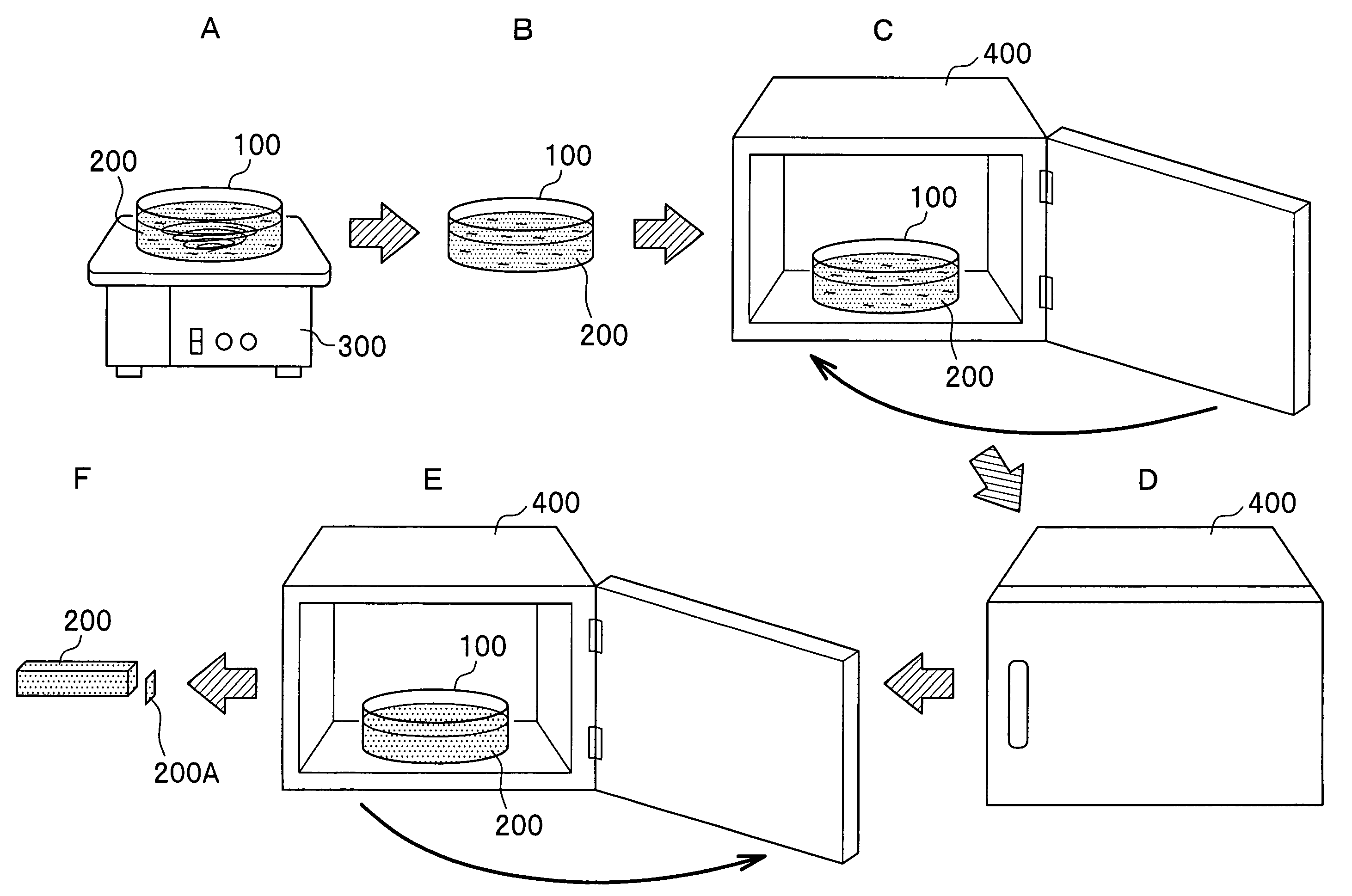
Method for preparing analytical standard, and analytical standard prepared by the same
a technology of analytical standards and analytical standards, applied in chemical methods analysis, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large gap between the element content of biological samples to be measured and the analytical standard of evaporation type, and uneven element distribution at the portion where mercury is located
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
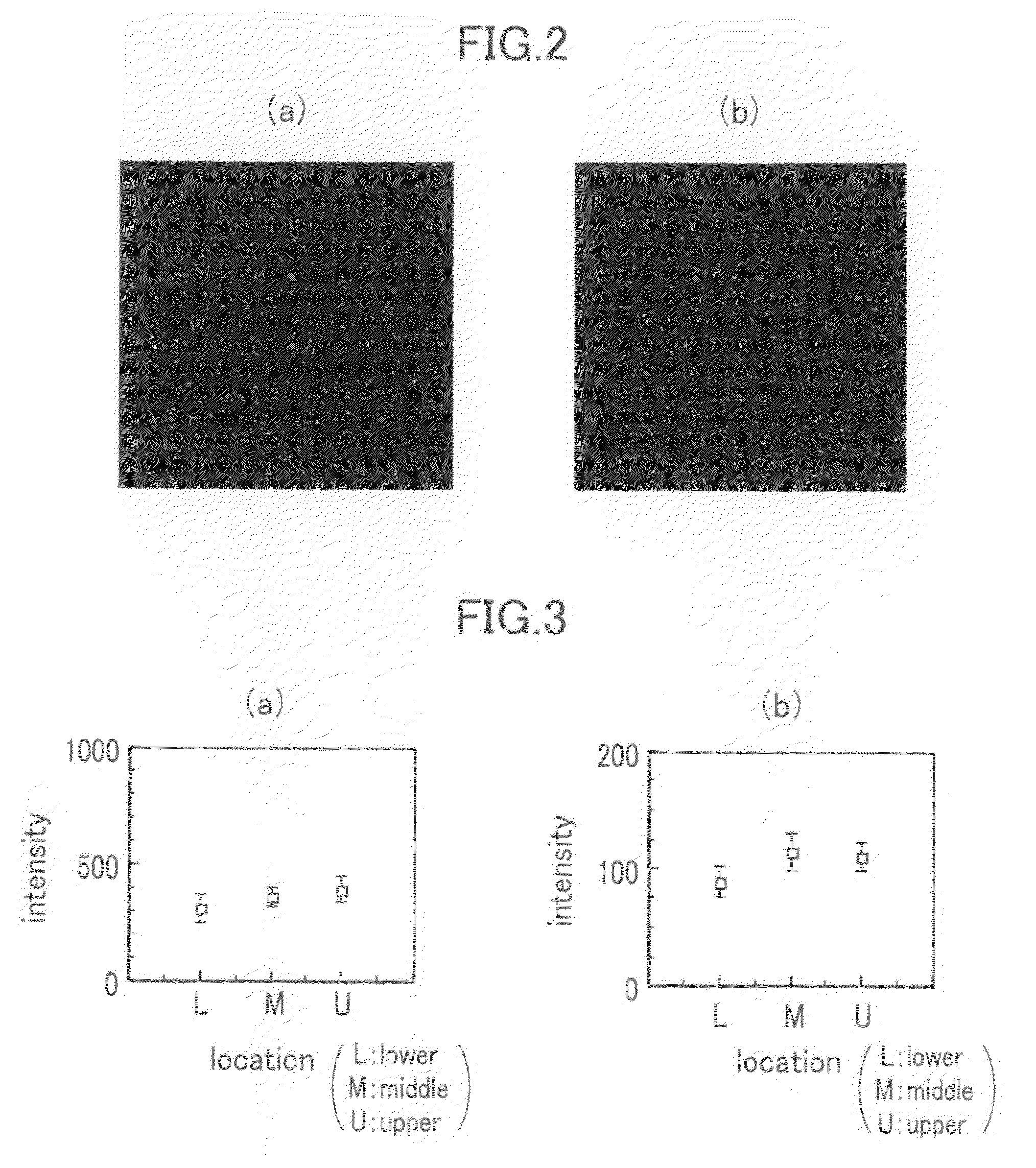
[0039]FIG. 2 shows elemental images of the analytical standard prepared by the method according to the embodiment described above in which: FIG. 2(a) shows a case where the element is zinc; and FIG. 2(b) shows a case where the element is selenium.
[0040]In an example illustrated in FIG. 2, 1.98 g of OTC compound was charged in a container (in a shape of an ellipsoid with a major axis of 27 mm, a minor axis of 22 mm and a depth of 4 mm) and 20 μl of an element solution (in the case of FIG. 2(a), a zinc chloride solution prepared by dissolving zinc chloride in distilled water to a concentration of 50,000 ppm in terms of zinc; and in the case of FIG. 2(b), a sodium selenite solution prepared by dissolving sodium selenite in distilled water to a concentration of 50,000 ppm in terms of selenium) was added to a final concentration of 500 ppm in terms of zinc in the OTC compound. A stirring bar (with a length of 15 mm and a diameter of 2 mm) was put in the container. The mixture was stirred...
example 2
[0041]FIG. 3 shows graphs of element distribution in a depth direction in the frozen block of the analytical standard prepared by the method according to the embodiment described above in which; FIG. 3(a) shows a case where the element is selenium; and FIG. 3(b) shows a case where the element is mercury.
[0042]In the general microbeam X-ray fluorescence analysis, due to the limitation in the detector property, a subject to be measured is X-ray fluorescence which is detectable in the energy region of approximately 1-20 keV. Therefore, in a case of the element with which X-ray fluorescence as K-line (main peak) is out of the above-mentioned energy region, the detection should be made with L-line or M-line, detection efficiency of which is lower than that of K-line. As a representative element having such a property, mercury was selected, and a comparison was made with selenium detectable with K-line. Mercury is one of the elements with which it is difficult to obtain excellent results ...
example 3
[0044]FIG. 4 shows calibration curves of the analytical standard prepared by the method according to the embodiment described above in which: FIG. 4(a) shows a case where the element is selenium; FIG. 4(b) shows a case where the element is zinc; and FIG. 4(c) shows a case where the element is mercury.
[0045]In an example illustrated in FIG. 4, an element solution (in the case of FIG. 4(a), a sodium selenite solution, in the case of FIG. 4(b), a zinc chloride solution, and in the case of FIG. 4(c), a mercuric chloride solution) was added to the OTC compound to the final concentrations of 100, 250 and 500 ppm. Other conditions are substantially the same as those in Example 1. For each sample, 3 areas of 500×500 μm2 were scanned with nanobeam (an integrated current of 0.24 μC) using substantially the same analyzer as that of Example 2, and a mean value and standard deviation of the resultant intensity were plotted, to thereby obtain a calibration curve. It was found that, with respect t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com