Method for recognizing non-gauged star map
A star map recognition and non-calibration technology, applied in the field of star map recognition, can solve the problems of grid algorithm influence, grid deviation, focal length change, etc., to achieve the effect of speeding up speed and efficiency, reducing occupation, and reducing storage space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
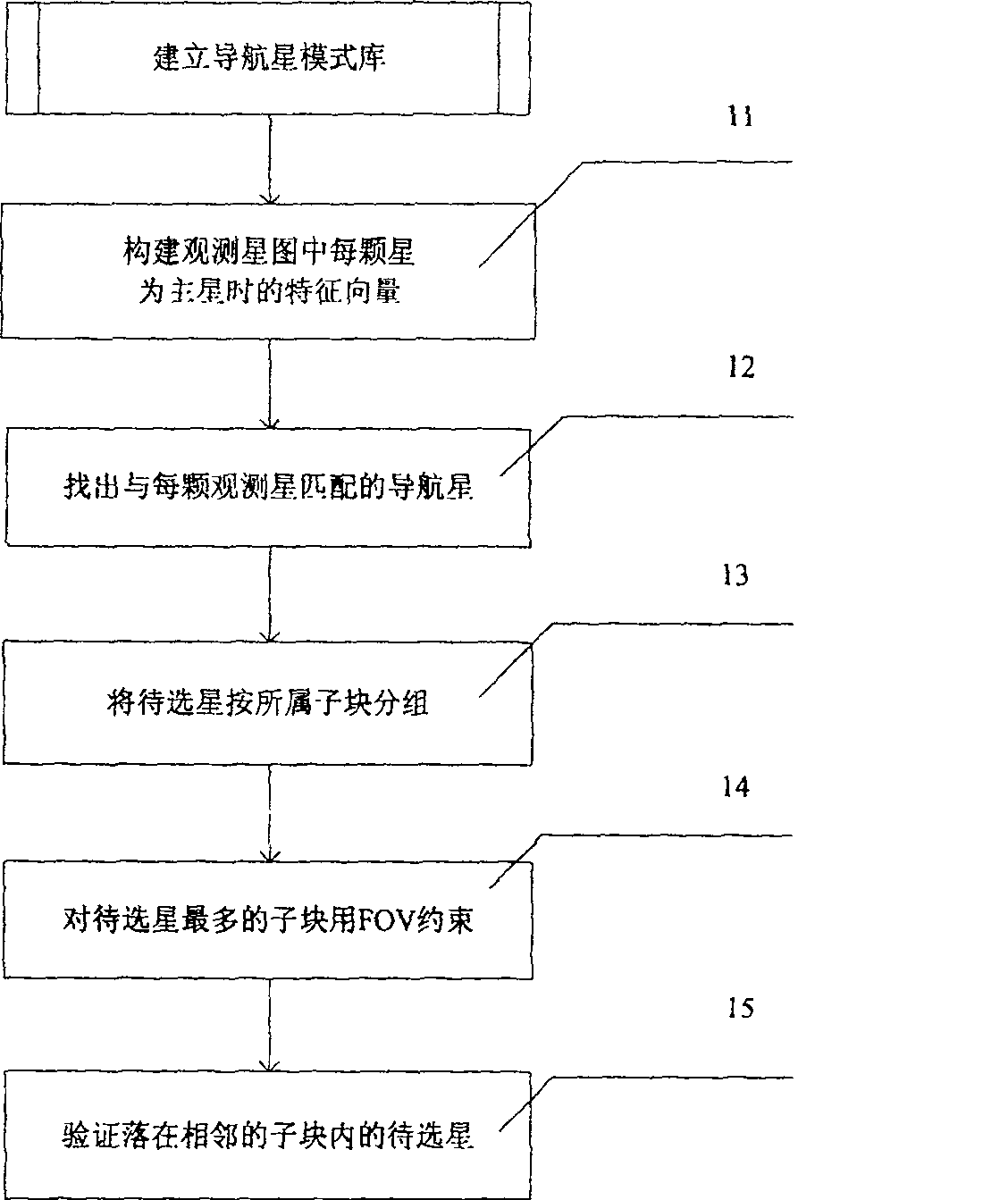
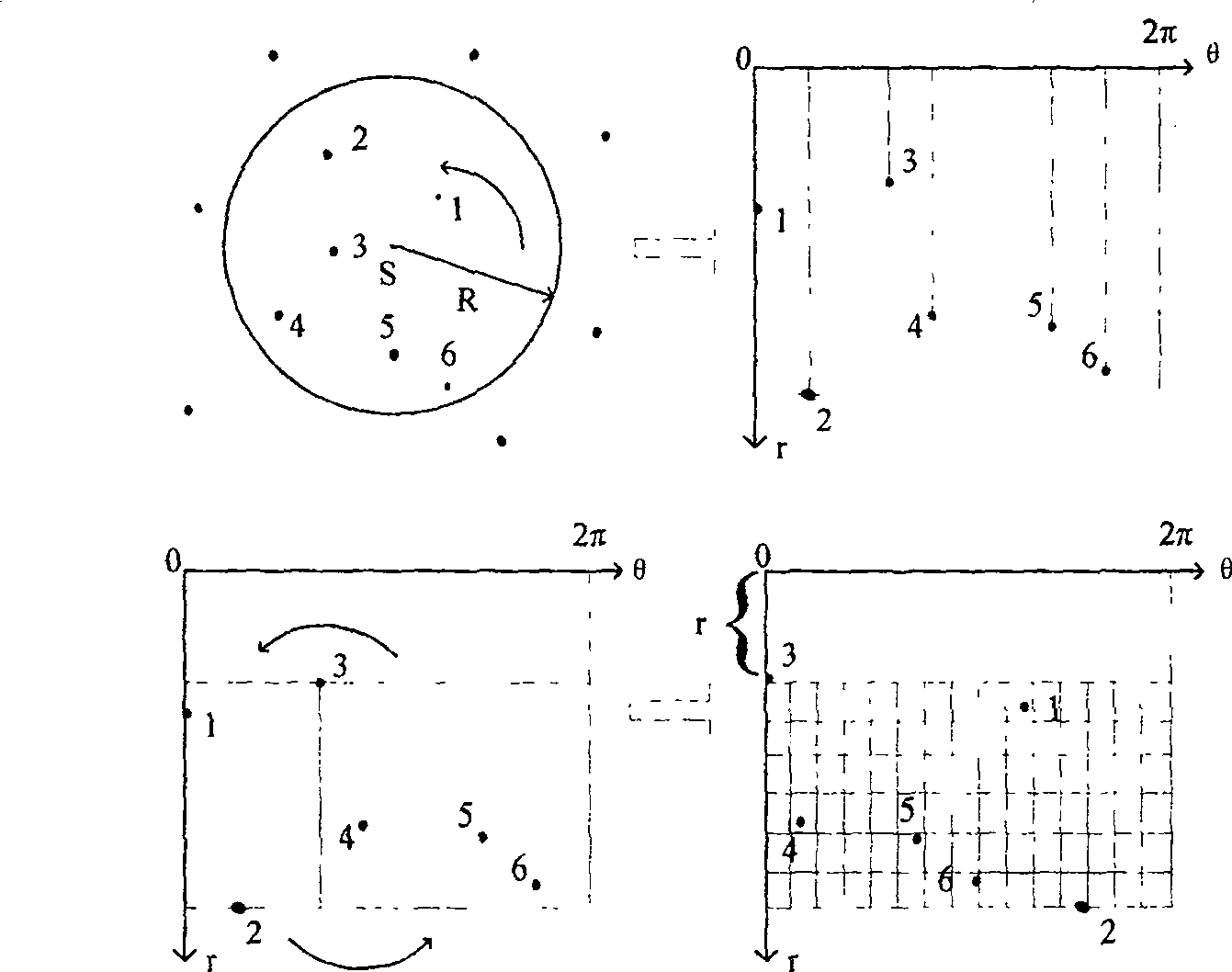
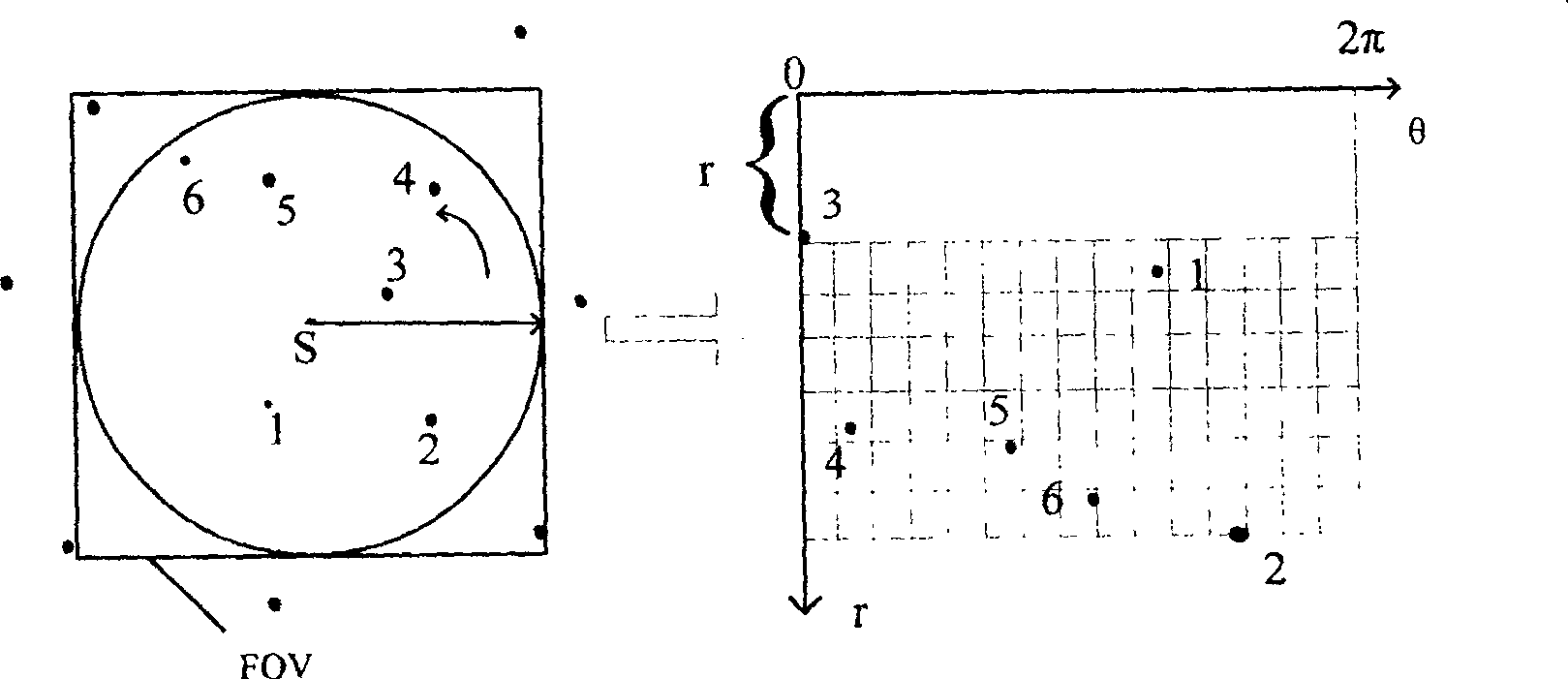
[0030] The main idea of the present invention is: extract the feature vector of the navigation star, set up a navigation star pattern library based on raster data storage; extract the feature vector according to the pattern of the navigation star from the observation star map, and then use the observation star map and the navigation star pattern library According to the initial matching result of the star to be selected, the star to be selected is determined, and the star to be selected is grouped according to the uniform division method of the celestial sphere, and the direction of the field of view is determined according to the sub-block attribution of the star to be selected.
[0031] Wherein, the extraction of the feature vector of the star map mainly uses the radial feature and the circular feature.
[0032] figure 1 It is the realization flowchart of the star...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com