Tubular nanosized magnetic wires with 360° magnetic domain wallu
a magnetic wire and nano-sized technology, applied in the field of tubular nano-sized magnetic wires, can solve the problems of instability and slow speed of magnetic domain walls, limited propagation of domain walls in planar nanowires, and inability to move domain walls uniformly, so as to achieve the effect of not annihilating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
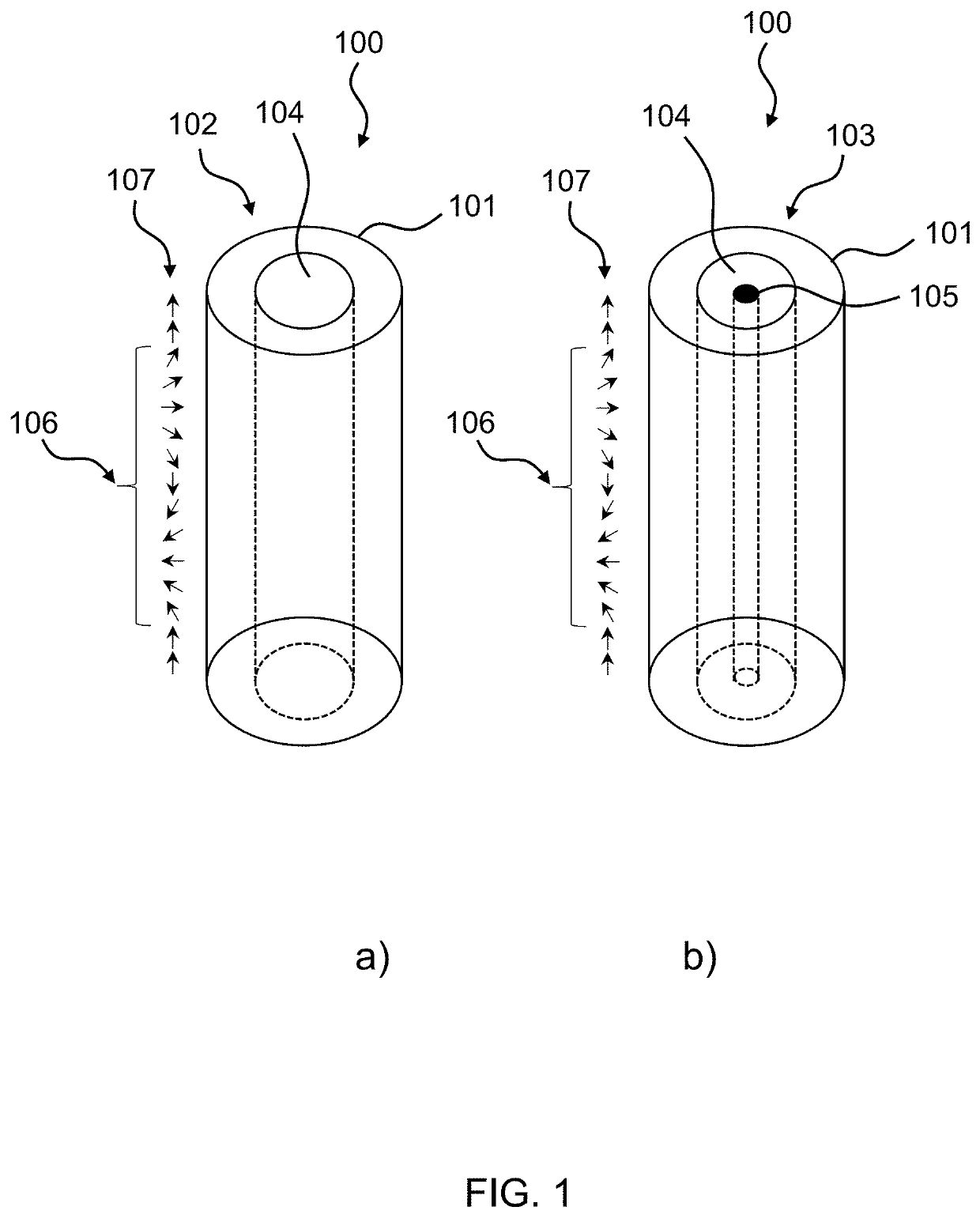
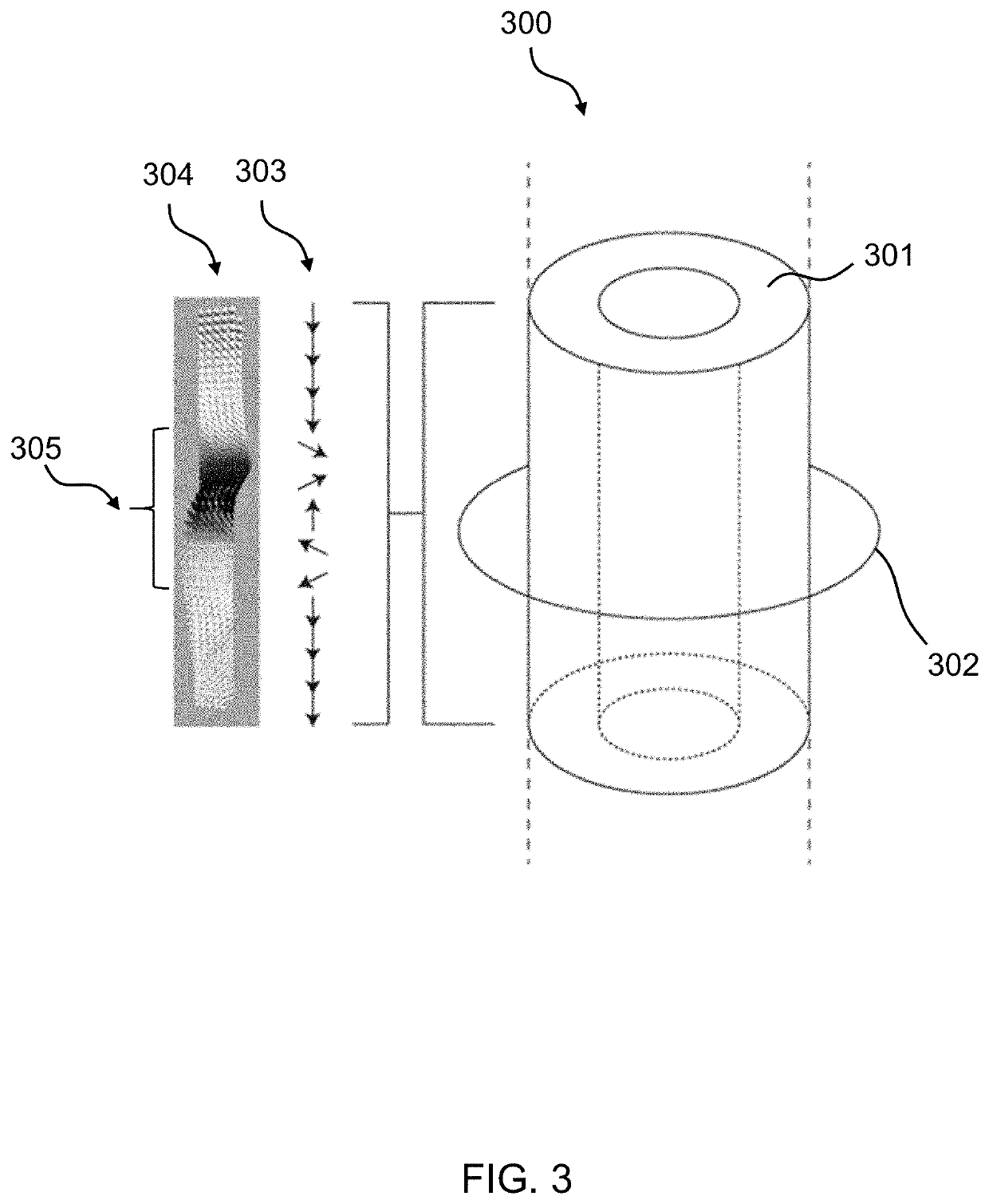
[0027]FIG. 1a) is a perspective view of one embodiment of the present invention showing a magnetic wire 100 with a tubular shell 101. According to FIG. 1a) the magnetic wire 100 is a magnetically hollow tube 102. The wording “magnetically hollow” refers to the case that the inner core 104 of the tubular magnetic wire 100 can be either empty or filled with a non-ferromagnetic, that is dia-, para-, or antiferromagnetic material.
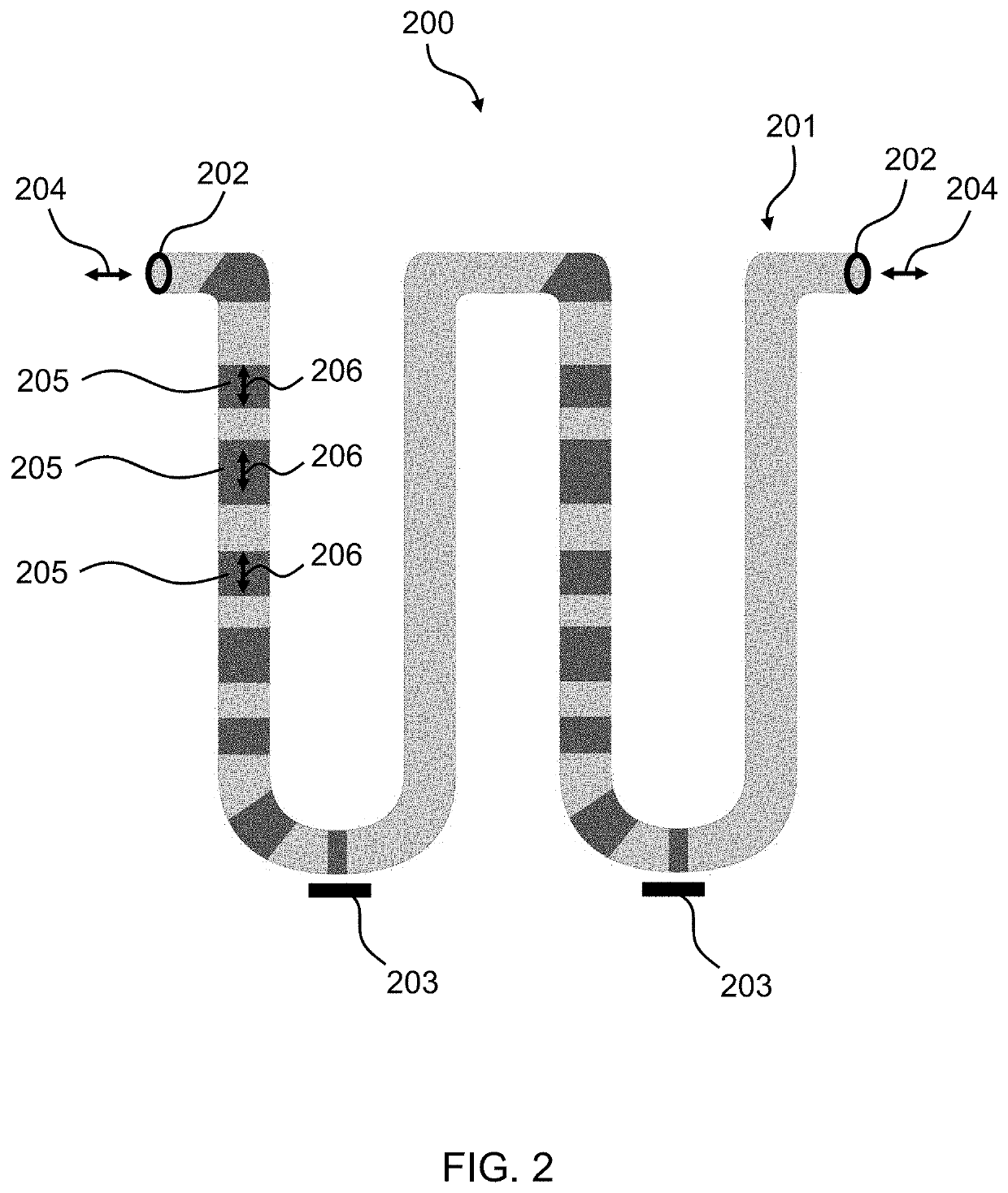
[0028]The 360° domain walls 10 are perpendicular to the axis of the wire 100 with magnetization 107 going from parallel to perpendicular, to parallel alignment with regard to the wire 100 axis. The 360° domain walls 106 are stabilized by the morphology of the tubular hollow shell 101. Therefore one advantage of the proposed tubular nanosized magnetic wire 100 comprising a self-stabilizing, 360° magnetic domain wall 106 is that due to its chirality a 360° domain wall 106 can be moved through the system using field and current pulses. The proposed tubular nanosiz...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com