Memory controller
A control device and memory technology, applied in memory systems, instruments, memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve problems such as inability to access SDRAM808 useless cycles, inability to store bank 1 output address, inability to access SDRAM, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
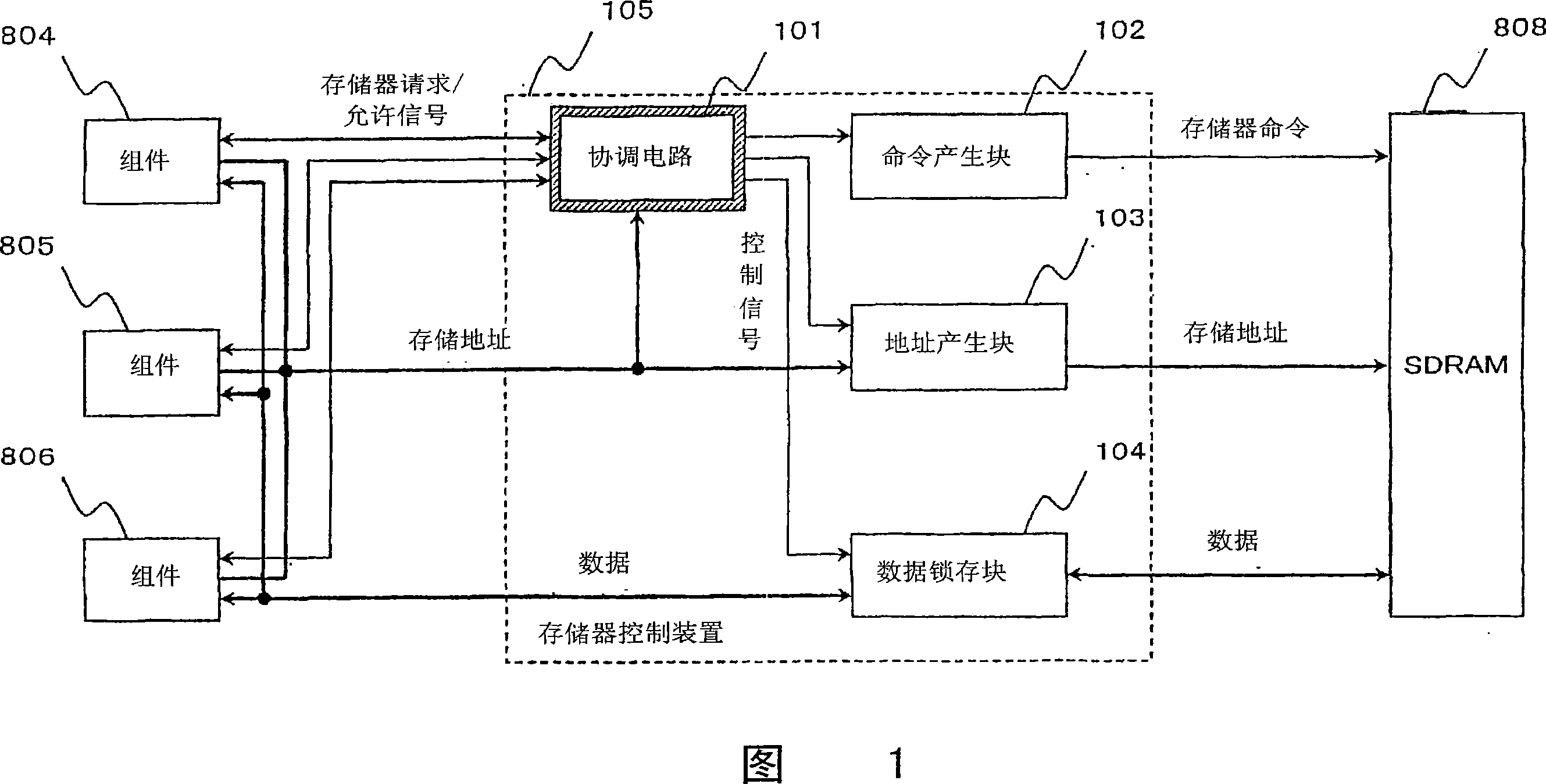
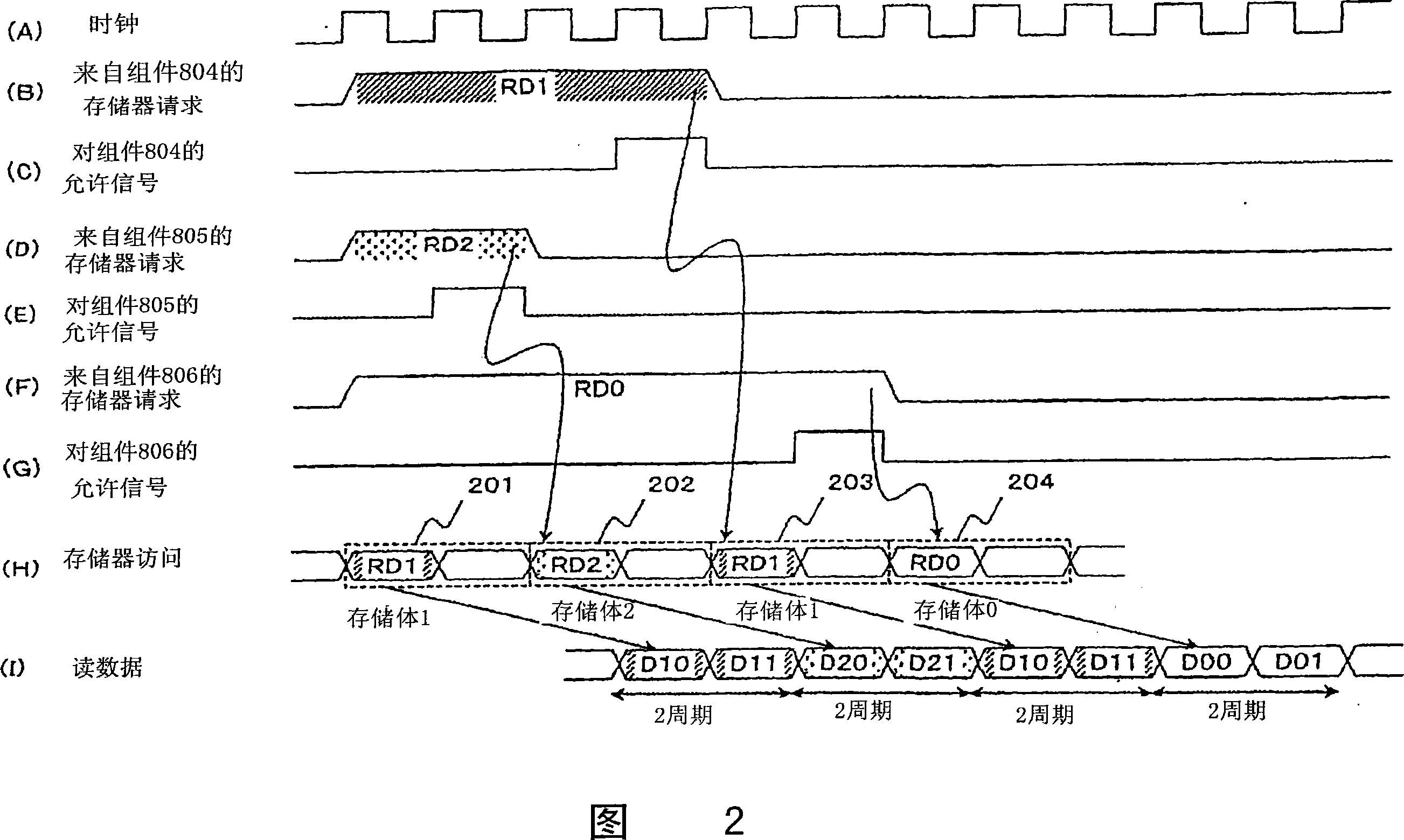
[0086] Next, embodiments of the first to eighth present inventions will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 , 2 , 8 and 9 . 4 is a block diagram of a memory control device according to Embodiment 1, FIG. 2 is a timing diagram of main signals in FIG. 1 , and FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing a coordination circuit according to Embodiment 1.
[0087] As shown in Figure 1, the components of this memory control device 105 include a coordinating circuit 101 for coordinating the memory access requests sent by multiple components 804, 805, and 806 for accessing the SDRAM 808, and a command generation block for generating memory commands to the SDRAM 808 102. Receive the storage address sent by the component that the coordination circuit 101 allows access to and output it to the address generation block 103 of the SDRAM 808, and write data sent by the component that the coordination circuit 101 allows access to Or the data latch block 104 that latches the data read from the SDRAM 8...
Embodiment approach 2
[0152] Next, embodiments of the ninth to fourteenth present inventions will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 , 3 , 10 and 11 . FIG. 3 is a main signal timing diagram of the second embodiment, FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing the coordination circuit 101 of the second embodiment, and FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing the data latch block 104 of the second embodiment.
[0153] The configuration of the memory control device 105 is the same as that of Embodiment 1 (FIG. 1), and the reference numerals in the figure are the same, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0154] As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 10 , the components of the coordinating circuit 101 include components that receive memory requests and storage addresses from the multiple components 804, 805, and 806 and judge that memory access is allowed at present according to the received storage addresses. Whether the second half memory bank and the first half memory bank of the next memory access request are to t...
Embodiment approach 3
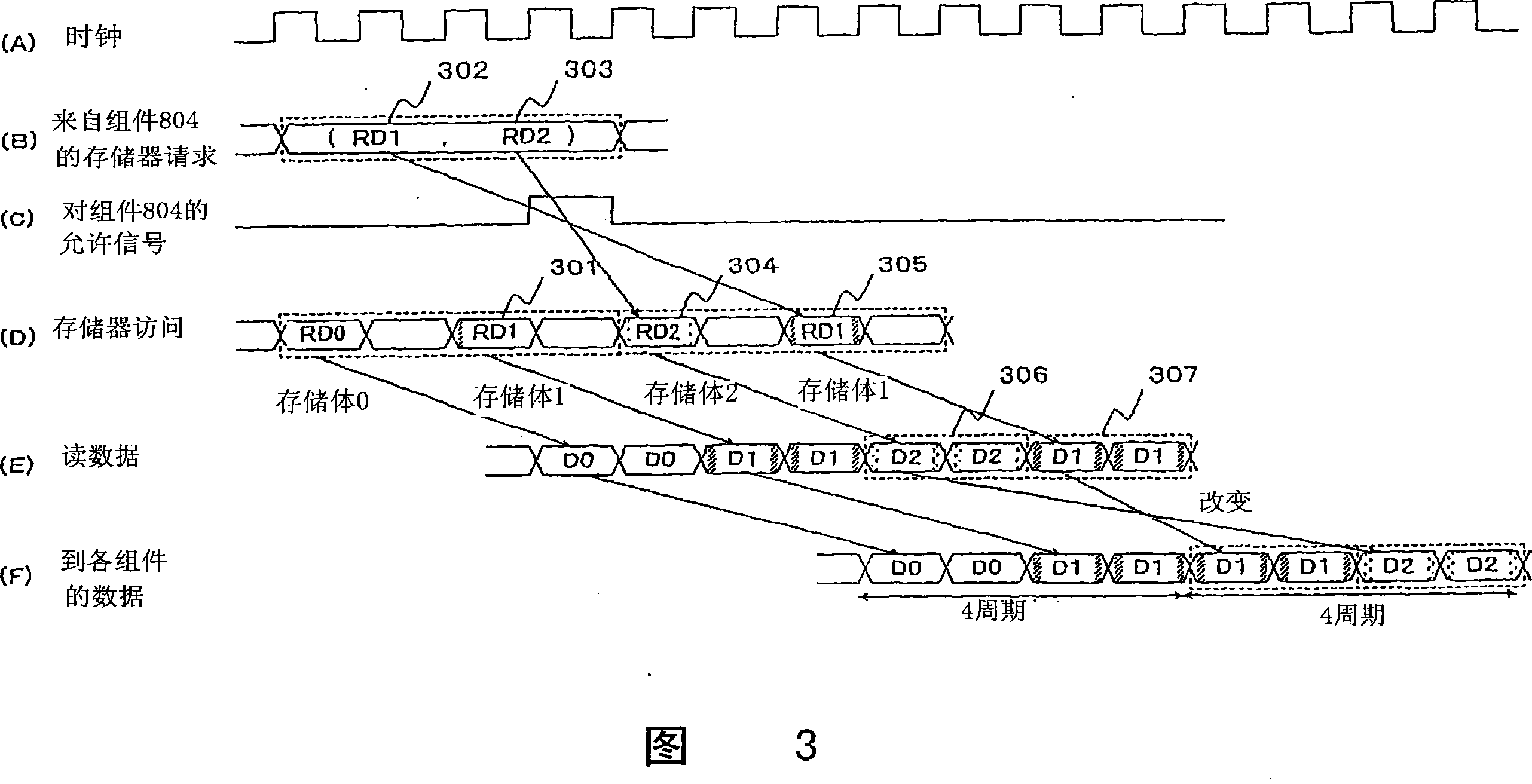
[0186] Next, embodiments of the fifteenth to nineteenth inventions will be described with reference to FIG. 1 , FIG. 4 and FIG. 12 . FIG. 4 is a main signal timing diagram of Embodiment 3, and FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing a coordination circuit of Embodiment 3. As shown in FIG.
[0187] The configuration of the memory control device 105 is the same as that of Embodiment 1 (FIG. 1), and the reference numerals in the figure are the same, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0188] As shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 12, the components of the coordinating circuit 101 include data units that receive memory requests from the multiple components 804, 805 and 806 and determine the requested memory access according to the received memory requests The data unit judging unit 1402 further instructs the request receiving block 1401 that generates a permission signal, the memory access priority specifying unit 1003 that specifies the priority of memory access from the plurality of comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com