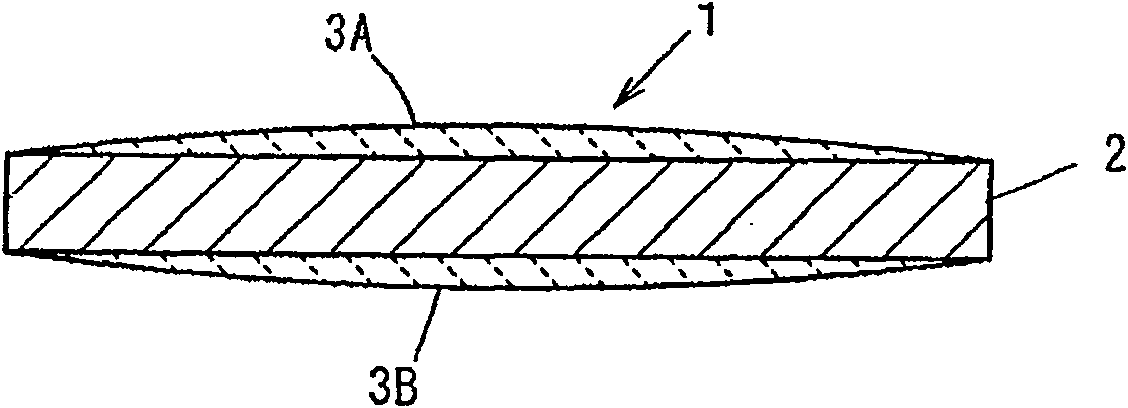
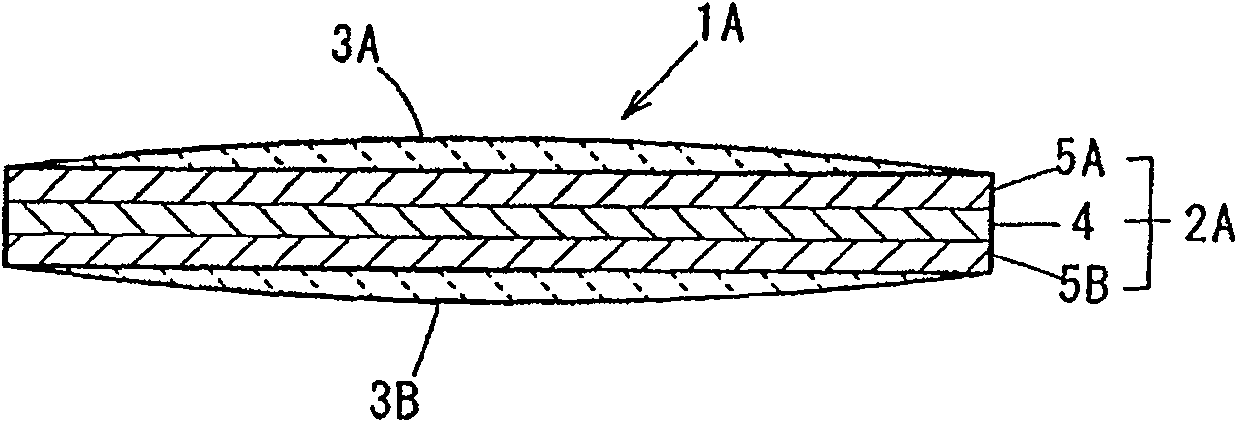
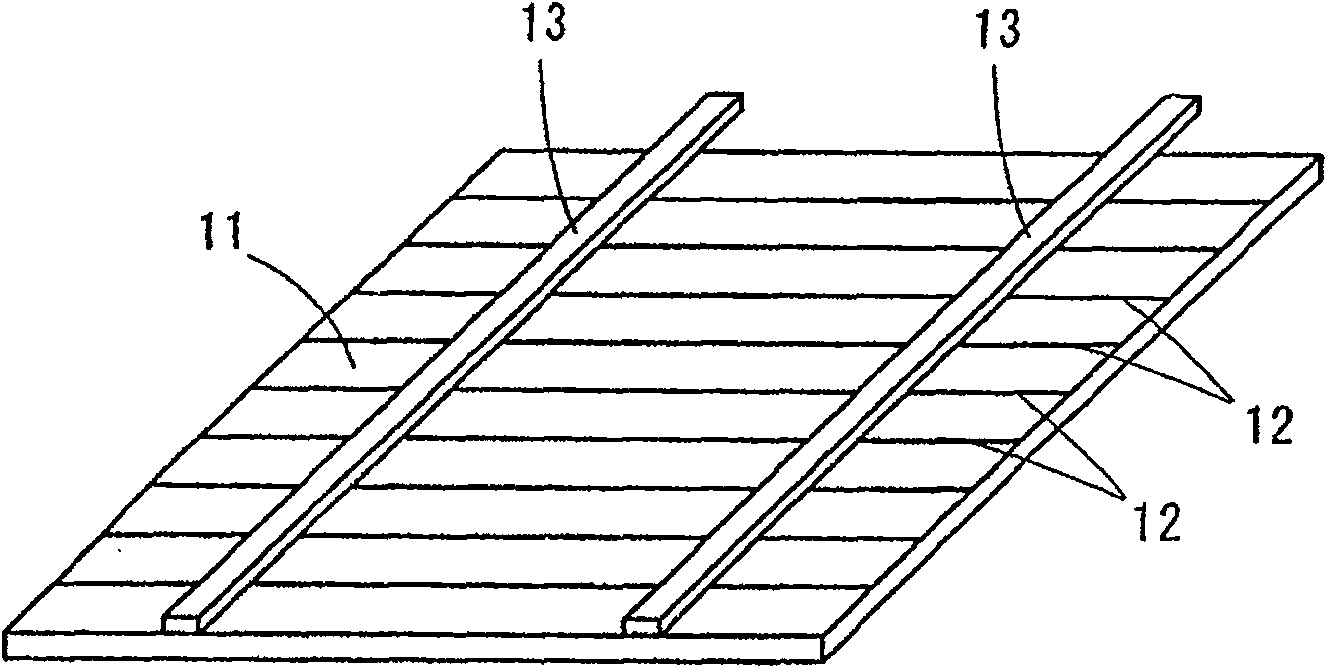
Process for producing electrode wire for solar battery
A technology of solar cells and manufacturing methods, which is applied to circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as semiconductor substrates that are prone to cracks, and achieve excellent power generation efficiency and excellent conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Various clad materials having a plate thickness of 160 μm having intermediate layers of various thicknesses were produced. The above-mentioned cladding material is produced by the following method: on both sides of the intermediate layer raw material composed of an aluminum plate (material JIS 1N90, Al: 99.90mass%, annealed material) or an invar alloy plate (Fe-36.5mass% Ni, annealed material) , superimpose the surface layer raw material composed of oxygen-free copper plate (Cu: 99.97mass%, O: 15ppm, plate thickness 1.0mm, annealed material), press-bond the superimposed material at a reduction rate of 70%, and further press-bond the superimposed material at a reduction rate of 50-80%. The reduction rate of the crimping material is fine-rolled. Table 1 shows the ratio of the total reduction rate from the layered material to the cladding material and the thickness of the intermediate layer to the overall thickness of each cladding material. On the other hand, the above-m...
Embodiment 2
[0050] An aluminum plate (thickness: 0.5 mm) and a copper plate (thickness: 1.0 mm) made of oxygen-free copper were prepared to prepare a clad material with a final thickness of 200 μm. The above-mentioned cladding material is produced by superimposing the above-mentioned copper plate on both sides of the above-mentioned aluminum plate, crimping the superposed material at a reduction rate of 65-75%, and further finishing rolling the crimped material. The total reduction from superimposed material to cladding material is 92%. On the other hand, a copper plate (plate thickness: 2.5 mm) of oxygen-free copper was rolled to produce a Cu single-layer material (copper plate) with a thickness of 200 μm. Thereafter, these cladding materials and Cu single-layer materials were cut, respectively, to produce strip-shaped primary core materials with a width of 2 mm. The cladding material and the Cu single-layer material described above respectively constitute the core material raw material...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com