Telescopic nonwoven fabric
A non-woven, stretchable technology, used in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, one-component polyolefin rayon, etc., can solve the problems of low modulus, insufficient hysteresis of expansion and contraction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
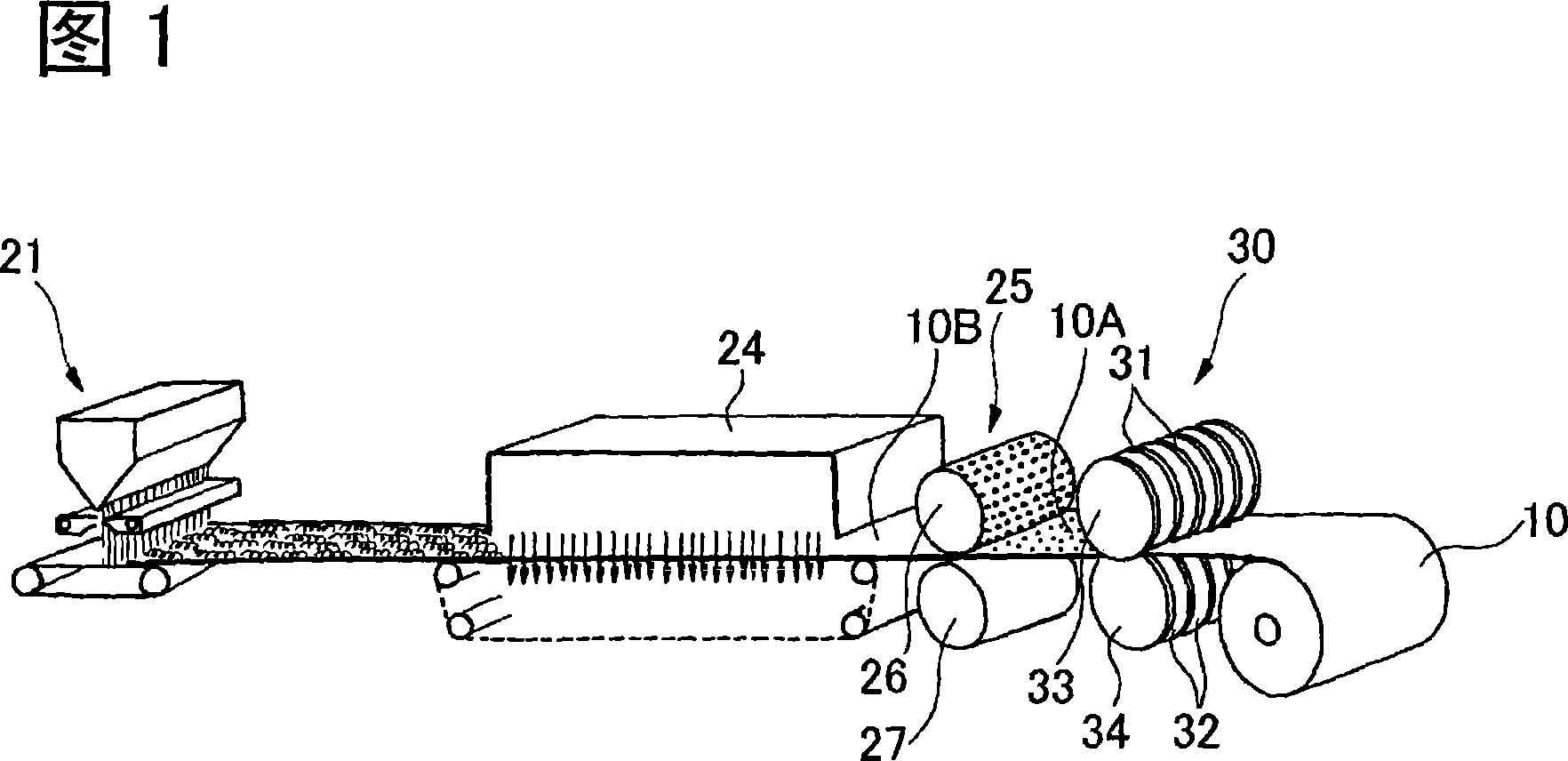
[0136] This embodiment is an embodiment of the first invention. Stretchable nonwoven fabrics were manufactured using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1 . First, an elastic web is formed as follows. As the block copolymer, SEPTON (registered trademark) 2004, a styrene-ethylene-propylene-styrene block copolymer manufactured by Kuraray Corporation, was used. The block copolymer contained 18% by weight of styrene as polymeric block A and 82% by weight of ethylene-propylene as polymeric block B. The dynamic viscoelasticity measurement of this block copolymer was carried out, and the elastic storage modulus at 20°C and 2Hz was 1.9×10 5 Pa, the dynamic loss tangent value tanδ is 0.02. In addition, a polypropylene resin (homopolymerization) having an MFR of 60 g / 10 min was used as a different resin for inelastic fibers. An elastic fiber web composed of mixed fibers of two kinds of resins is formed using the above-mentioned resins. Two extruders are used to form the fiber web, each res...
Embodiment 1-2
[0140] This embodiment is an embodiment of the first invention. As the block copolymer, SEPTON (registered trademark) 2002, a styrene-ethylene-propylene-styrene block copolymer manufactured by Kuraray Corporation, was used. The block copolymer contained 30% by weight of styrene as polymer block A and 70% by weight of ethylene-propylene as polymer block B. The dynamic viscoelasticity measurement of this block copolymer was carried out, and the elastic storage modulus at 20°C and 2Hz was 3.0×10 5 Pa, the dynamic loss tangent value tanδ is 0.03. Except for this, a stretchable nonwoven fabric was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1-1.
Embodiment 2-1
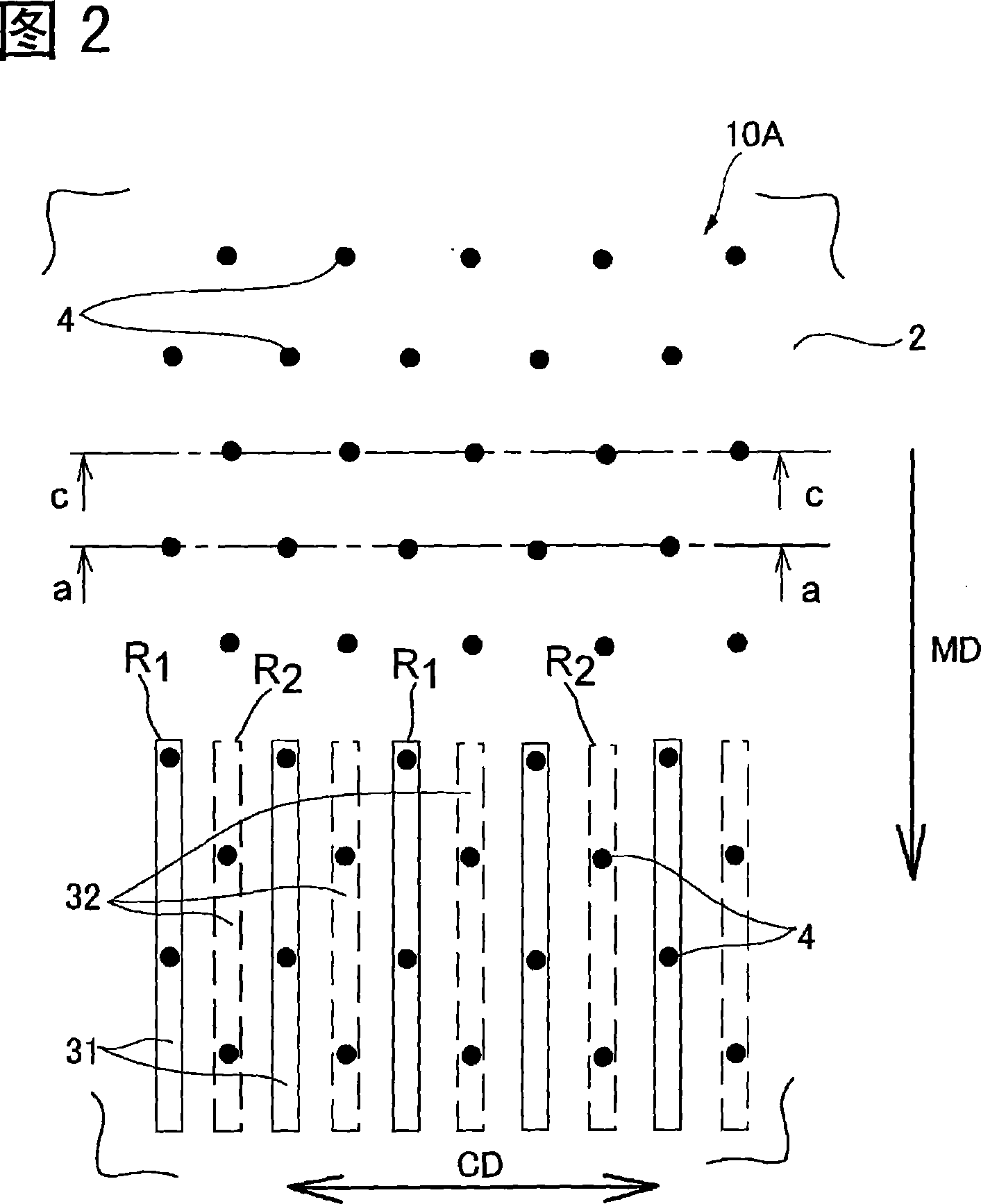
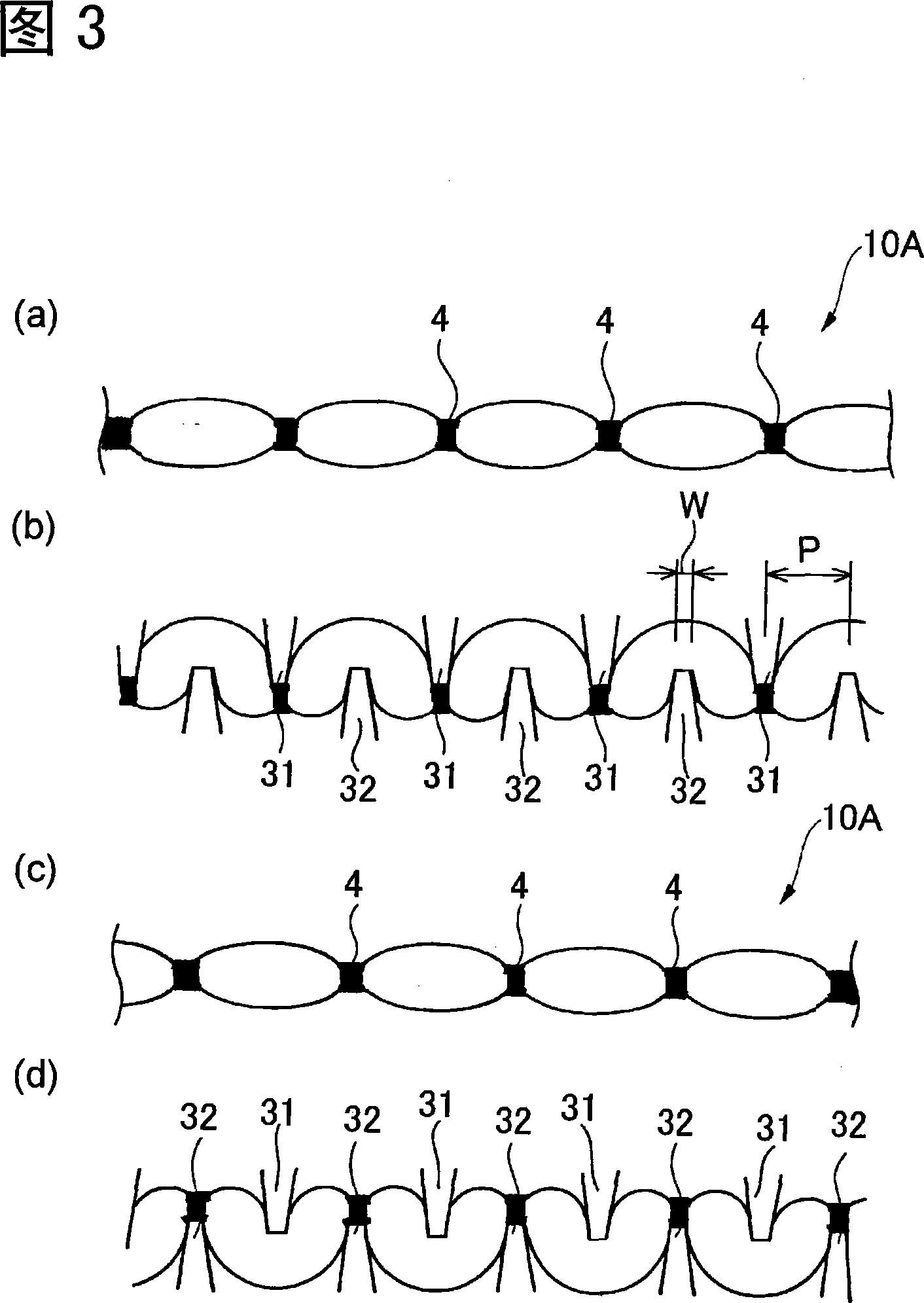
[0155] This embodiment is an embodiment of the second invention. The elastic web was formed as follows. As the resin used for the elastic fibers, SEBS having a melt viscosity of 300 Pa·s at 230° C. and a melt tension of 1.3 cN was used. In addition, a polypropylene resin (homopolymerization) having an MFR of 60 g / 10 min (230° C., 2.16 kg) was used as a different resin for other inelastic fibers. An elastic fiber web composed of mixed fibers of two kinds of resins is formed using the above-mentioned resins. The formation of the fiber web 1 uses two extruders, each resin is melted at a die temperature of 290°C with each extruder, and extruded from the spinning nozzle, and the fiber is formed on the web by the spinning and blowing method. accumulation. As shown in FIG. 6, the spinning nozzle has a shape in which each resin is extruded alternately. The weight ratio of SEBS and polypropylene was set at 50 / 50. The fiber diameter of the elastic fibers was 25 μm. The fiber diame...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melt viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melt tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com