Bias circuit
a bias circuit and circuit technology, applied in the field of bias circuits, can solve the problems of unsuitable class c conventional current mirrors (like, etc.), and achieve the effects of reducing the need for bias circuit adjustment, reducing the need for impedance, and restricting the generation of undesirable memory effects and non-linearity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
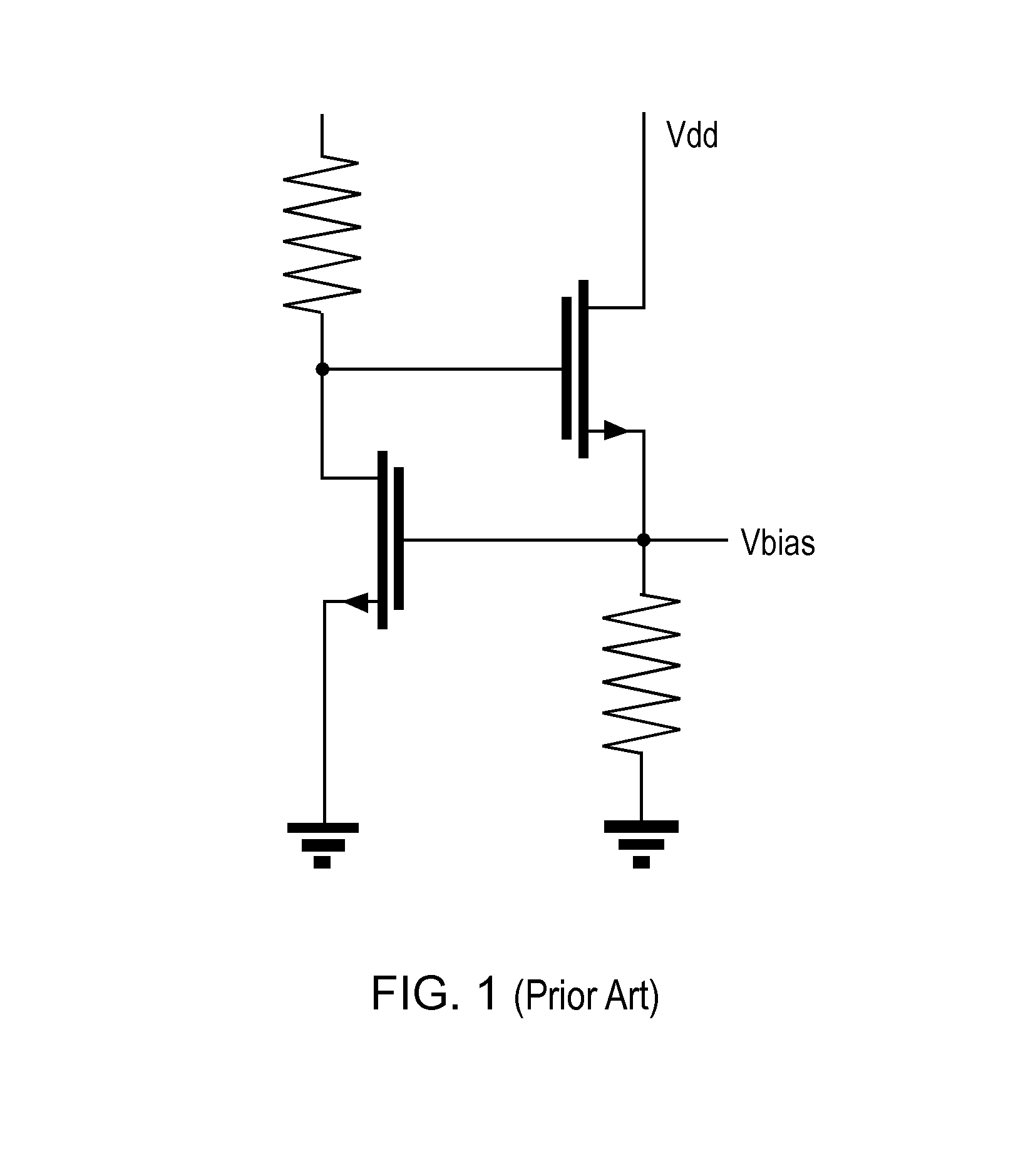
[0026]There is proposed a bias circuit which employs a current mirror circuit (similar to the conventional circuit arrangement shown in FIG. 1) to generate a bias voltage at an output terminal. The bias circuit also employs an additional transistor connected between the output terminal of the bias circuit and ground. This additional transistor can be controlled via a switch that is adapted to supply a control voltage to the control terminal (e.g. the gate) of the transistor.
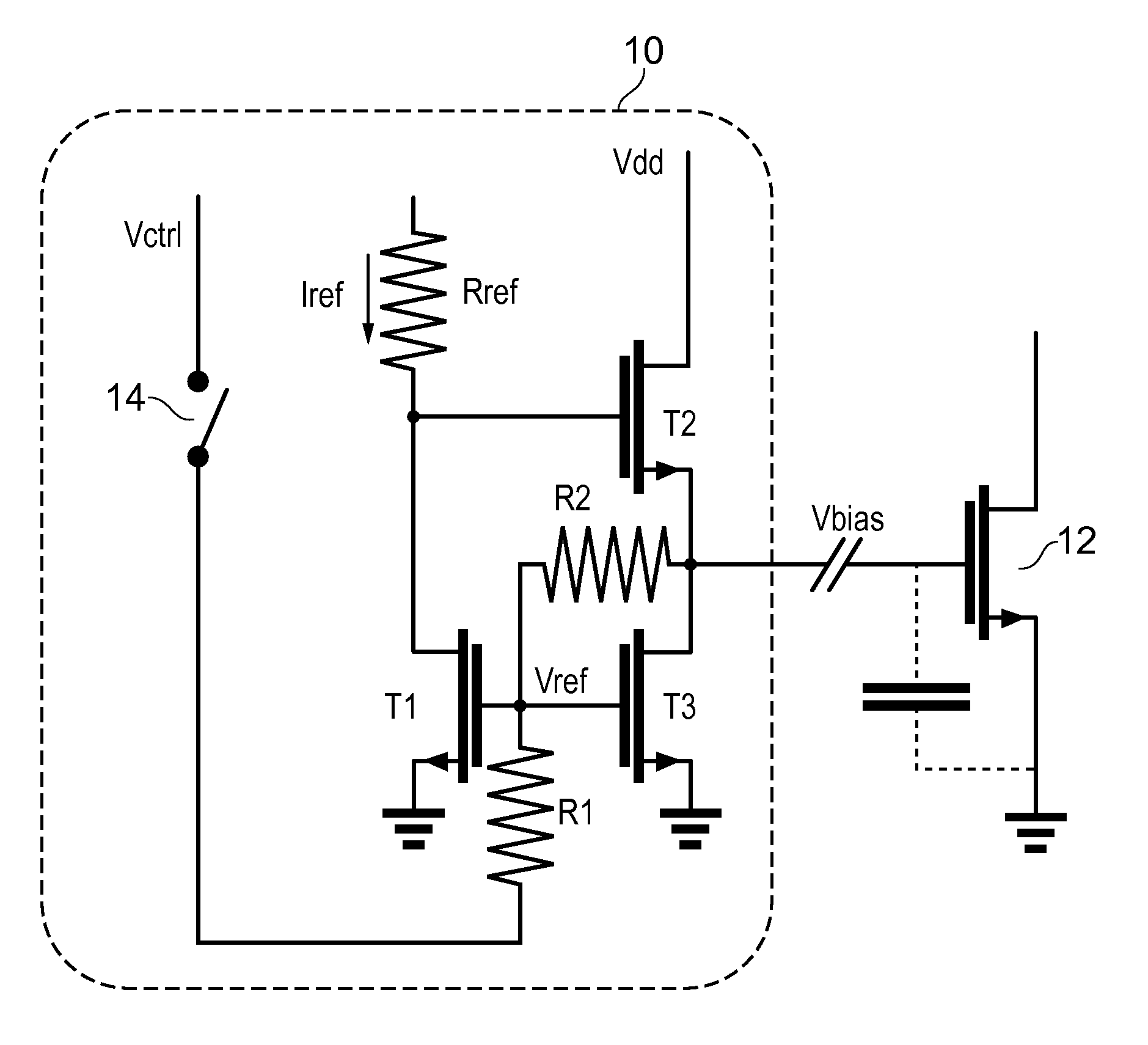
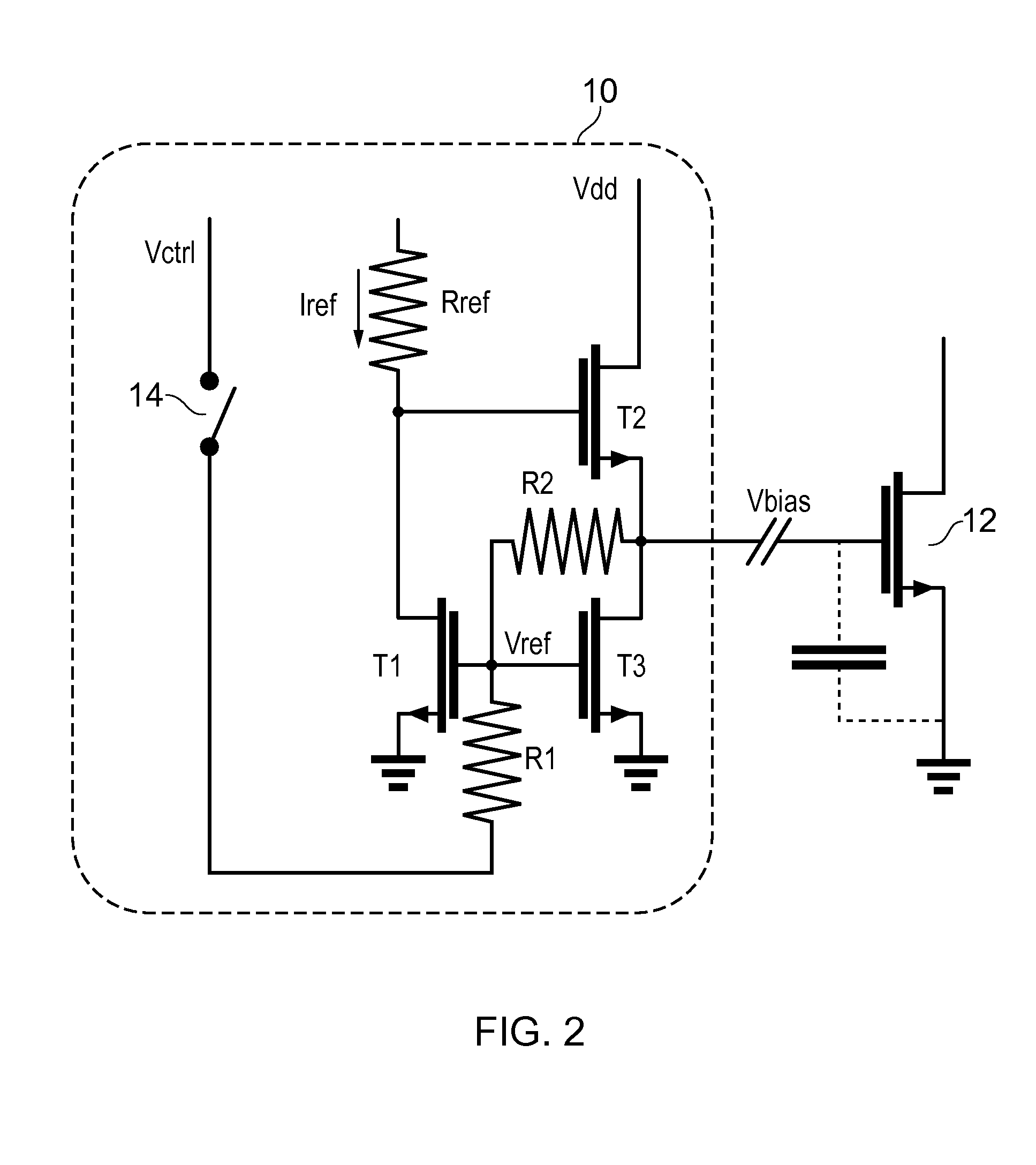
[0027]An embodiment of a bias circuit 10 is shown in FIG. 2. The bias circuit 10 comprises first T1 and second T2 transistors which are scaled versions of a RF transistor T2 to be biased. The first T1 and second T2 transistors are provided in a looped arrangement, similar to that shown in FIG. 1, wherein the drain of the first transistor T1 is connected to a current source Iref. The voltage source Vdd is connected to the drain of the second transistor T2 and the gate of the second transistor T2 is connected to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com