Heat exchanger and method of manufacturing heat exchanger
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
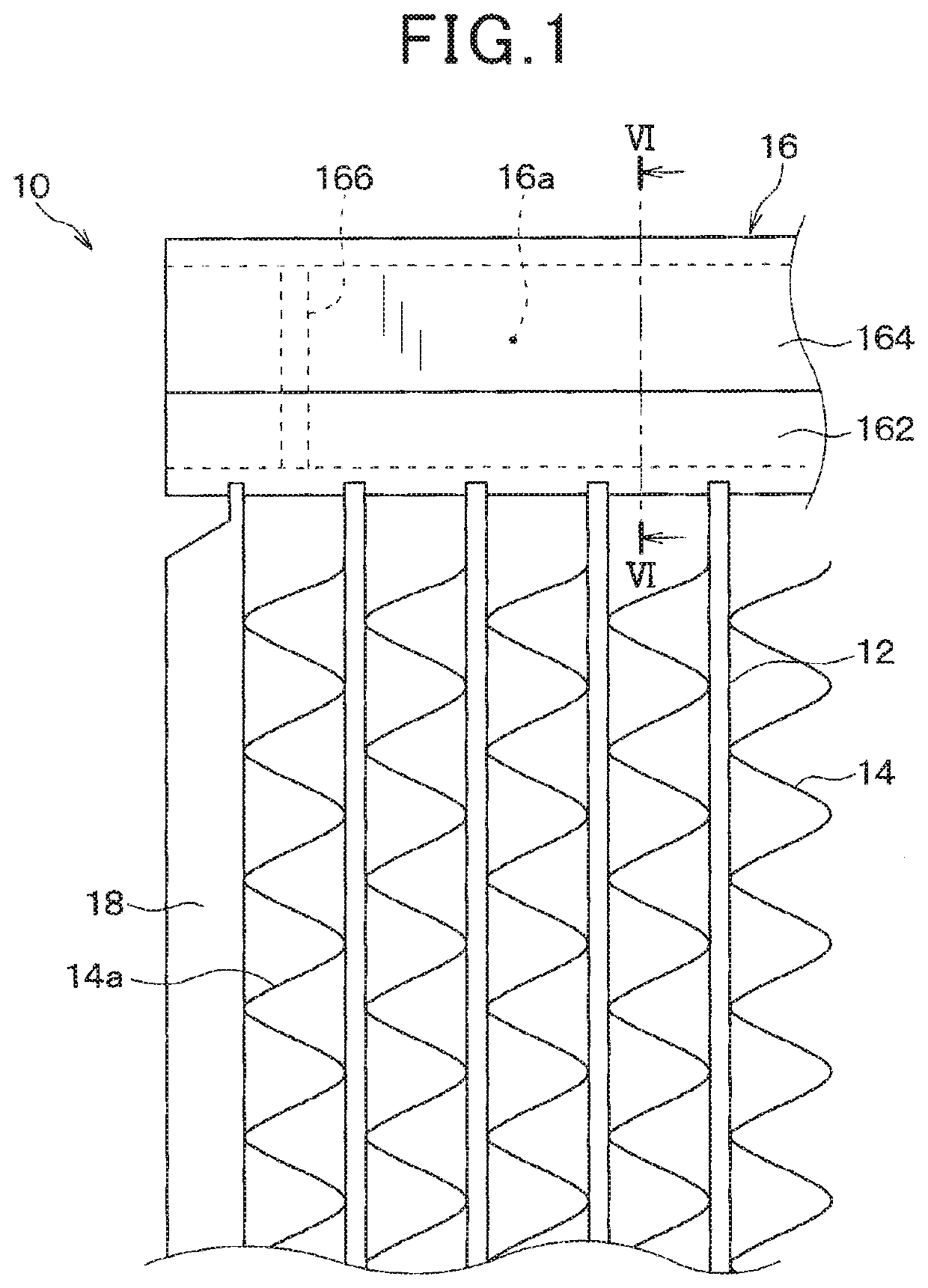
[0050]Referring now to the drawings, wherein like reference numerals designate identical or corresponding parts throughout the several view s thereof, and to FIG. 1, the present disclosure is described. As shown in FIG. 1, a heat exchanger 10 is a fin-tube type heat exchanger in this embodiment. The heat exchanger 10 includes multiple tubes 12 and multiple fins 14, two header tanks 16 and two side plates 18. In FIG. 1, how ever, only one of the two header tanks 16 is illustrated. Also, only one of the two side plates 18 is illustrated. The heat exchanger 10 exchanges heats of a first fluid flown in the multiple tubes 12 and a second fluid flown outside of the multiple tubes 12.
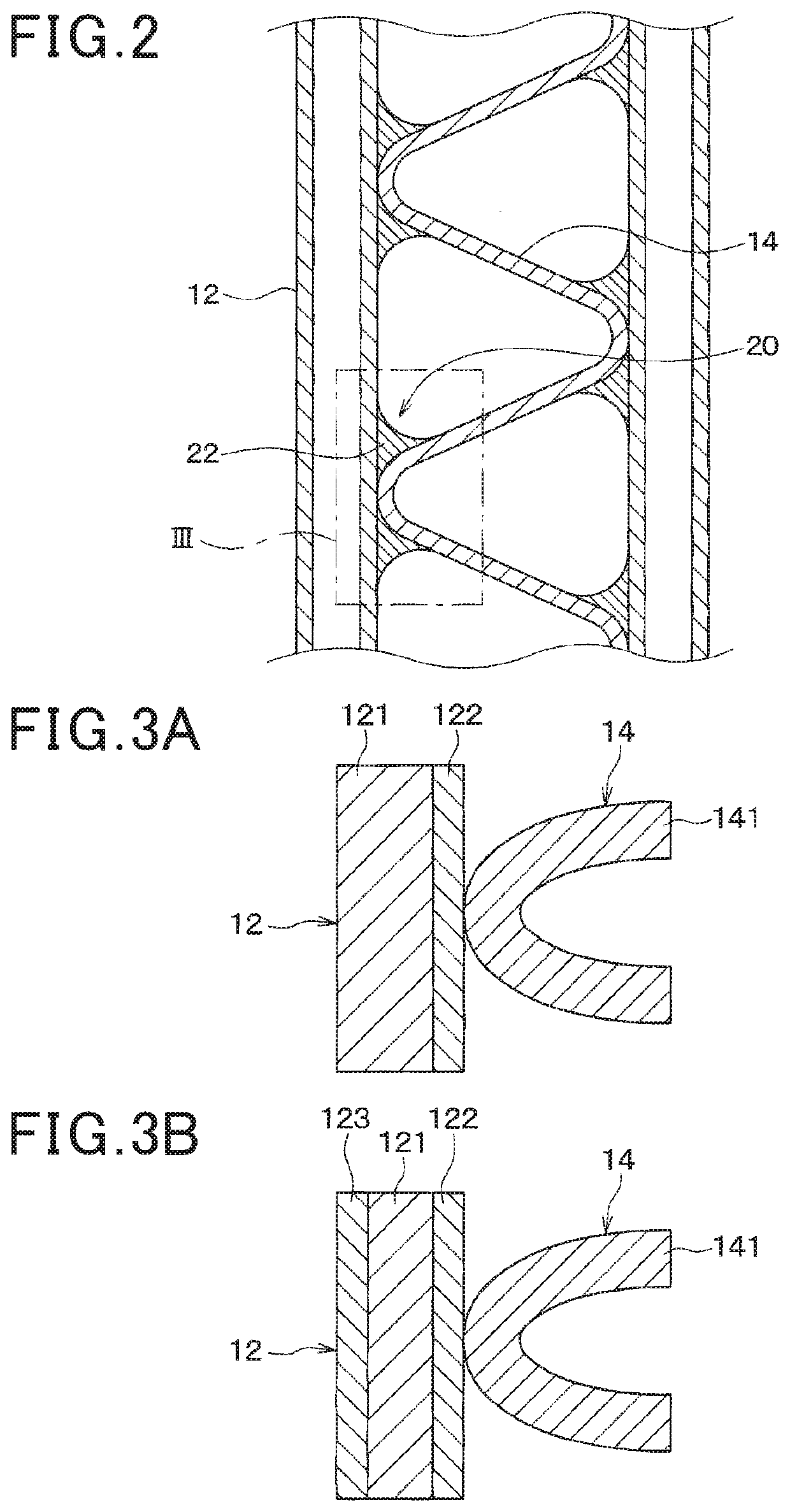
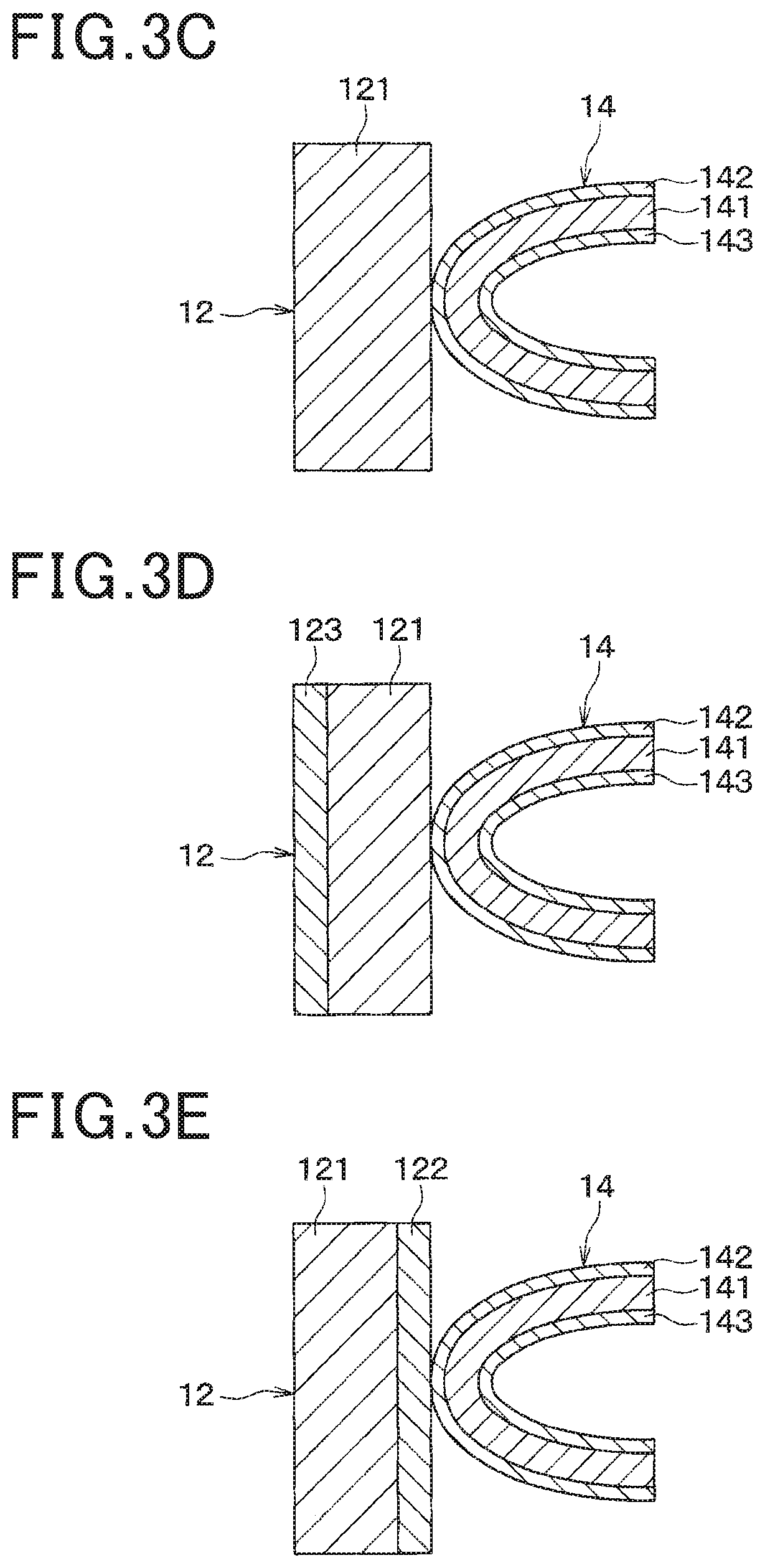
[0051]The tube 12 is a tubular flow channel forming member to form a flow channel for the first fluid. The tube 12 is prepared by molding an aluminum alloy plate into a hollow structure. The tube 12 is also a seam welded pipe prepared by machining a sheet metal. However, the tube 12 can be an extruded perforat...
second embodiment
[0097]Now, the present disclosure is described with reference to FIG. 19A. As shown there, a tube 12 is formed by brazing a plate member subjected to a bending process.
[0098]That is, the tube 12 includes a core material layer 121, a brazing material layer 124 and a cladding layer 125. The brazing material layer 124 is located on one side of the core material layer 121. The brazing material layer 124 is located on an outer surface of the tube 12. The brazing material layer124 may composed of an Al—Si-based alloy. The cladding layer 125 is located on the other side of the core material layer 121 opposite the brazing material layer 124. The cladding layer 125 is thus located inside of the tube 12. The cladding layer 125 is composed of an aluminum alloy (i.e., not a brazing material), such as Al—Zn-based alloy, etc., for example. Further, as shown in FIG. 19A, in each of regions R1 and R2 of the tube 12, the brazing material layer 124 and the cladding layer 125 are joined together.
[0099...
third embodiment
[0101]Now, the present disclosure is described with reference to FIG. 20. As shown in FIG. 20, a fin 15 is disposed inside of the tube 12. The tube 12 is brazed partially sandwiching the fin 15.
[0102]The tube 12 includes a core material layer 121, a brazing material layer 126 and a cladding layer 127. The brazing material layer 126 is located on one side of the core material layer 121. The brazing material layer 126 is located on an inner side of the tube 12. The brazing material layer 126 is composed of an Al—Si-based alloy. The cladding layer 127 is located on a side of the core material layer 121 opposite the brazing material layer 126. The cladding layer 127 is composed of an aluminum alloy excluding brazing material, for example, an Al—Zn-based alloy. The fin 15 may consist of the core material layer 151 composed of an Al—Mn-based alloy.
[0103]As shown in FIG. 20, in a region R3 of the tube 12, the brazing material layer 126 and the cladding layer 127 are joined together. As in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com