Method for preparing polylactic porous microball
A technology of porous microspheres and polylactic acid, which is applied in the preparation of microspheres, microcapsule preparations, etc., can solve the problems of many influencing factors, difficult control of porous structure, difficulty in ensuring the repeatability and quality of porous microspheres, and achieve mild implementation conditions , The effect of simple operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
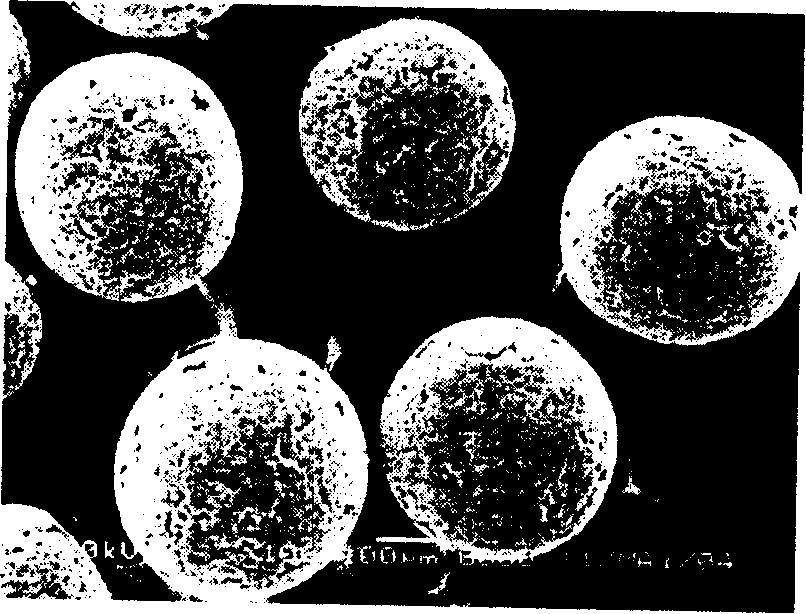
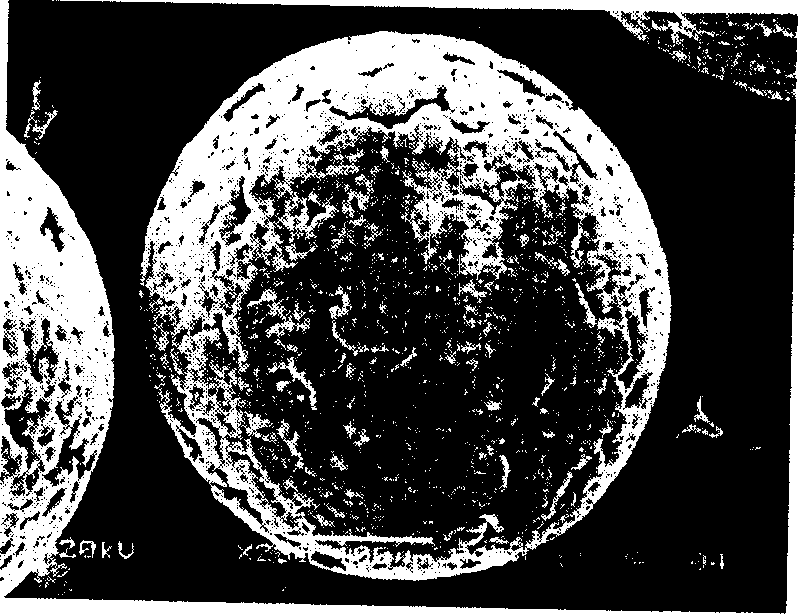
[0019] Example 1: Dissolve 0.5g of polylactic acid in 9ml of methylene chloride, add 1ml of n-hexane, mix well, and set aside. In a 200ml beaker, 100ml of polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution with a weight volume concentration of 0.8% was added. Start stirring at a stirring speed of 500 rpm, and pour the polylactic acid in dichloromethane / n-hexane solution. The temperature was 25°C, and the mixture was stirred for 24 hours to completely evaporate the organic solvent. After the stirring was stopped, the microspheres were suspended on the surface of the solution, filtered, washed repeatedly with deionized water, collected and dried under vacuum at 35°C for 3 days. Yield is 98%, microsphere number-average particle diameter d=290 micron, see figure 1 ;The apparent density is 0.2891g / cm 3 , with an average internal pore diameter of 16±3 microns, see Figure 2a ~ Figure 2d .
example 2
[0020] Example 2: Dissolve 0.5g of polylactic acid in 9ml of dichloromethane, add 1ml of n-octane, mix well, and set aside. In a 200ml beaker, 100ml of polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution with a weight volume concentration of 0.8% was added. Start stirring at a stirring speed of 300 rpm, and pour the polylactic acid in dichloromethane / n-hexane solution. The temperature was 25°C, and the mixture was stirred for 24 hours to completely evaporate the organic solvent. After the stirring was stopped, the microspheres were suspended on the surface of the solution, filtered, washed repeatedly with deionized water, collected and dried under vacuum at 35°C for 3 days. Yield is 97.7%, microsphere average particle size d=471 micron, see image 3 ;The apparent density is 0.2136g / cm 3 , with an average internal pore diameter of 24 ± 4 microns, see Figure 4a ~ Figure 4d .
example 3
[0021] Example 3: Dissolve 0.5g of polylactic acid in 8ml of dichloromethane, add 2ml of n-hexane, mix well, and set aside. In a 200ml beaker, 100ml of polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution with a weight volume concentration of 0.8% was added. Start stirring at a stirring speed of 500 rpm, and pour the polylactic acid in dichloromethane / n-hexane solution. The temperature was 25°C, and the mixture was stirred for 24 hours to completely evaporate the organic solvent. After the stirring was stopped, the microspheres were suspended on the surface of the solution, filtered, washed repeatedly with deionized water, and dried under vacuum at 35° C. for 3 days after collection. Yield is 99%, microsphere mean diameter d=413 micron, see Figure 5 ;The apparent density is 0.1726g / cm 3 , with an average internal pore diameter of 30±5 microns, see Figure 6a ~ Figure 6d .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com