Antibodies directed against cellular coreceptors for human immunodeficiency virus and methods of using the same
a technology antibodies, which is applied in the field of infection by and pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus, can solve the problems of rapid development of viral strains, inability to infect cells, and inability to infect macrophage tropic strain ba-l
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
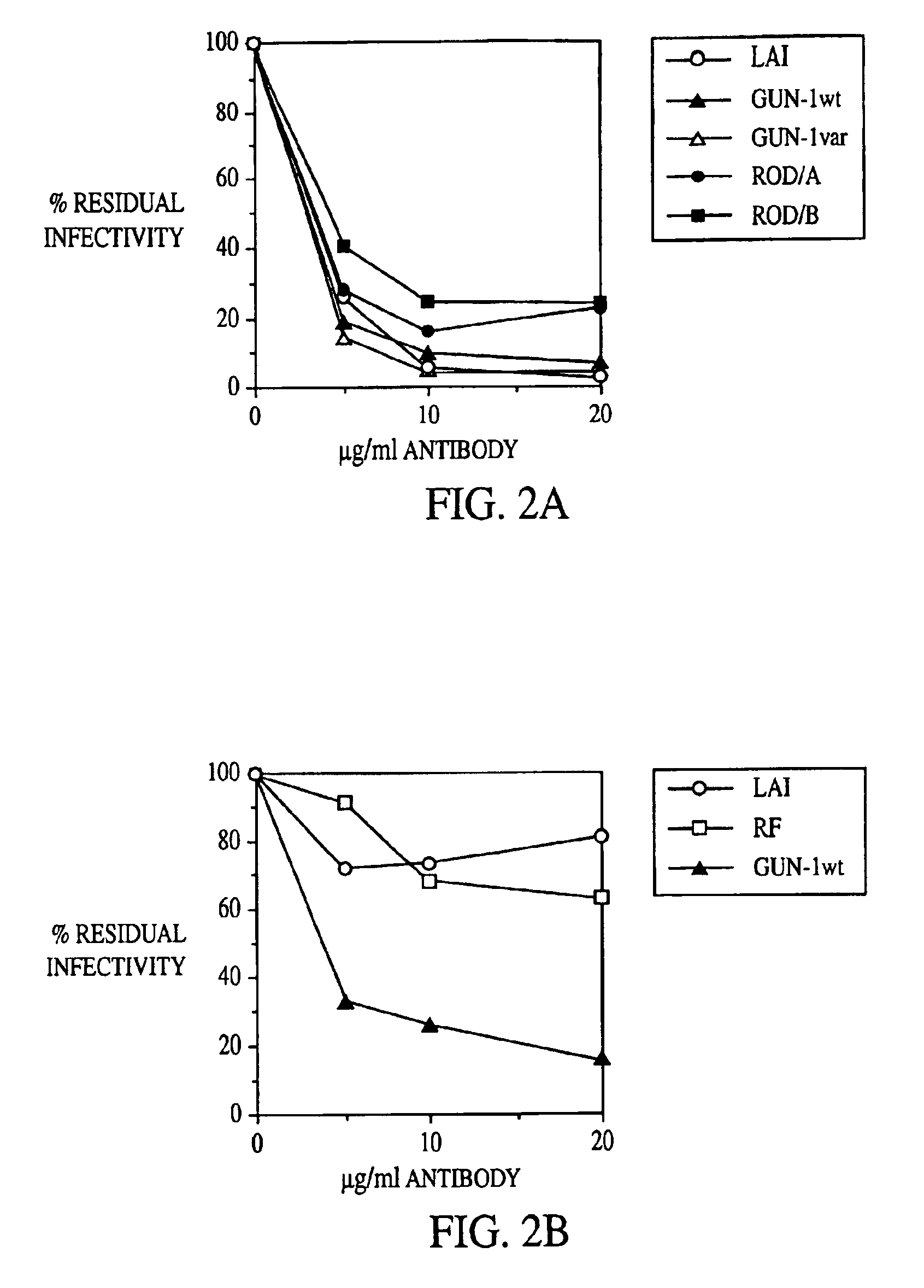
Inhibition of HIV by a Monoclonal Antibody to a Coreceptor (CXCR4) is both Cell Type and Virus Strain Dependent
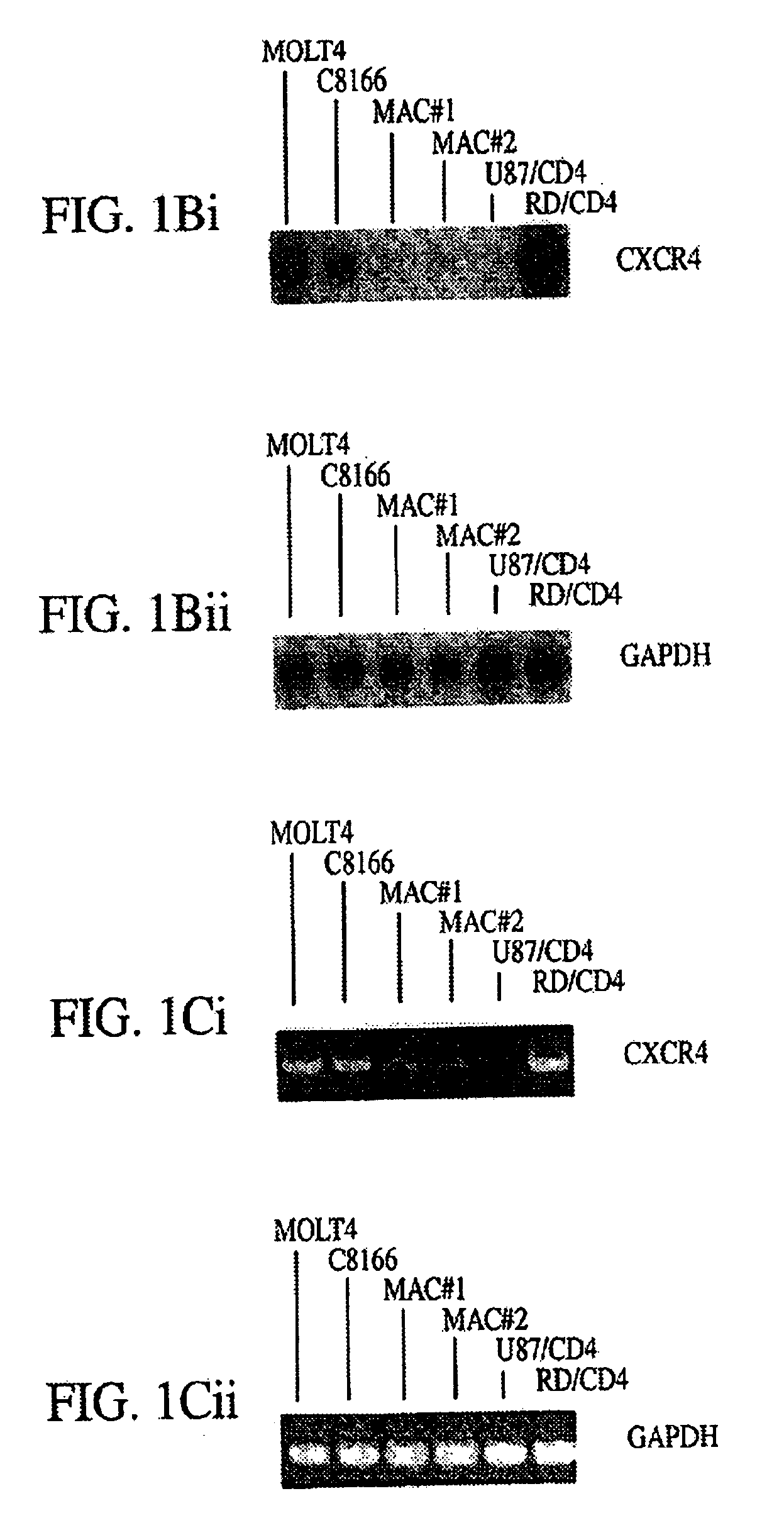
[0098]The data presented herein establish that 12G5 is a mouse MAb that specifically recognizes CXCR4 but not other members of the chemokine receptor family, including CCR1-5 and CXCR1 and CXCR2 (interleukin-8 receptors α and β, respectively).
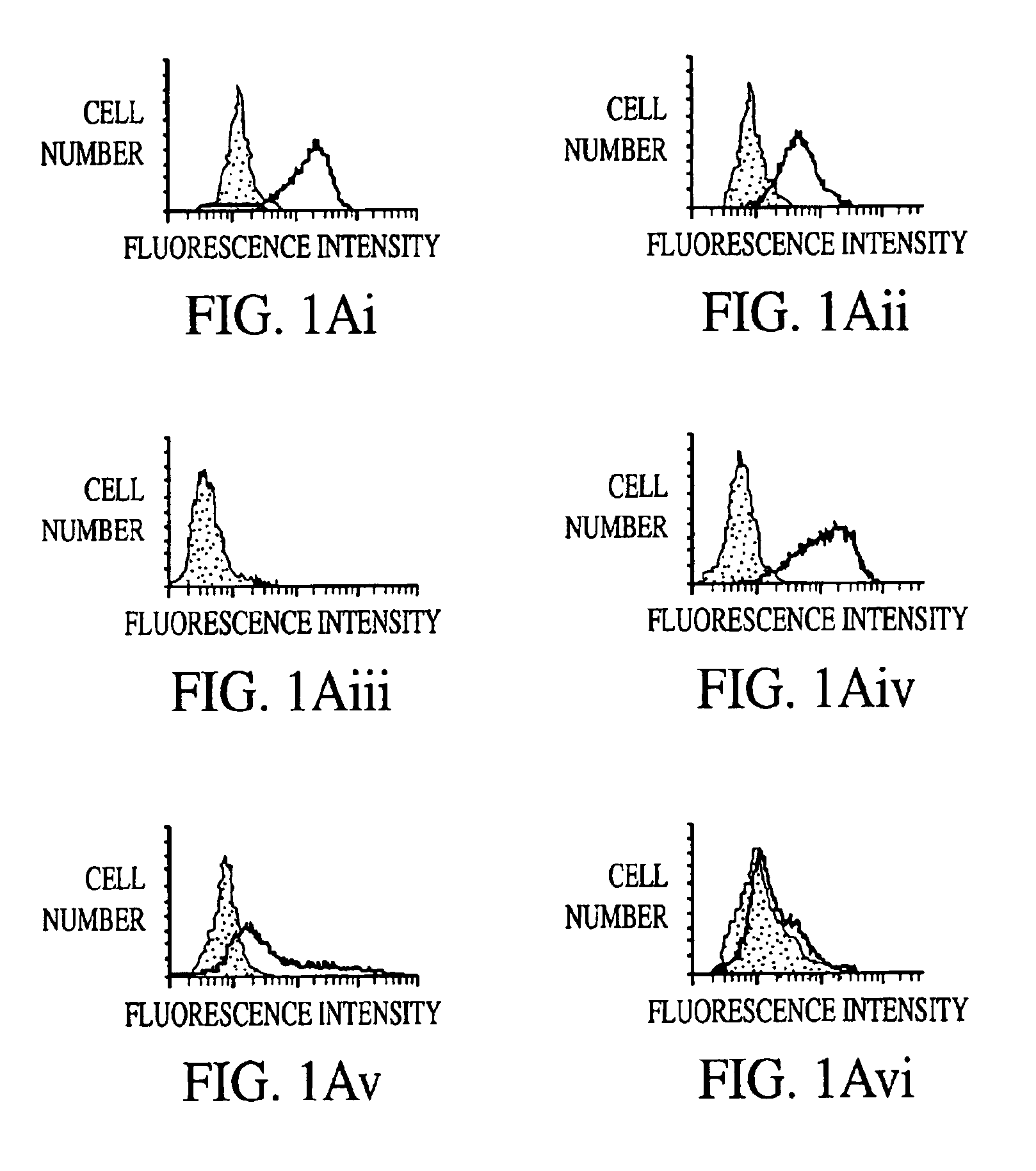
[0099]In FIG. 1A there is shown the levels of cell surface CXCR4 expression determined by flow cytometry following 12G5 staining of the CD4+ T-cell lines MOLT-4 and C8166, the CD4-transfected human rhabdomyosarcoma cell line RD, and the human glioma cell line U87 as well as primary macrophages purified by adherence to plastic and cultured for 1 or 5 days (McKnight et al., 1995, J. Virol. 69:3167-3170; and Simmons et al., 1995, Virology 209:696-700). Flow cytometry was carried out as previously described (McKnight et al., 1996, J. Virol. 70:4598-4606).
[0100]HIV infectivity of macrophages or PBMCs is routinely estimated by infecting cell...
example 2
CD4-Independent Infection by HIV-2 is Mediated by Fusin / CXCR4
[0115]The Experimental Procedures used in Example 2 are now described. Cells CD4-positive human T lymphoid cell lines, Sup-T1, Hut-78, H9, CEM, Molt4-clone8, and the TxB cell hybrid line, CEMx174, have been described previously (Hoxie et al., 1986, Science 234:1123-1127; Hoxie et al., 1988, J. Virol. 62:2557-2568; LaBranche et al., 1994, J. Virol. 68:5509-5522). CD4-negative T lymphoid lines HSB and CEMss4− are described (Weiner et al., 1991, Pathobiol. 59:361-371 and Nara et al., 1987, AIDS Res. and Hum. Retroviruses 3:283-202, respectively) and BC7 was derived from Sup-T1 cells, as described in Table 4. Human B cell lines, Nalm6, KM3.79, and REH are described (McKnight et al., 1995, J. Virol. 69:3167-3170; McKnight et al., 1996, J. Virol. 70:4598-4606) Hela, RD, and Daudi cells have been described previously (Clapham et al., 1991, supra 5; Clapham et al., 1992, supra). 293T and CCCS-L-cells are well known in the art and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com