Capsule endoscope
a technology of endoscope and capsule, which is applied in the field of endoscope of capsule, can solve the problems of large capsule size, design requires additional labor, and the oval dome size to become larger, and achieves the effect of easy and inexpensive manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
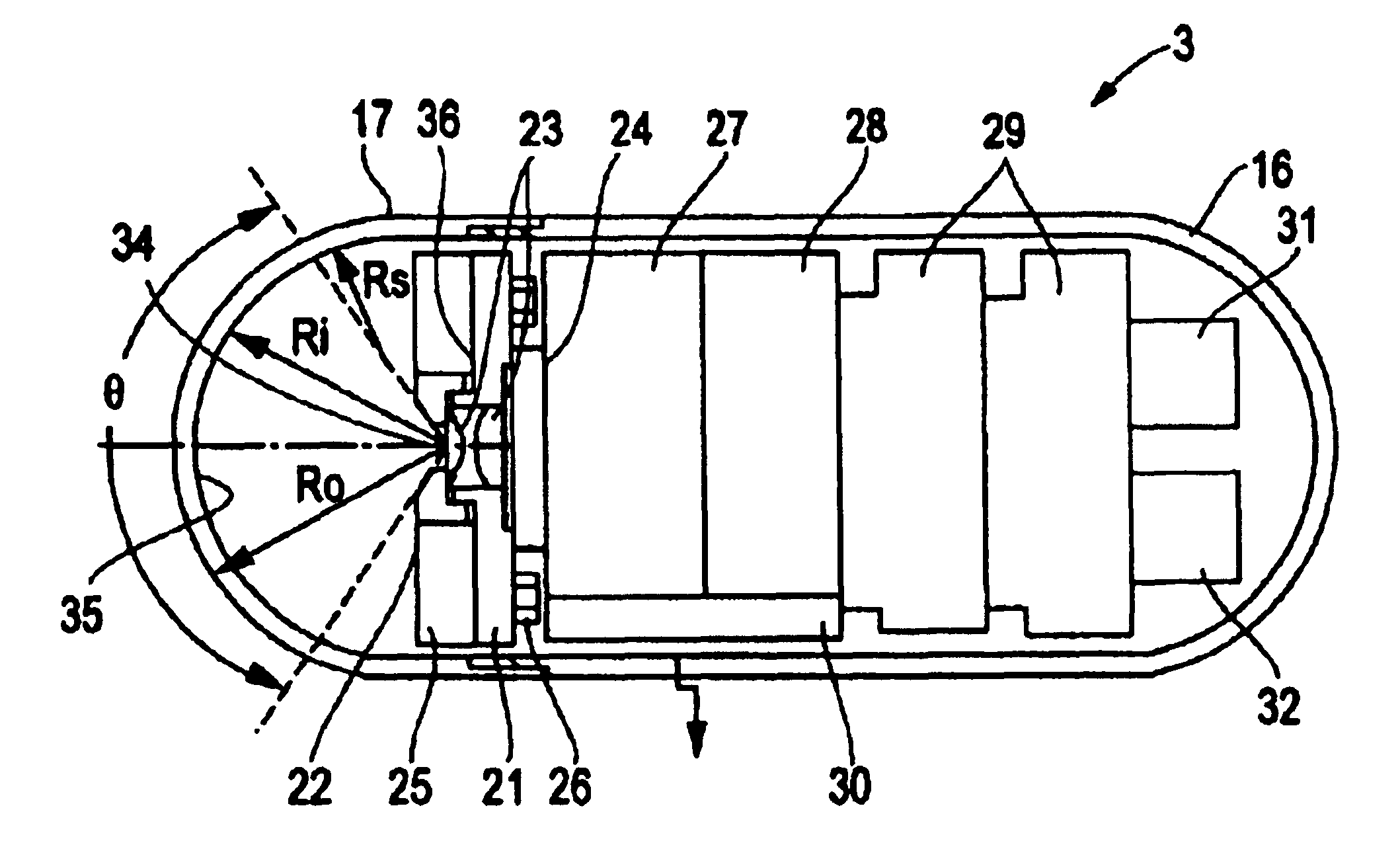
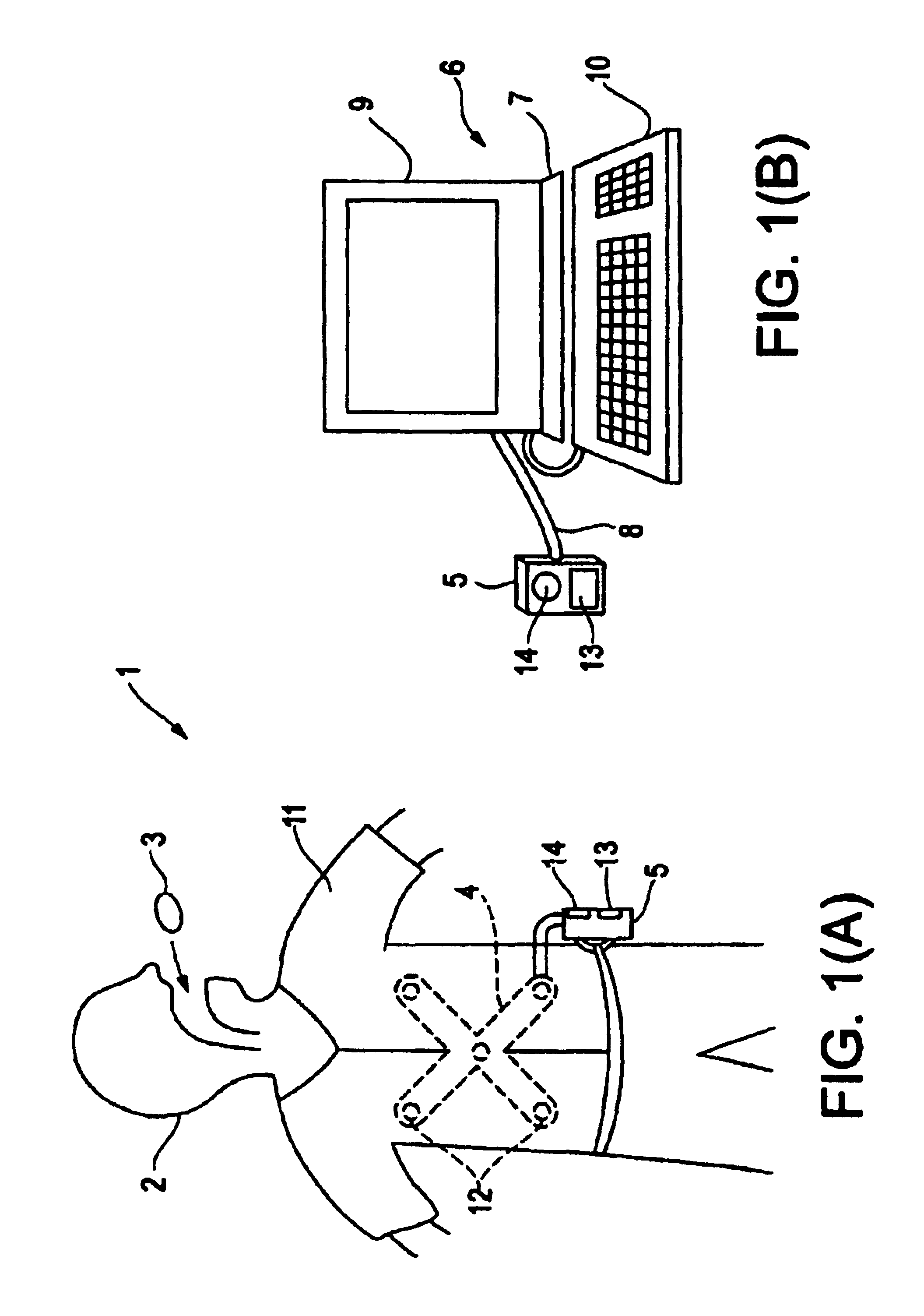
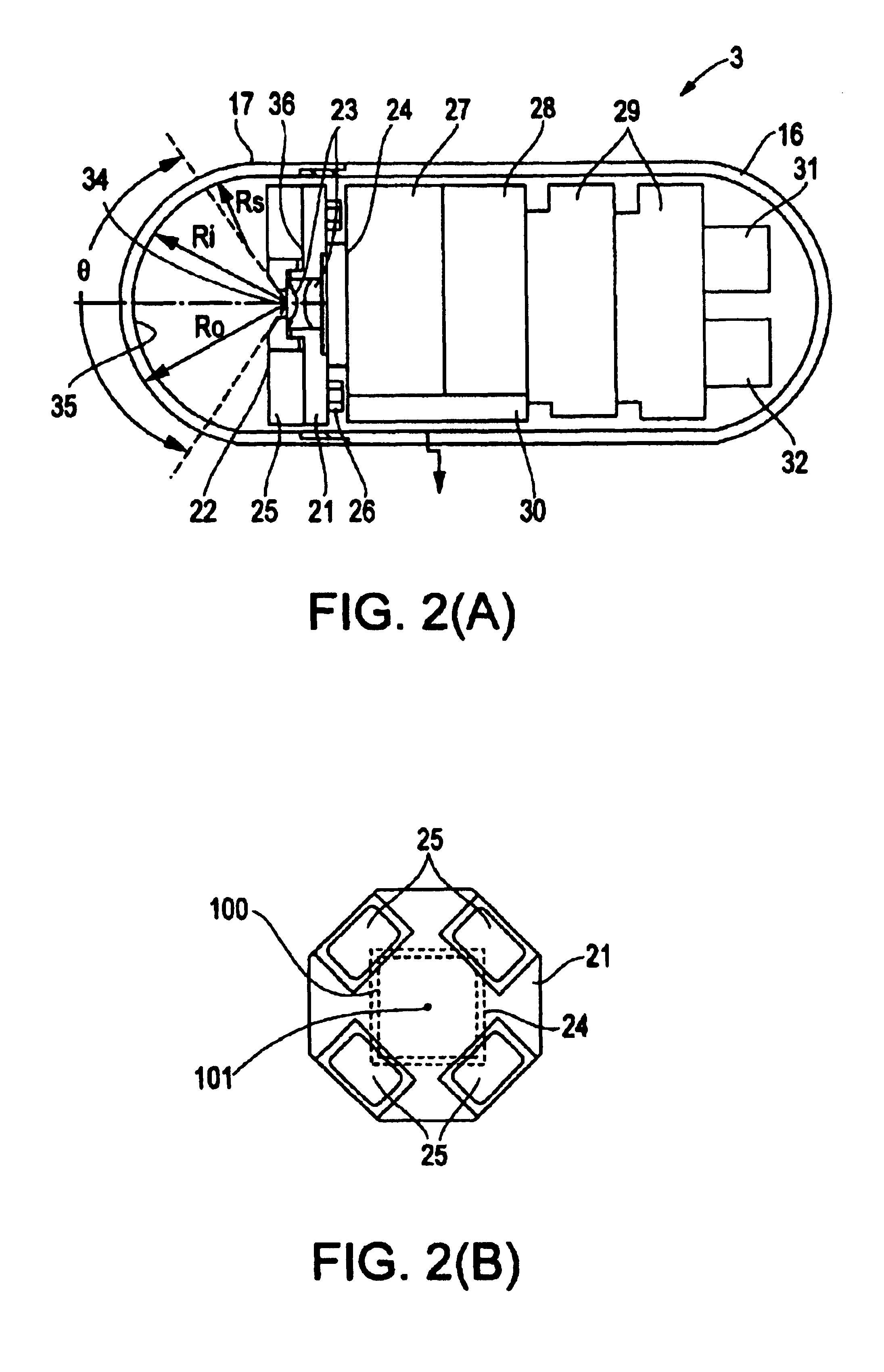
[0037]Embodiment 1 will be described with reference to FIGS. 1(A)-4(B). FIGS. 1(A) and 1(B) show a capsule endoscope system which uses a capsule endoscope according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. FIG. 2(A) is a section view showing the internal structure of the capsule endoscope. FIG. 2(B) is an illustration showing the positional relationship between the image detecting means and the illumination means when viewing the capsule endoscope axially from the object side. FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of the objective optical system. FIGS. 4(A) and 4(B) show the effects of an objective optical system that uses a semi-spherical window, with FIG. 4(A) illustrating the situation of the illuminating light being positioned at the center of curvature of the semi-spherical transparent cover, and with FIG. 4(B) illustrating the situation of the illuminating light being positioned somewhere else.
[0038]As shown in FIG. 1(A), a capsule endoscope system 1 uses a capsule endoscope 3 according...
embodiment 2
[0074]Embodiment 2 of the present invention will now be described with reference to FIG. 5. FIG. 5 is a schematic view showing the structure of the capsule endoscope 3B of Embodiment 2. The thickness of the transparent cover 17B in this embodiment is no longer uniform. Instead, the transparent cover 17B is thicker on axis and tapers so as become thinner toward the peripheral regions of the field of view. The transparent cover 17B is provided with an inner surface having a radius of curvature Ri, for example, equal to 5.5 mm within the visual field angle θ, with the center of curvature coinciding with the center of the entrance pupil 34 of the objective optical system 23.
[0075]On the other hand, the outer surface of the transparent cover 17B has a radius of curvature Ro, for example, equal to 5.5 mm within the visual field angle θ. The center of curvature of the outer surface is located on the optical axis but is positioned on the object side of the entrance pupil position 34 of the ...
embodiment 3
[0082]FIG. 10(A) is a cross-sectional view of an capsule endoscope 51 of Embodiment 3 of the present invention. FIG. 10(B) is an illustration showing the positional relationship between the illumination means and the image detecting element when viewing the capsule endoscope axially from the object side. Referring to FIG. 10(A), the capsule endoscope 51 includes a transparent front cover 52 that has a cylinder form with a semi-spherical front end and a rear cover 53 which also is shaped as a cylinder that has a semi-spherical rear end. The rear end of the transparent front cover 52 and the front end of the rear cover are fitted to each other and sealed so as to create a watertight capsule container in which an objective optical system 54 and other elements are housed.
[0083]The objective optical system 54 is formed of a first lens supported by a first lens frame 55 and a second lens supported by a second lens frame 56, and is positioned along the axis of symmetry of the capsule with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com