Prevention and treatment of synucleinopathic and amyloidogenic disease
A technology of synuclein, disease, applied in the field of prevention and treatment of synucleinopathies and amyloidosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0331] Immunization of human α-synuclein transgenic mice with human α-synuclein results in high titers of anti-α-synuclein antibodies capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier
[0332]The full-length recombinant human α-SN was resuspended in 1X phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at a concentration of 1 mg / ml. For each injection, 50 μl of α-SN was used; to give a final concentration of 50 μg per injection, an additional 150 μlX PBS was added. Freund's complete adjuvant was then added 1:1 to [alpha]-SN or PBS alone (control), vortexed and sonicated to completely resuspend the emulsion. For the initial injection, eight single-transgenic D-line human α-SN transgenic (tg) mice (Masliah et al., Science 287:1265-1269 (2000)) aged 4-7 months received human α-SN transgenic (tg) mice in CFA. -SN injection, as a control, 4 line D human α-SN tg mice received PBS injection in CFA. Mice received a total of 6 injections. Three injections were given two weeks apart, and three subsequent inj...
Embodiment II
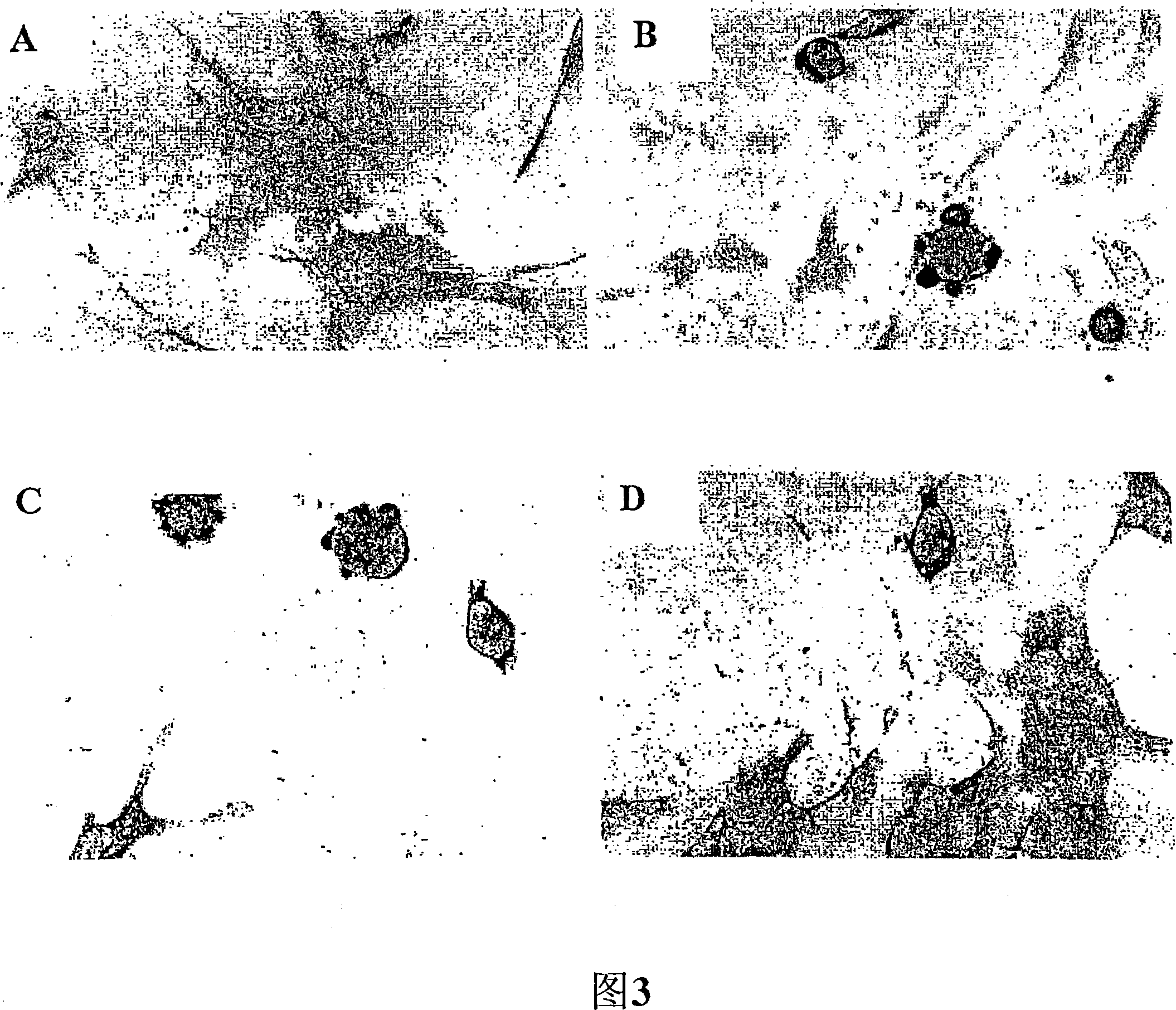
[0335] In vitro screening of antibodies that clear synuclein inclusion bodies
[0336] GT1-7 neuronal cells (Hsue et al. Am.J.Pathol.157:401-410 (2000)) were transfected with pCR3.1-T expression vector expressing murine α-SN (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), and Comparison with cells transfected with the expression vector alone (Figure 3, experimental groups B and A, respectively). Cells transfected with the carrier alone (experimental group A) showed fibrosis, while the cells transfected with α-SN were round, and the inclusion bodies on the cell surface could be observed by optical and confocal scanning microscopes . Then use rabbit pre-immune serum (experimental group C) or 67-10, the rabbit polyclonal antibody (Iwai et al., Neuron 14: 467 (1995) against mouse α-SN C-terminal residue 131-140 of affinity purification ) (experimental group D) treated transfected cells. It can be seen that the levels of synuclein in the cytoplasmic fraction were not significantly changed by treatm...
Embodiment III
[0339] Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of immunization with alpha-synuclein
[0340] i. Immunization of human α-synuclein transgenic mice
[0341] For this study, heterozygous human α-SN transgenic (tg) mice (strain D) (Masliah et al, 2000, Science 286: 1265-69) and non-transgenic (nontg) controls were used. Experimental animals were divided into 3 groups. For group I, the preventive effect of early immunization was determined by immunizing mice for 8 months starting from 2 months of age. For group II, young adult mice were immunized starting at 6 months of age for 8 months to determine whether immunization reduced disease progression once the appropriate pathology had been established. For Group III, adult mice were immunized for 4 months at 12 months of age to determine whether immunization reduced the severity of symptoms once stronger pathology had established. For all groups, mice were immunized with recombinant human α-SN plus CFA or CFA only, and 20 transgenic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com