Camera-based positioning system using learning
a technology of learning and camera, applied in the field of wireless devices, can solve the problems of requiring substantial time and computational resources to perform effective camera-based localization, and may be difficult to communicate with a remote satellite, and achieve the effects of reducing memory overhead, significant computational efficiency, and reducing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
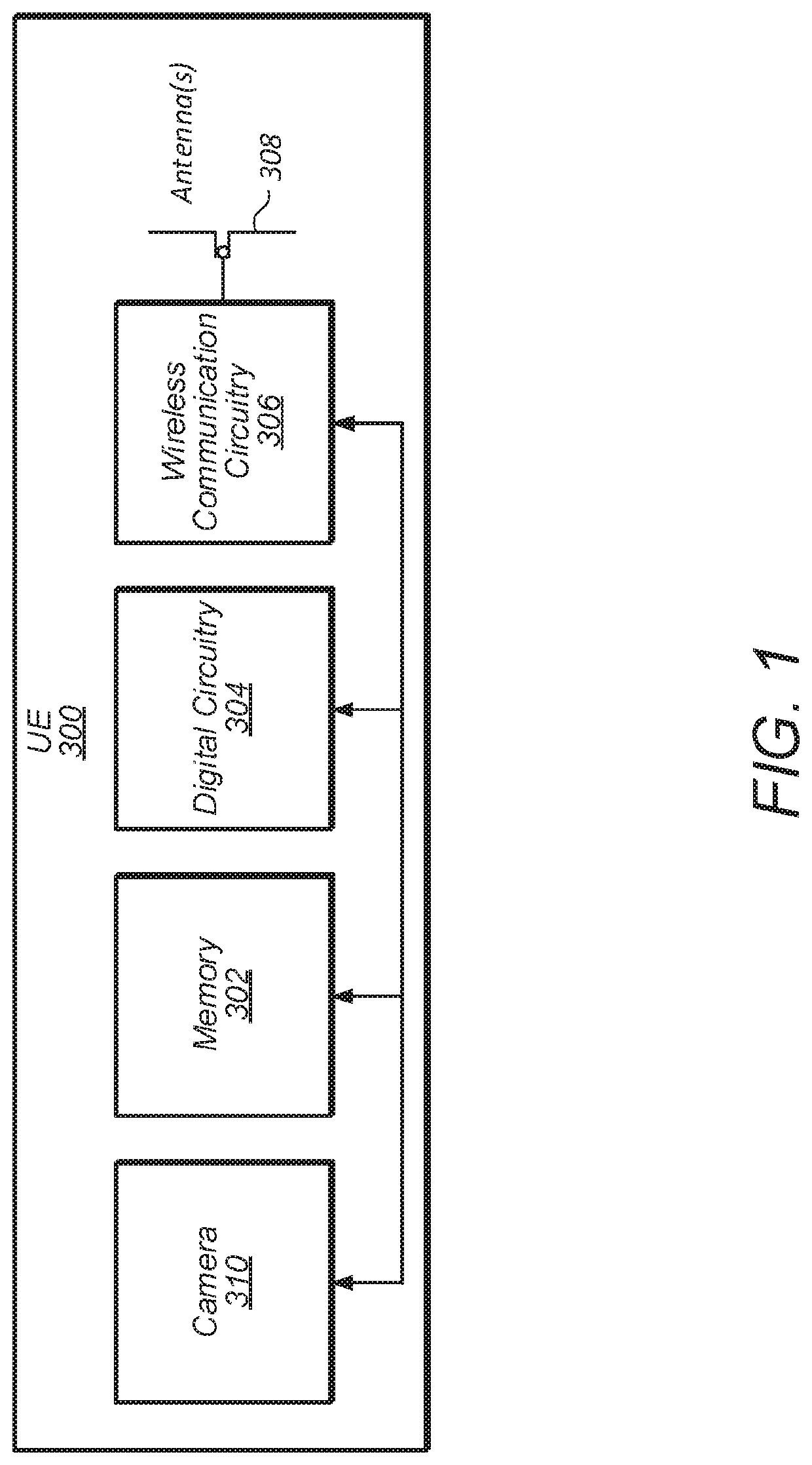
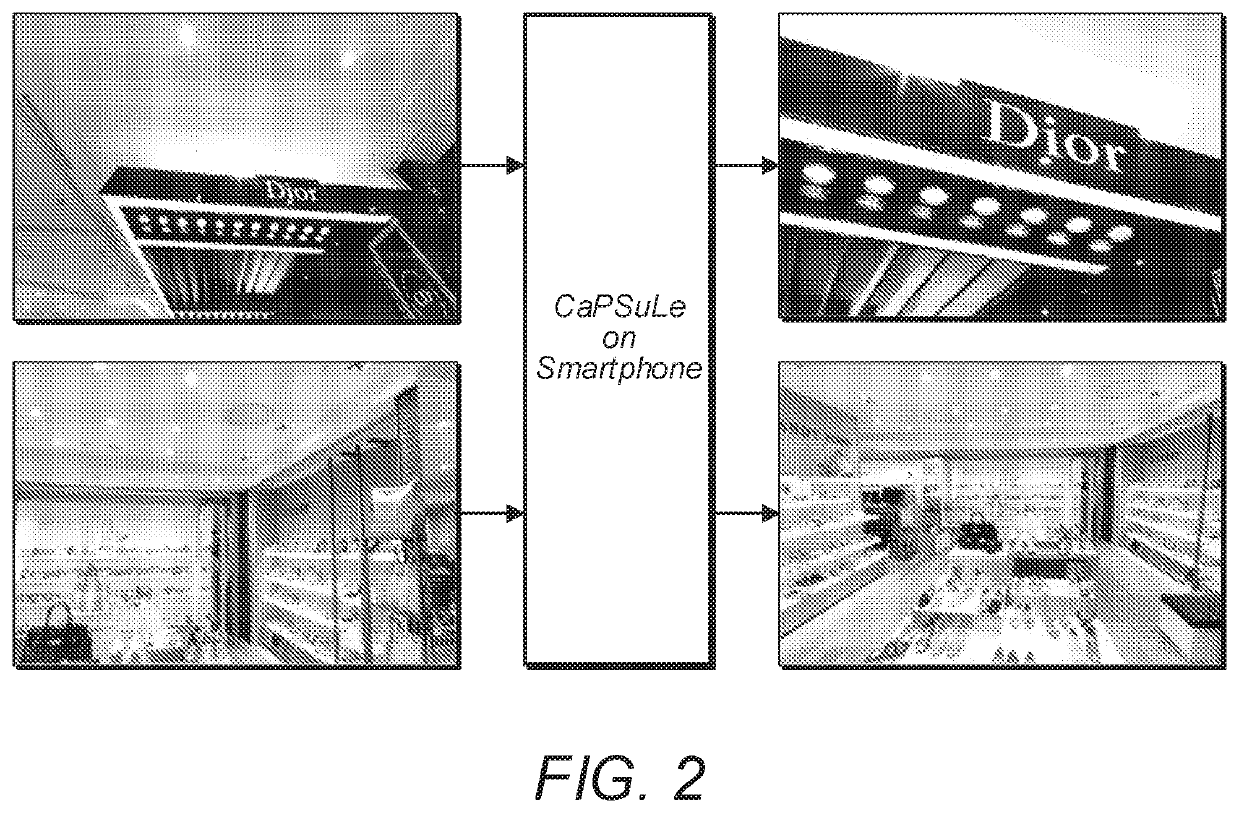
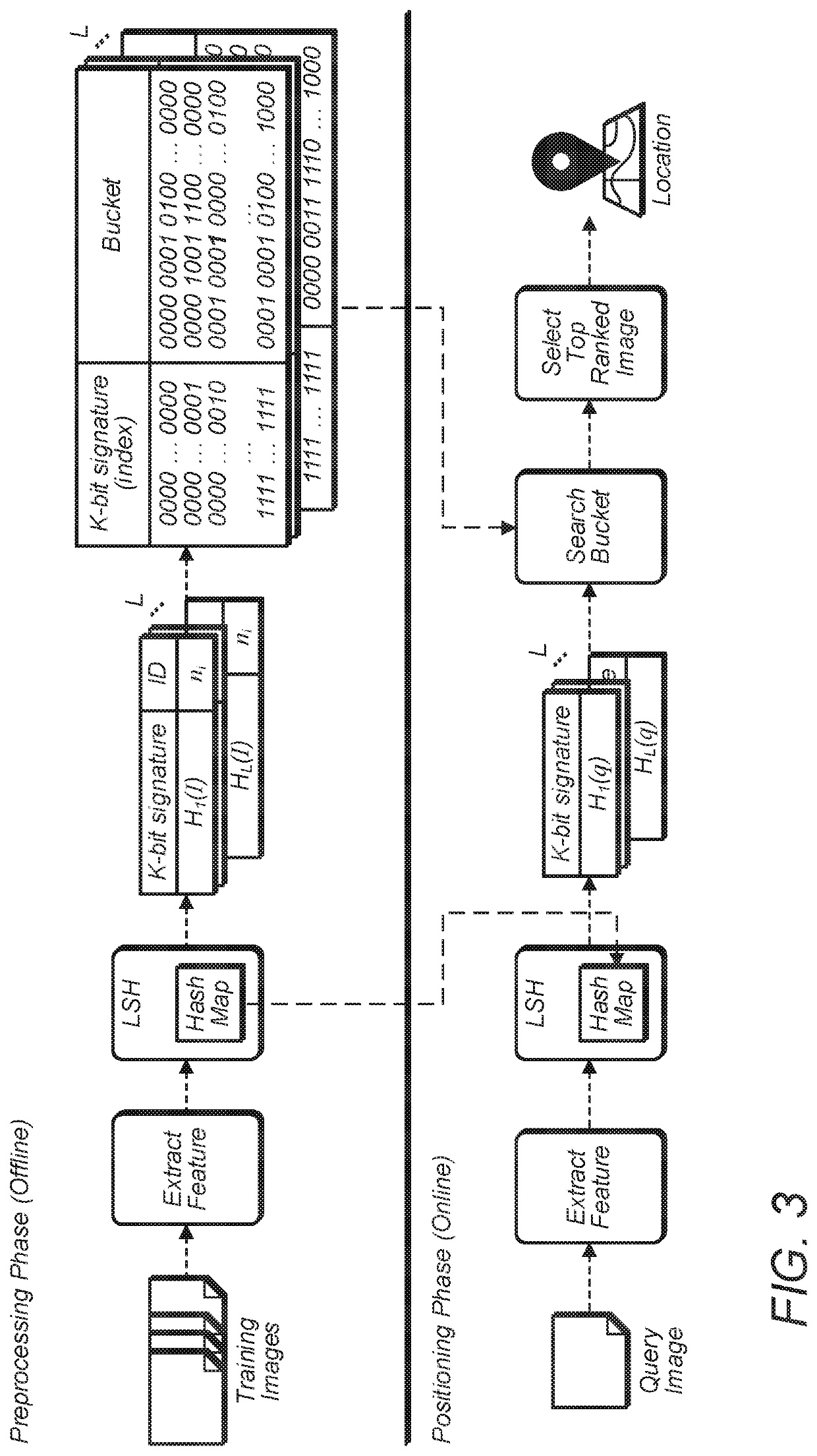
[0029]Embodiments herein describe a camera based (privacy-preserving) indoor mobile positioning system, Camera-based Positioning System using Learning (CaPSuLe), which may not involve any communication (or data transfer) with any other device or the cloud. According to some embodiments, to determine position of a device in an indoor environment accurately, instead of using GPS, Wi-Fi or any cloud based service, a user of a UE may take a picture and algorithmically determine the location of the UE, using computationally cheap on-device hash lookups of the taken image. The indoor mobile positioning may utilize inexact computing, wherein a small decrease in accuracy is used to obtain significant computational efficiency.
[0030]Embodiments herein may provide sustainable and private navigation, e.g., in mall, campuses, indoor building etc., without involving any network or cloud service. The navigation may be privacy preserving (the position of the user is never calculated outside the dev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com