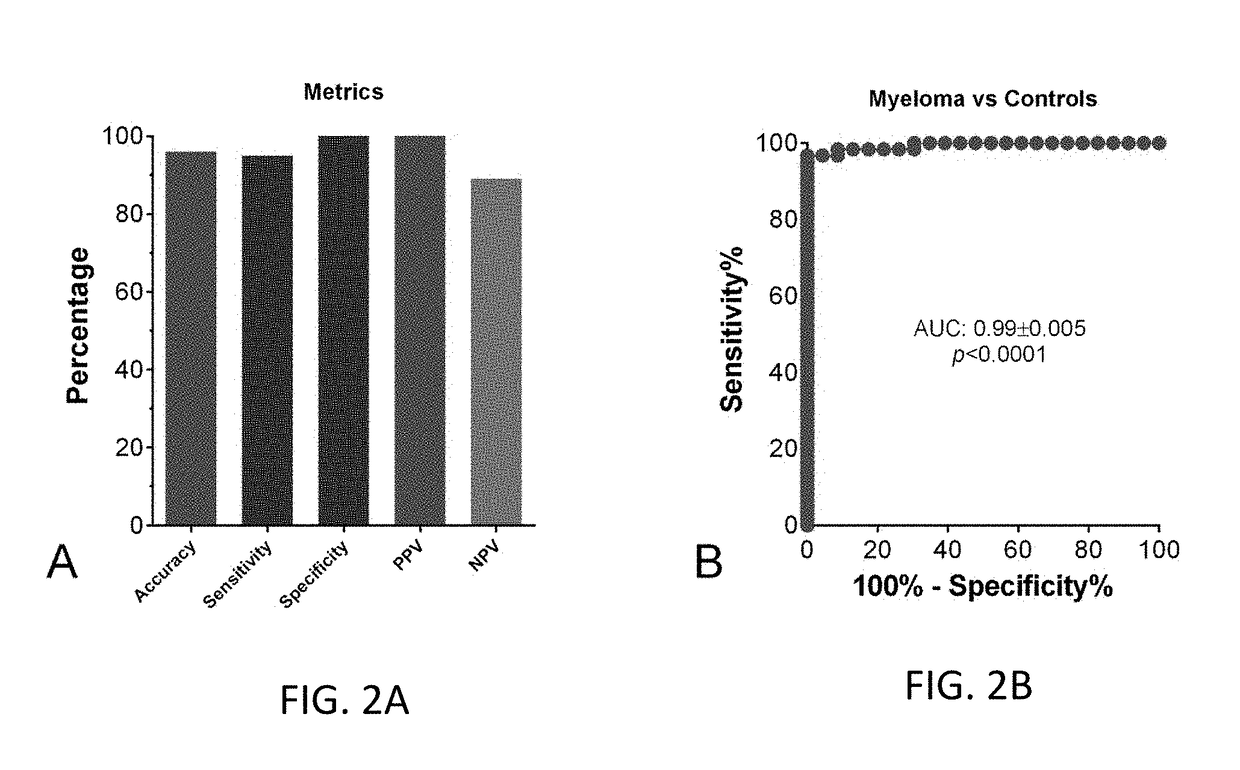
[0088]In the test set 1, the data for the utility of the test to differentiate patients with active myeloma disease (n=57) from controls (n=23) are included in Table 3. The receiver operator cuver analysis and metrics are included in FIG. 2B. The score exhibited an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.99. The metrics are: sensitivity >95%, specificity 100%, PPV 100%, NPV 88.5%. The overall accuracy is 96%. The tool can therefore differentiate between controls and aggressive and stable myeloma disease.
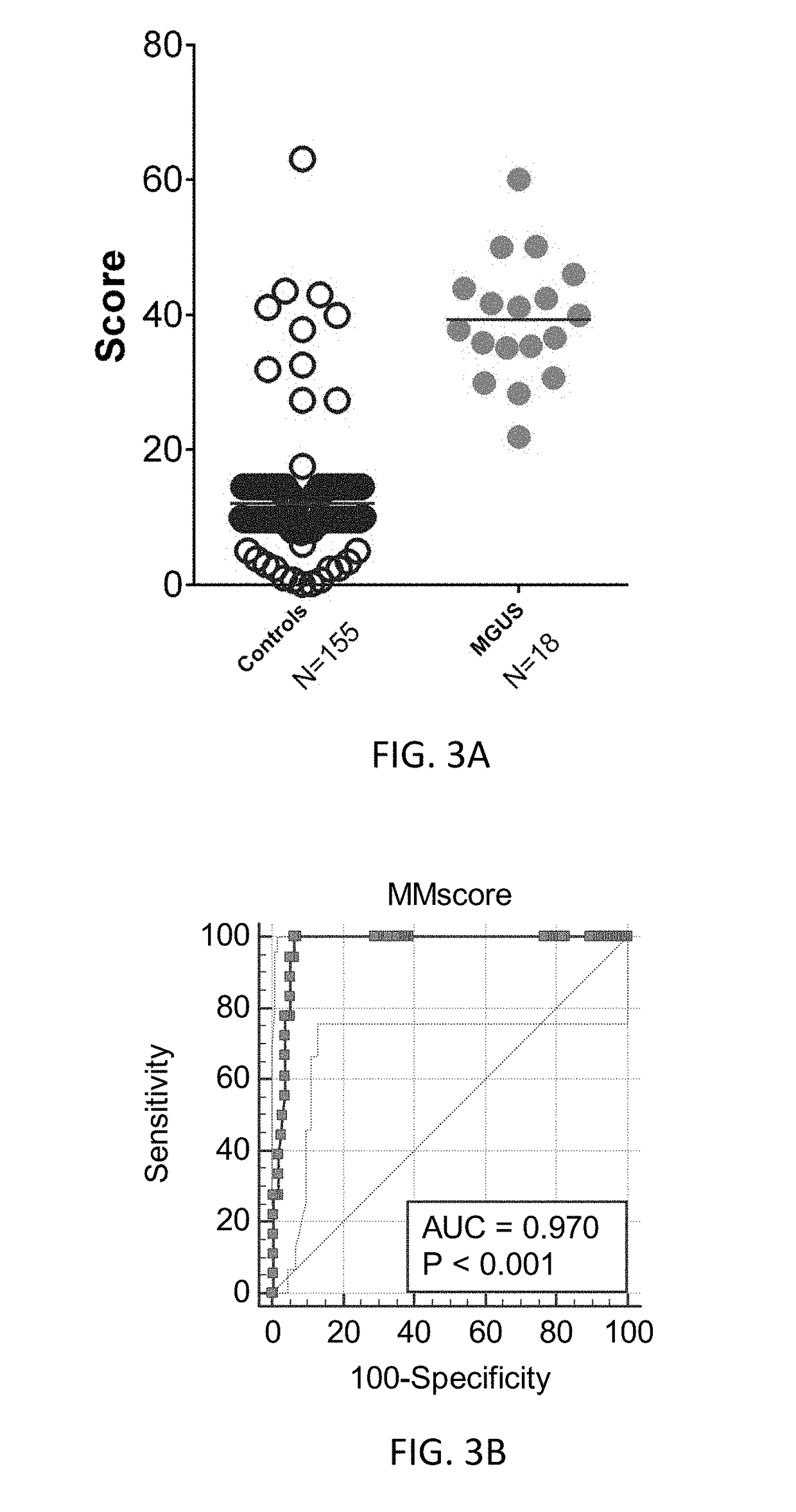
[0089]Specific evaluation of the MGUS identified significant differences between this plasma cell dyscrasia (n=18; MyelomX=39±9) and controls (n=155, 12±8, p<0.0001) (FIG. 3A). The AUC for differentiating MGUS from controls 0.97 (FIG. 3B).
[0090]Specific evaluation of the multiple myeloma sub-groups identified significant differences between newly diagnosed patients (n=53; MyelomX=75±25), clinically stable disease (n=56, 31±20, p<0.0001) and refr...
example 3
Identification of Minimal Residual Disease
[0092]Effective therapy (n=40), decreased the score from 59±14 to 35±12 which was associated with complete remissions (FIG. 6). Evaluation of the MRD group identified ten patients all with high scores (≥40) who relapsed at an early time point (within one year). The MyelomX score can therefore biochemically define MRD and identify those who have progressive disease and will relapse at an early time-point.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fluorescent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| plasma cell dyscrasia | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com