Middle-high-temperature solar vacuum heat-collecting tube glass end cap packaging structure and fabrication technology
A vacuum heat collector tube and packaging structure technology, applied in the field of solar thermal utilization, can solve the problems of heat loss of metal end caps, low lead sealing temperature, etc., and achieve the effects of overcoming large heat loss, improving use reliability, and reliable connection and sealing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
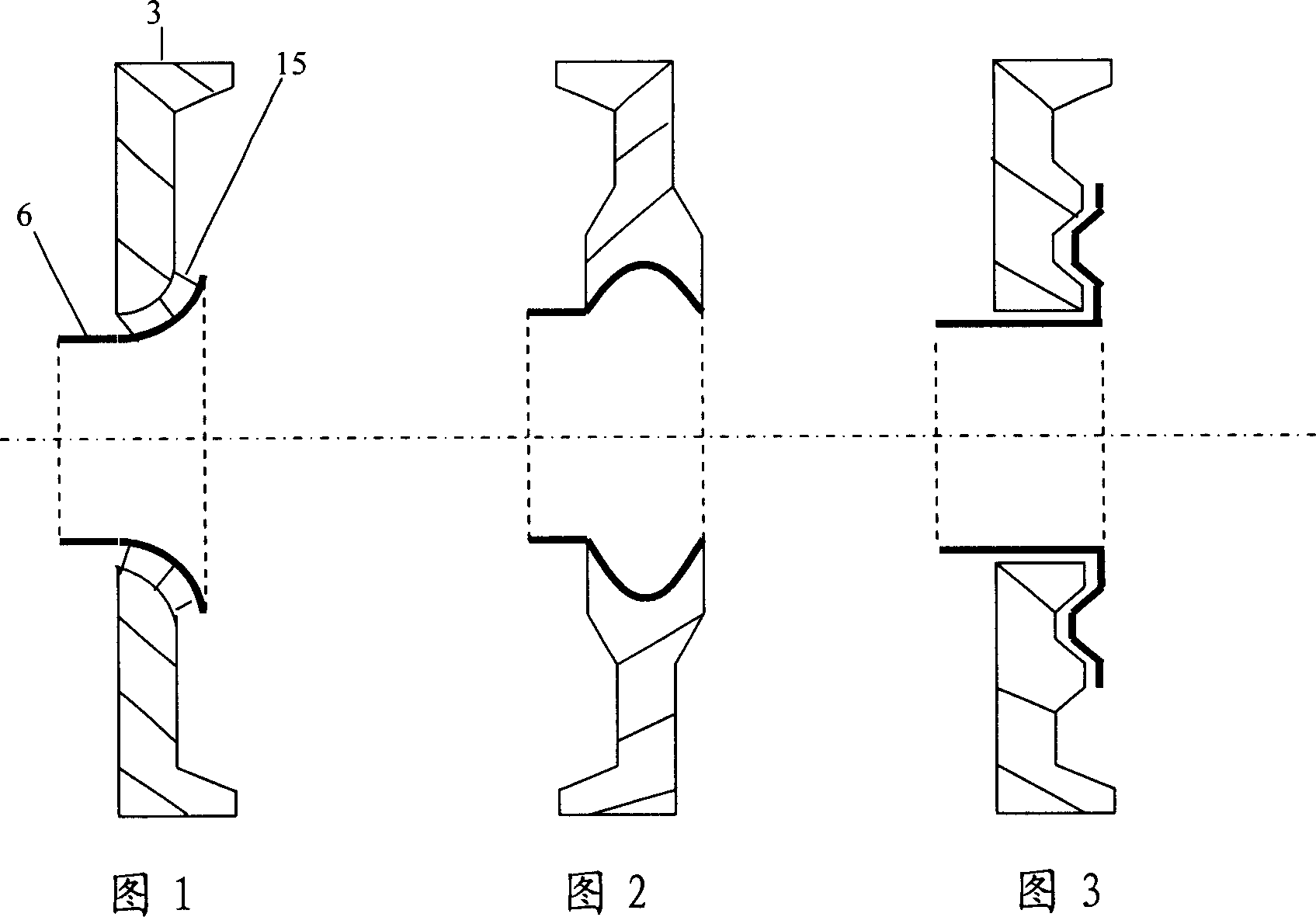
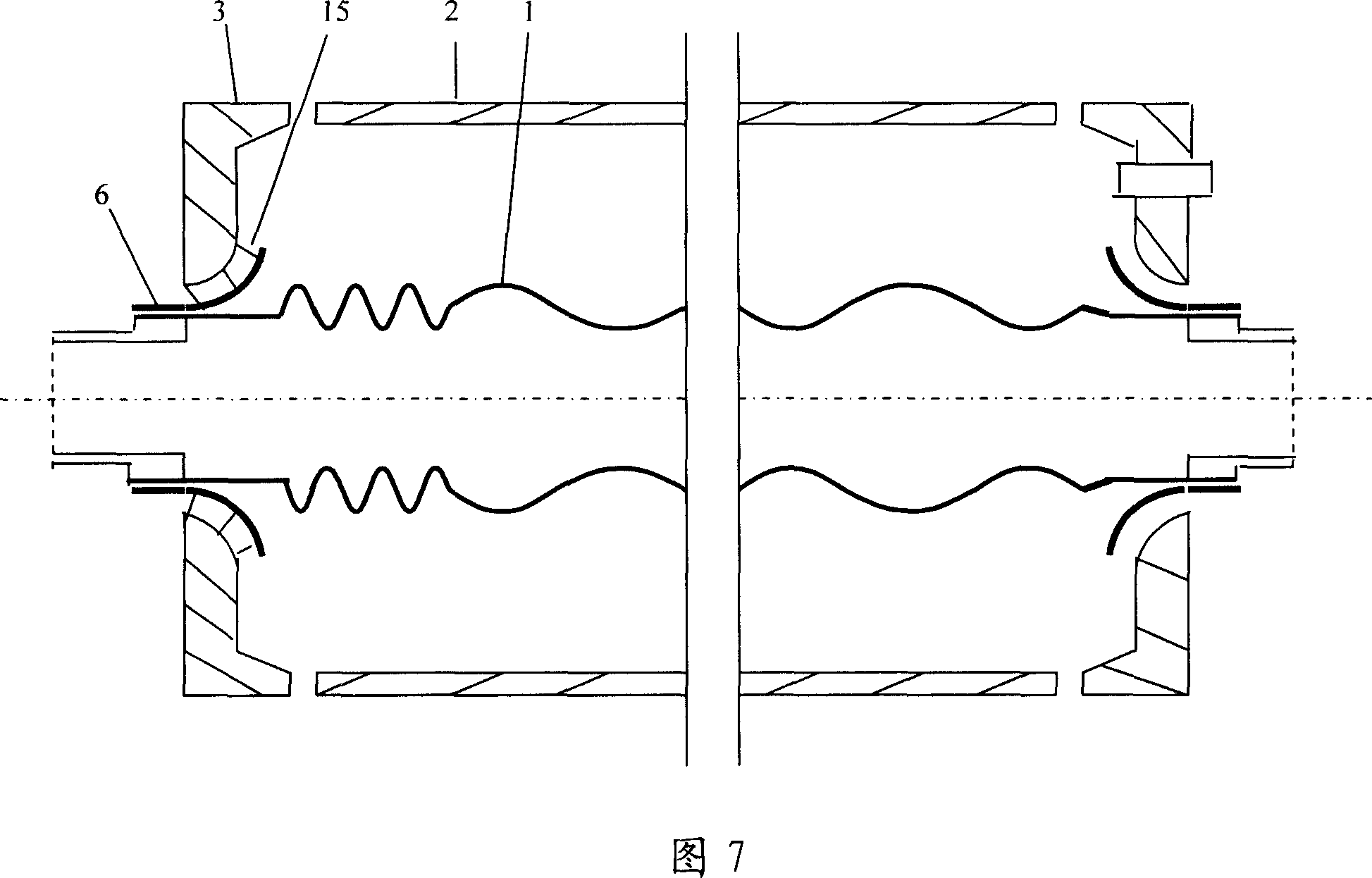
[0030] The iron-nickel alloy kovar 6 is subjected to hydrogen-protected high-temperature atomization treatment after stretching, so that the chemical bonds on the atomized layer of the iron-nickel alloy remain compatible with the high boron glass. The high-boron glass frit melted at high temperature in the furnace is poured into the mold cavity. Before the glass frit is poured, the spherical tubular iron-nickel alloy kovar piece 6 is placed in the mold, preheated together with the mold, and then the droplet is pressed into shape. After discharge, heat treatment according to the glass operating regulations, annealing and stress relief, and then use it as a component for spare use. When making solar vacuum heat collecting tubes, glass end caps 3 are placed between the inner and outer tubes at both ends. One end of the iron-nickel alloy kovar piece 6 welded on the glass end cover 3 is argon-arc welded with the metal inner tube 1 and the pipe joint 4 . In order to be suitable for...
Embodiment 2
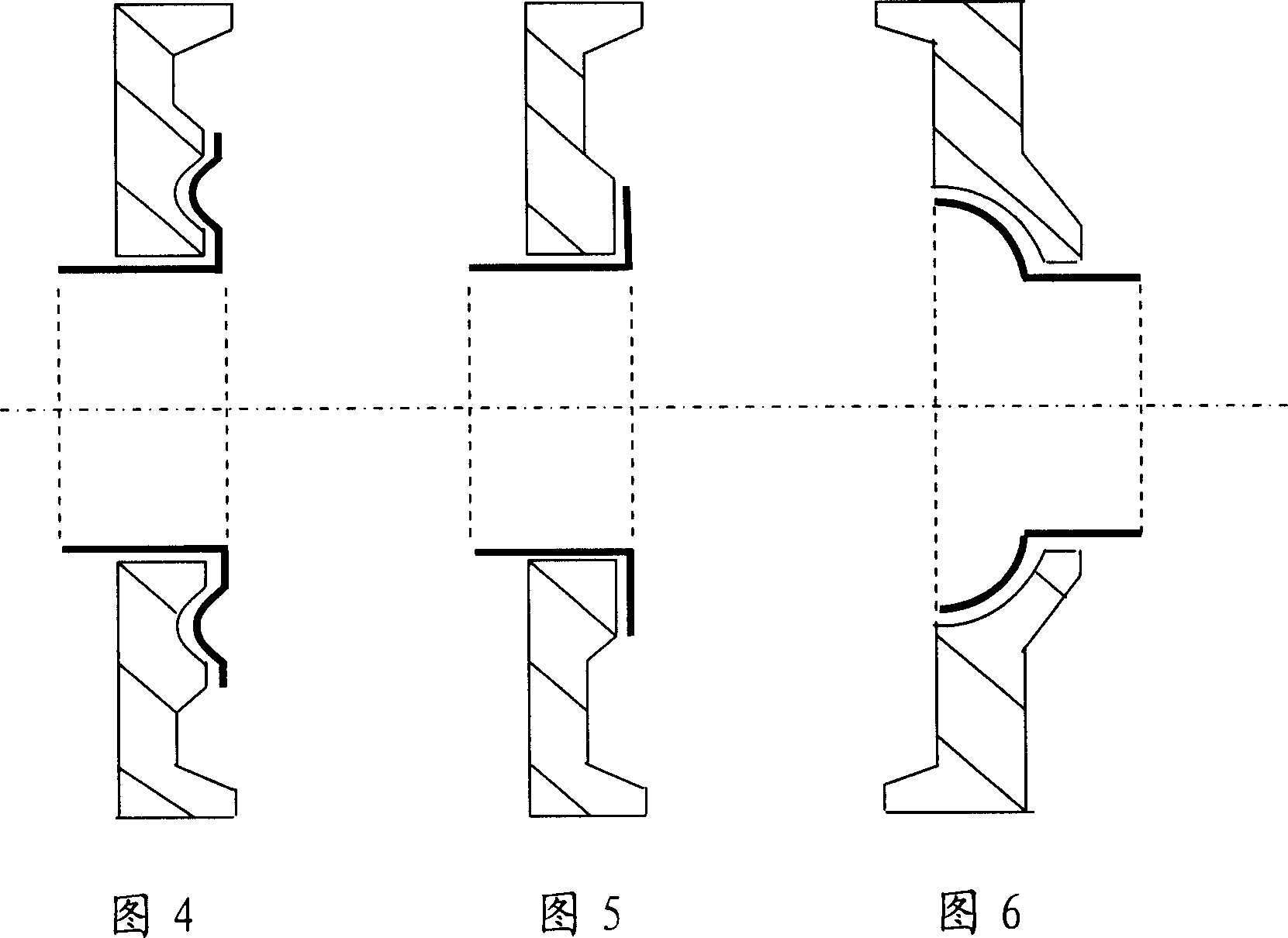
[0033] The new glass end cap 3 is made of the same material glass tube material, cut into sections, placed in the mold cavity for melting, and pressed by the mold to form a sealing surface end cap with a hemispherical tubular center and a flared tubular shape with outward flanging, or It is calcined from ceramic and glass-ceramic materials. The outer circle of the glass end cap 3 can be designed into various connection shapes, so that it can be welded with the glass outer tube 2 on the glass lathe, and the end caps made of ceramics and glass-ceramic materials can be welded indirectly. The iron-nickel Kovar alloy piece 6 is prefabricated into a corresponding hemispherical tubular shape and a trumpet tubular shape, and placed in the center of the glass end cover 3. Before placing, the glass sealing material 15 is placed between the two, and is selected in a high-temperature furnace. Welding iron-nickel Kovar alloy parts 6 at a temperature suitable for melting glass transition ma...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The new glass end cap 3 is formed by pressing a glass tube of the same material after melting in a mold cavity, or by calcining ceramics or glass-ceramic materials. Flat or grooved and corrugated sealing surfaces are pressed in the center. The iron-nickel Kovar alloy piece 6 is made into a T-shaped tube, and the top of the T-shaped top is prefabricated with a corresponding flat or grooved or corrugated connection surface, and placed in the center of the matching glass end cover 3 for welding; The T-shaped planar structure can also use the patent of pure aluminum pressure sealing. Other processes are the same as above. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, and Figure 5.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Linear expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Softening temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com