UV-VIS-IR imaging optical systems
a technology of optical systems and uv-vis, applied in the field of broadband imaging optics, can solve the problem of rare to find designs that are truly apochromatic, and achieve the effect of high quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
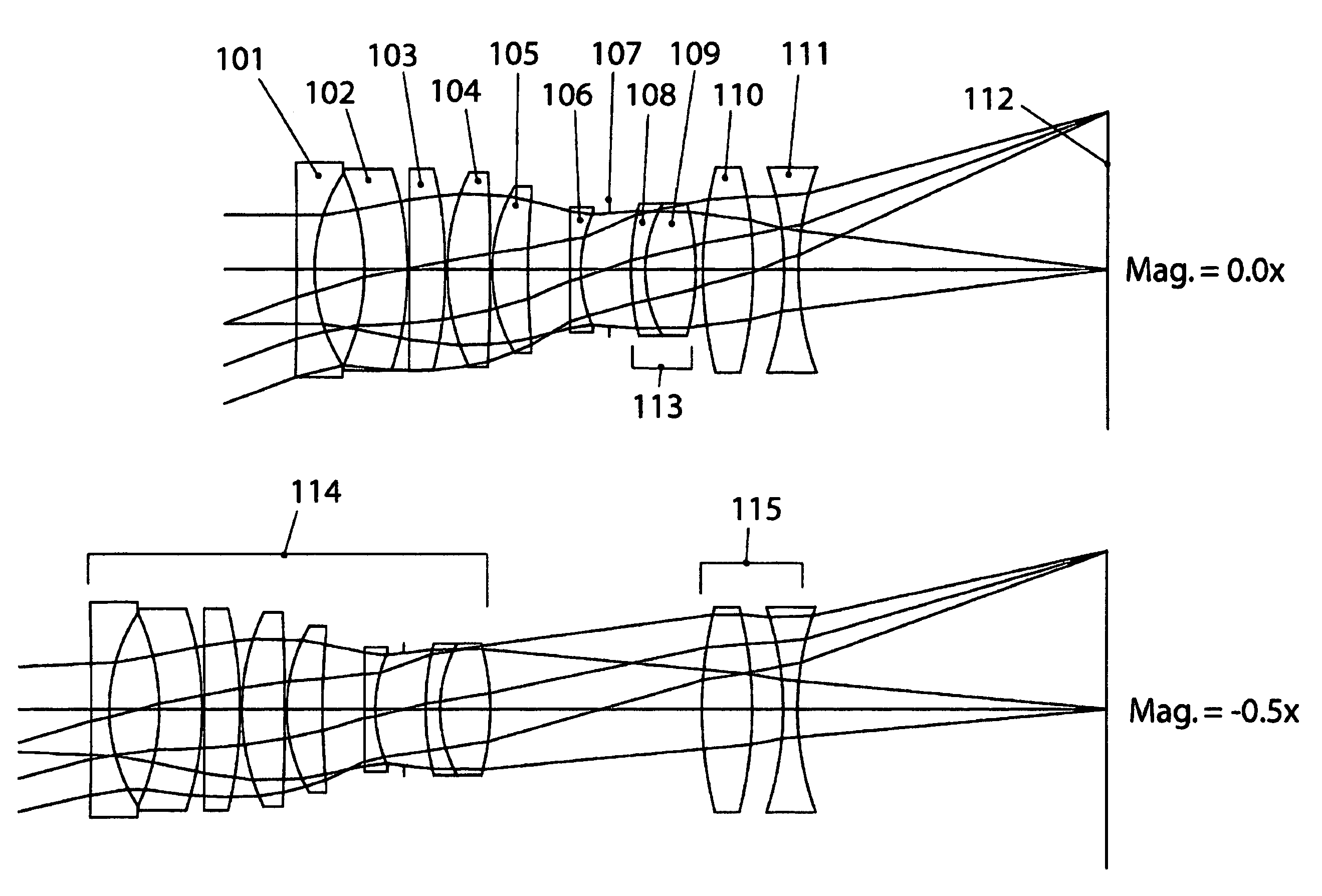
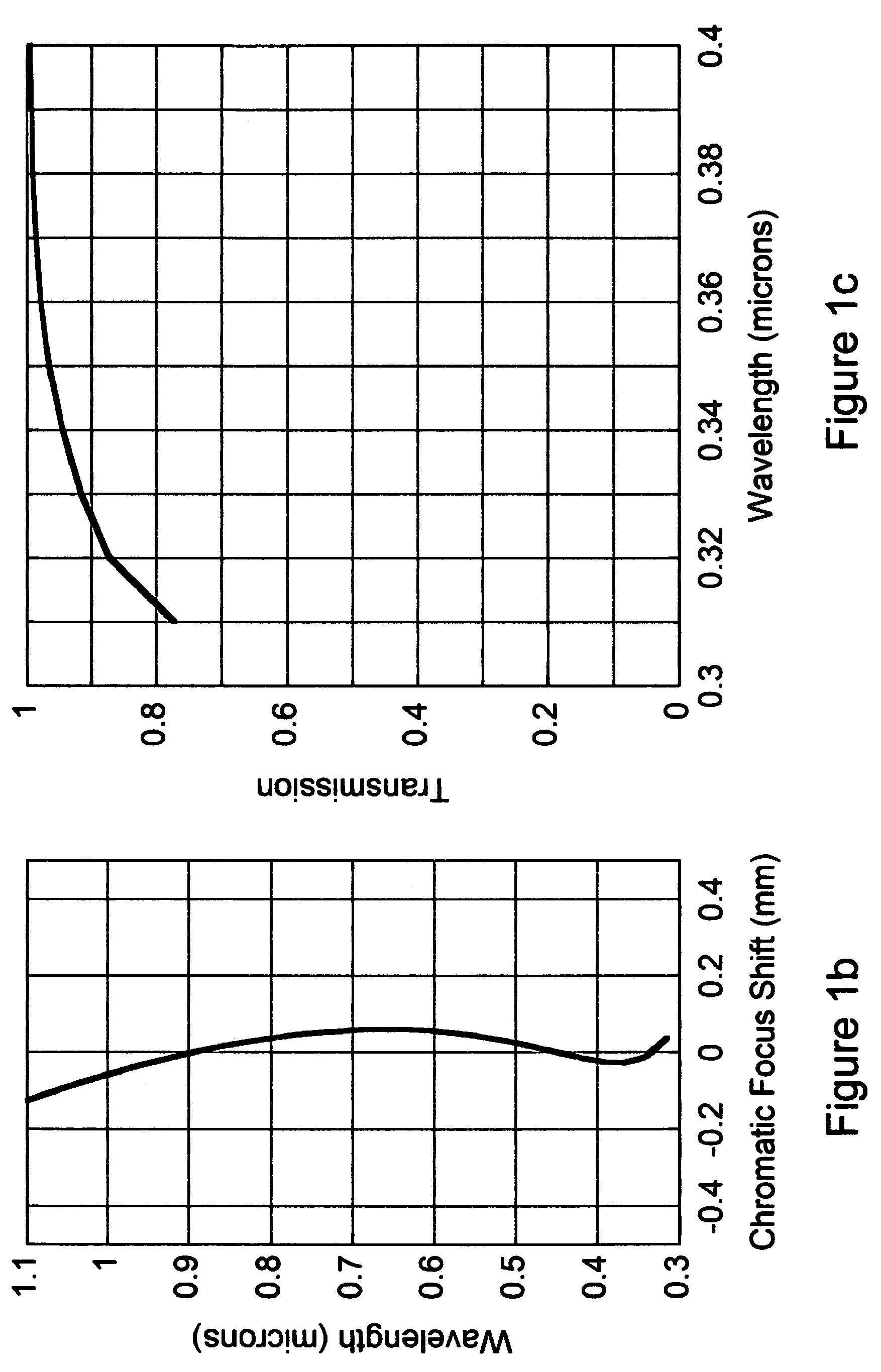
[0060]Example 1, which is a 60 mm focal length macro-focusing photographic objective for 35 mm format, is illustrated in FIG. 1a, which shows cross-sectional layouts at magnifications of 0 and −0.5×. Elements 101, 103, 104, 105, and 109 are made from CaF2; elements 102, 108, 110 and 111 are made from fused silica (SiO2); and element 106 is made from Ohara S-LAL18. Element 107 is the aperture stop and 112 is the image plane. This design has a very high internal transmission throughout the 315 nm-1100 nm waveband because there is just a single thin element (106) that is not CaF2 or fused silica. The addition of a negative-powered S-LAL18 element 106 enables the apochromatic color correction to be far superior in the near infrared to apochromats made solely from CaF2 and SiO2.
[0061]Example 1 is composed from just three different optical materials, however despite this simplicity it has the combination of both good optical correction and good transparency over the entire 315 nm-1100 nm ...
example 2
[0064]Example 2, which is a 35 mm focal length wide-angle photographic objective for 35 mm format, is illustrated in FIG. 2a, which shows cross-sectional layouts at magnifications of 0 and −0.25×. Elements 206, 211 and 212 are made from CaF2; elements 202 and 204 are made from Ohara S-FPL51; elements 203, 205, 207 and 213 are made from Ohara S-FSL5; element 201 is made from Ohara S-BAL42; and element 210 is made from Ohara S-LAL14. Element 209 is the aperture stop and 214 is the image plane. In this design, S-FPL51 has been used as a substitute for CaF2 in the larger elements 202 and 204 in order to reduce costs. However, this reduces the transmission at 315 nm. S-LAL14 and S-BAL42 are used as matching flints. Separating the design into two independently moving groups 216 and 217 eliminates variation of lateral chromatic aberration and astigmatism during focusing.
[0065]Element 208 is a 5 mm thick filter with plane parallel surfaces made of S-BSL7. It is anticipated that in ordinary ...
example 3
[0069]Example 3, which is a 24 mm focal length wide-angle photographic objective for 35 mm format, is illustrated in FIG. 3a, which shows cross-sectional layouts at magnifications of 0 and −0.15×. Elements 301, 305 and 314 are made from fused silica (SiO2); elements 303, 304, 306, 308, 312 and 313 are made from CaF2; element 302 is made from Ohara S-FPL51Y; element 309 is made from Ohara S-FPL51; element 307 is made from Ohara S-BAL42; and element 311 is made from Ohara S-LAL18. Element 310 is the aperture stop and 315 is the image plane. Example 3 bears a resemblance to Example 2, but in Example 3 there is more extensive use of CaF2, SiO2 and S-FPL51Y. As a result, Example 3 has a significantly higher transmission at 315 nm than Example 2. Apochromatic performance has been achieved by pairing CaF2 and S-FPL51Y with S-LAL18 and S-BAL42. Separating the design into two independently moving groups 317 and 318 eliminates variation of lateral chromatic aberration and astigmatism during f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com