Patents
Literature
30 results about "Racetrack memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
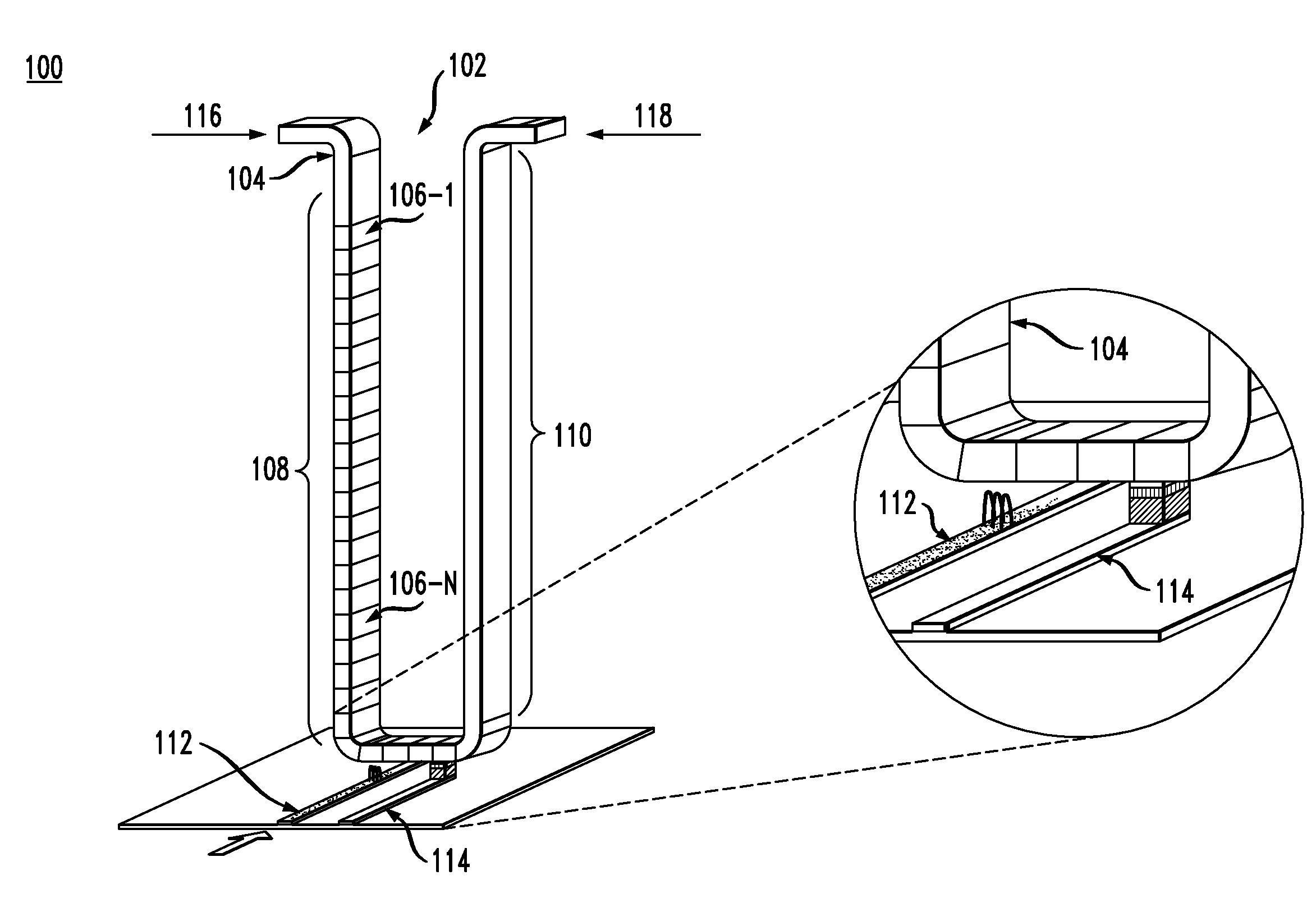
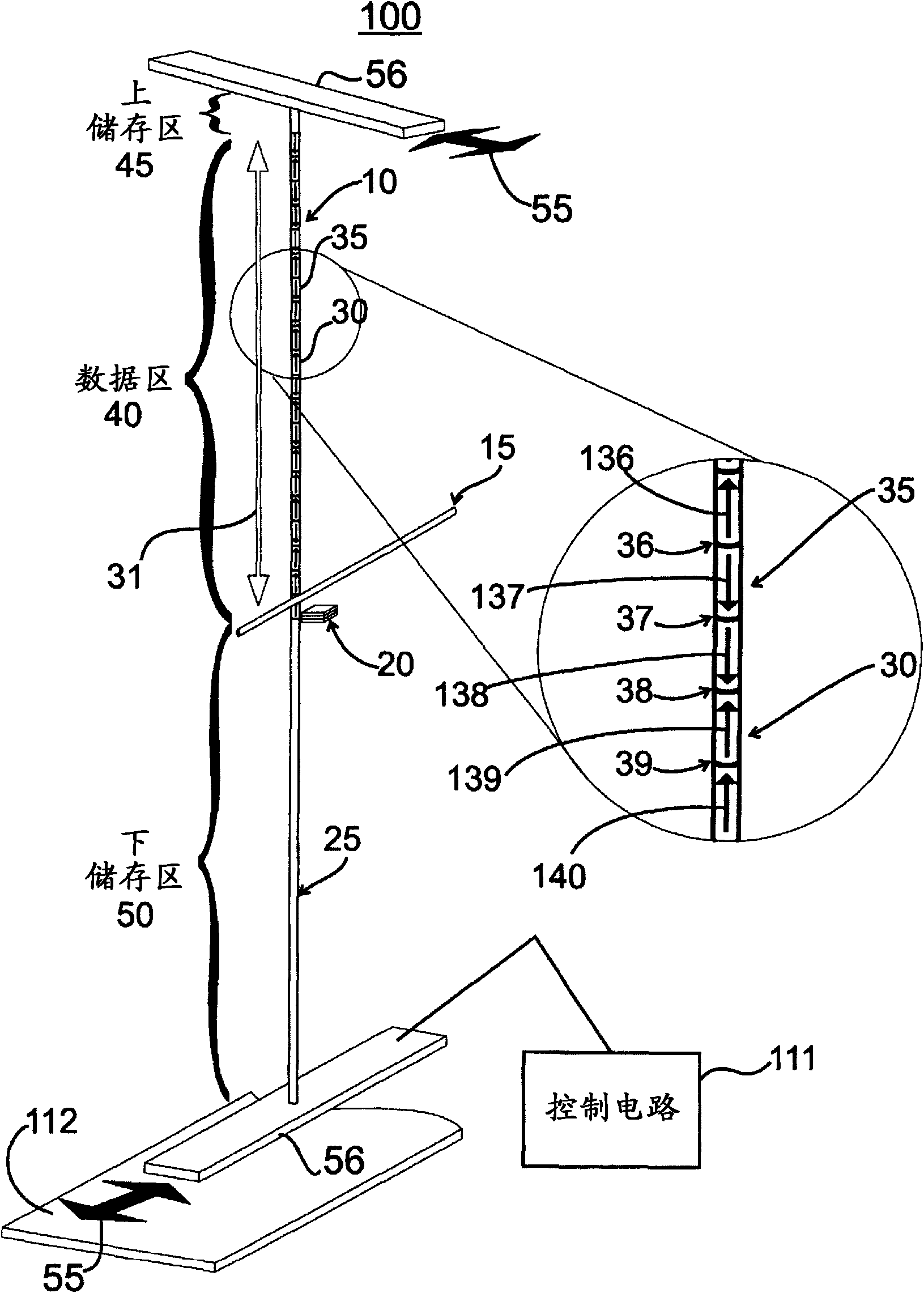
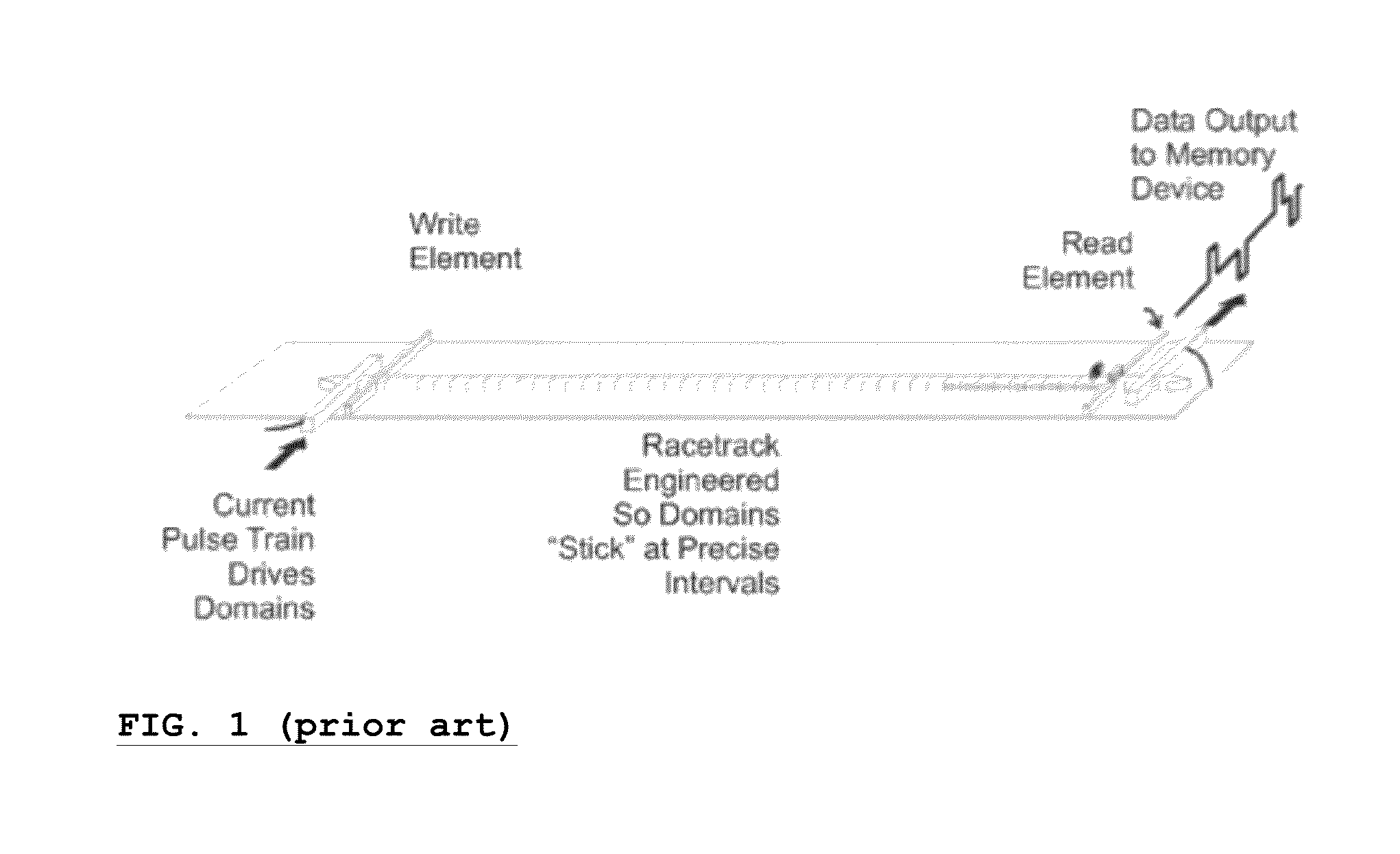
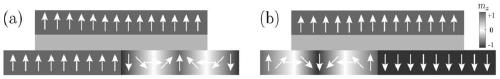
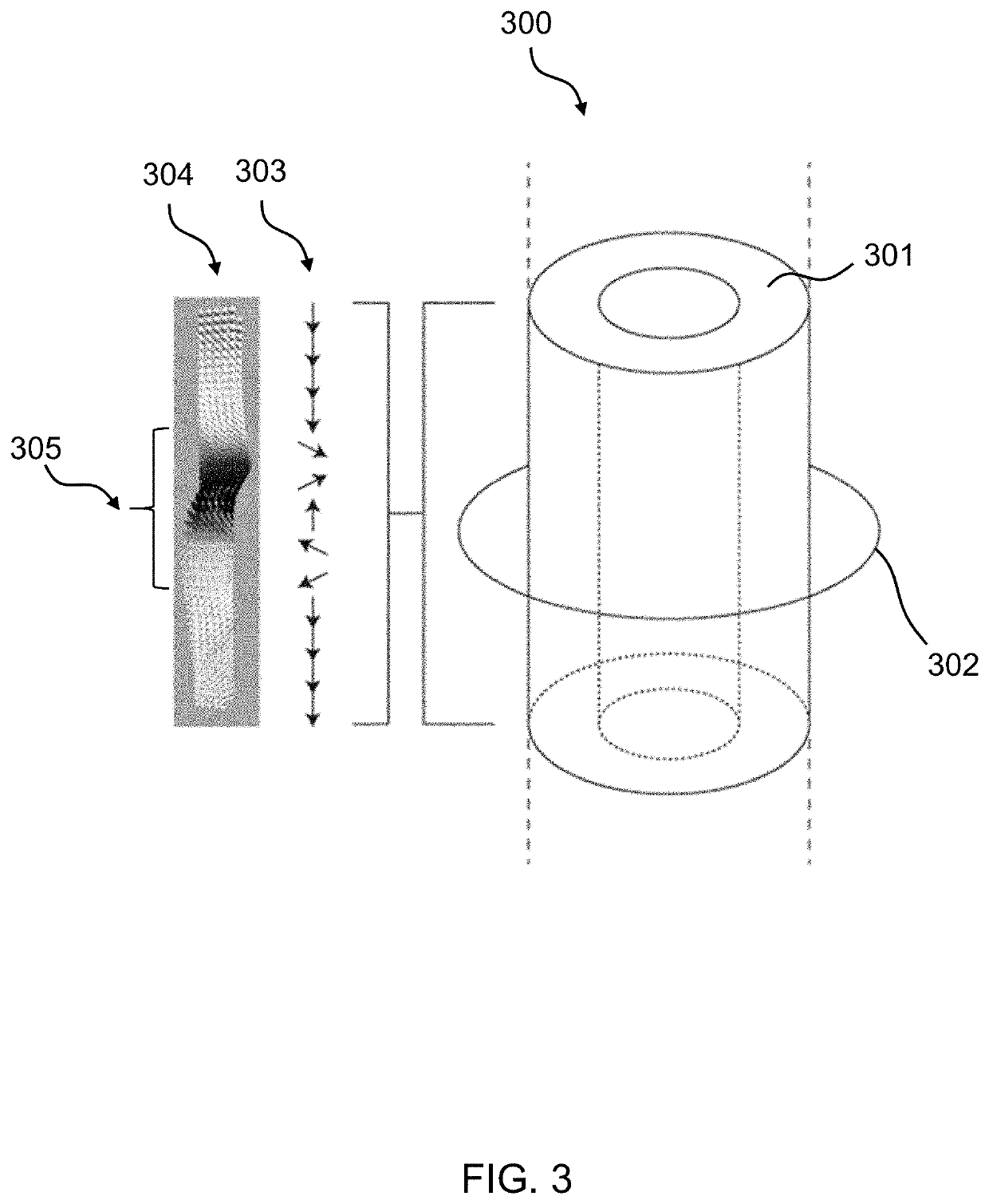
Racetrack memory or domain-wall memory (DWM) is an experimental non-volatile memory device under development at IBM's Almaden Research Center by a team led by physicist Stuart Parkin. In early 2008, a 3-bit version was successfully demonstrated. If it were to be developed successfully, racetrack would offer storage density higher than comparable solid-state memory devices like flash memory and similar to conventional disk drives, with higher read/write performance.
Racetrack memory based on magnetic skyrmions
ActiveCN108492845ARealize reading and writingRealize the storage functionDigital storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic skyrmion
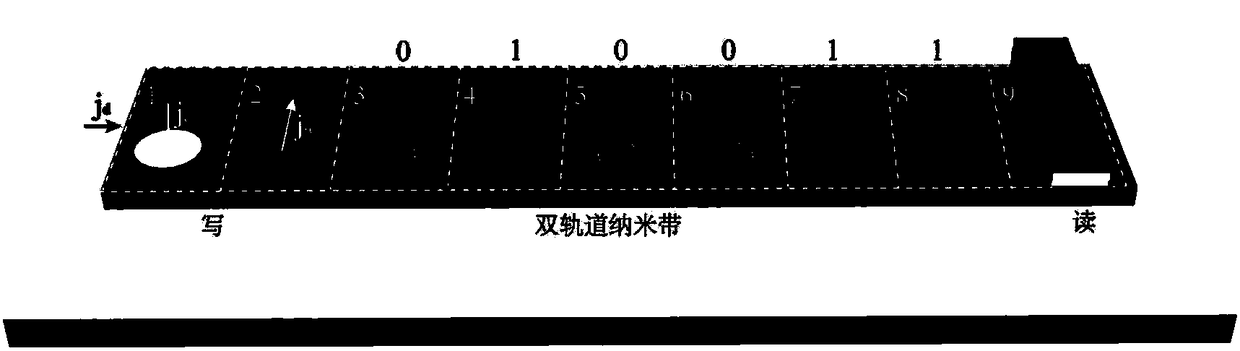
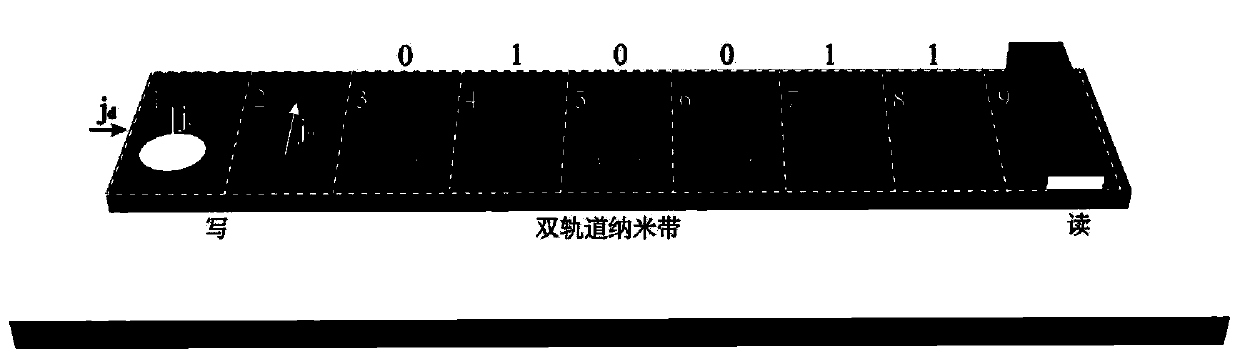
The invention provides a racetrack memory based on magnetic skyrmions, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic devices. The racetrack memory comprises an antiferromagnetic coupling twin-track magnetic nano belt, and the magnetic nano belt is divided into an information input part, an information storage part and an information reading part sequentially in the track direction. The magnetic skyrmions with the opposite polarity are utilized for presenting binary number zero or one, and the magnetic skyrmions move from the information input part to the information reading part in the trackdirection of the twin-track magnetic nano belt. The magnetic skyrmions are periodically generated in one of the track of the twin-track magnetic nano belt where the information input part is located,whether the polarity of the generated magnetic skyrmions needs to be changed or not is determined according to the input data, and accordingly whether the magnetic skyrmions need to be moved to the other track of the twin-track magnetic nano belt or not is determined. The information storage part is divided into a plurality of storage units in the track direction of the magnetic nano belt, and onemagnetic skyrmion is stored in one storage unit. The information reading part is used for reading the polarity of the magnetic skyrmions passing through.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Racetrack memory with electric-field assisted domain wall injection for low-power write operation
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Wall nucleation propagation for racetrack memory
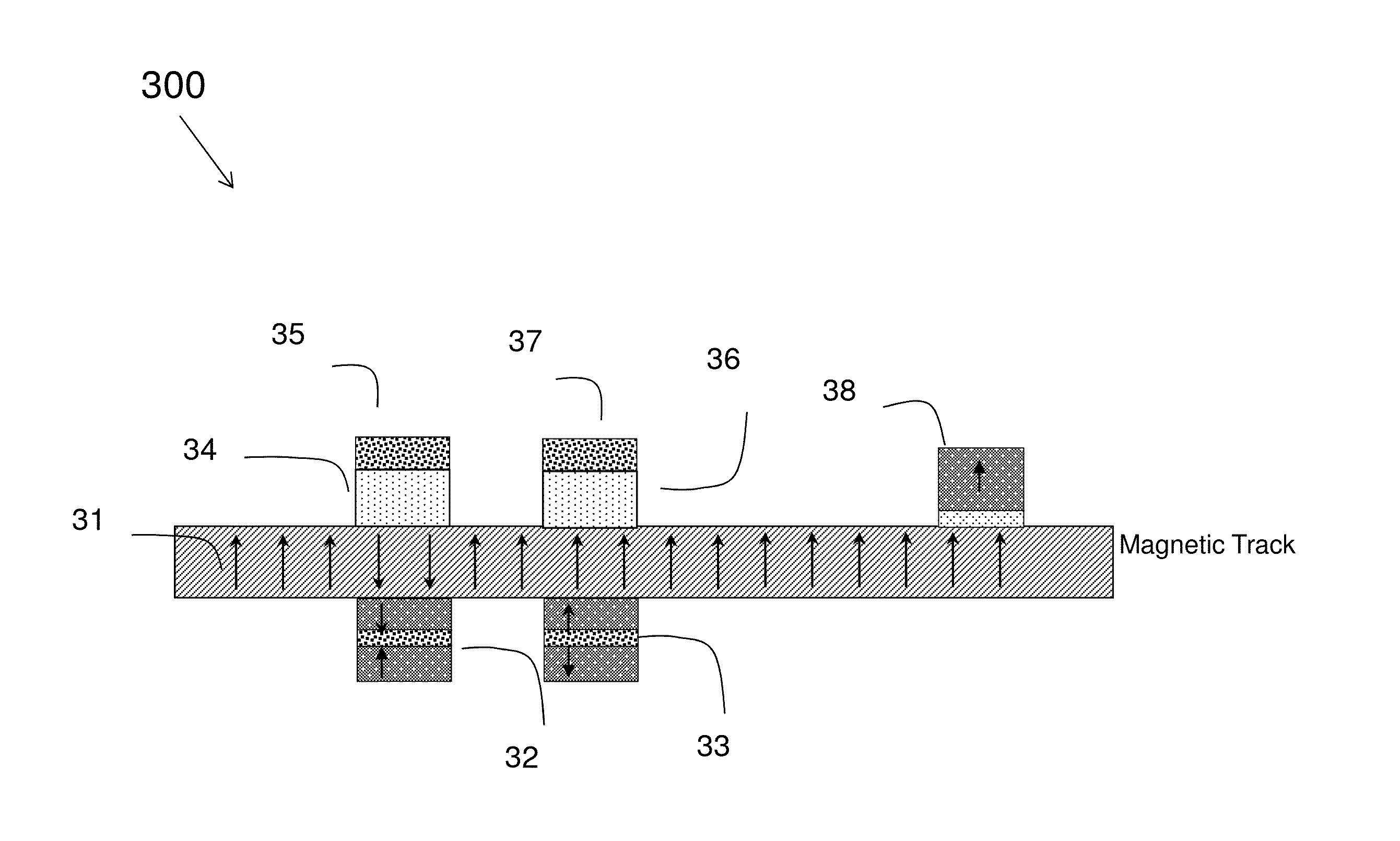
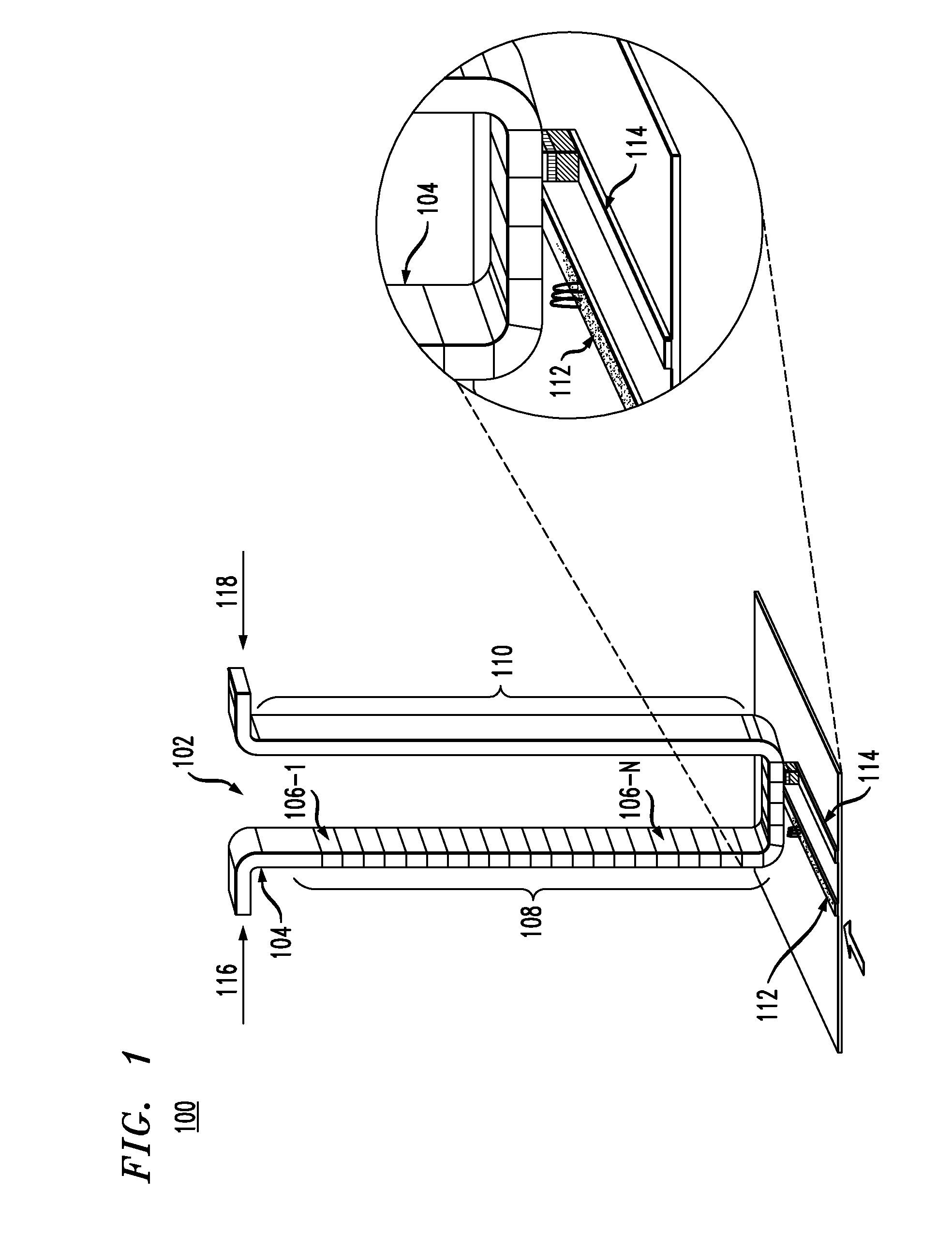
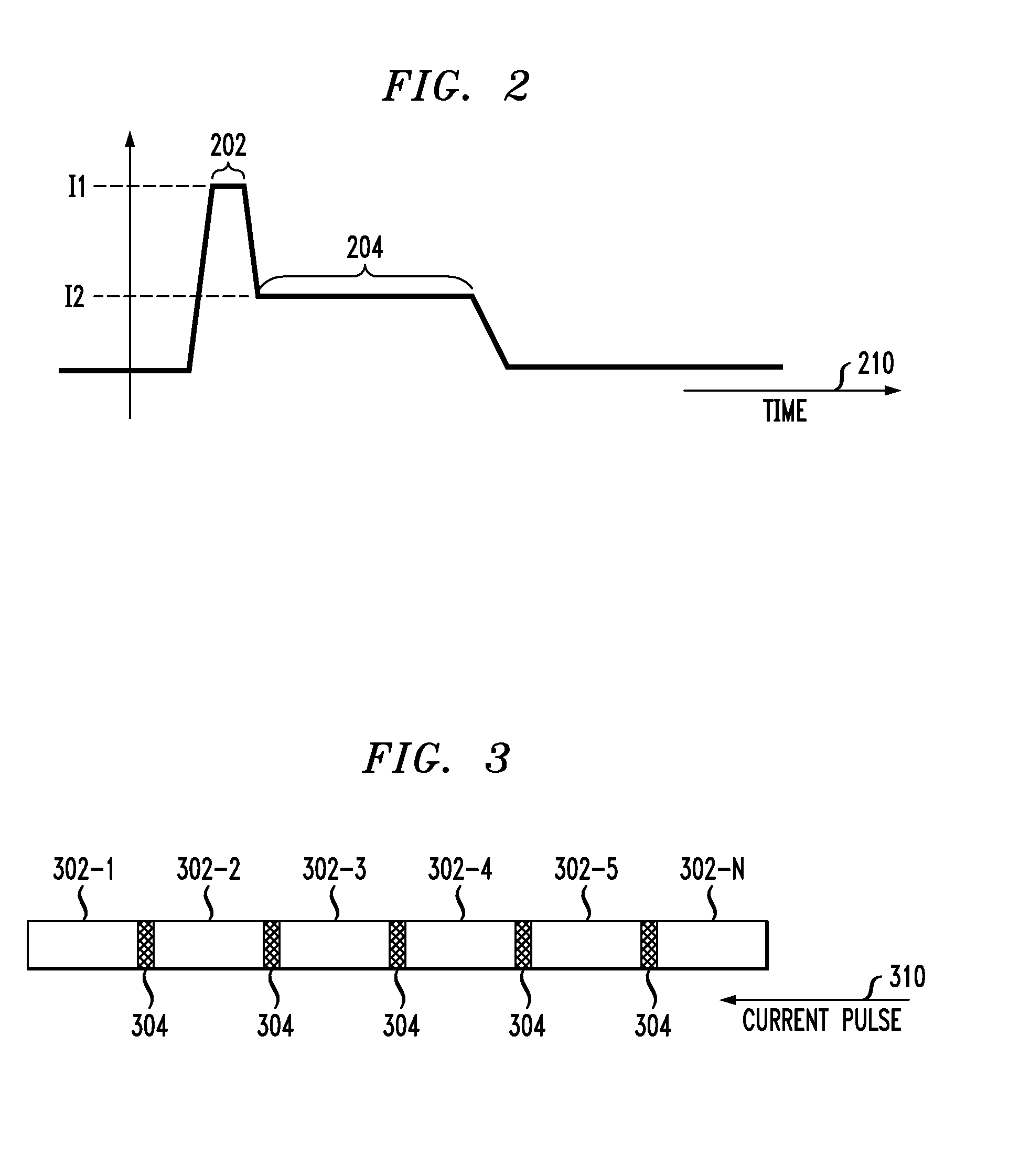
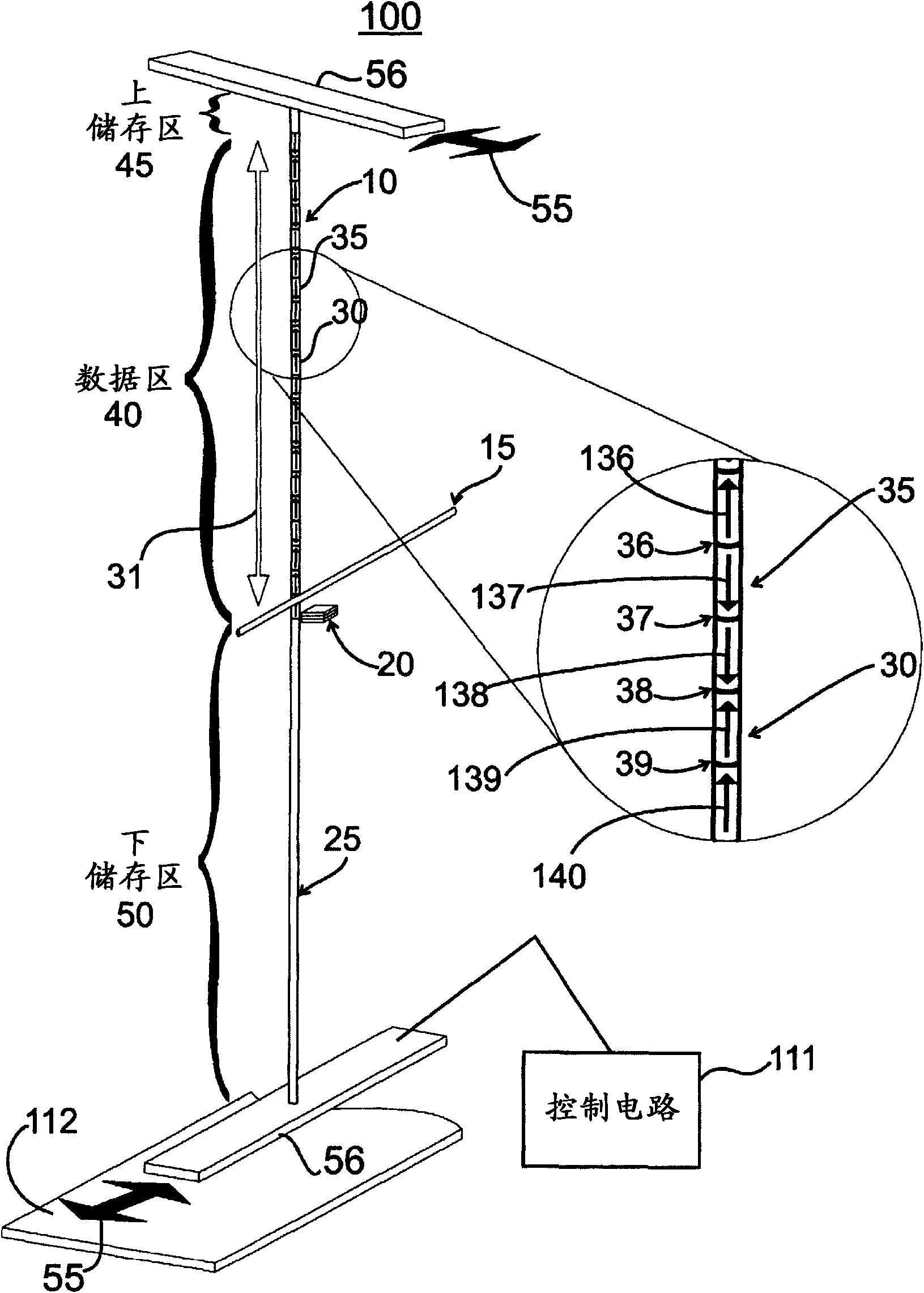
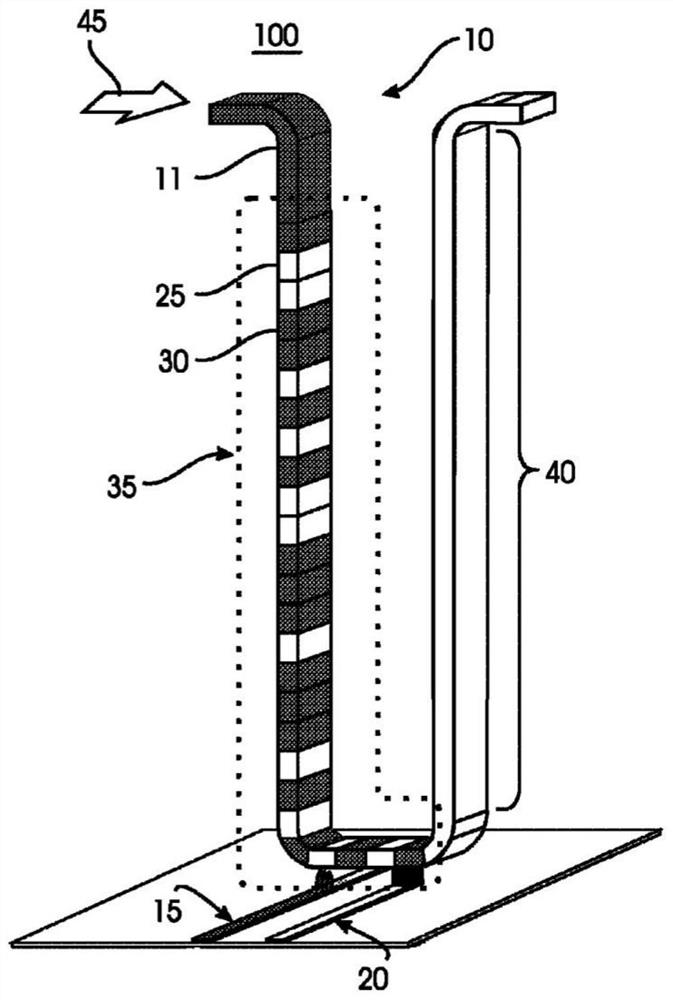
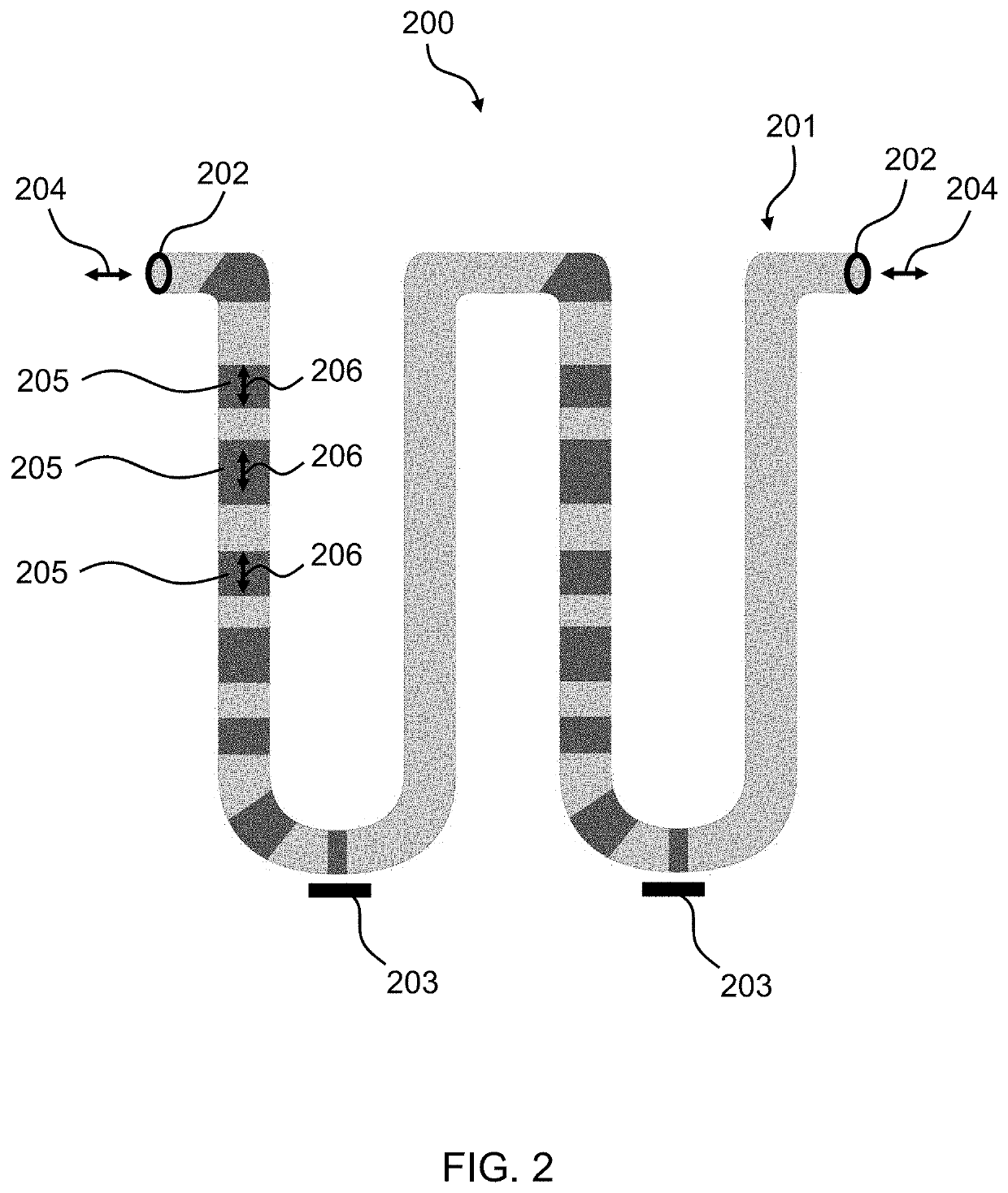
A shift register is provided, the shift register comprising at least one track including a storage region. The storage region comprises a plurality of magnetic domains for storing data. A given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains is adjacent to a given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains. The given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains and the given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains are arranged in a linear configuration. Further, the given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains and the given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains are separated from one another by at least one layer of non-magnetic material. The at least one layer of non-magnetic material preventing a propagation of a nucleated wall from traveling between the given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains and the given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains. The shift register is configured such that an electric current applied to the track is operative to shift data stored within at least one of the plurality of magnetic domains of the storage region, along the track, in a direction of the electric current. The data stored within the at least one of the plurality of magnetic domains is shifted as a function of the direction of the electric current.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wall Nucleation Propagation for Racetrack Memory
InactiveUS20100085793A1Hinders its propagationEncourage wall nucleationDigital storageShift registerProcessor register
A shift register is provided, the shift register comprising at least one track including a storage region. The storage region comprises a plurality of magnetic domains for storing data. A given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains is adjacent to a given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains. The given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains and the given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains are arranged in a linear configuration. Further, the given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains and the given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains are separated from one another by at least one layer of non-magnetic material. The at least one layer of non-magnetic material preventing a propagation of a nucleated wall from traveling between the given first one of the plurality of magnetic domains and the given second one of the plurality of magnetic domains. The shift register is configured such that an electric current applied to the track is operative to shift data stored within at least one of the plurality of magnetic domains of the storage region, along the track, in a direction of the electric current. The data stored within the at least one of the plurality of magnetic domains is shifted as a function of the direction of the electric current.
Owner:IBM CORP
Quota control temperature based racetrack memory chip and control method therefor
ActiveCN105426316AMemory architecture accessing/allocationReducing temperature influence on carrierDiffusionComputer science
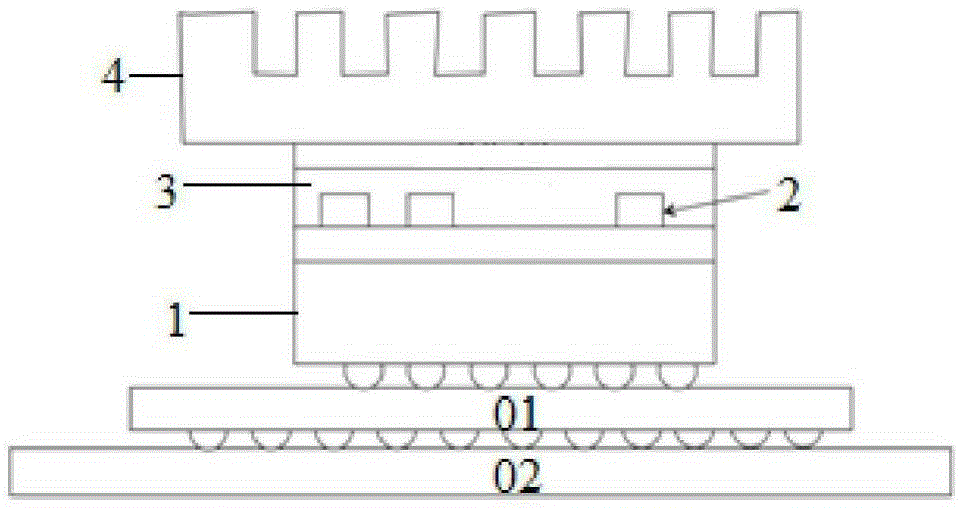
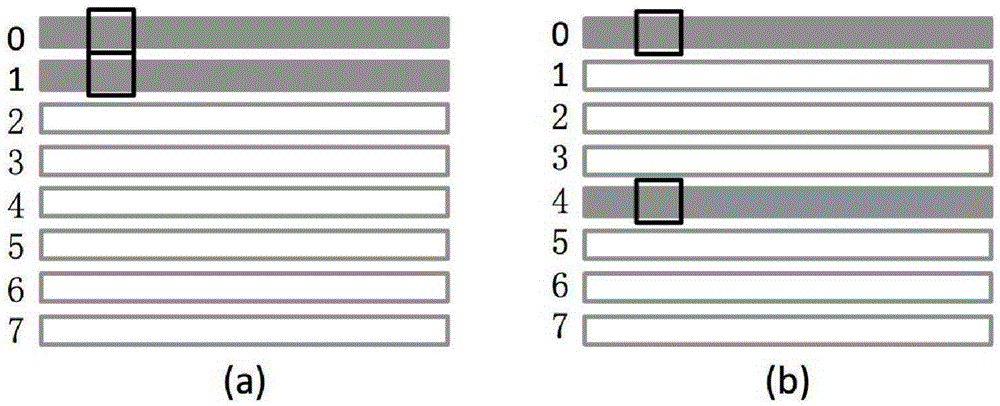
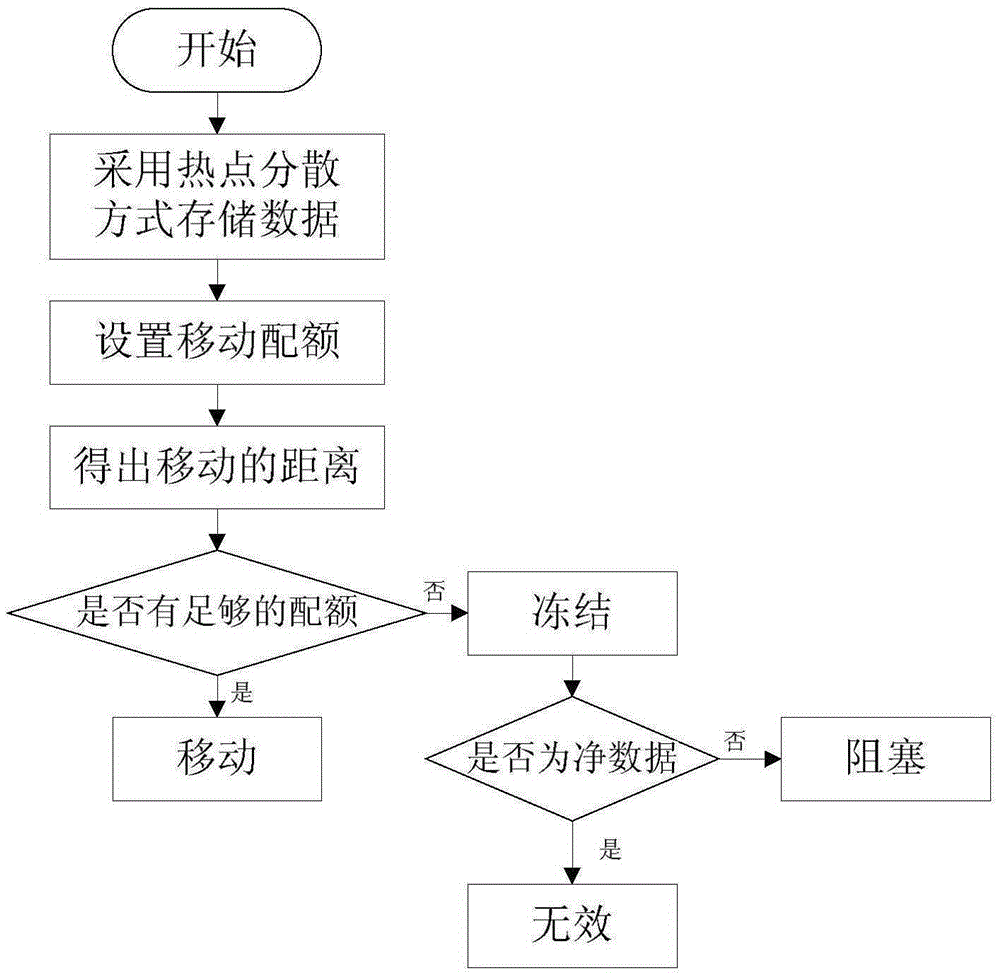
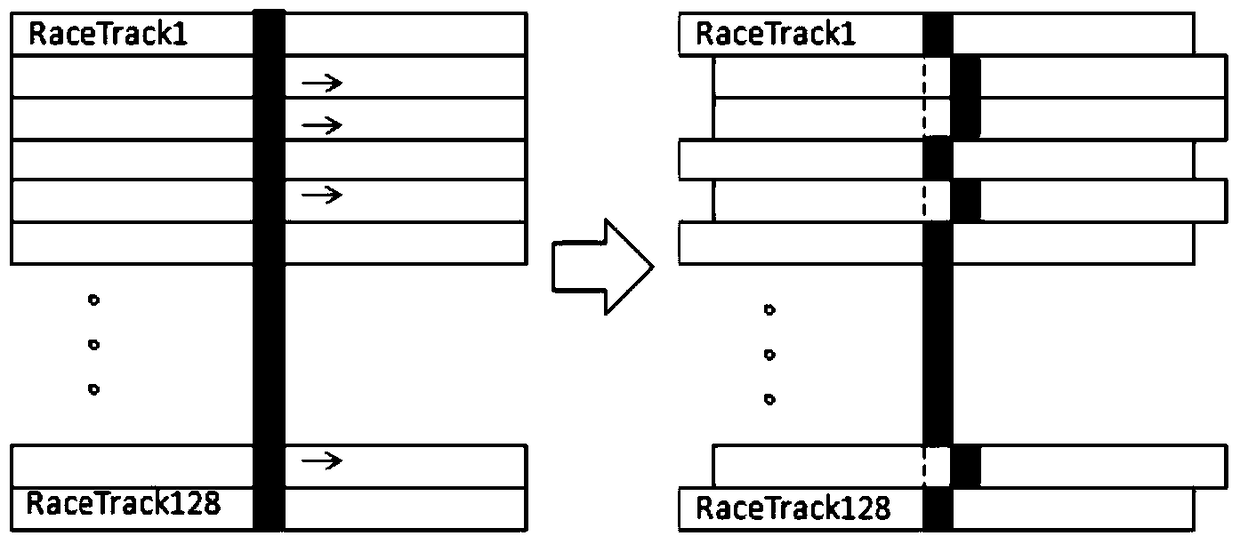
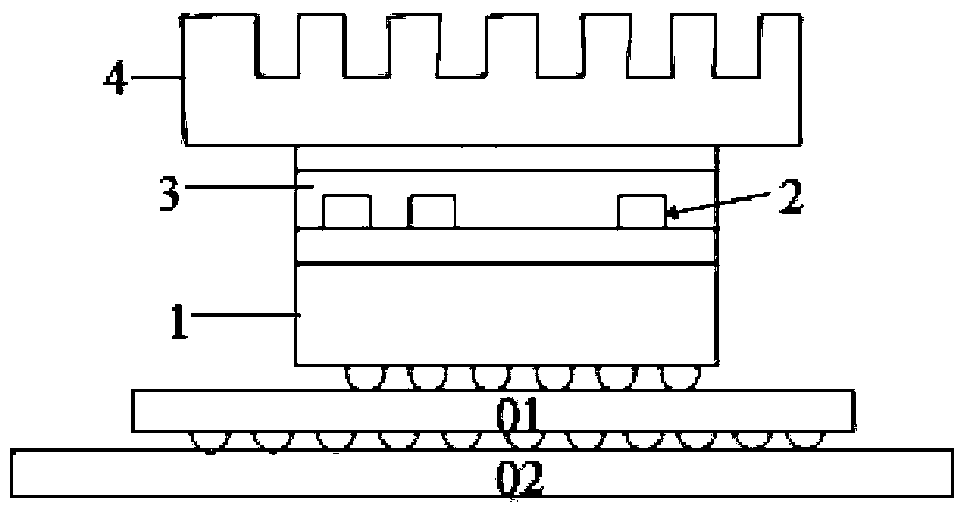
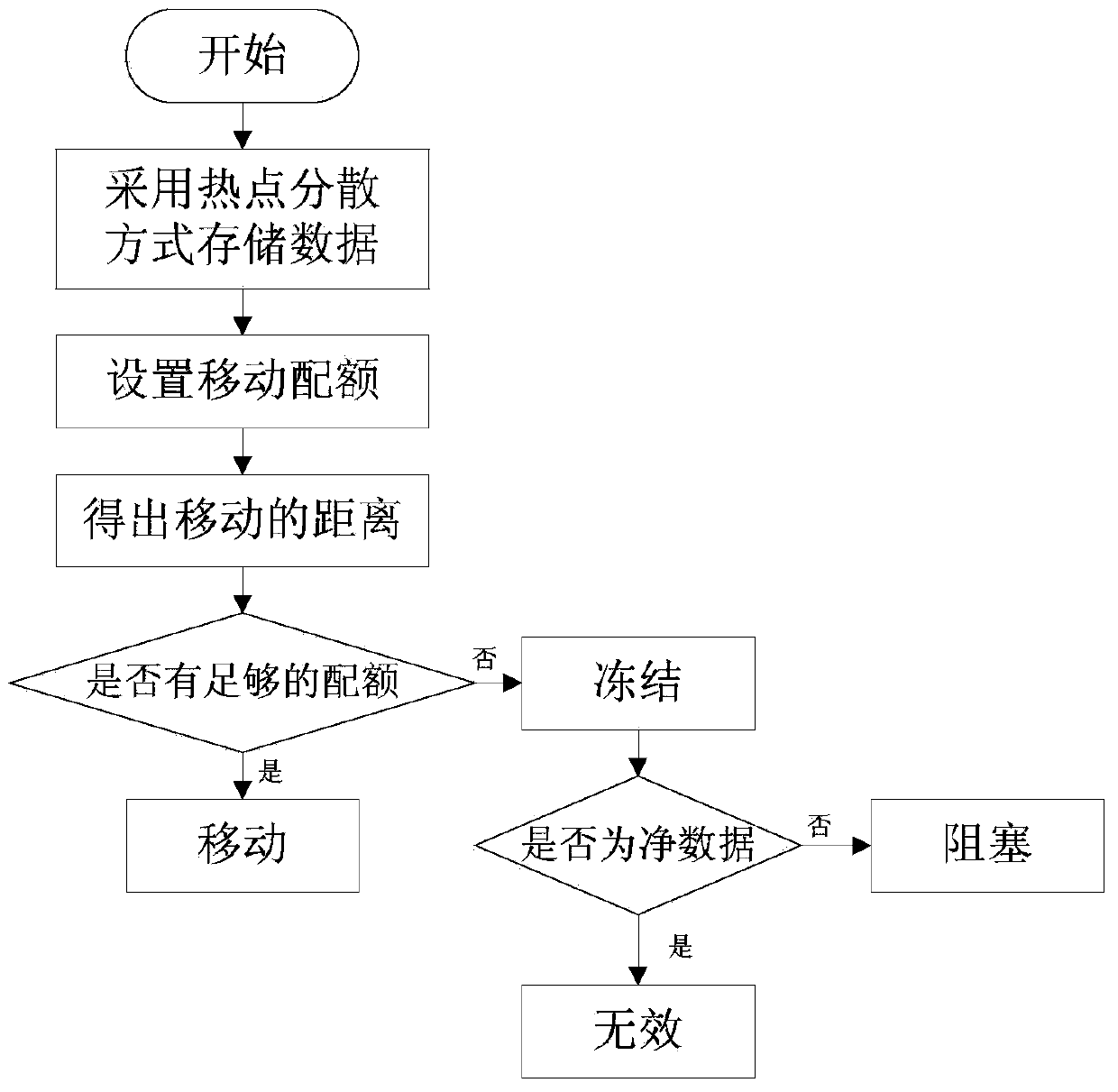
The invention discloses a quota control temperature based racetrack memory chip and a control method therefor. The racetrack memory chip comprises a substrate, racetrack memory strips, a filling layer and a heat dissipation apparatus. A mobile quota is set in a program running interval, so that hot spot dispersion is performed in time; and moreover, a data block is stored in the non-adjacent racetrack memory strips, so that hot spot dispersion is performed in space. The invention provides a control method for a temperature rise of a racetrack memory due to mobile operation. The method comprehensively considers hot spot diffusion in time and space, so that the temperature rise of the chip can be reduced as far as possible; and due to analog display, the performance loss caused by the method is only 5% averagely.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
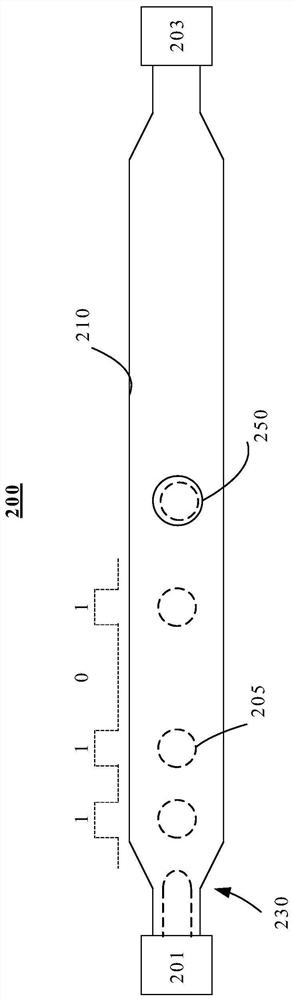
Embedded system on-line program refreshing method
InactiveCN104750531ANo need to increase production costsReduce the cost of after-sales serviceProgram loading/initiatingMemory addressApplication software
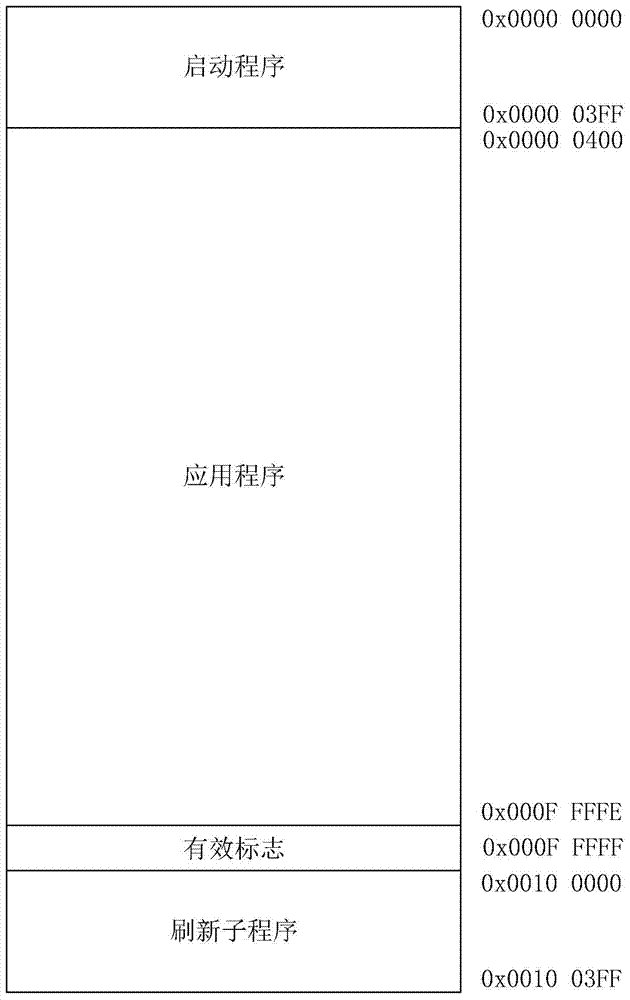
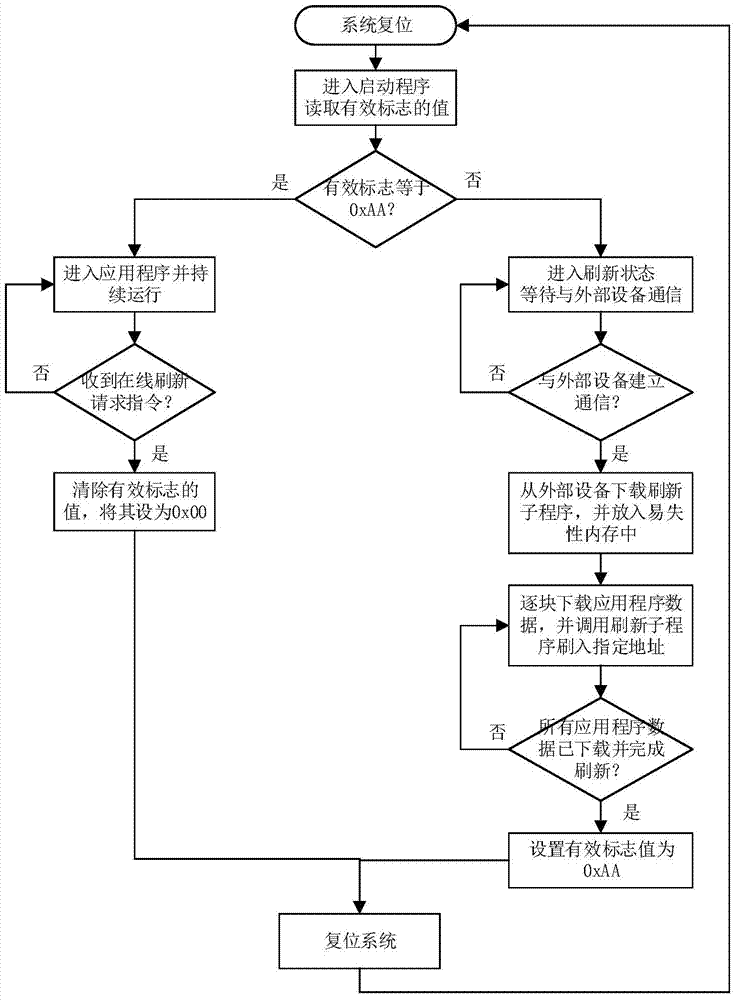
The invention discloses an embedded system on-line program refreshing method. The method includes the steps: placing a starting program, an application program and effective markers into a racetrack memory of an embedded system; firstly executing the starting program after the embedded system resets, reading values of the effective markers by the starting program, judging whether a current application program is effective or not, entering and continuously running the application program if the application program is effective, entering a refreshing state and establishing communication with an external device if not, and downloading refreshing subprograms from the external device; storing the downloaded refreshing subprograms into the racetrack memory, downloading application programs needing to be refreshed from the external device after the subprograms are downloaded, circularly calling and refreshing the subprograms, and flushing data of each downloaded application program needing to be refreshed into a designated address of the racetrack memory. By the method, software of the embedded system can be updated in an online refreshing manner, a software program is improved, and excessive product cost increase is avoided.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
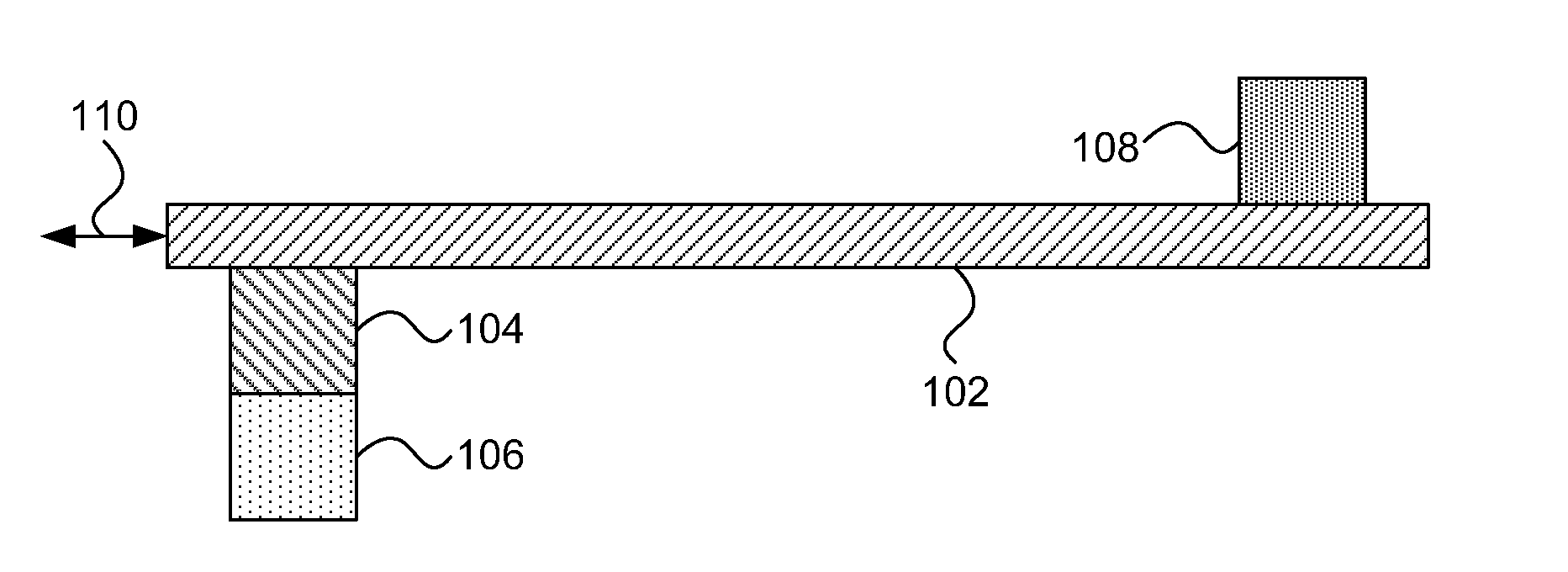
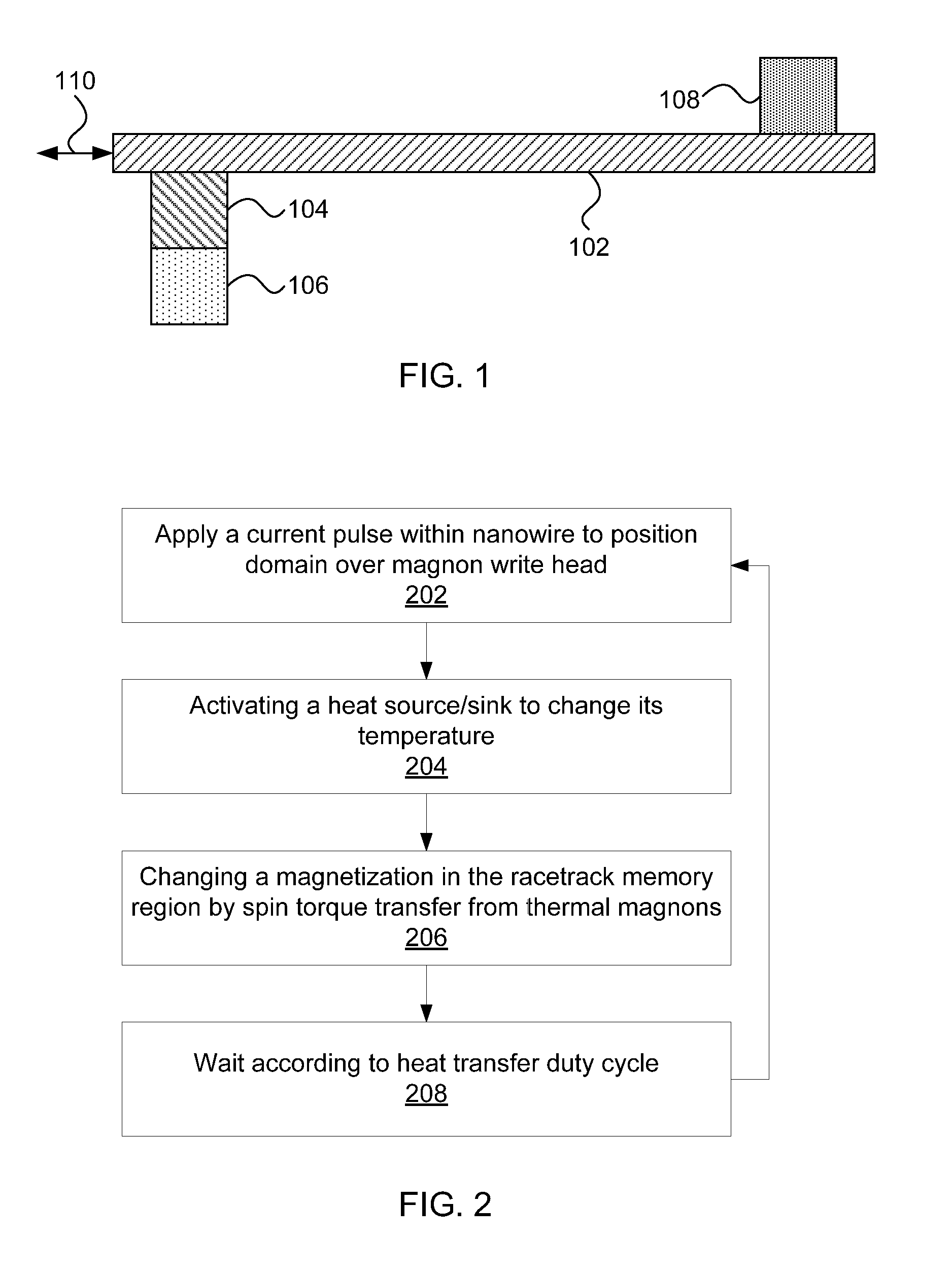
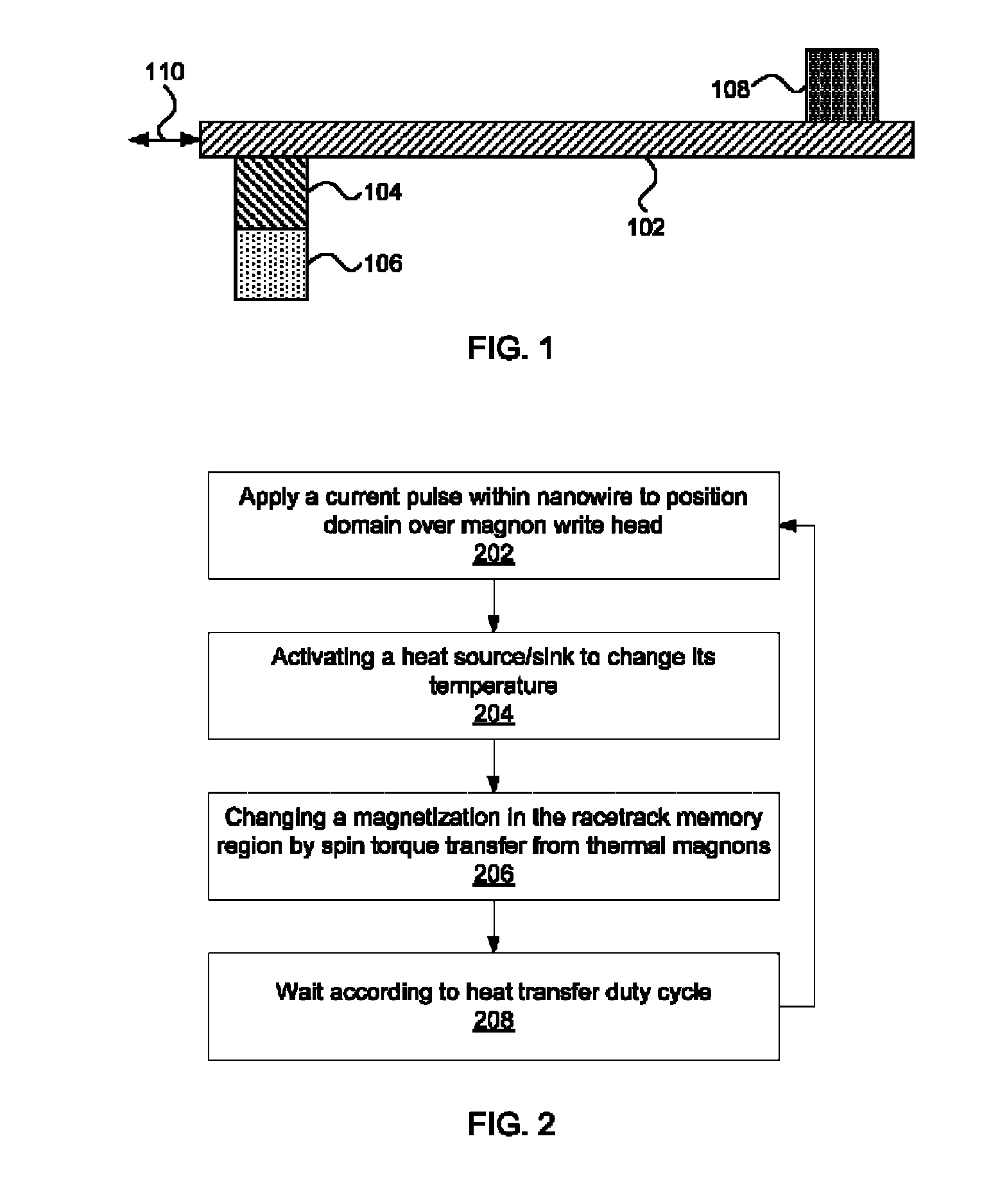
Racetrack memory with low-power write
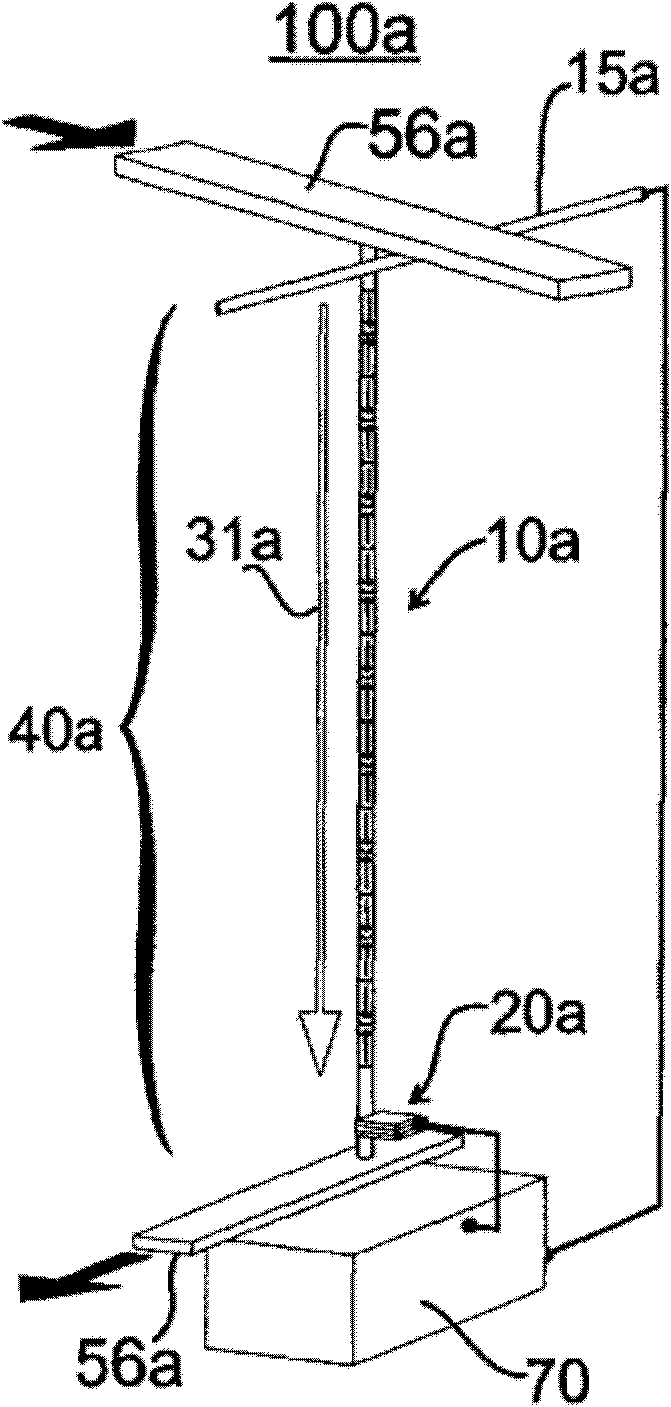
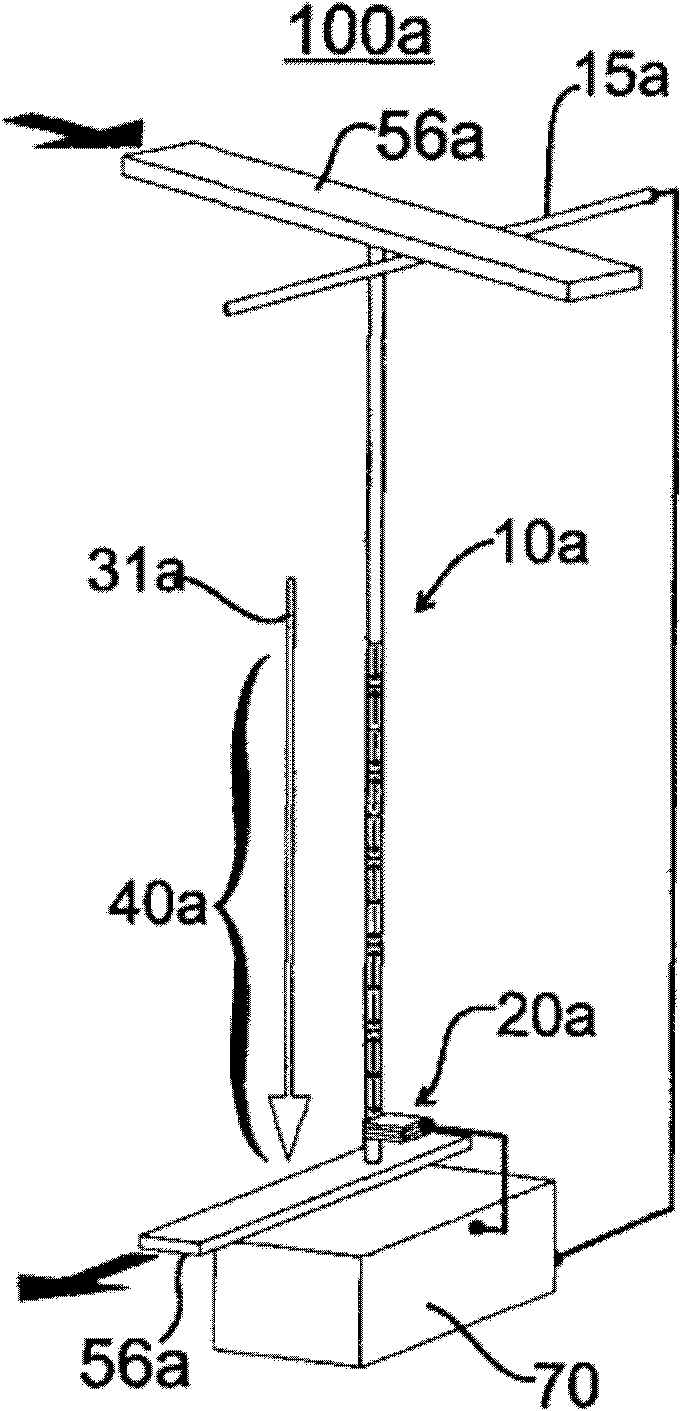
Racetrack memory units and methods for writing include a racetrack memory medium; a heat source / sink configured to change temperature according to an applied current; and a magnon source material in contact with the racetrack memory medium and the heat source / sink, such that a temperature of the heat source / sink causes a magnon flow in the magnon source material that injects a domain wall in the racetrack memory medium.
Owner:IBM CORP
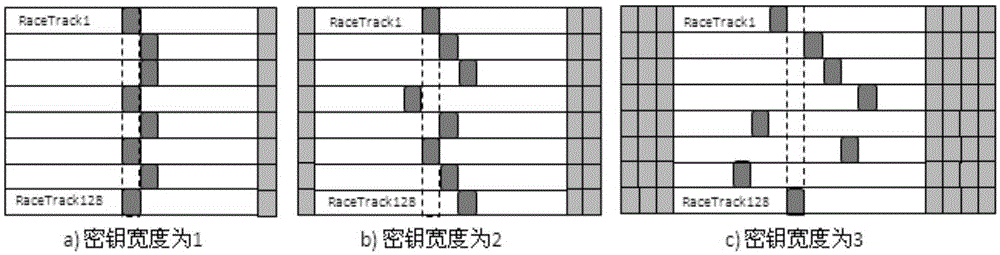
Data encryption/decryption method and system based on racetrack memory
ActiveCN105426786AImprove protectionEnsure safetyDigital data protectionDigital storageElectricityStatic random-access memory
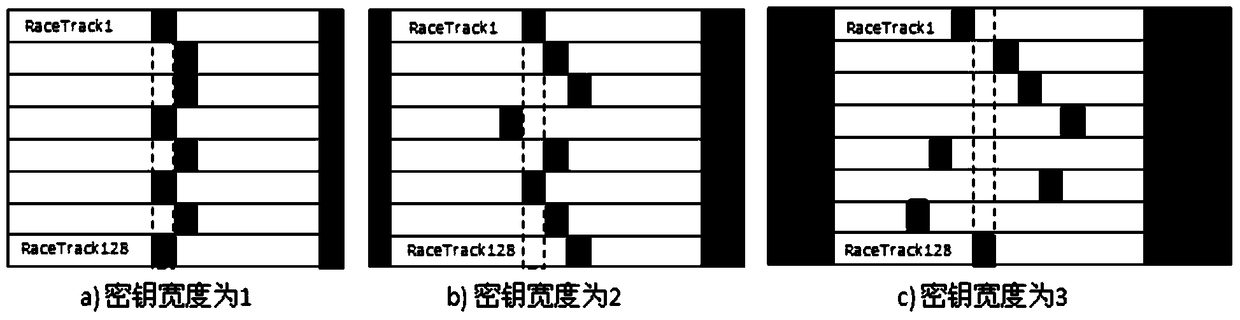
The invention discloses a data encryption / decryption method based on a racetrack memory, comprising the following steps: dividing a racetrack memory array into a plurality of encryption areas with preset size as basic units of encryption storage, and setting an independent encryption key Shift-key for each encryption area; when a system is initialized, generating a Shift-key based on a random number for each storage area as an encryption key of the storage area, and storing the Shift-keys in a volatile static random access memory; after the keys are generated, performing shift encryption on each storage area according to the key; and when data is read or written, performing encryption / decryption on each storage area according to the key. The data encryption / decryption method can better protect data in the racetrack memory, ensure the security of data and avoid potential safety hazards caused by power failure or physical power stealing of the system. The invention further discloses a data encryption / decryption system based on a racetrack memory.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Racetrack memory with electric-field assisted domain wall injection for low-power write operation
Embodiments are directed to injecting domain walls in a magnetic racetrack memory. In some embodiments, a racetrack comprising a nanowire is coupled with a gate in order to manipulate an anisotropy associated with the nanowire. The racetrack and gate is coupled with a pinning layer configured to establish a magnetization direction in the nanowire.
Owner:IBM CORP
racetrack memory device
ActiveCN102282624ASimple designSimplify the manufacturing processNanotechDigital storageCMOSComputer architecture
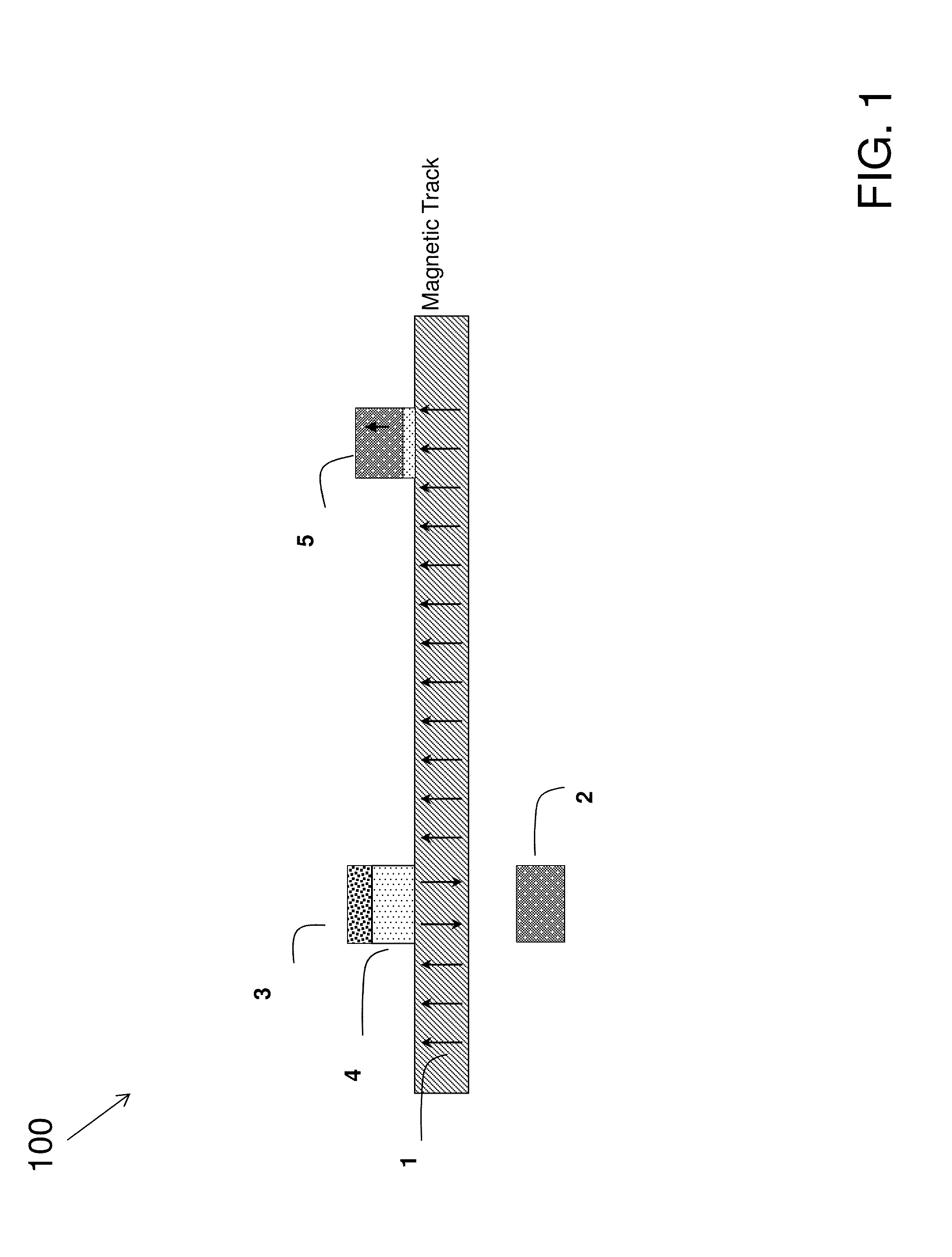
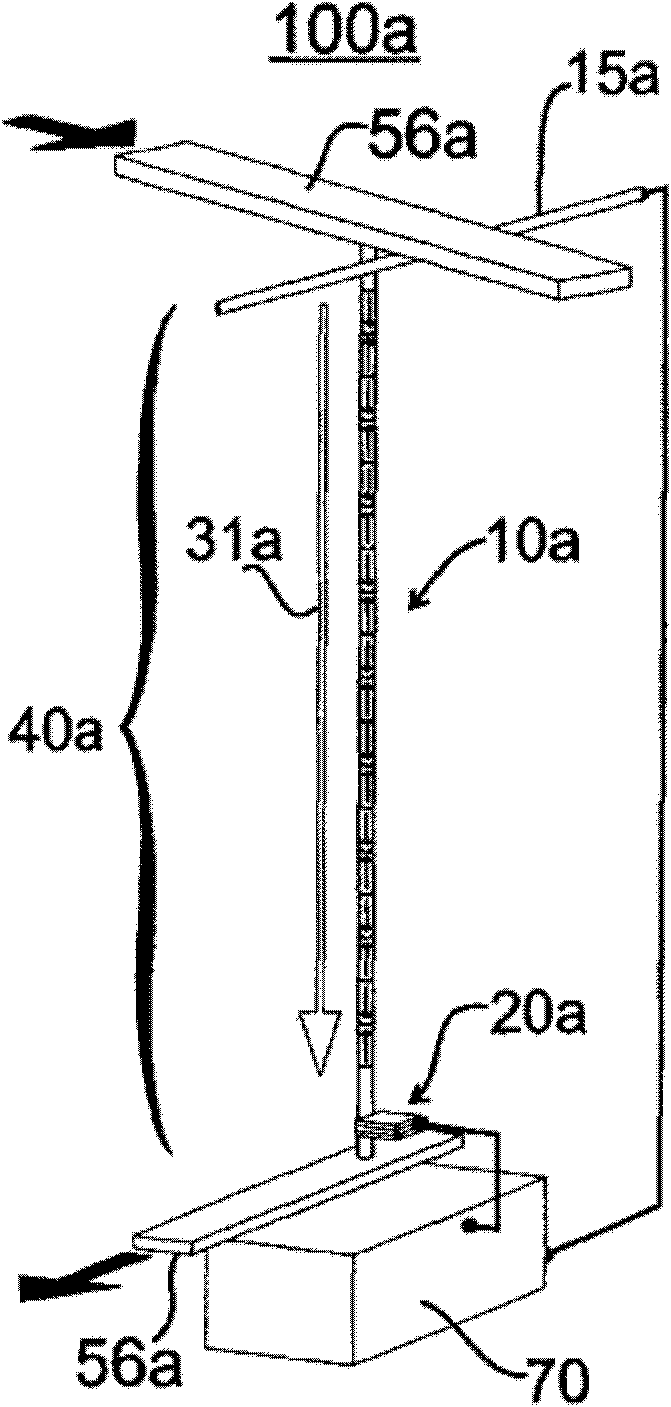
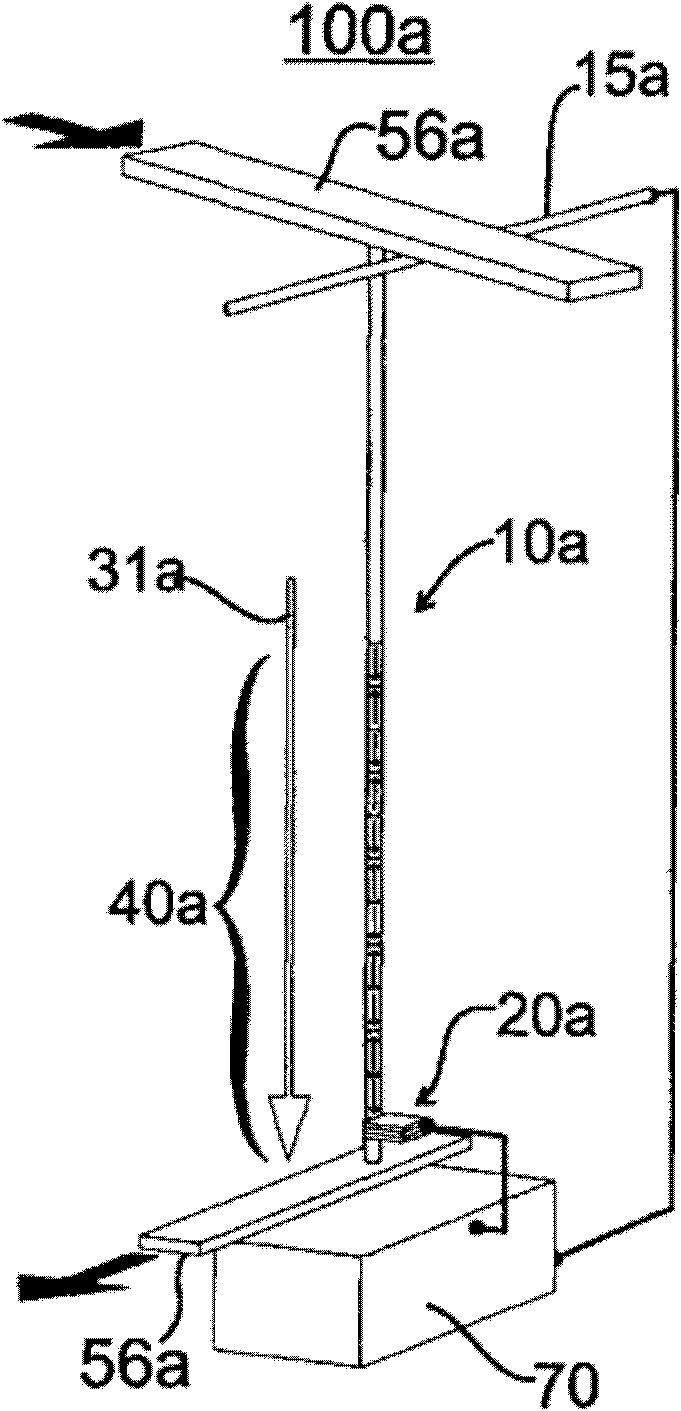
A racetrack memory storage device moves domain walls along the racetrack in one direction only. The reading element can be positioned at one end of the racetrack (rather than in the middle of the racetrack). The domain walls are annihilated upon moving them across the reading element but their corresponding information is read into one or more memory devices (e.g., built-in CMOS circuits). The information can then be processed in circuits for computational needs and written back into the racetrack either in its original form (as it was read out of the racetrack) or in a different form after some computation, using a writing element positioned at the end of the racetrack opposite to the reading element. Such a racetrack can be built more simply and has greater reliability of operation than previous racetrack memory devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Racetrack memory with low-power write
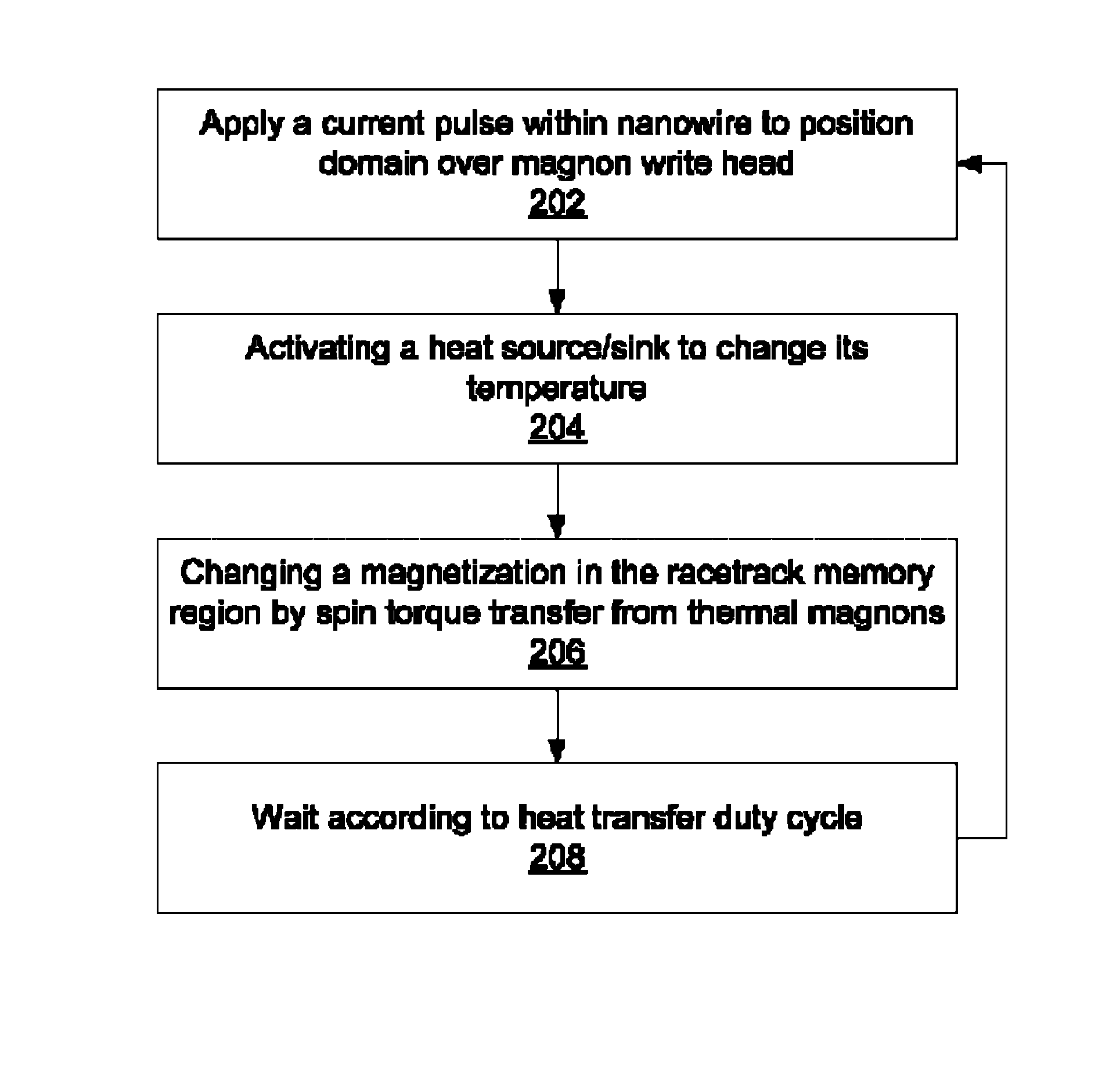
Methods for writing include applying a current pulse to a racetrack memory medium to position a domain in proximity to a thermally triggered magnon source in contact with the racetrack memory medium; activating a heat source / sink in contact with the magnon source to create a thermal gradient in the magnon source, generating a magnon flow in the magnon source; and changing a magnetization in the racetrack memory medium by spin torque transfer from the magnon flow.
Owner:IBM CORP
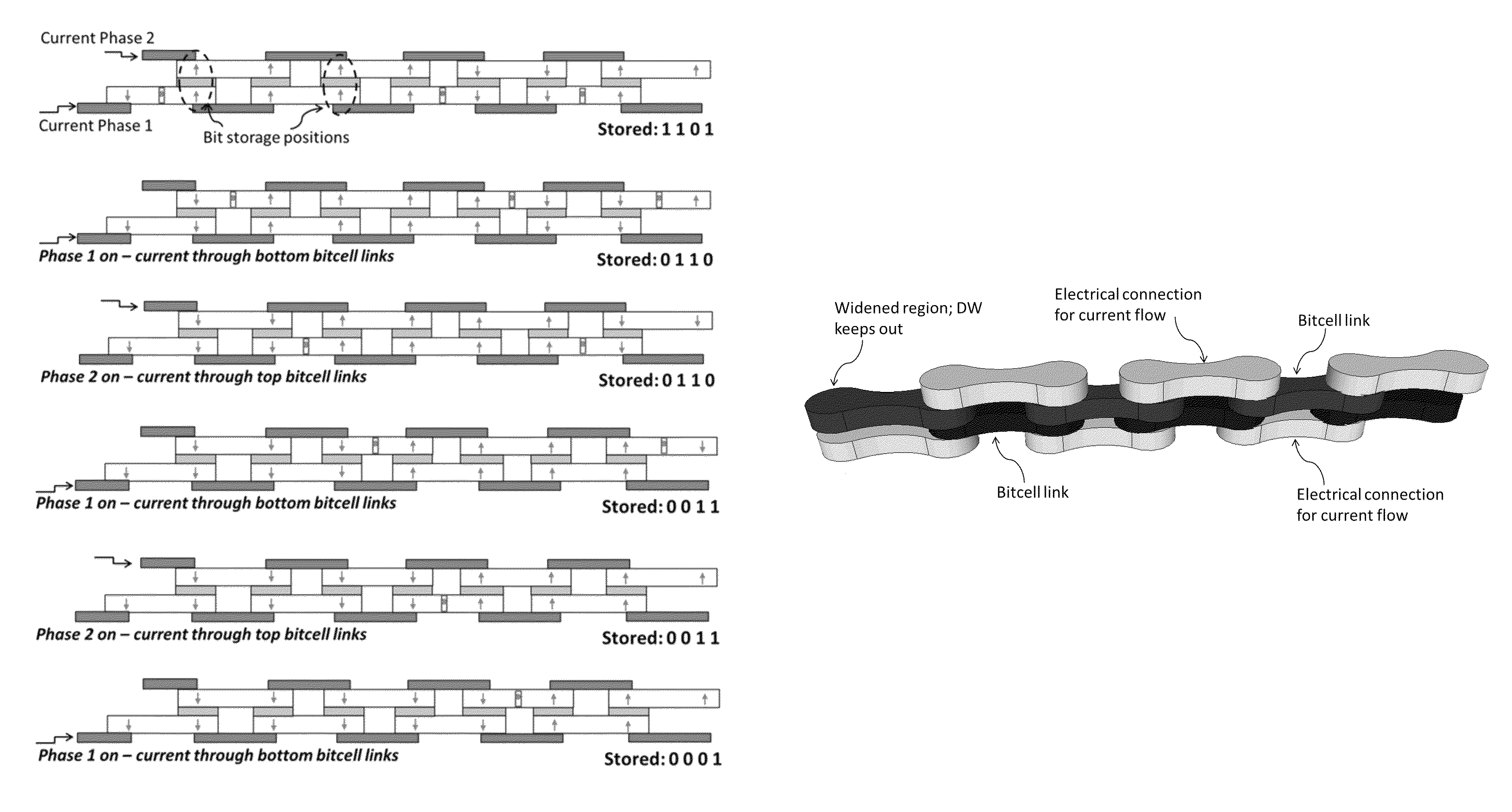
Chainlink memory
A nonvolatile alternative to DRAM or Flash is disclosed. It involves a new “magnetic shift register” that avoids the bit annihilation problem that plagues magnetic racetrack memories. Using this new “chainlink memory” approach, one avoids the annihilation problem inherent in racetrack memory by breaking up the racetrack into magnetically coupled links, where each link preferably handles one bit exclusively. Depending upon the implementation, the “bit” can be, for example, the magnetization of a link, presence or absence of a domain wall, or the polarity of a domain wall. Numerous examples and applications of this new chainlink technology are disclosed.
Owner:IRON CITY INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Racetrack memory with electric-field assisted domain wall injection for low-power write operation
Embodiments are directed to injecting domain walls in a magnetic racetrack memory. In some embodiments, a racetrack comprising a nanowire is coupled with a gate in order to manipulate an anisotropy associated with the nanowire. The racetrack and gate is coupled with a pinning layer configured to establish a magnetization direction in the nanowire.
Owner:IBM CORP
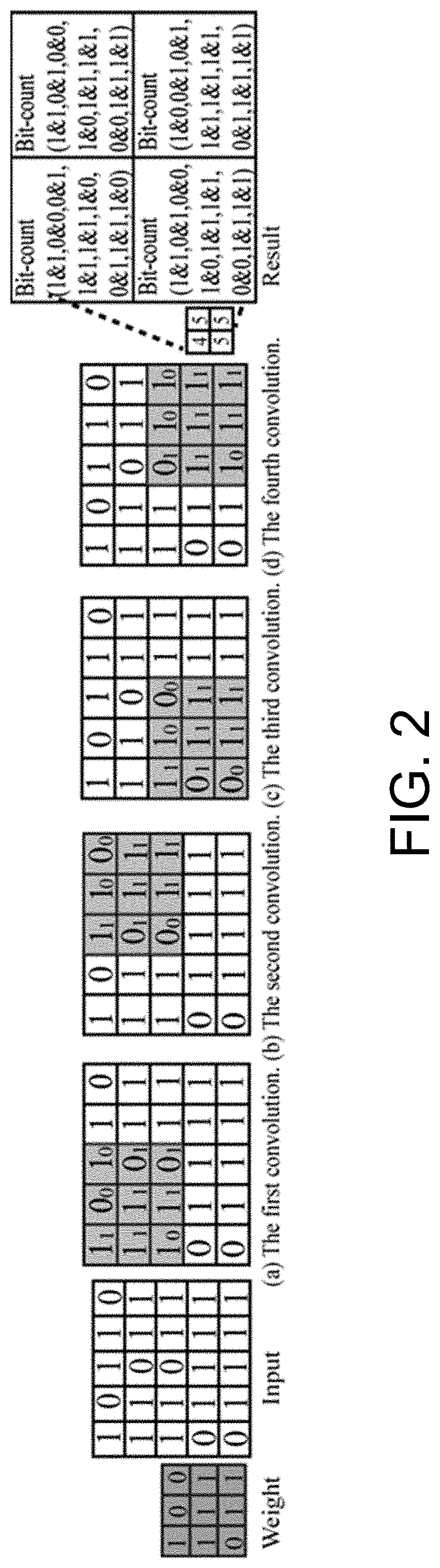
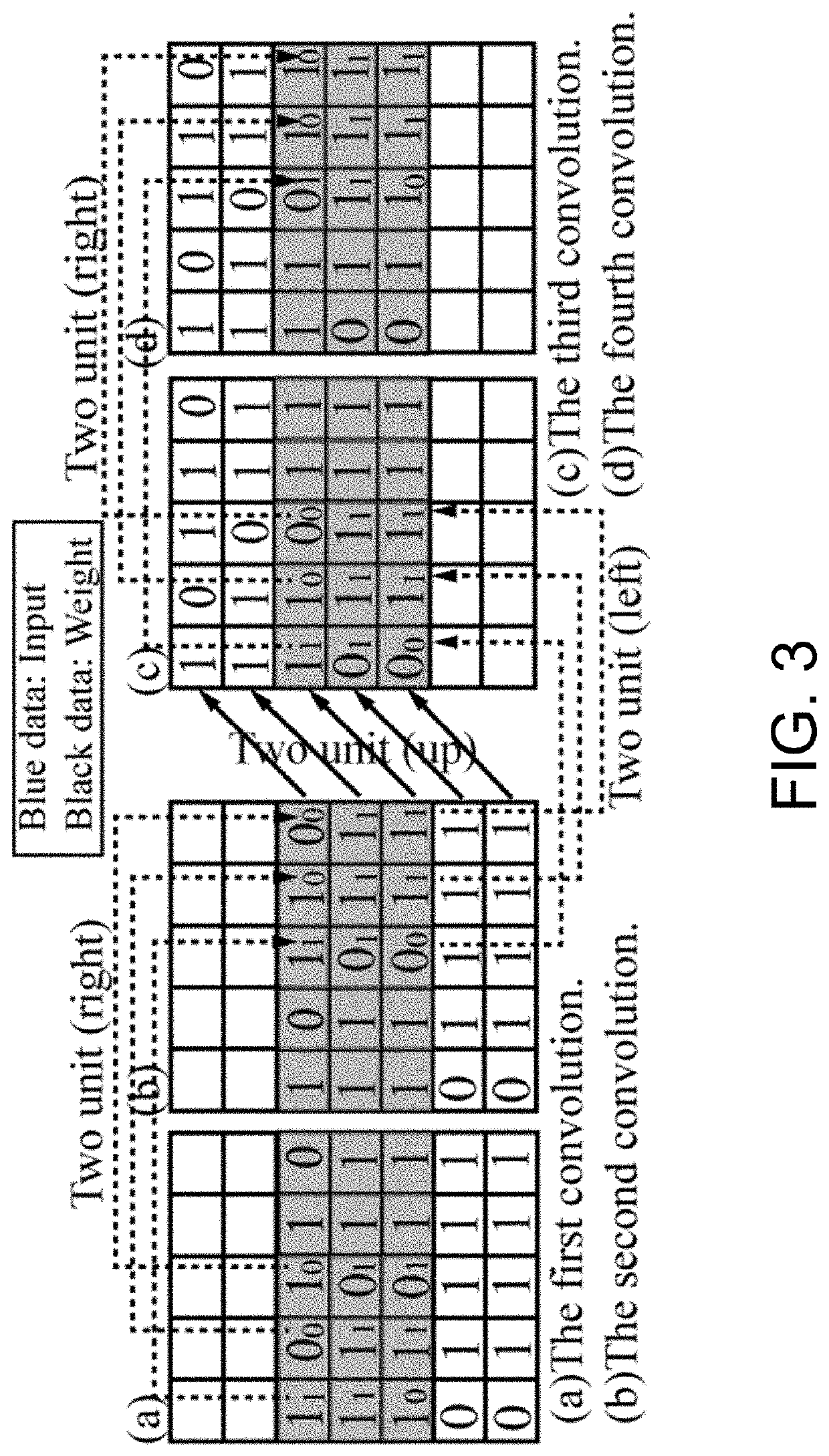
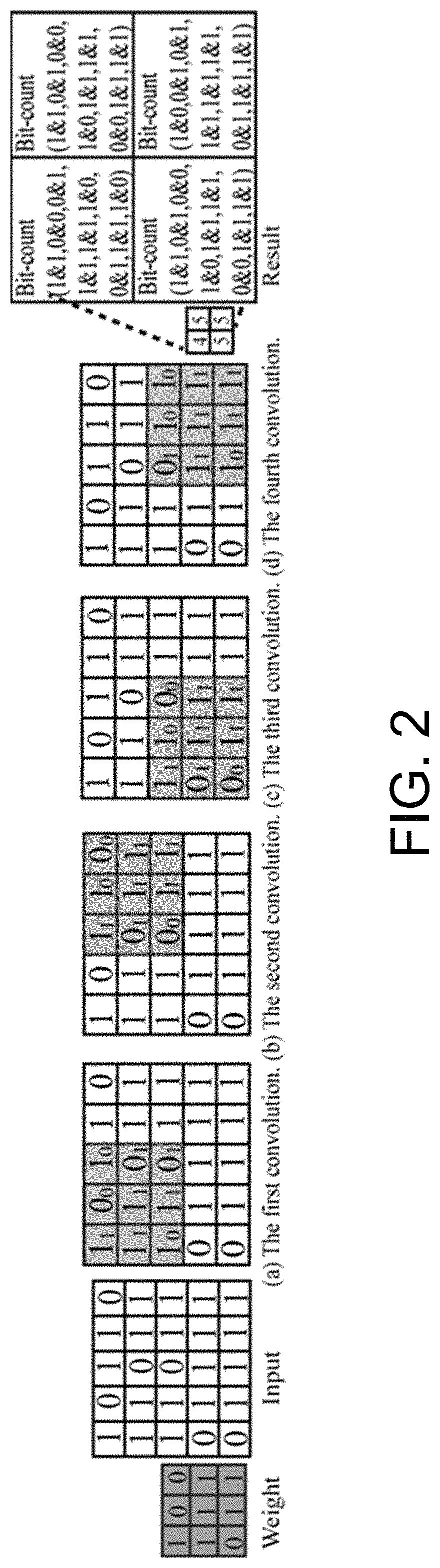
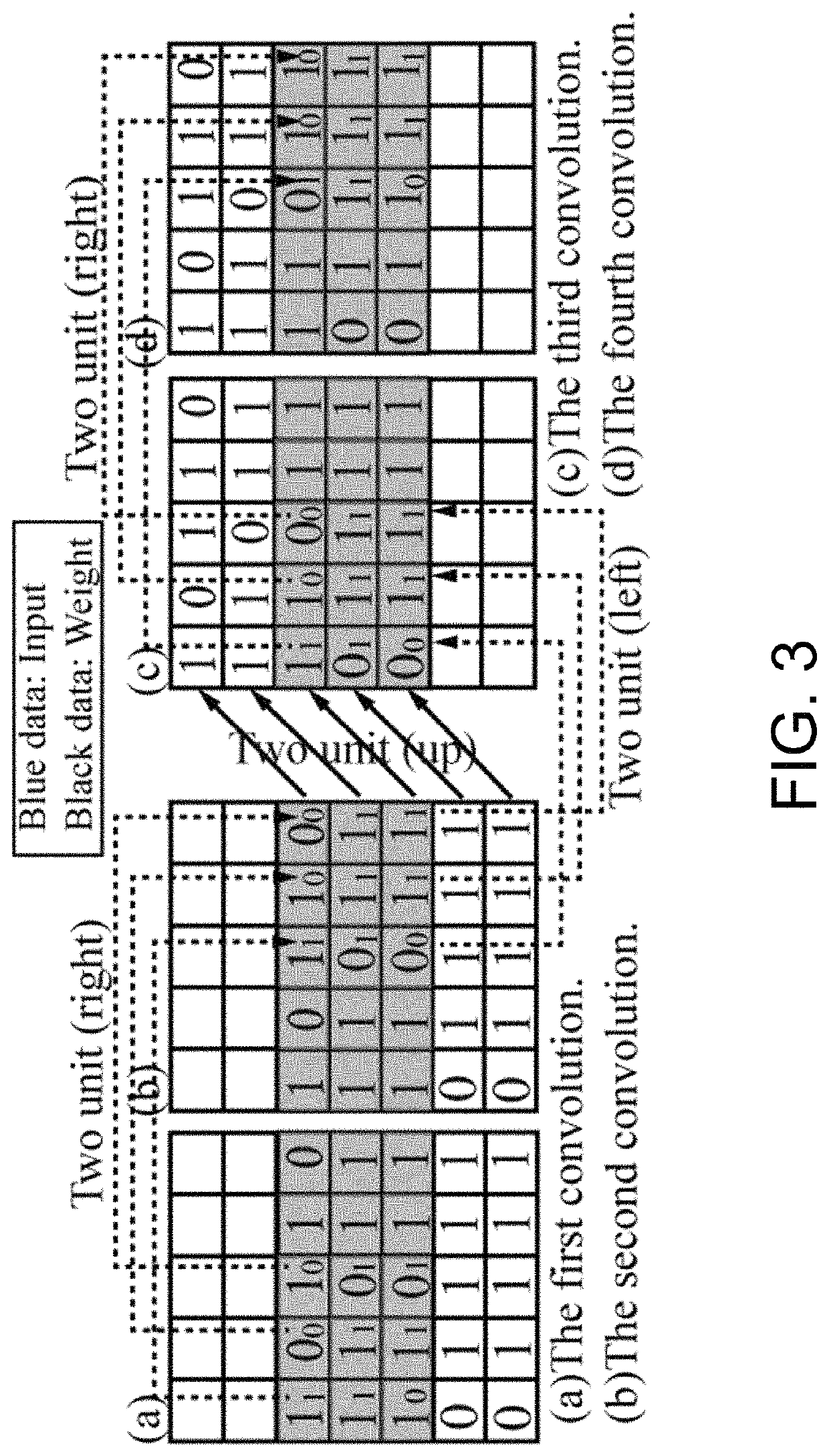
Computing in-memory system and method based on skyrmion racetrack memory
ActiveUS20210019596A1Reduce memory accessLighten the computational burdenDigital storageNeural architecturesComputer architectureMode control
A computing in-memory system and computing in-memory method based on a skyrmion race memory are provided. The system comprises a circuit architecture of SRM-CIM. The circuit architecture of the SRM-CIM comprises a row decoder, a column decoder, a voltage-driven, a storage array, a modified sensor circuit, a counter Bit-counter and a mode controller. The voltage-driven includes two NMOSs, and the two NMOSs are respectively connected with a selector MUX. The modified sensor circuit compares the resistance between a first node to a second node and a third node to a fourth node by using a pre-charge sense amplifier. The storage array is composed of the skyrmion racetrack memories. The computing in-memory architecture is designed by utilizing the skyrmion racetrack memory, so that storage is realized in the memory, and computing operation can be carried out in the memory.
Owner:HEFEI INNOVATION RES INST BEIHANG UNIV +1
A track memory based on magnetic skyrmions
ActiveCN108492845BImprove stabilityHigh information storage densityDigital storageMagnetic skyrmionAntiferromagnetic coupling
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
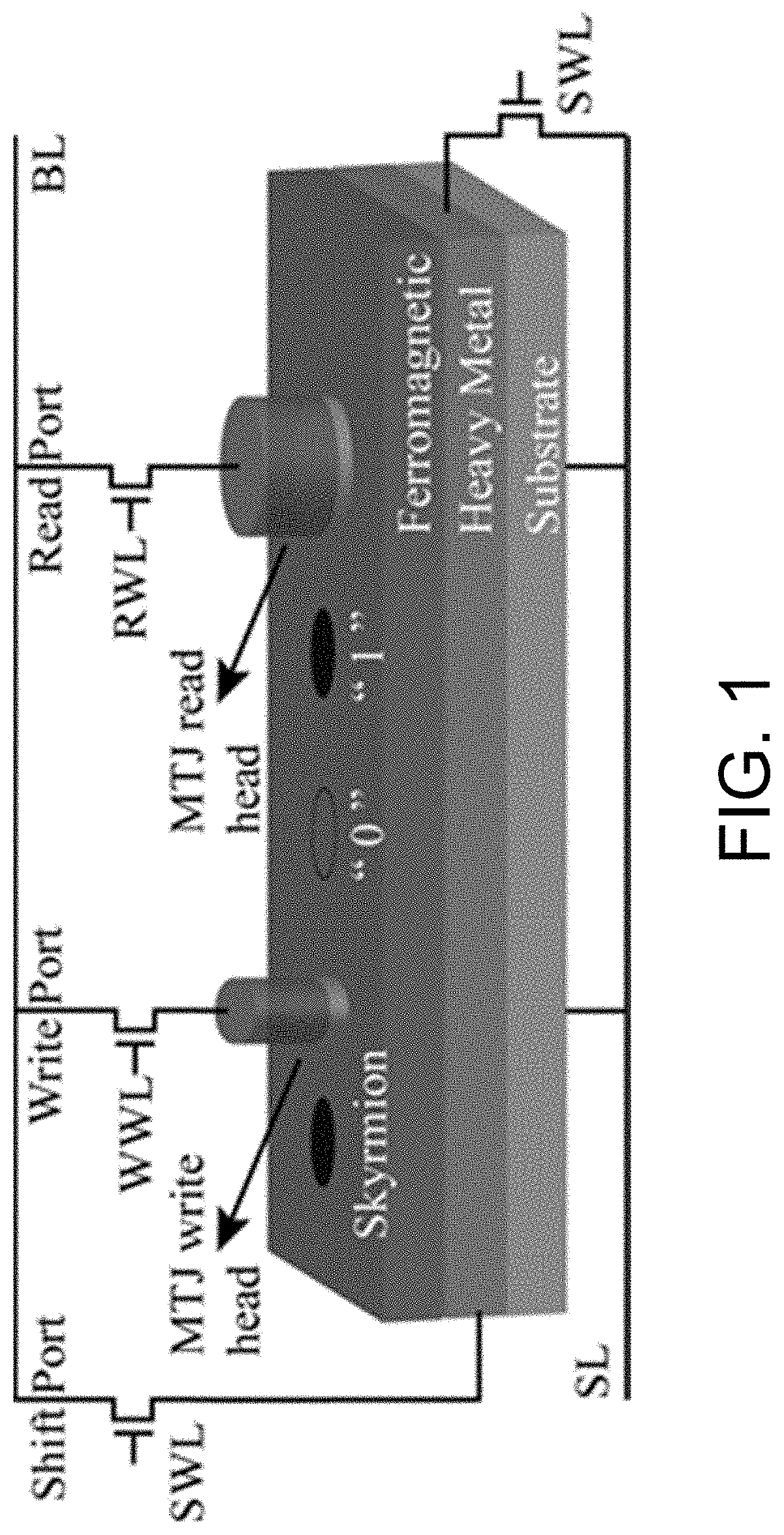
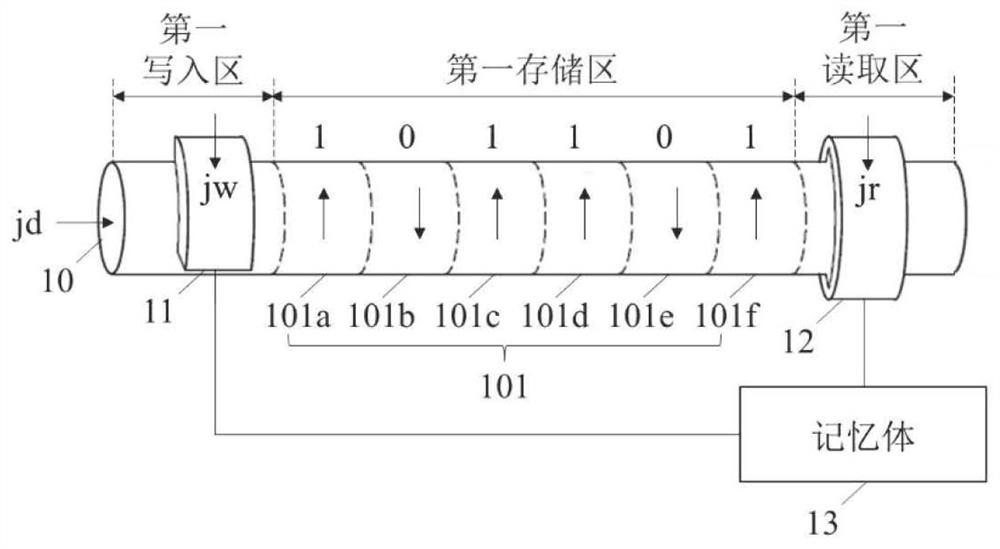
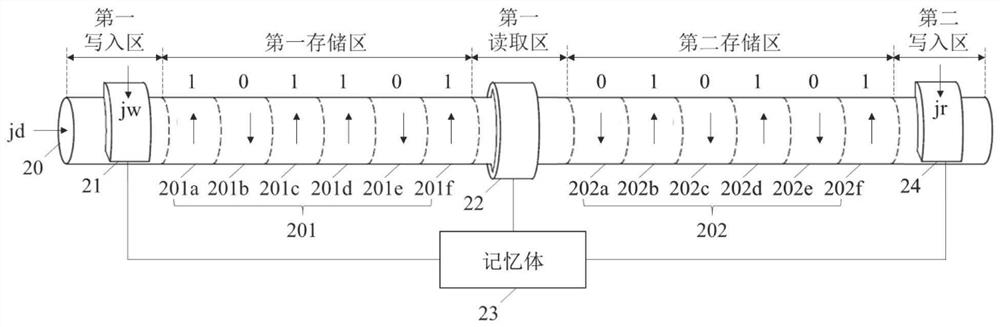
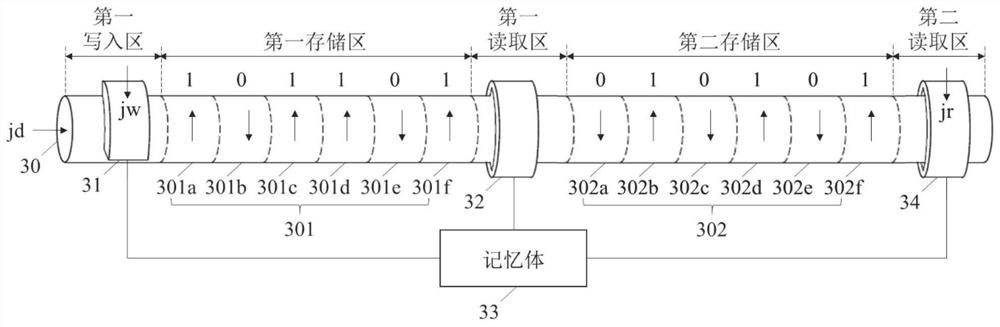
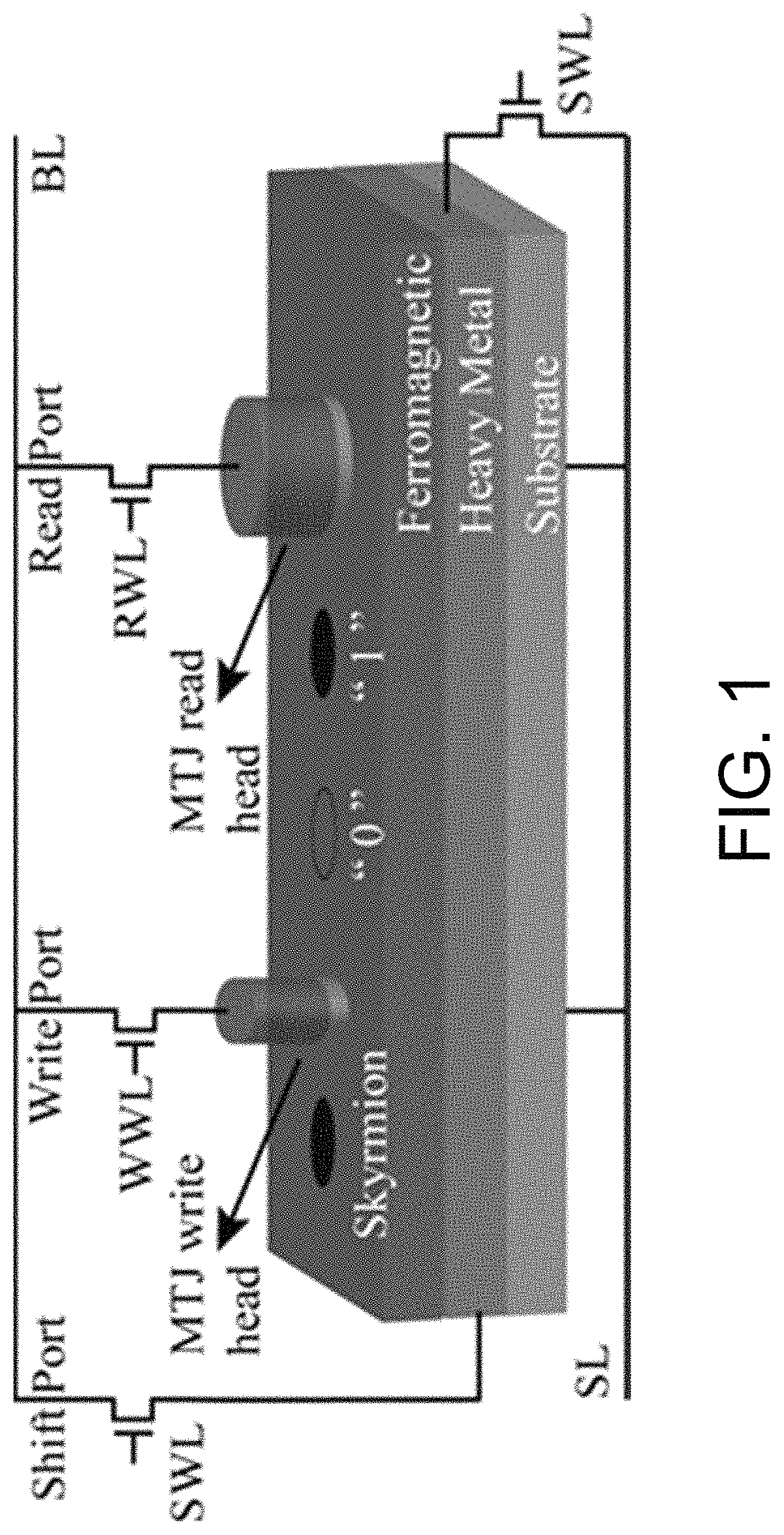
Racing track memory, reading and writing method thereof and racing track memory device
A racetrack memory includes a magnetic nanotube, a first write magnetic tunnel junction, a first read magnetic tunnel junction, and a memory connected to the first write magnetic tunnel junction and the first read magnetic tunnel junction for temporarily storing storage data obtained through the first read magnetic tunnel junction, and the first write-in magnetic tunnel junction is used for writing the second write-in magnetic tunnel junction into the plurality of first storage units again in the form of skyrmion. By introducing the memory, the stored data can be reset, and the storage densityof the magnetic nanotubes is further improved.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
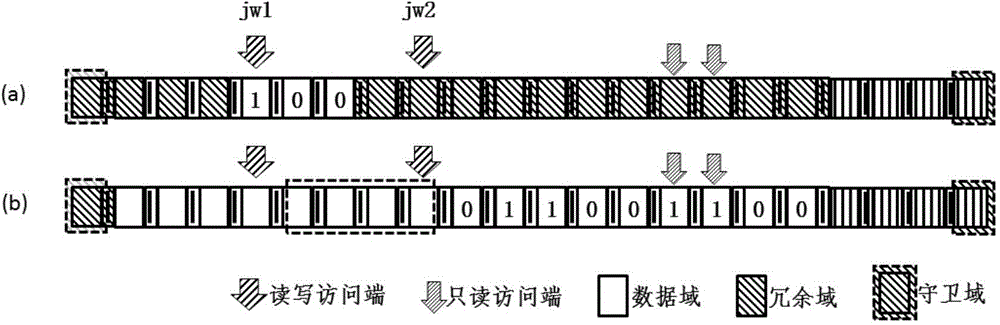
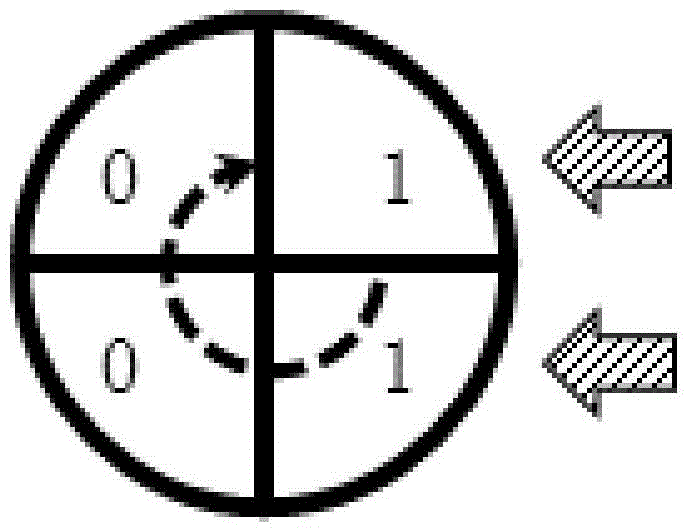
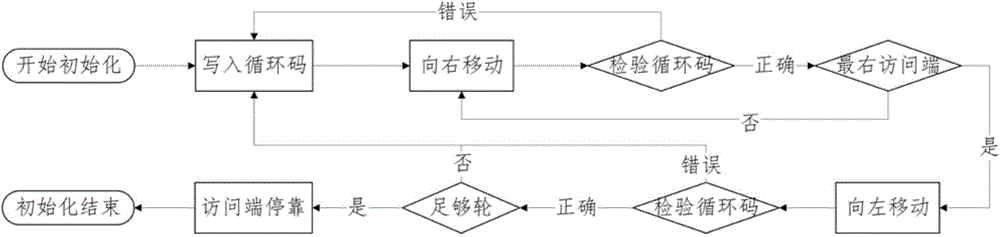
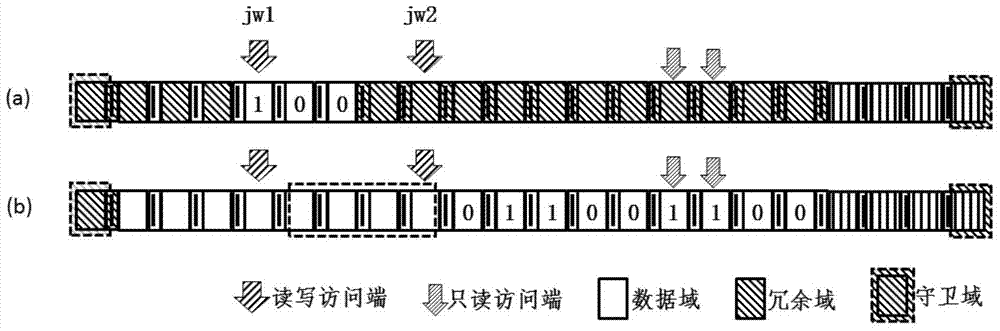
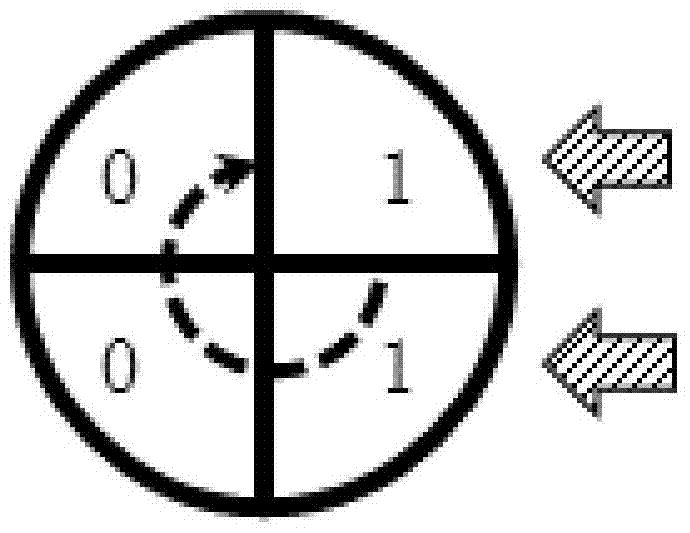
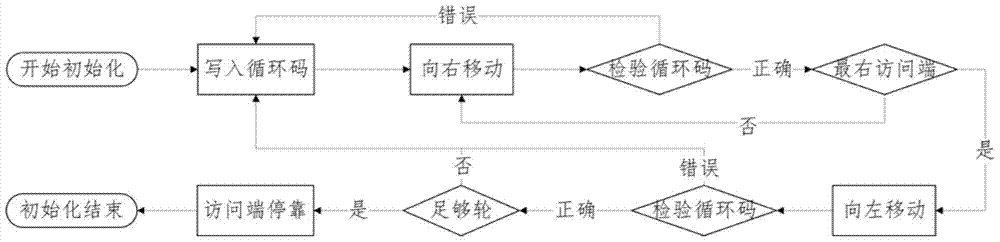
Coding method of racetrack storage position error correcting code and error correcting method
The invention discloses a coding method of a racetrack storage position error correcting code and an error correcting method. The coding method of the correcting code comprises the steps of coding positions of one or more read-only access ends of a racetrack memory stripe (RS) relative to the RS as circulating codes, storing the circulating codes into the RS, enabling the position of the RS to correspond to partial circulating codes read from the RS at the moment, obtaining a position code by virtue of the circulating codes, and utilizing the position code as an error correcting code of the racetrack storage position. The circulating code is set as a continuous sequence of a plurality of circulating units, and the bit number of each circulating unit is one or more bits. According to the error correcting method, the error-type position error can be detected and corrected by comparing the position code stored in the access end position of a register and a position code obtained by decoding the circulating codes stored in the racetrack storage stripe, so that the problem of the error of the error-type position can be effectively solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Data encryption and decryption method and system based on track memory
ActiveCN105426786BImprove protectionEnsure safetyDigital data protectionDigital storageElectricityStatic random-access memory
The invention discloses a data encryption / decryption method based on a racetrack memory, comprising the following steps: dividing a racetrack memory array into a plurality of encryption areas with preset size as basic units of encryption storage, and setting an independent encryption key Shift-key for each encryption area; when a system is initialized, generating a Shift-key based on a random number for each storage area as an encryption key of the storage area, and storing the Shift-keys in a volatile static random access memory; after the keys are generated, performing shift encryption on each storage area according to the key; and when data is read or written, performing encryption / decryption on each storage area according to the key. The data encryption / decryption method can better protect data in the racetrack memory, ensure the security of data and avoid potential safety hazards caused by power failure or physical power stealing of the system. The invention further discloses a data encryption / decryption system based on a racetrack memory.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A racetrack memory chip with temperature control based on quota and its control method
ActiveCN105426316BReducing temperature influence on carrierMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory chipDiffusion
The invention discloses a quota control temperature based racetrack memory chip and a control method therefor. The racetrack memory chip comprises a substrate, racetrack memory strips, a filling layer and a heat dissipation apparatus. A mobile quota is set in a program running interval, so that hot spot dispersion is performed in time; and moreover, a data block is stored in the non-adjacent racetrack memory strips, so that hot spot dispersion is performed in space. The invention provides a control method for a temperature rise of a racetrack memory due to mobile operation. The method comprehensively considers hot spot diffusion in time and space, so that the temperature rise of the chip can be reduced as far as possible; and due to analog display, the performance loss caused by the method is only 5% averagely.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Computing in-memory system and method based on skyrmion racetrack memory
ActiveUS11151439B2Reduce memory accessLighten the computational burdenDigital storageNeural architecturesComputer architectureMode control
Owner:HEFEI INNOVATION RES INST BEIHANG UNIV +1
Data programming method, memory control circuit unit and memory storage device
The invention provides a data programming method, a memory control circuit unit and a memory storage device. The method comprises the steps of setting a first class entity erasing unit as a current writing-in region and recording the current writing-in data size. The method further comprises the step of calculating a data size threshold value according to the first class entity erasing unit. The method further comprises the step of receiving data. The method further comprises the steps of adopting a first programming mode for programming the data to at least one first class entity erasing unit if the current writing-in data size is smaller than the data size threshold value; setting a second class entity erasing unit as a current writing-in region if the current writing-in data size is not smaller than the data size threshold value, and adopting a second programming mode for programming the data into at least one second class entity erasing unit. The problem that a rewritable type racetrack memory module cannot be used due to the fact that the erasing frequency of some entity erasing units is excessively large can be avoided.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
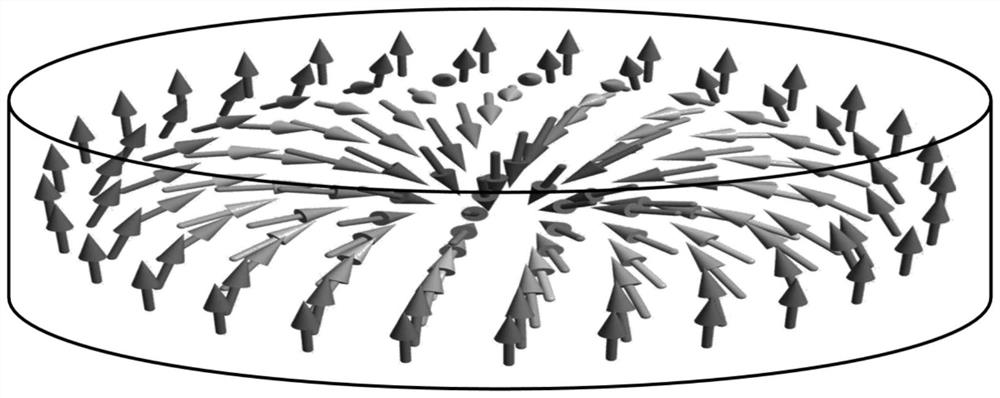
Topological magnetic structure, writing method of magnetic skyrmion and memory
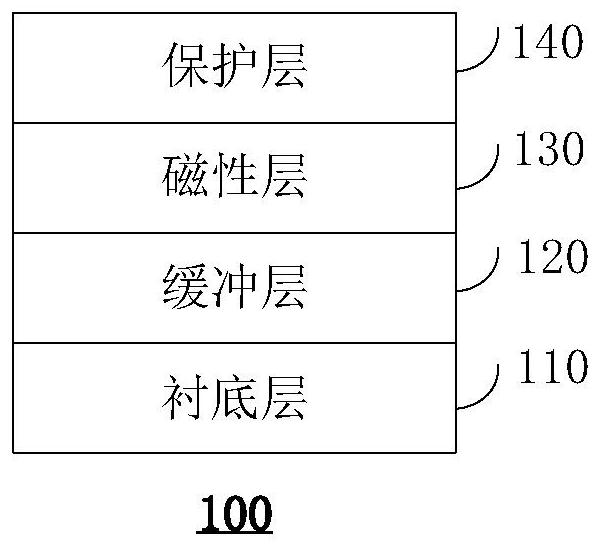
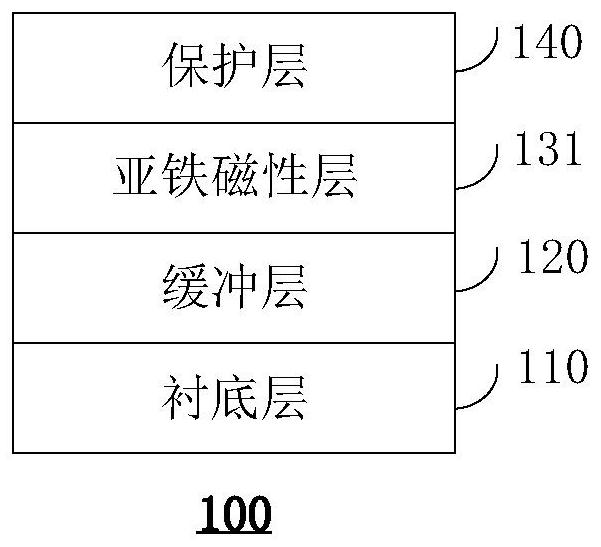
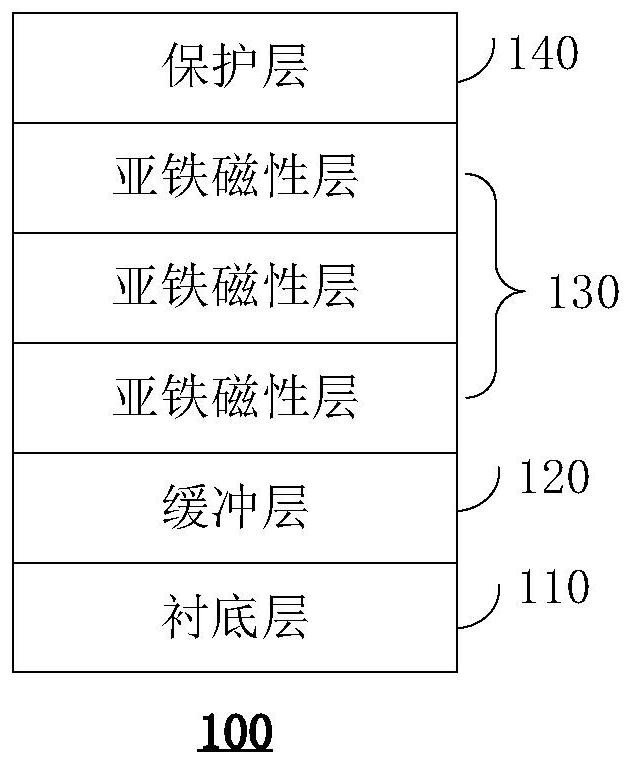
The invention relates to a topological magnetic structure, a magnetic skyrmion writing method, a magnetic skyrmion storage, a magnetic skyrmion read-write system and a magnetic skyrmion track storage. The topological magnetic structure comprises a substrate layer; a buffer layer, which is arranged on the substrate layer, wherein the surface roughness of the buffer layer is smaller than that of the substrate layer; a magnetic layer, which is arranged on the buffer layer and comprises at least one ferrimagnetic layer, and is used for generating the magnetic skyrmion under a preset condition; and a protective layer, which is arranged on the magnetic layer and is used for protecting the magnetic layer. The device based on the ferrimagnetic material has the advantages of being insensitive to magnetic field disturbance, high in intrinsic frequency and the like, and therefore the device has wide application prospects in the fields of ultra-high density information storage, terahertz (Tera Hertz, THz) and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
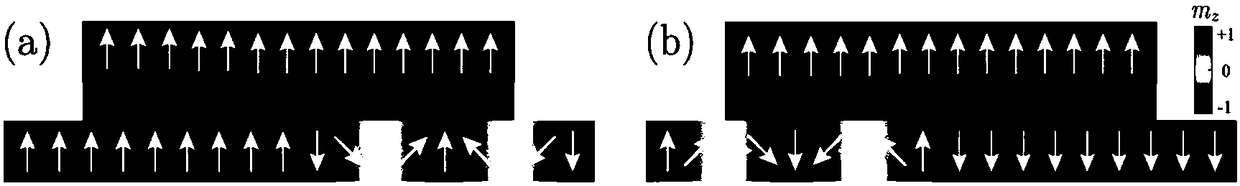
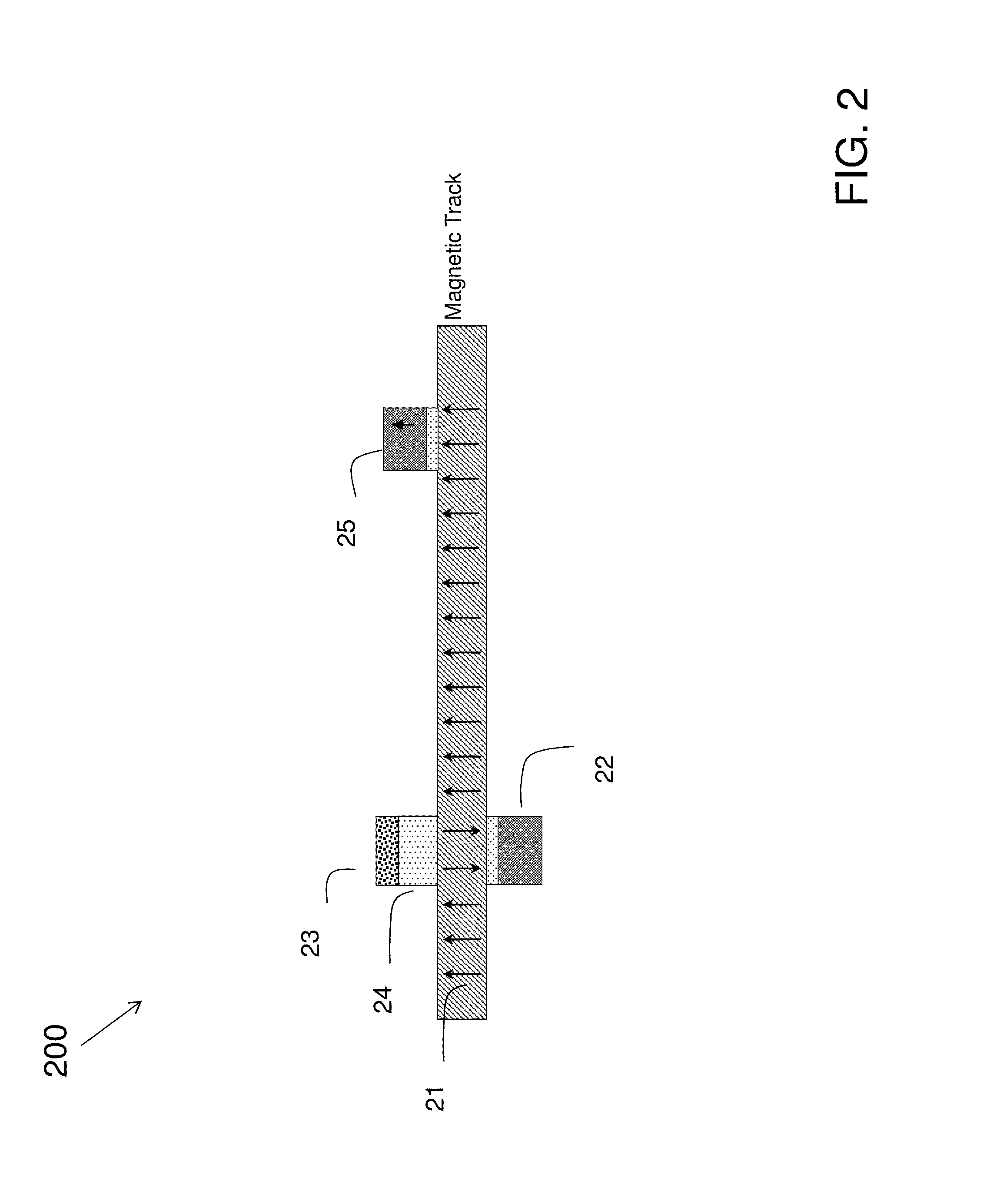
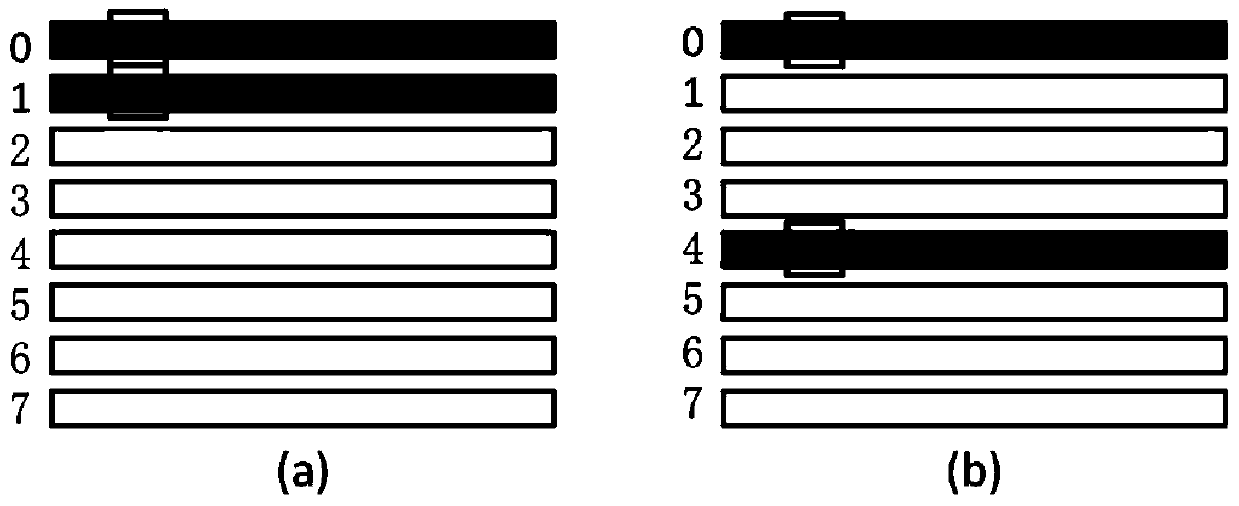
Race-track memory with improved domain wall motion control
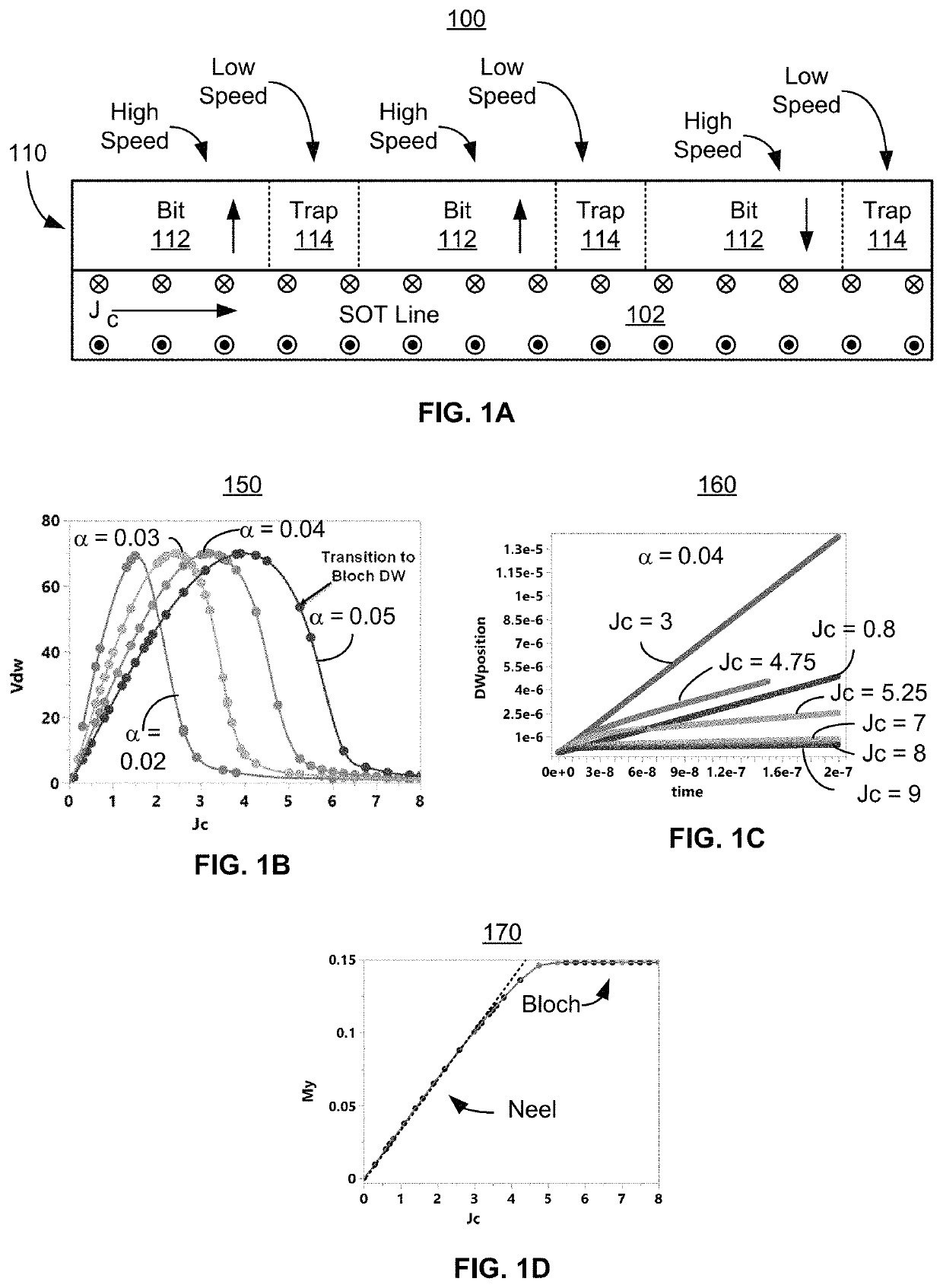
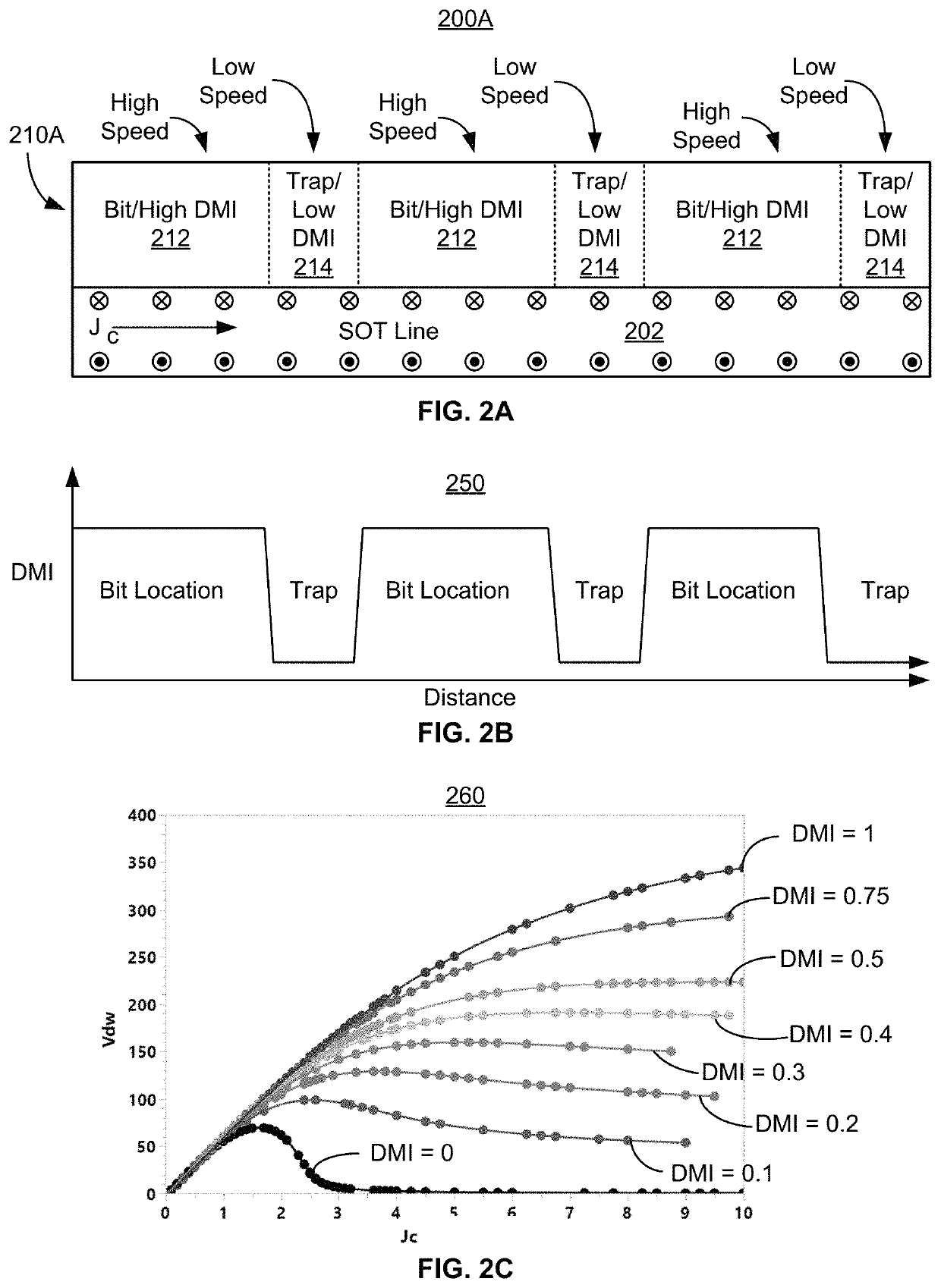
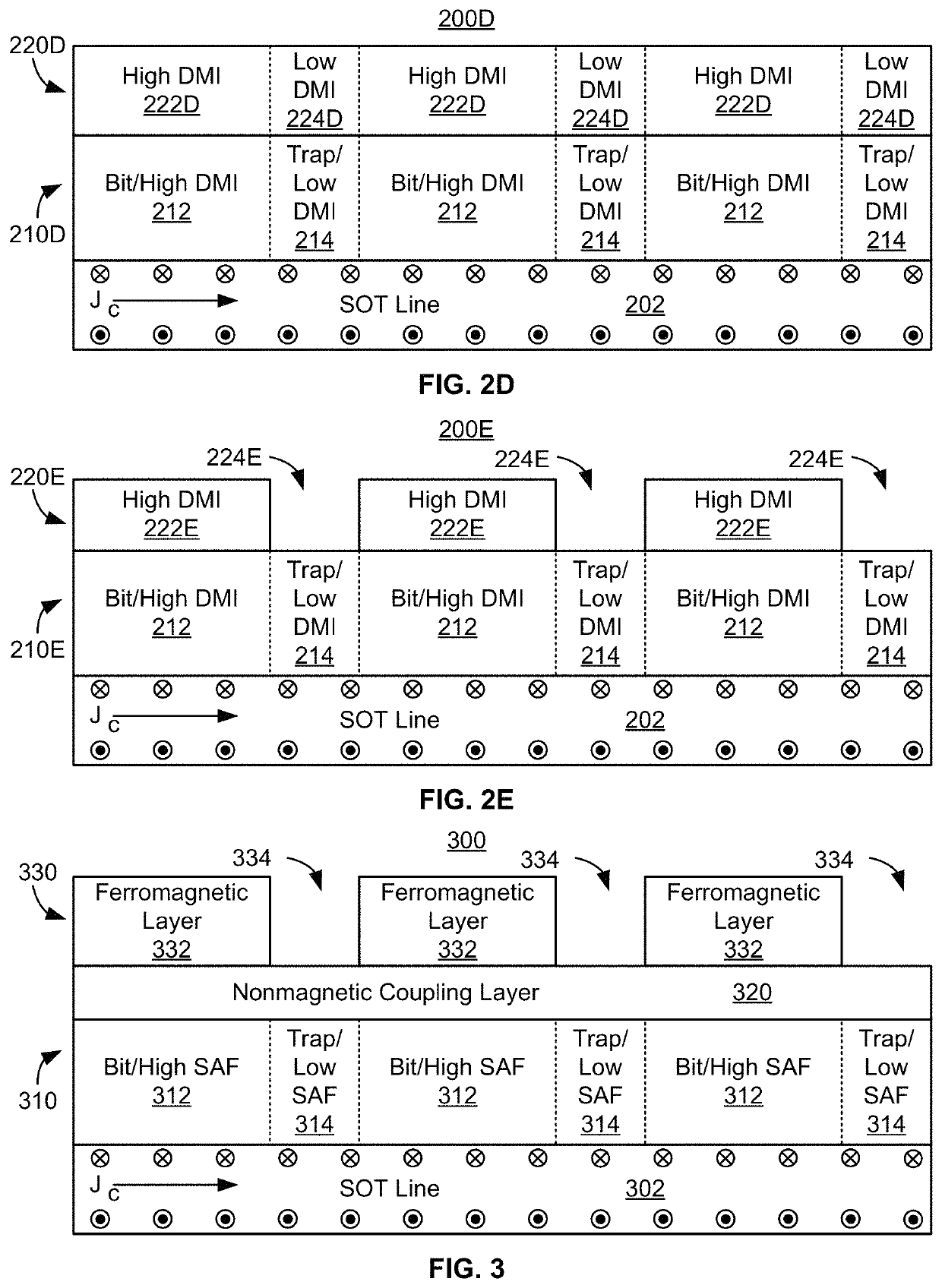
A system including a racetrack memory layer is described. The racetrack memory layer includes a plurality of bit locations and a plurality of domain wall traps. The bit locations are interleaved with the domain wall traps. Each of the bit locations has a first domain wall speed. Each of the domain wall traps has a second domain wall speed. The first domain wall speed is greater than the second domain wall speed. The first domain wall speed and the second domain wall speed are due to at least one of a Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction variation in the racetrack memory layer, a synthetic antiferromagnetic effect variation in the racetrack memory layer, and a separation distance for the plurality of domain wall traps corresponding to an intrinsic travel distance. The separation distance is less than one hundred nanometers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
racetrack memory device
ActiveCN102282624BSimple designSimplify the manufacturing processNanotechDigital storageCMOSComputer architecture
A racetrack-type memory storage device that moves domain walls along the racetrack in only one direction. The reading unit can be placed at one end of the runway (rather than in the middle of the runway). Once the domain walls are moved across the read member, the domain walls disappear, but their corresponding information is read into one or more memory devices (eg, built-in CMOS circuits). The information can then be processed in circuitry for computational needs and written to either in its original form (eg, read from the racetrack) using a writing component placed on the opposite end of the racetrack from the reading component. out) or written back to the runway in a different form after some calculation. Such racetracks are simpler to construct and have higher operational reliability than previous racetrack-type memory devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Track memory based on magnetic skyrmion
The invention relates to a track memory based on magnetic skyrmion. The track memory based on magnetic skyrmion may include a storage track and a read component disposed on the storage track. The memory track is formed of a spin Hall effect layer and a magnetic layer formed on the spin Hall effect layer for storing Skyrmion, and includes a shift write terminal provided at at least one end thereof.The shift write terminal includes a narrow portion, a wide portion, and an expansion portion connecting the narrow portion and the wide portion. The narrow portion has a first width for receiving a shift write current and generating a skyrmion. The wide portion extends to be connected to a main body portion of the storage rail to receive and move the skyrmion and has a second width greater than the first width. The first end, connected with the narrow part, of the expanding part has the first width, the second end, connected with the wide part, of the expanding part has the second width, andthe expanding part gradually expands from the first width of the first end to the second width of the second end.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
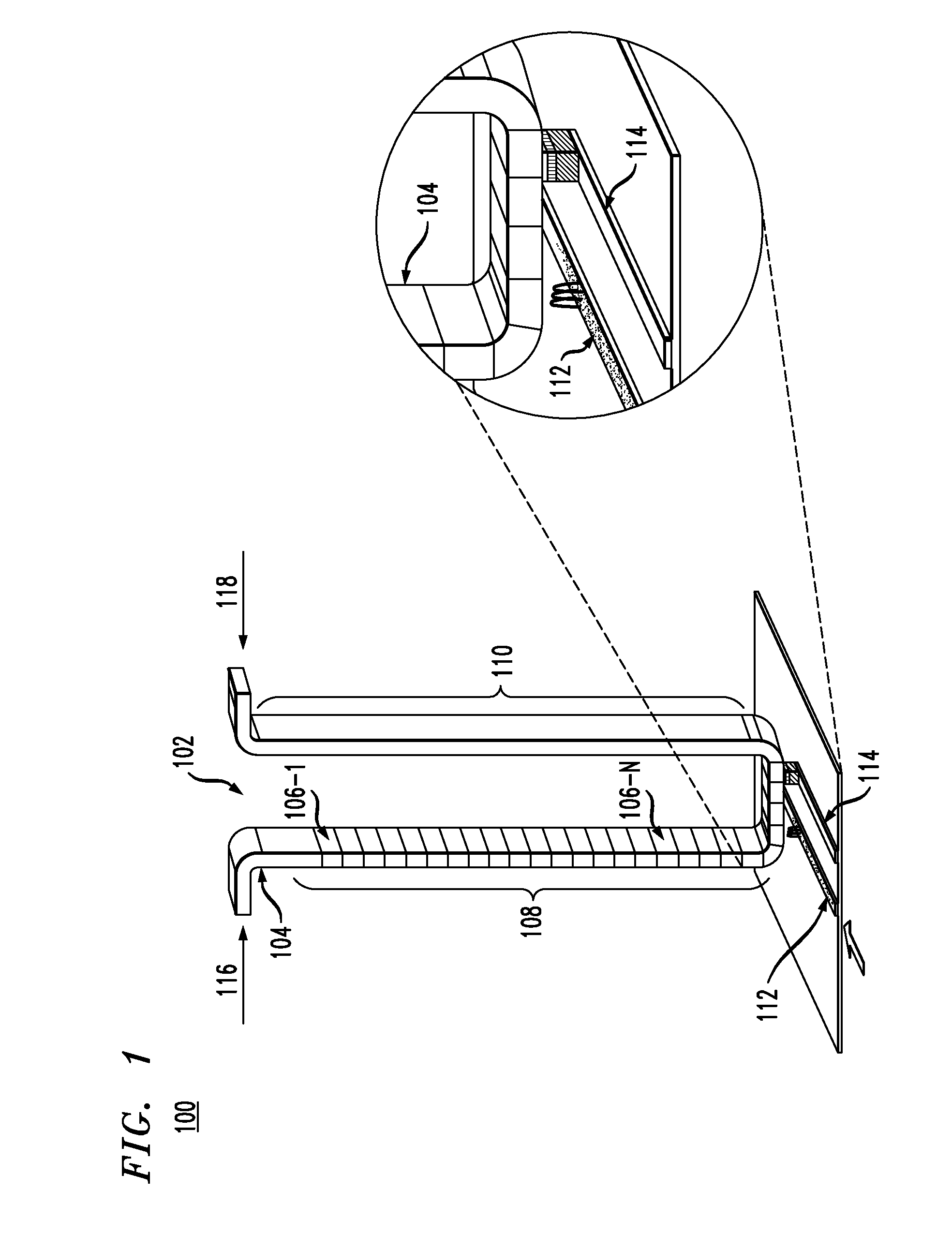
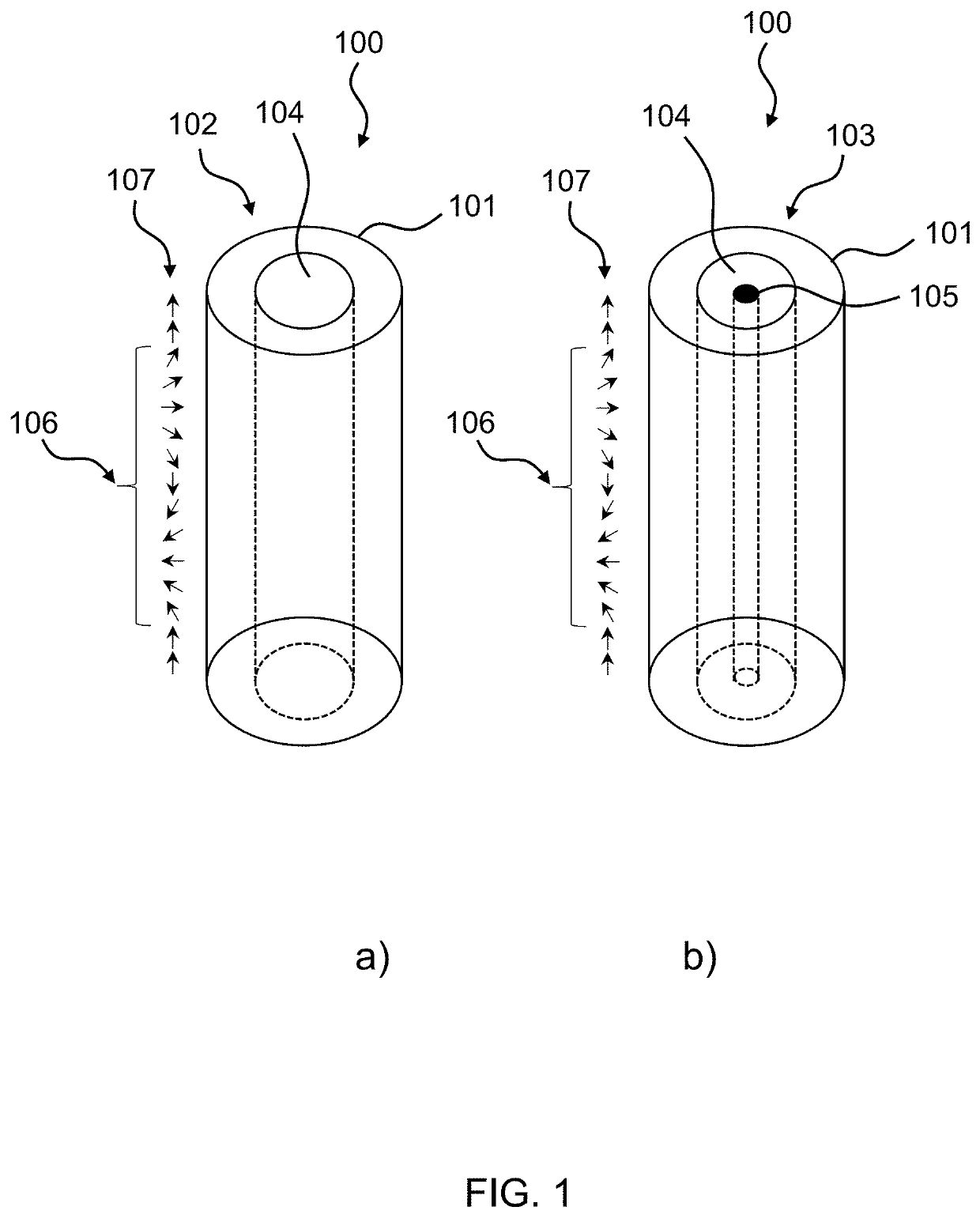
Tubular nanosized magnetic wires with 360° magnetic domain wallu
The present invention is directed towards a tubular nanosized magnetic wire, wherein the nanosized magnetic wire comprises: a tubular magnetic shell surrounding a longitudinal axis of the wire, at least one region of the tubular magnetic shell is capable of providing a 360° magnetic domain wall, wherein the 360° magnetic domain wall is self-stabilizing and has a magnetization going from a parallel alignment to a perpendicular alignment and to a parallel alignment with regards to the wire axis. The present invention also provides a practical method capable of making a tubular nanosized magnetic wire with a self-stabilizing, 360° magnetic domain wall. The present invention also relates to the use of the tubular nanosized magnetic wire in a racetrack memory device.
Owner:UNIV DUISBURG ESSEN
Coding method and error correction method of error correction code for track storage location
InactiveCN104575617BReduce Uncorrectable ErrorsValid checkStatic storageProcessor registerPosition error
The invention discloses a coding method of a racetrack storage position error correcting code and an error correcting method. The coding method of the correcting code comprises the steps of coding positions of one or more read-only access ends of a racetrack memory stripe (RS) relative to the RS as circulating codes, storing the circulating codes into the RS, enabling the position of the RS to correspond to partial circulating codes read from the RS at the moment, obtaining a position code by virtue of the circulating codes, and utilizing the position code as an error correcting code of the racetrack storage position. The circulating code is set as a continuous sequence of a plurality of circulating units, and the bit number of each circulating unit is one or more bits. According to the error correcting method, the error-type position error can be detected and corrected by comparing the position code stored in the access end position of a register and a position code obtained by decoding the circulating codes stored in the racetrack storage stripe, so that the problem of the error of the error-type position can be effectively solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Magnetic track memory cell
The invention relates to the technical field of memories, in particular to a magnetic track memory cell which comprises a magnetic nanowire track and a writing device; the magnetic nanowire track is provided with a magnetic domain, the writing device comprises an insulating layer and a metal wire, and the insulating layer separates the metal wire from the magnetic nanowire track; when current passes through the metal wire, a magnetic field generated by the current causes the change of the magnetization direction of a magnetic domain in the magnetic nanowire track, so that data are written in, wherein an electric field is arranged at a magnetic domain interface where data needs to be written; the electric field can cause the change of the characteristics of the magnetic material and reduce the anisotropic performance of the magnetic domain, thereby effectively reducing the write current and write power consumption of the magnetic track memory cell .
Owner:普赛微科技(杭州)有限公司
A magnetic domain wall writing unit and method based on multiferroic heterostructure
ActiveCN112002361BReduce the size of the unitImprove storage densityDigital storageHeterojunctionEngineering
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
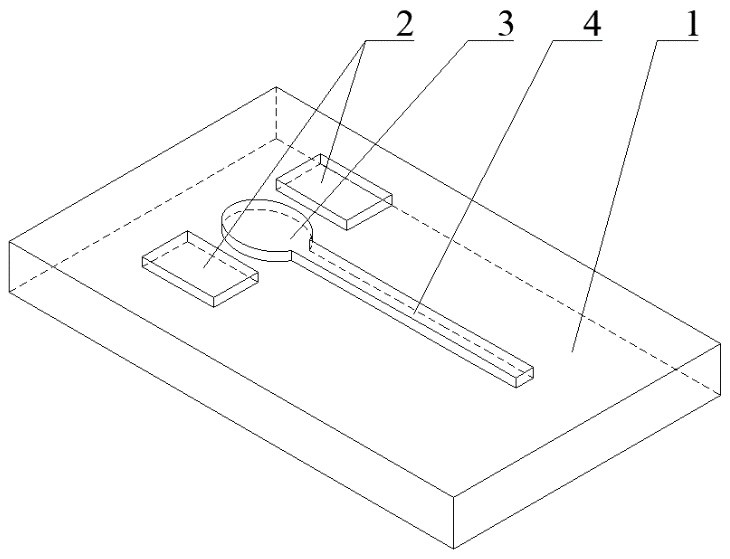
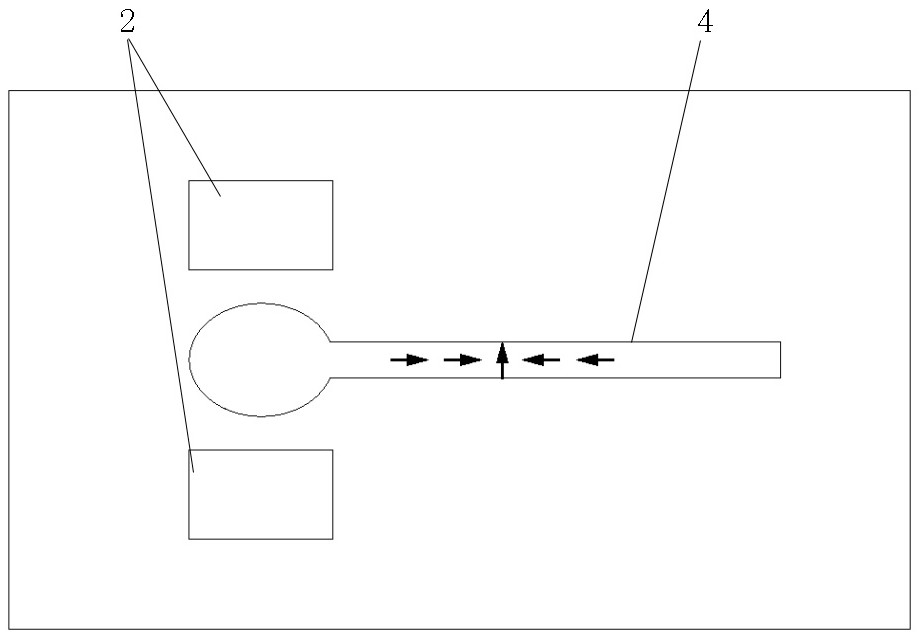
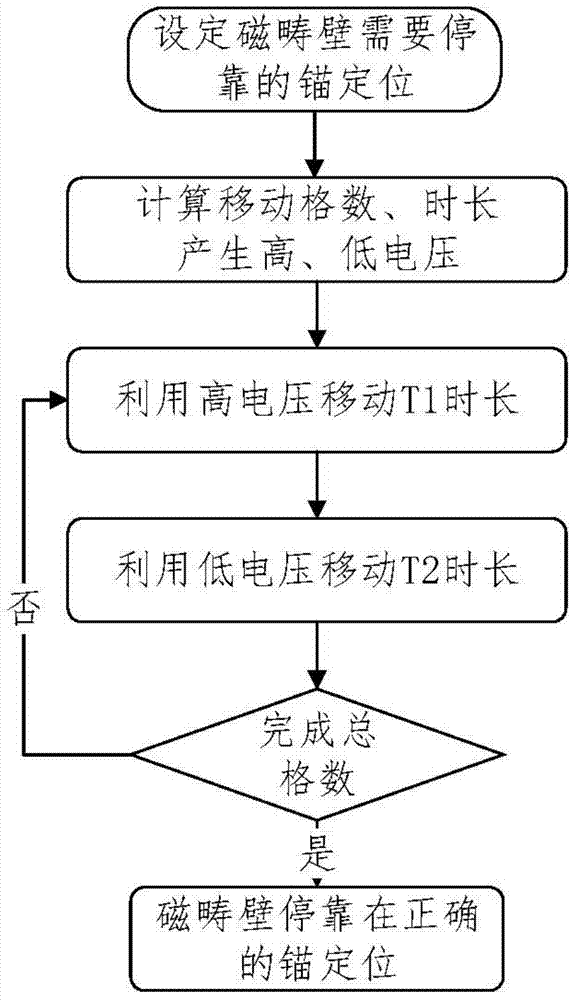
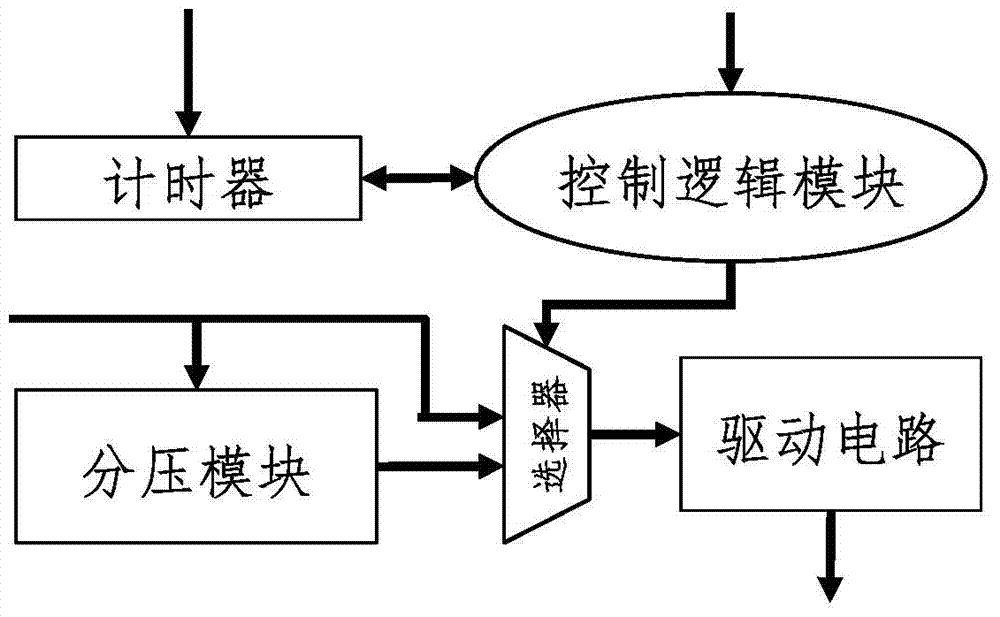
Domain wall shift control method and circuit based on sub-threshold current
The invention discloses a domain wall shift control method and circuit based on sub-threshold current. According to the method, current less than a threshold is called as sub-threshold current; and a domain wall is pushed to shift outside an anchoring region through the sub-threshold current to supplement a shift position of the domain wall. The method comprises a single-step shift mode and a multi-step shift mode, and sequentially comprises the steps: setting an anchoring site, and preparing shift length and needed voltage; driving the domain wall by high-threshold current for a period of time; driving the domain wall by the sub-threshold current for a period of time; and judging whether the total sum of a shift distance reaches a distance needing to be shifted of the domain wall or not until the domain wall stops on the anchoring site. According to the domain wall shift control method and circuit based on the sub-threshold current, the accuracy of a racetrack on memory of the shift of the domain wall is improved, and the shift of the domain wall can be relatively rapidly finished; and the problem which is caused possibly by the random shift of the domain wall is prevented so that the reliability and the stability of the racetrack memory are improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com