Glass bulb for a cathode ray and a method of producing the same
a glass bulb and cathode ray technology, applied in the direction of cathode ray tubes/electron beam tubes, electric discharge tubes, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of instantaneous release of temporal distortion, cracks in glass, and shrinkage of glass inside, so as to prevent or delay cracks, reduce the difference of brightness, and light weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the drawings.
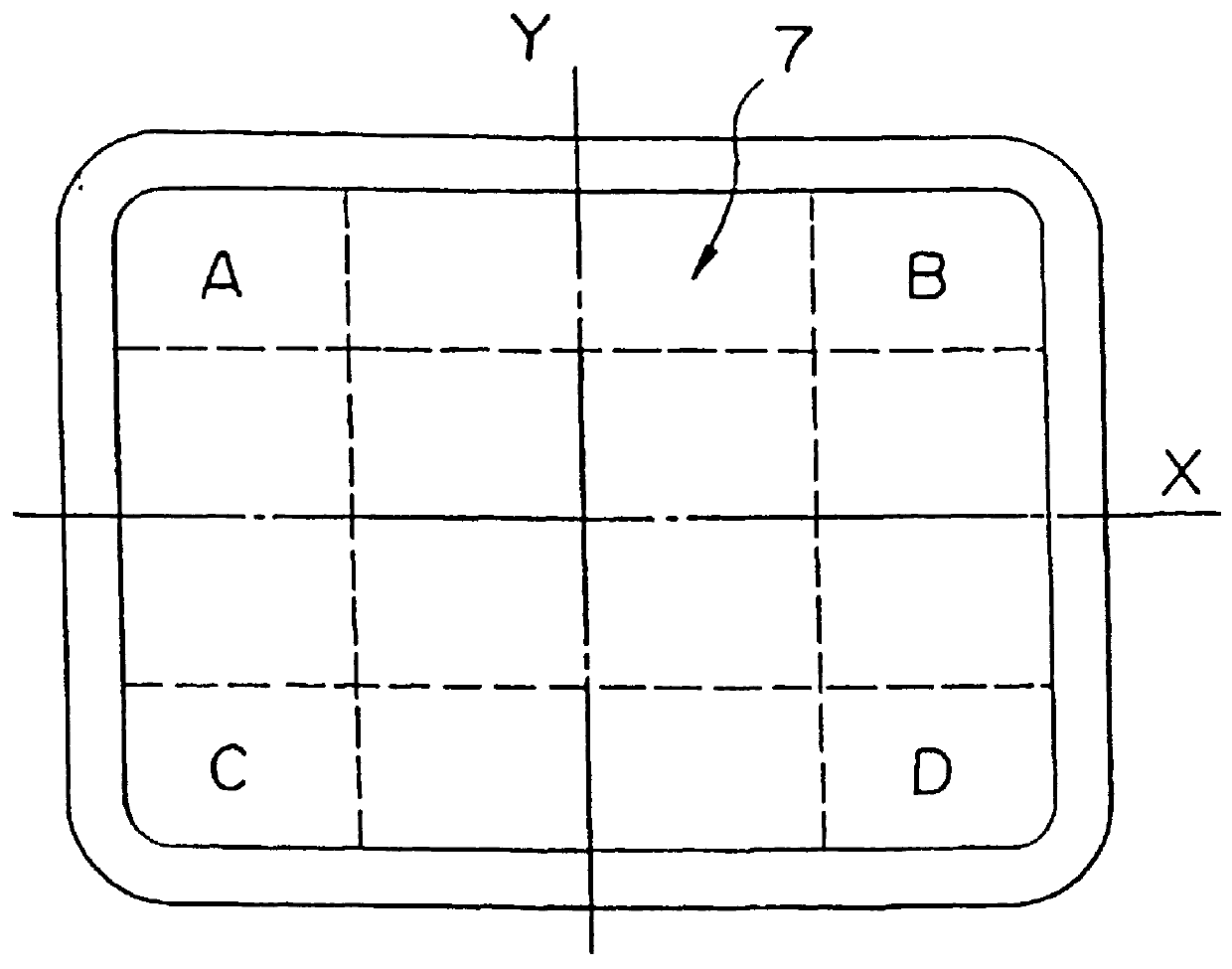
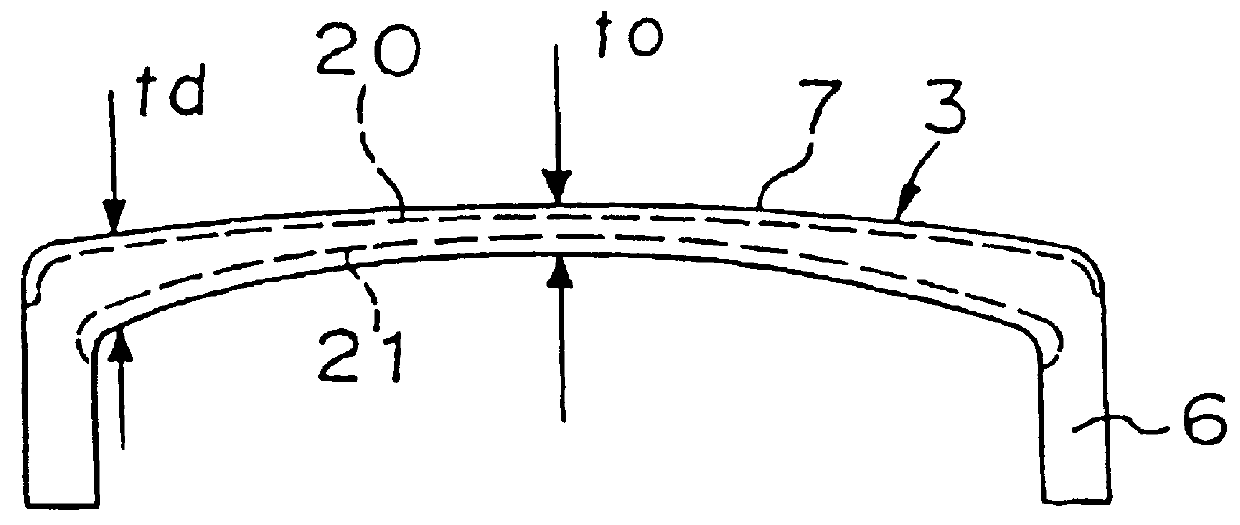
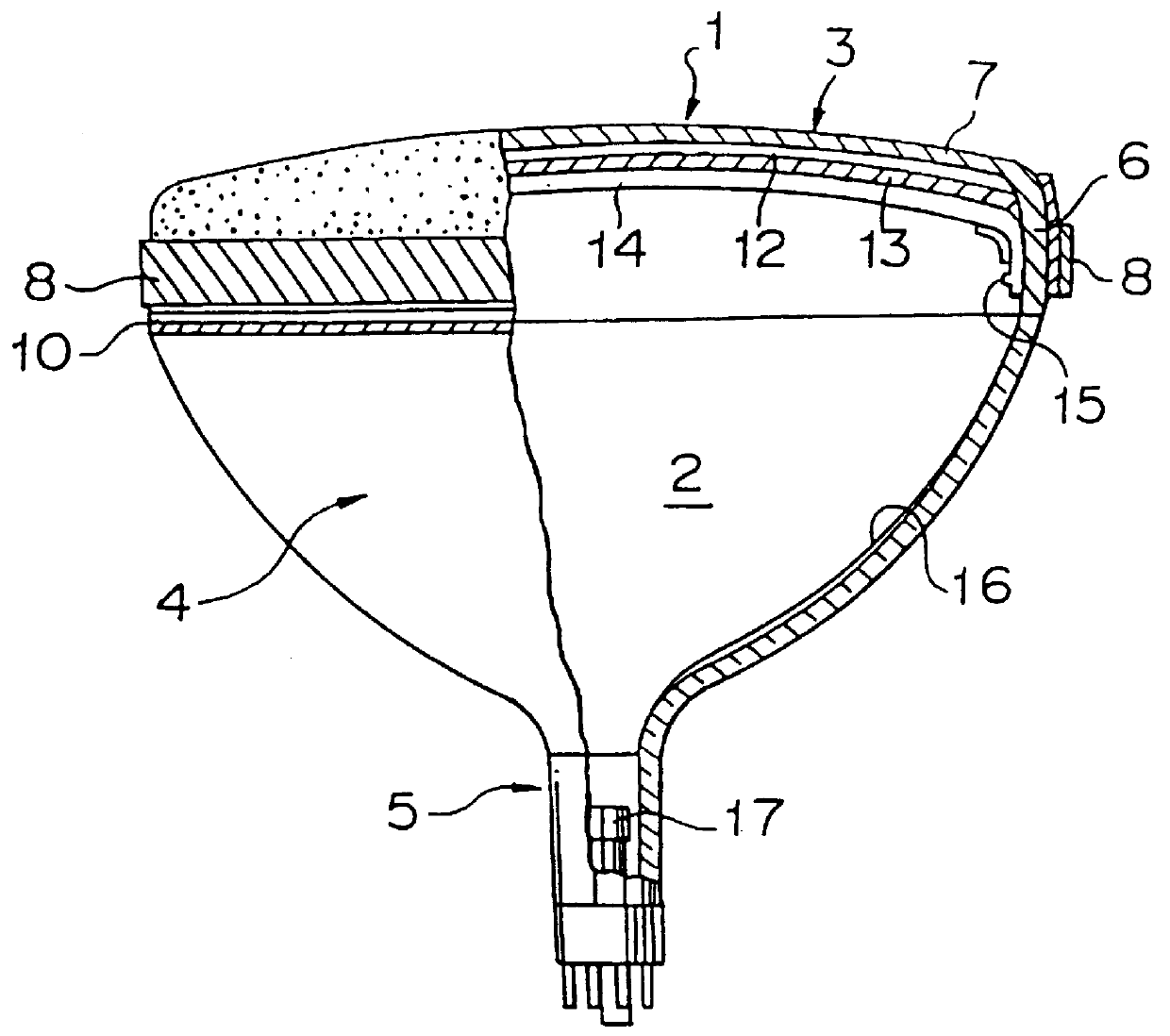
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of an embodiment of the glass panel 3 for a glass bulb for a cathode ray tube. The glass panel is formed so as to be 1.0.ltoreq.t.sub.d / t.sub.o .ltoreq.1.2 where t is the wall thickness of the central portion of a face portion 7 and t.sub.d is the wall thickness of a peripheral portion of the face portion 7. Namely, the glass panel has a uniform wall thickness by determining the ratio of the thicknesses of the central portion to the thickness of the peripheral portion of the face portion to be 1 or a new value. Thus, the light transmittance and the absorptivity coefficient of glass are substantially uniform in the entirety of the face portion, and the difference of brightness between the central portion and the peripheral portion is small, whereby the picture surface can be easily watched.
FIG. 2 is a plane view of the face portion 7 of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com