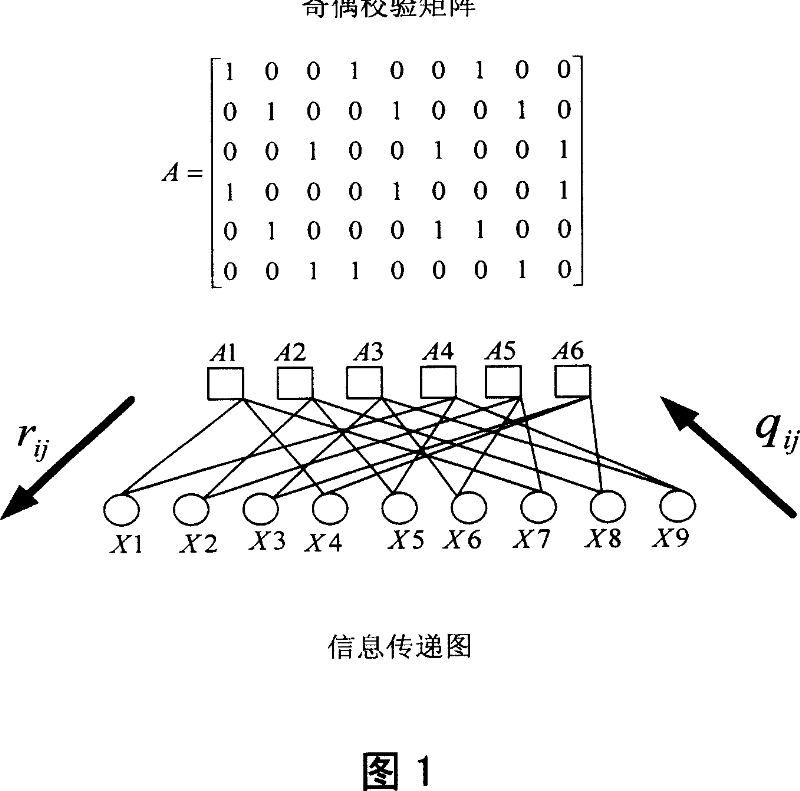
High-order coded modulation method based on low density check code
A technology of low-density parity check code and coded modulation, applied in the field of high-order coded modulation, which can solve problems such as uncertainty, not being accurate, and not being able to analyze the UEP characteristics of regular LDPC codes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Fig. 8 shows a schematic diagram of a high-order modulation method of a general LDPC code. First, assume that the high-order modulation is m-order, that is, consists of m bits (a 1 …a m ) to select a modulation symbol on the constellation diagram, and set a 1 to a m are sorted from strong to weak. The source data block S is encoded by LDPC to obtain the encoded data block U, and the protection ability of each bit of the encoded data block is sorted from small to large to obtain the sorted data block V. The protection capability here is equivalent to the protection level of each bit defined in [Document 27] mentioned above, and a fixed sorting table can be calculated in advance, and each sorting is equivalent to an interleaving operation. Divide the sorted data block V equally into m sorted sub-data blocks, V={V 1 , V 2 ,...,V m ) (if V is not divisible by m, coded bits with no real meaning (all 1 or all 0 or other appropriate bit sequences) can be added appropria...
Embodiment 2
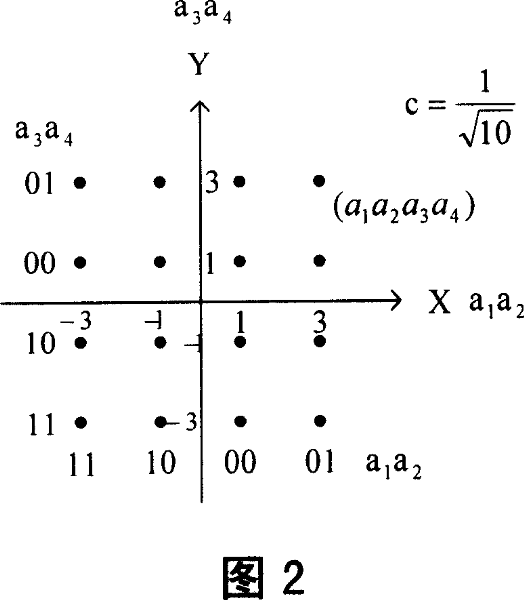
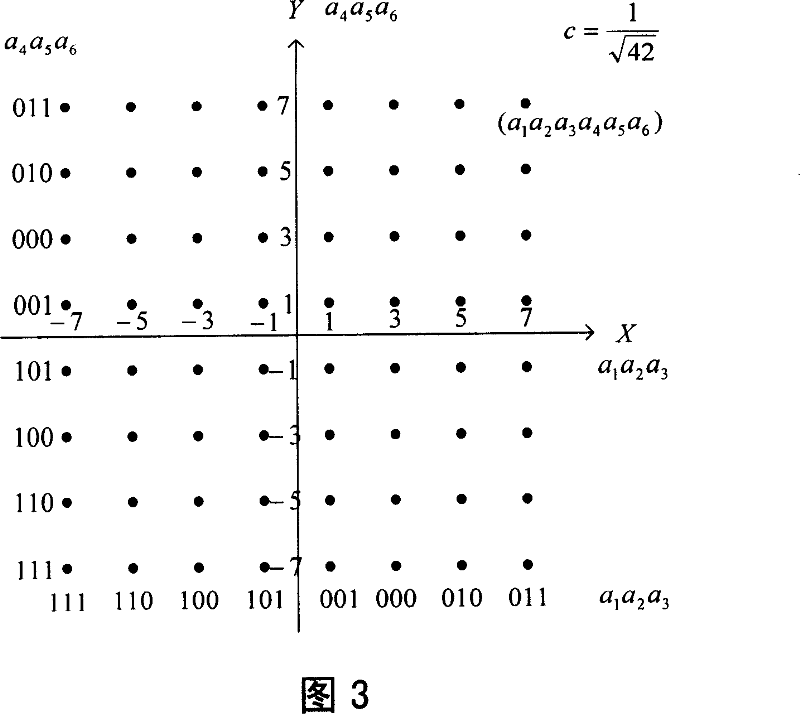
[0058] In practical application, high-order modulation usually adopts the way of I / Q channel symmetrical modulation. For 16QAM shown in Figure 2 and 64QAM shown in Figure 3, the Gray mapping used by the I and Q paths is the same. Without loss of generality, it is assumed that in the m-order high-order modulation, the I channel adopts bits, while the Q way uses bits, from a 1 arrive in order from strong to weak, and with is perfectly symmetrical. Therefore, the high-order modulation bits in the symmetrical mode have levels.
[0059] Figure 9 shows the high-order modulation method of the LDPC code with symmetrical I / Q modulation. The source data block S is encoded by LDPC to obtain the encoded data block U, and the protection ability of each bit of the encoded data block is sorted from small to large to obtain the sorted data block V. A fixed sorting table can be calculated and obtained in advance, and each sorting is equivalent to an interleaving operation. Di...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3 FIG. 10 is a high-order modulation method of LDPC code modulated by 16QAM. 16QAM adopts the constellation mapping diagram of 16QAM Gray (Golay) coding shown in FIG. 2 . The source data block S is encoded by LDPC to obtain the encoded data block U, and the protection ability of each bit of the encoded data block is sorted from small to large to obtain the sorted data block V. A fixed sorting table can be calculated and obtained in advance, and each sorting is equivalent to an interleaving operation. Divide the sorted data block V into 2 sorted sub-blocks equally, V={V 1 , V 2}. Among them, V 1 is a data block with low protection ability, and V 2 It is a data block with high protection capability. Each sorted sub-data block undergoes serial-to-parallel conversion, and then performs its own interleaving to obtain the interleaved sub-data block W 1 and W 2 . The interleaving here should ensure that the bits belonging to the same parity formula are plac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com