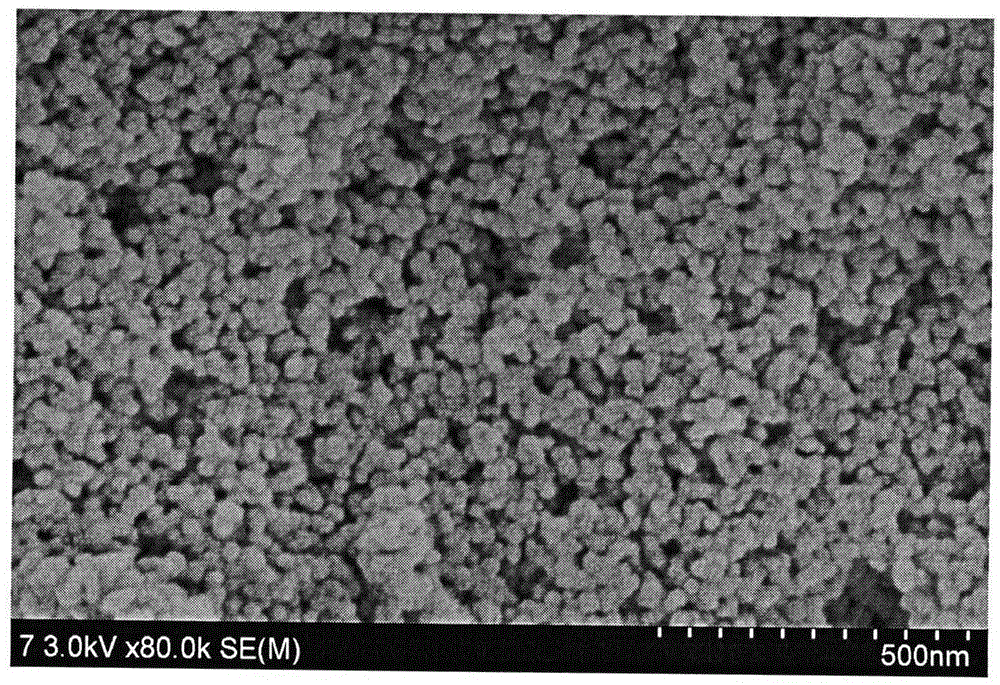
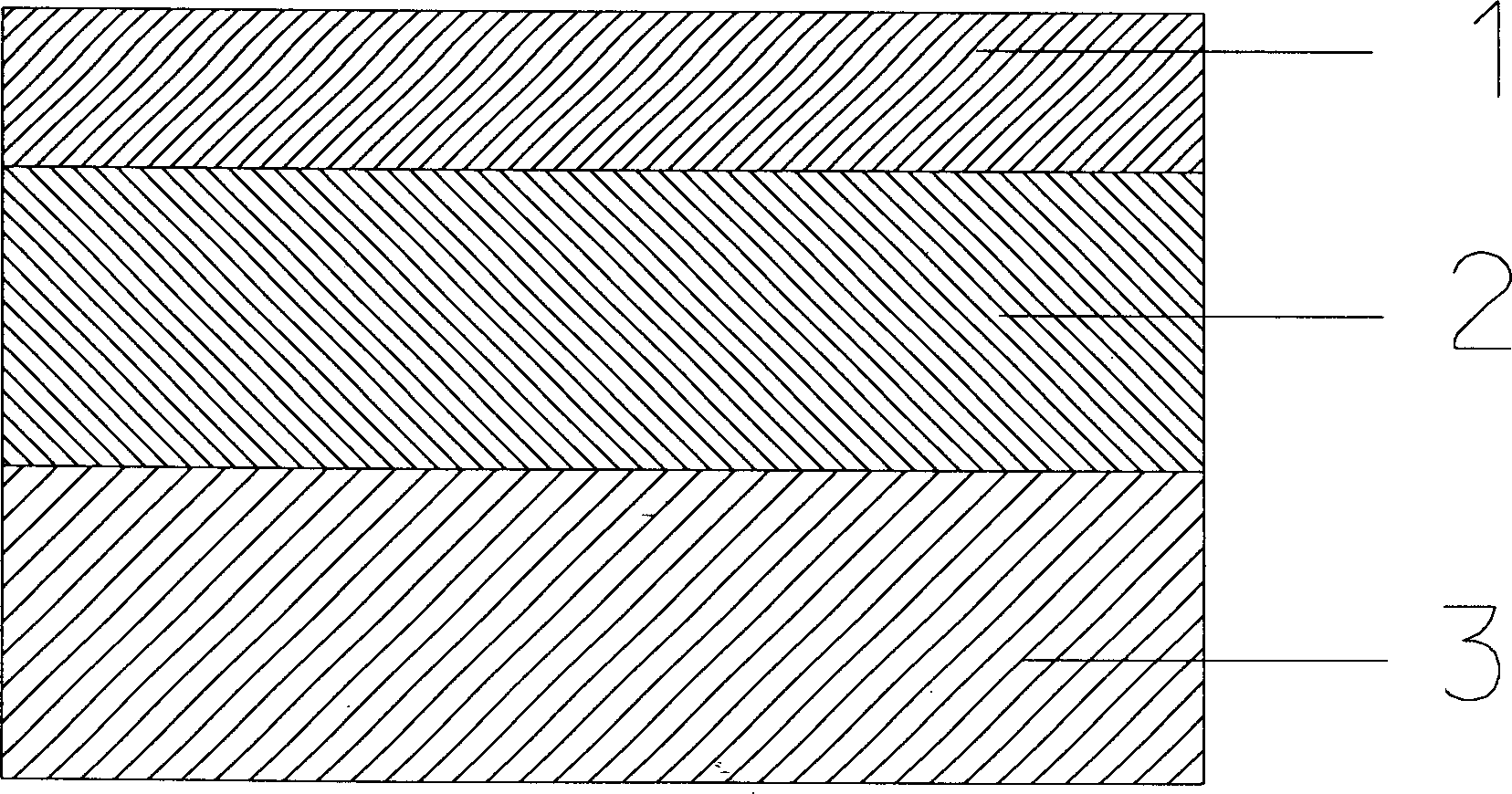
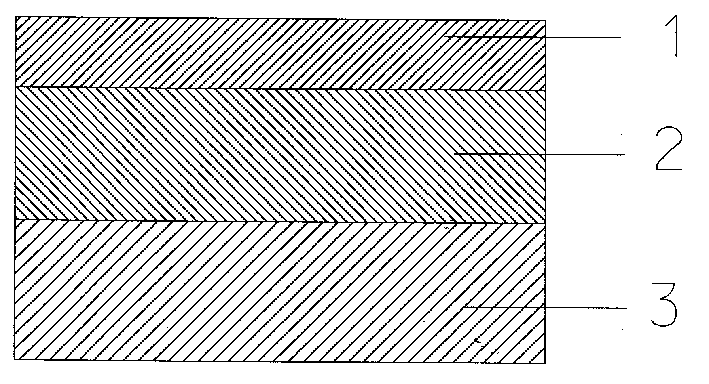
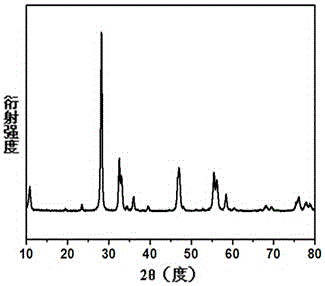
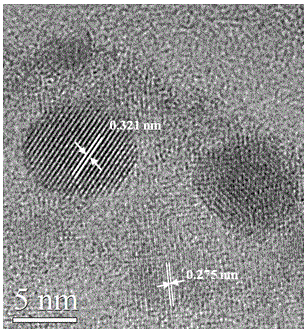
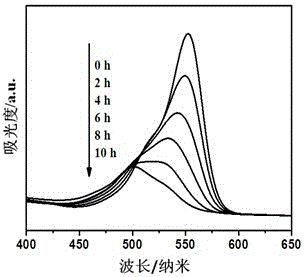
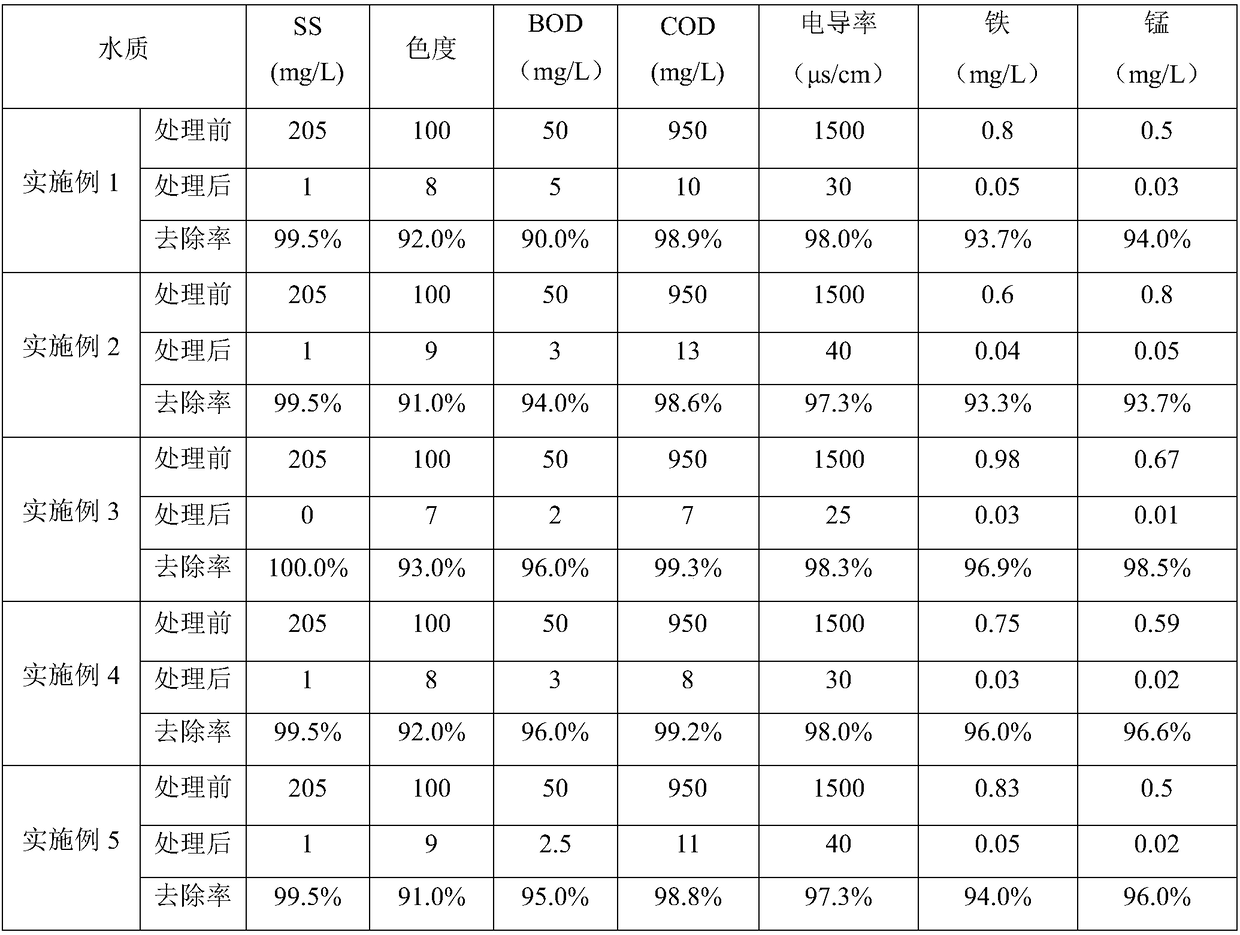
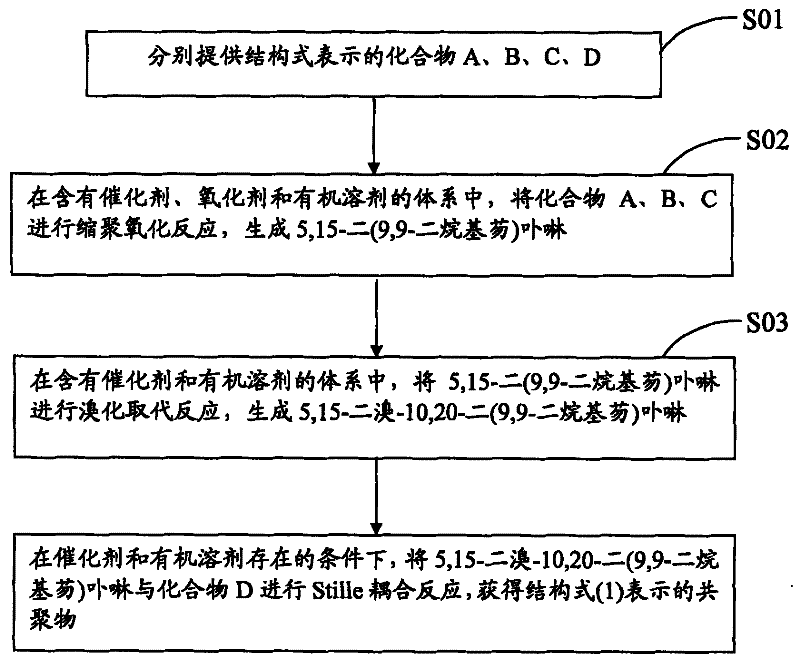
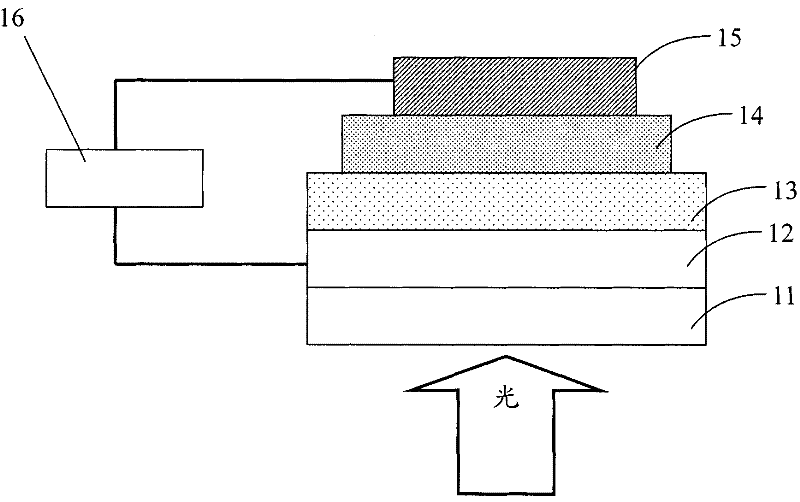
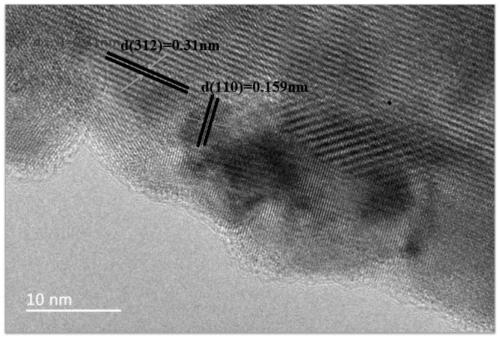
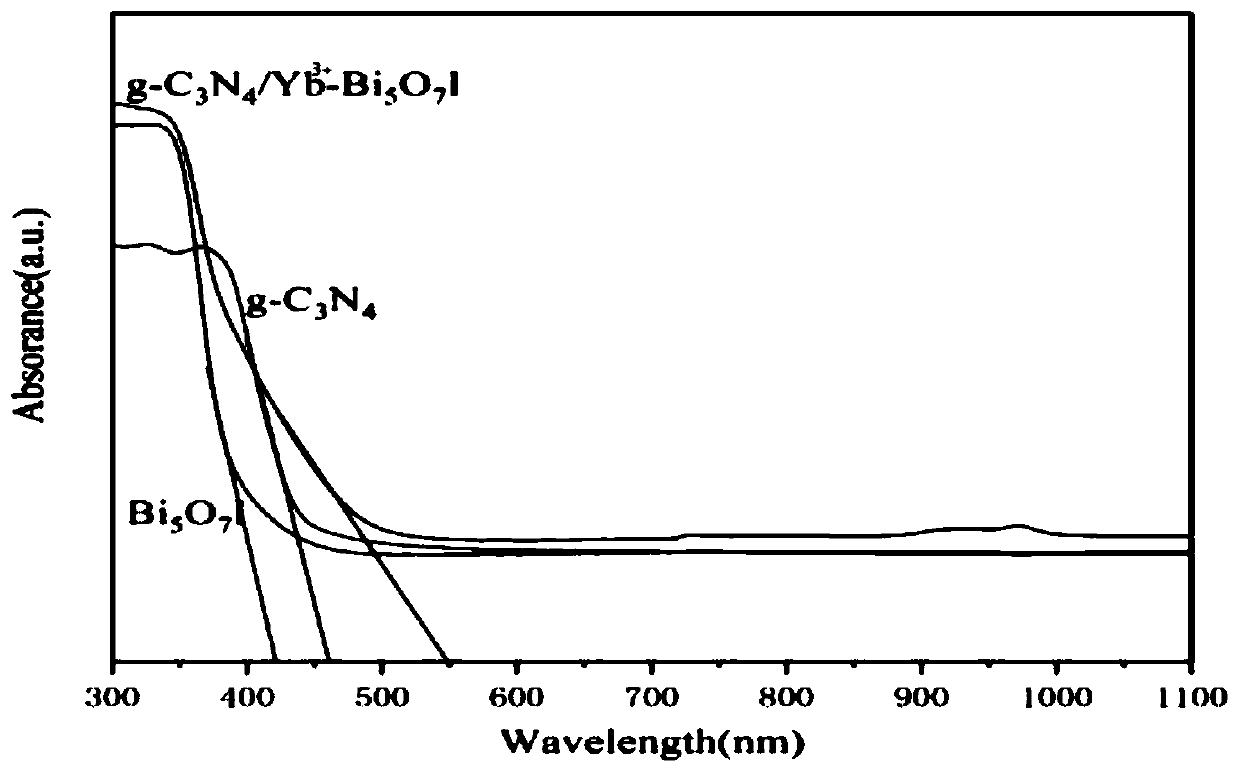
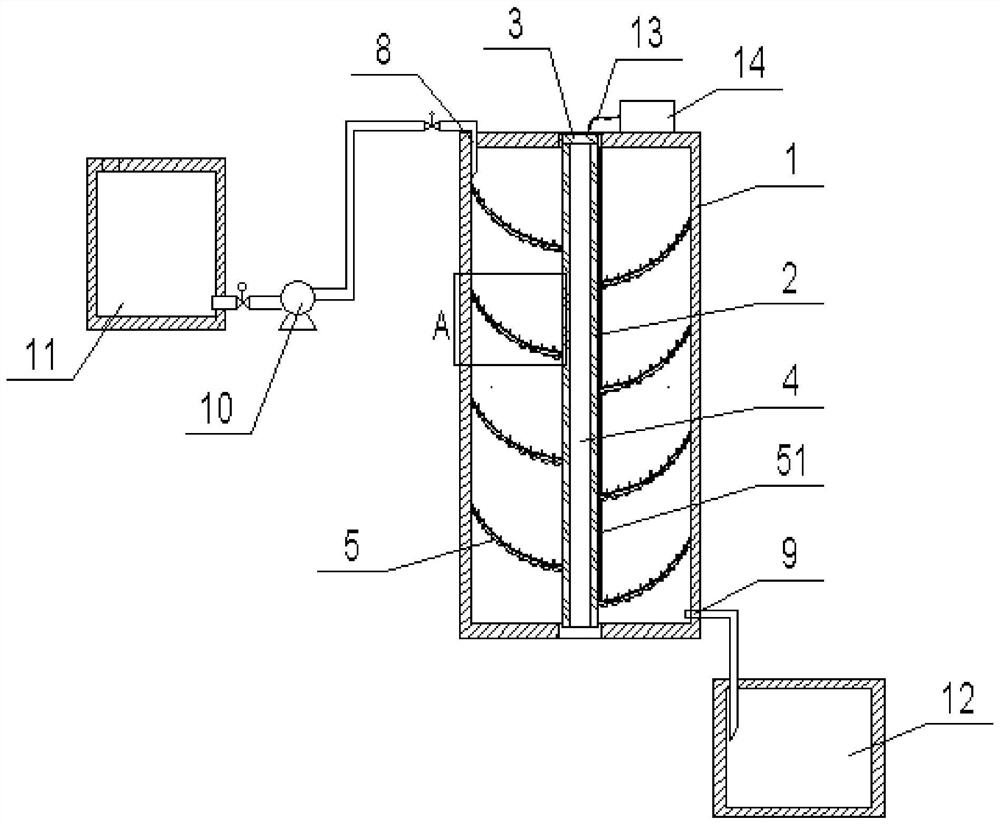
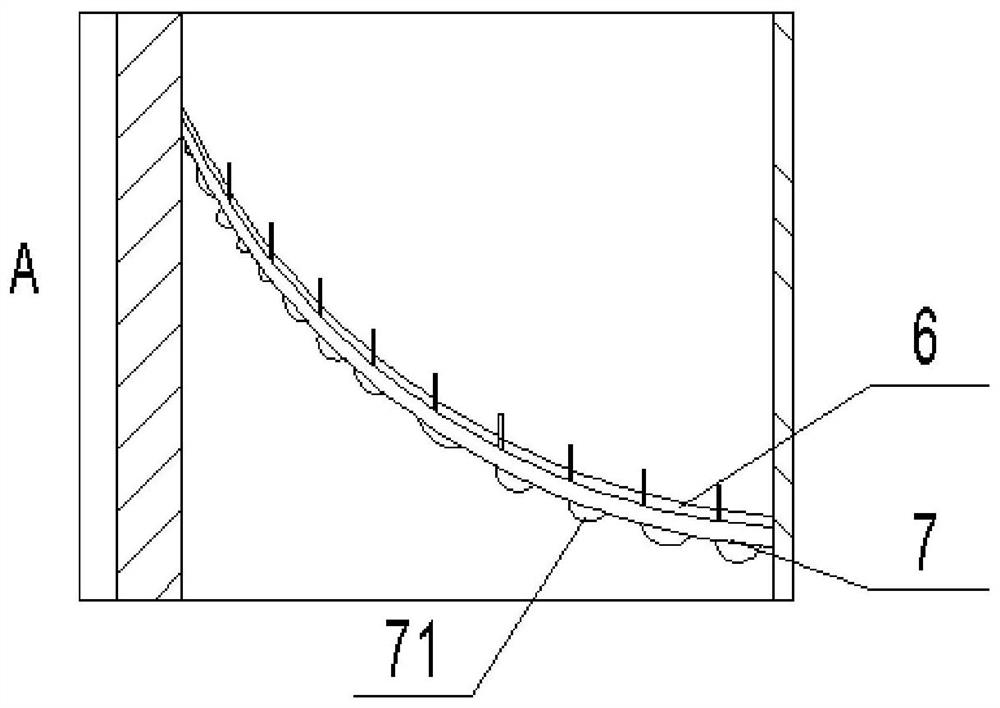
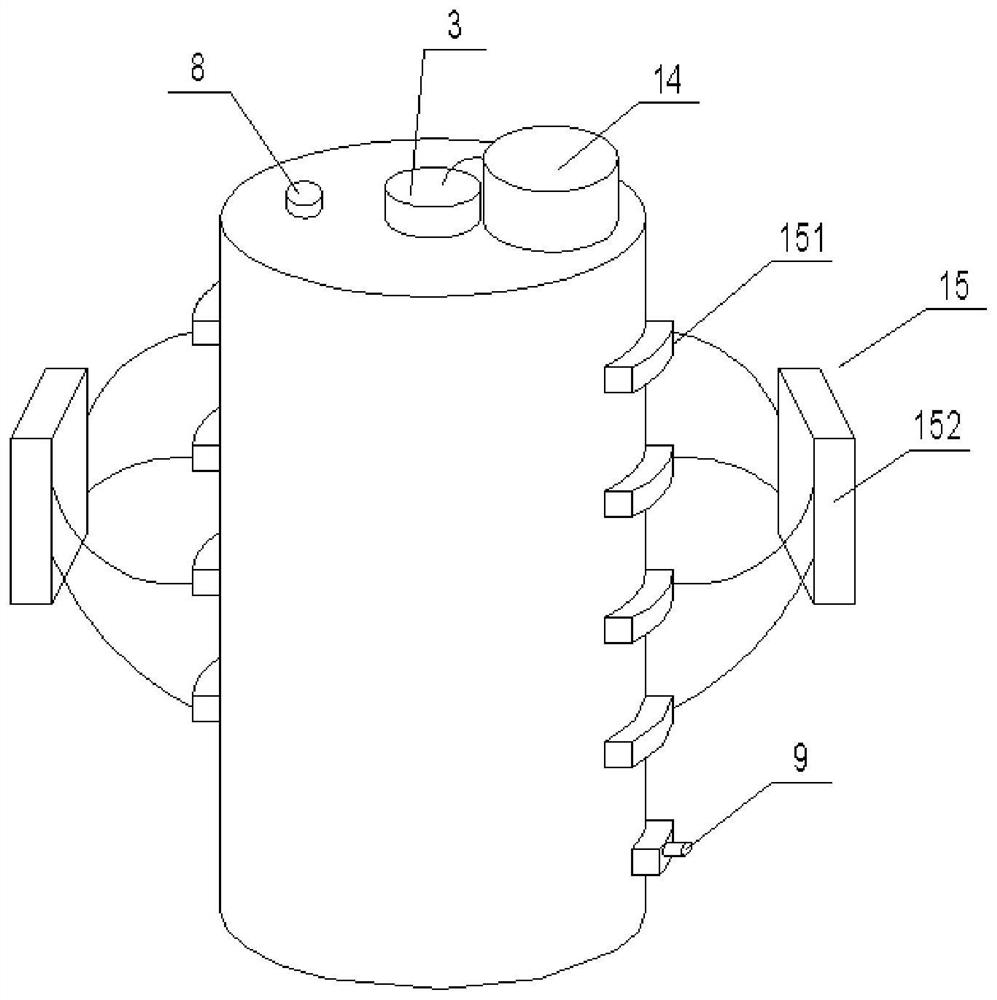
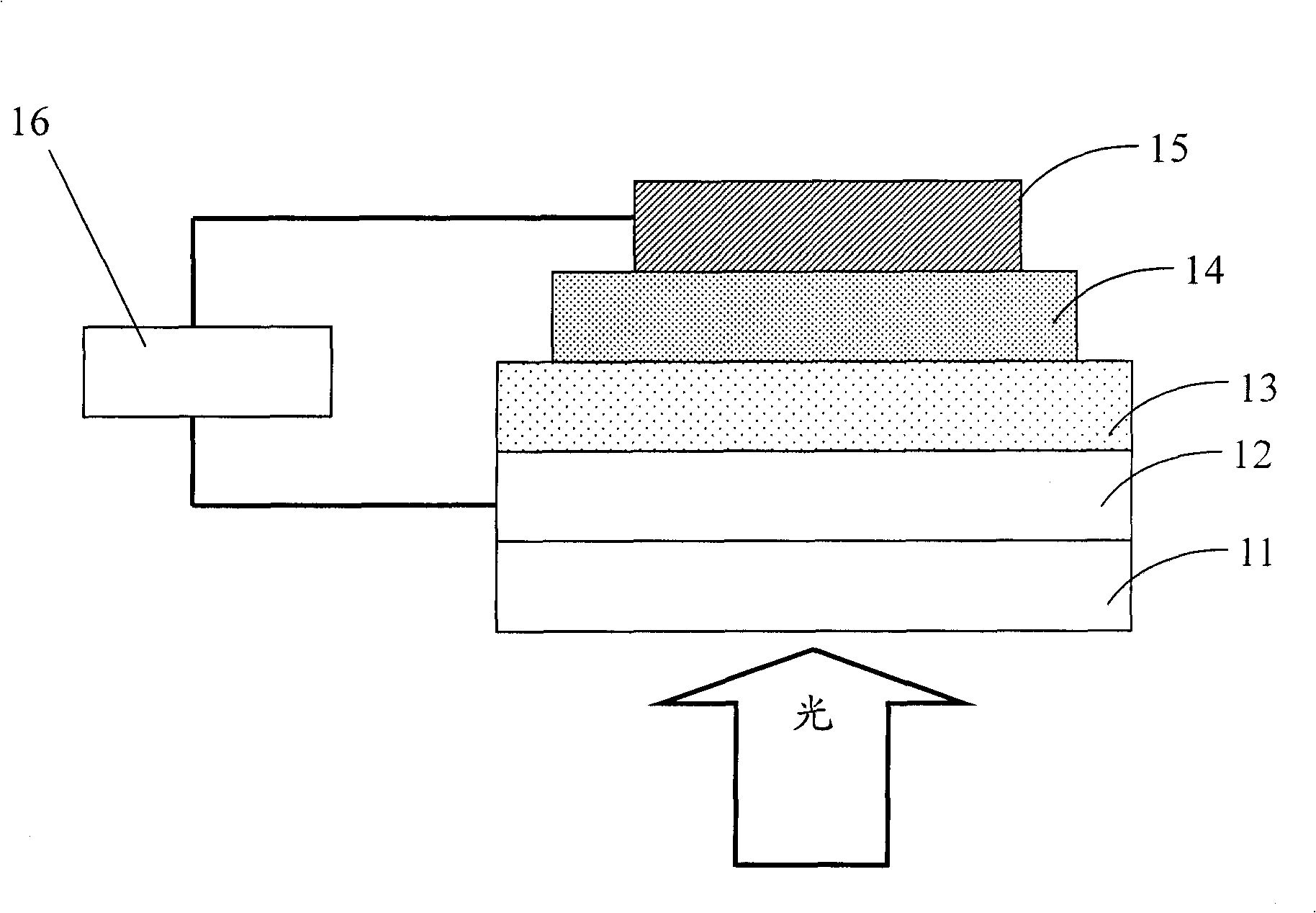
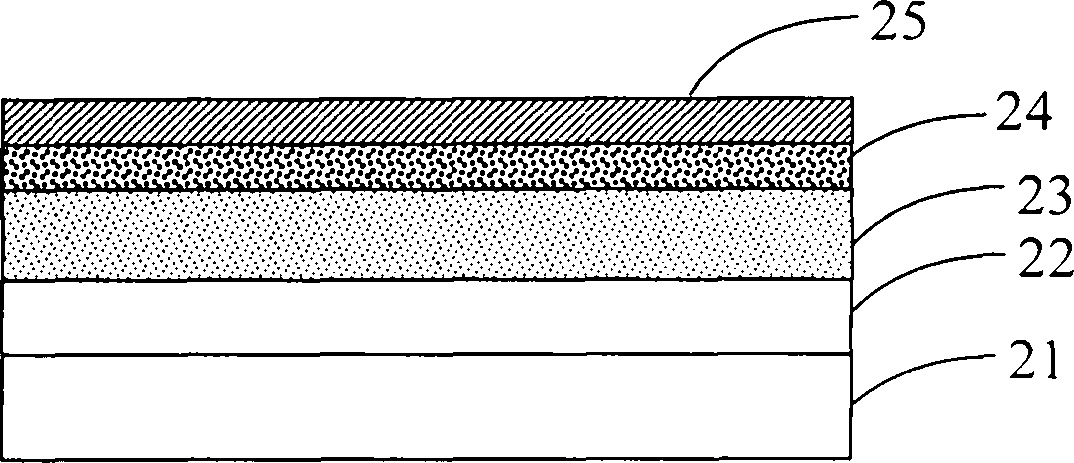
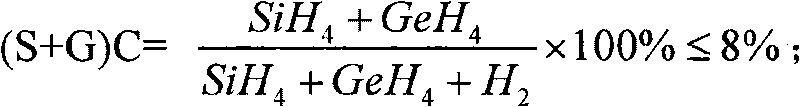Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Extended Spectral Response Range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital alloy absorber for photodetectors
ActiveUS20100155777A1Extended Spectral Response RangeImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotodetectorPhotovoltaic detectors
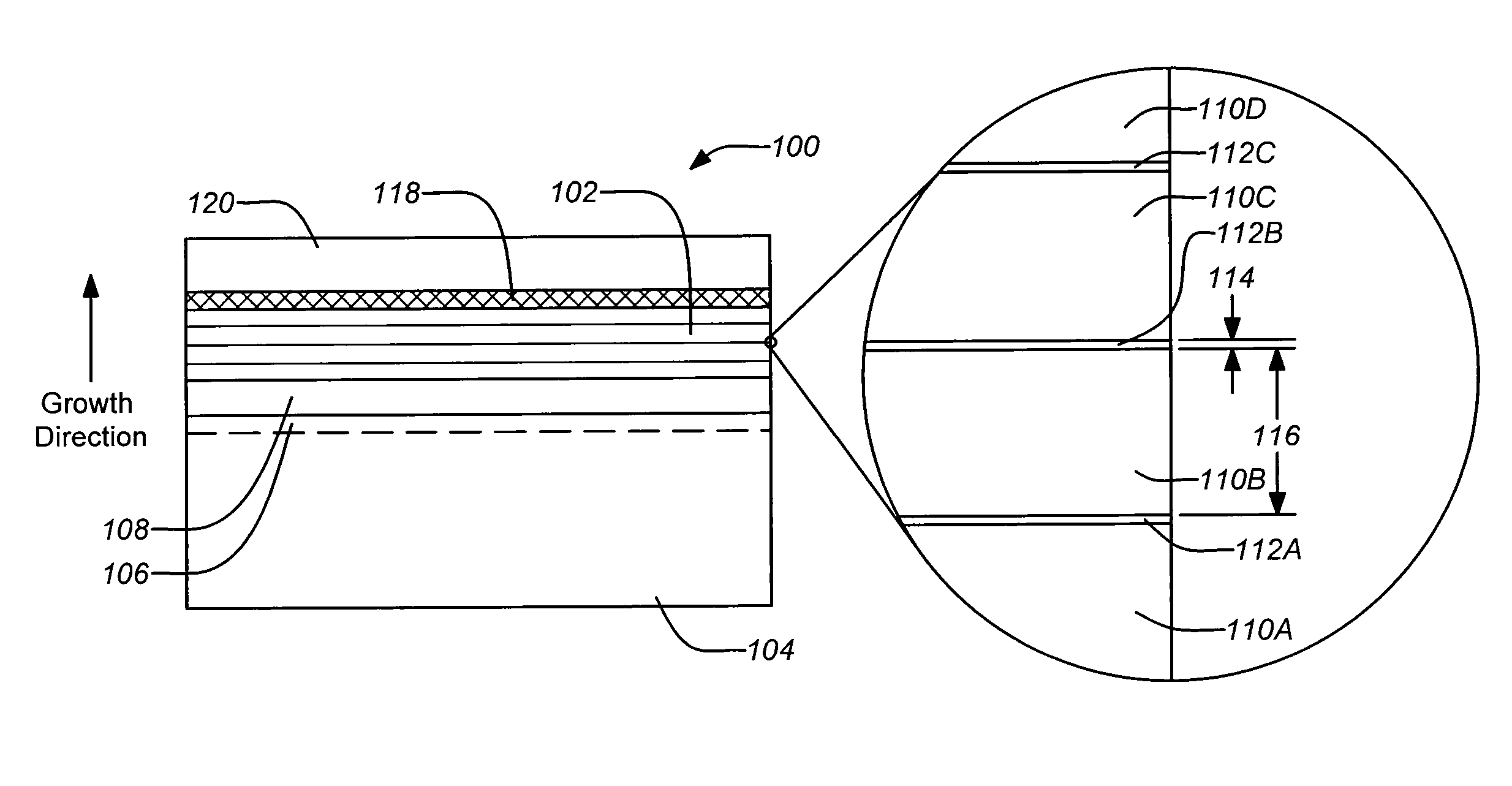
In order to increase the spectral response range and improve the mobility of the photo-generated carriers (e.g. in an nBn photodetector), a digital alloy absorber may be employed by embedding one (or fraction thereof) to several monolayers of a semiconductor material (insert layers) periodically into a different host semiconductor material of the absorber layer. The semiconductor material of the insert layer and the host semiconductor materials may have lattice constants that are substantially mismatched. For example, this may performed by periodically embedding monolayers of InSb into an InAsSb host as the absorption region to extend the cutoff wavelength of InAsSb photodetectors, such as InAsSb based nBn devices. The described technique allows for simultaneous control of alloy composition and net strain, which are both key parameters for the photodetector operation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Multi-level hole TiO2/quantum dot/dye lamination thin-film solar cell photo-anode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103560009AEasy transferImprove adsorption capacityLight-sensitive devicesState of artQuantum dot
The invention discloses a multi-level hole TiO2 / quantum dot / dye lamination thin-film solar cell photo-anode. A bottom layer is a multi-level hole TiO2 thin film prepared on a transparent conductive substrate. A middle layer is an I-III-VI-group quantum dot thin film. A secondary upper layer is a semiconductor oxide barrier layer. An upmost layer is a dye layer. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the multi-level hole TiO2 / quantum dot / dye lamination thin-film solar cell photo-anode. The method comprises the steps of firstly, preparing the bottom layer, namely the multi-level hole TiO2 thin film, on the conductive substrate, then, preparing the I-III-VI-group quantum dot thin film, namely the middle layer thin film, on the multi-level hole TiO2 thin film by means of the chemical sedimentation method or the continuous ionic adsorption method, then preparing the secondary upper layer, namely the semiconductor oxide barrier layer, on the middle layer, namely the I-III-VI-group quantum dot thin film, by means of the dipping film-drawing method, and finally soaking the lamination layers in a dye solution to obtain the upmost layer, namely the dye layer. Compared with the prior art, the multi-level hole TiO2 / quantum dot / dye lamination thin-film solar cell photo-anode is of the multi-level hole structure, and has the high specific surface area, dispersion and adsorption of dye and an electrolyte are facilitated, sunlight of different spectra is absorbed due to the synergistic effect of the lamination structure, the absorption spectrum range is broadened, and the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of a solar cell is improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
Preparing method and application of compound titanate nanotube photocatalyst
InactiveCN101229514AImproving UV Photocatalytic PerformanceSimple processMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsUltraviolet lightsNanotube
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite titanate nano tube photocatalyst and application thereof, which relates to a preparation method of a nano tube photocatalyst and application thereof. The invention solves the problems that the present composite titanate nano tube photocatalysts have complicate preparation techniques, small loading which is only excited by ultraviolet light with poor stability. The method of the invention is as follows: metal salt is dissolved into ionized water, in which concentrated nitric acid is dripped, then the solution obtained is dripped into the solution prepared by titanium ester and diluent to be stirred, dried and sintered, then yield obtained is dispersed into oxyhydrogen sodium solution; after being reacted for 24-72 hours, the solution is washed to neutral before being carried out temperature reduction and heat preservation. The photocatalyst of the invention has high metal loading or the oxide loading which not only can be excited by the ultraviolet light but also can be excited by visible light. The catalytic performance of the invention is 3-15 times higher than common catalyst activity and can be used more than 100h stably, and service life thereof is 100-1000 hours. The method of the invention has simple technique.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Composite titanium-base film photoelectrode and its making process
InactiveCN1389932ASimple processImprove performanceFinal product manufactureCatalyst activation/preparationSpectral responseVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to the area of the semiconductor catalysis technique, especially relates to the thin film photoelectric pole responding to visible light in mixed mode as well as the preparing method. The thin film photoelectric pole comprises following layers is sequence: the titanium substrate, the titanium dioxide thin film with the composite adulteration of cobalt and rethenium, and the titanium dioxide thin film. The photoelectric pole is prepared by using the sol-gel method with features of simple technique and easy to adjust the adulterated density. The invented thin film photoelectric pole possesses the characters of the wide spectral response, stable performance. The invention is applicable to the applicable to the areas of solar utilization, photovoltaic conversion, photocatalysis for degrading the organic contaminant.
Owner:SINOPEC OILFIELD EQUIP CORP
Composite laminated perovskite solar cell and manufacturing method therefor
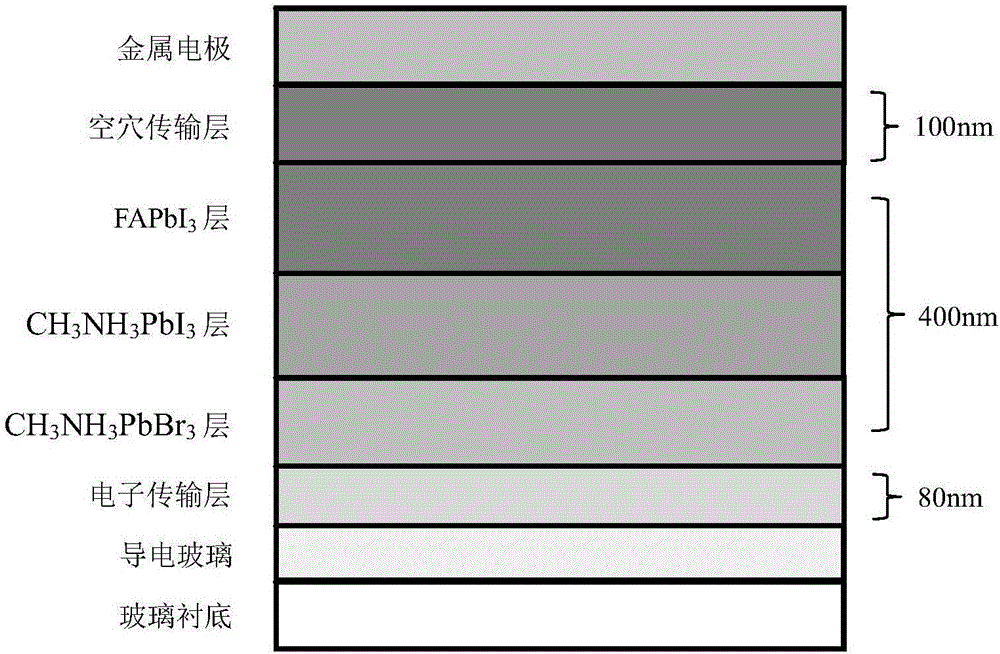
InactiveCN106450001AWide spectral response rangeGood UV Spectral ResponseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron holeSpectral response
The invention belongs to the field of solar cells, and specifically relates to a composite laminated perovskite solar cell and a manufacturing method therefor. According to the invention, CH3NH3PbBr3, CH3NH3PbI3 and NH2CHNH2PbI3 are prepared together according to a degressive sequence of band gap from the top to the bottom, and a composite laminated perovskite light-absorption layer. The introduction of the composite laminated perovskite light-absorption layer remarkably enlarges the spectral response range of the perovskite solar cell to natural light, improves the carrier concentration, and further improves the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell. Meanwhile, the main function of the perovskite light-absorption layer is to generate an electron-hole pair, and the generated electron-hole pair can be conducted by an electron transmission layer and a hole transmission layer through an external electrode. Compared with a conventional multijunction solar cell, no multistage solar cell is needed, and no tunnel junction needs to be introduced, thereby simplifying the preparation technology.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Near-infrared response carbon quantum dots/Bi2MoO6 photocatalyst and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105771962APromote absorptionImprove efficiencyMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlcoholAqueous solution
A near-infrared response carbon quantum dots (CQDs) / Bi2MoO6 photocatalyst is composed of Bi2MoO6 and CQDs, wherein CQDs are distributed on Bi2MoO6, and the mass ratio of CQDs to Bi2MoO6 is 1-15%:85-99%. The invention further provides a preparing method of the photocatalyst.Bi(NO3)3.5H2O aqueous solution and Na2MoO4.2H2O aqueous solution are mixed to obtain light yellow suspension liquid; CQDs aqueous solution is added to the light yellow suspension liquid and then transferred into a hydrothermal kettle for reaction at 140-180 DEG C, a product is washed with absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water in sequence, then centrifugation is conducted, and sediment is dried, so that the CQDs / Bi2MoO6 composite photocatalyst with near-infrared photocatalytic activity is obtained. The photocatalyst has a wide spectral response range, high current carrier separation efficiency and high photocatalytic activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for printing and dyeing wastewater purification treatment in different steps
InactiveCN108467156AAchieve decolorizationIncrease profitWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsMicrofiltration membraneCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a method for printing and dyeing wastewater purification treatment in different steps. The method comprises the following steps: I, filtering with multiple mediums; II, performing visible light catalytic oxidation; III, filtering with a micro-filtration membrane; IV, filtering with an amphoteric ion-exchange resin. By adopting the treatment method disclosed by the invention, sewage can be purified step by step, that is, the sewage is treated with processes of grids, coagulating sedimentation, anaerobic hydrolysis and aerobic aeration tanks, and printing and dyeing wastewater effluent is fed through a multi-medium filtering layer from top to bottom; large-size garbage is firstly removed through the grids, further through coagulating sedimentation, impurities which can be relatively easily settled down are removed, meanwhile, decoloring is achieved, and further purification is carried out through the multi-medium filtering layer, so that the method has the advantages of high efficiency and environment protection.
Owner:许欠欠
Perovskite photoelectric detector for accelerating electron filtering
ActiveCN106356457AExtended Spectral Response RangeImprove mobility and exciton lifetimeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuenchingSpectral responsivity
The invention discloses a perovskite photoelectric detector for accelerating electron filtering. The perovskite photoelectric detector comprises a substrate, an anode, an active layer and a compound cathode, wherein a hole-transporting layer is arranged between the anode and the active layer and an electron filtering layer is arranged between the active layer and the compound cathode. According to the invention, a perovskite material, which is characterized by high migration rate, low exciton binding energy, longer exciton life and longer exciton diffusion length, is taken as the active layer of the photoelectric detector, so that the loss of heat exciton in the device is greatly reduced. A novel electron filtering layer is creatively provided; the electrons can be effectively transmitted to the cathode and then collected; the recombination probability of exciton and the quenching effect of electrode to exciton can be greatly reduced; the obtained perovskite photoelectric detector has higher external quantum efficiency and spectral responsivity; the performance is obviously promoted.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
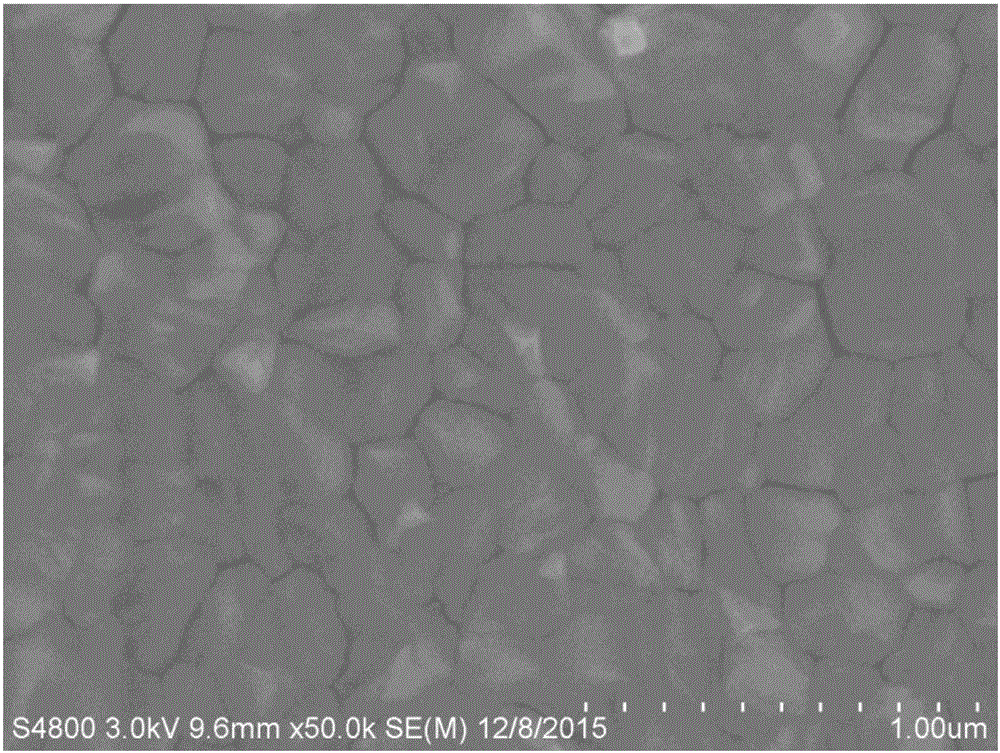
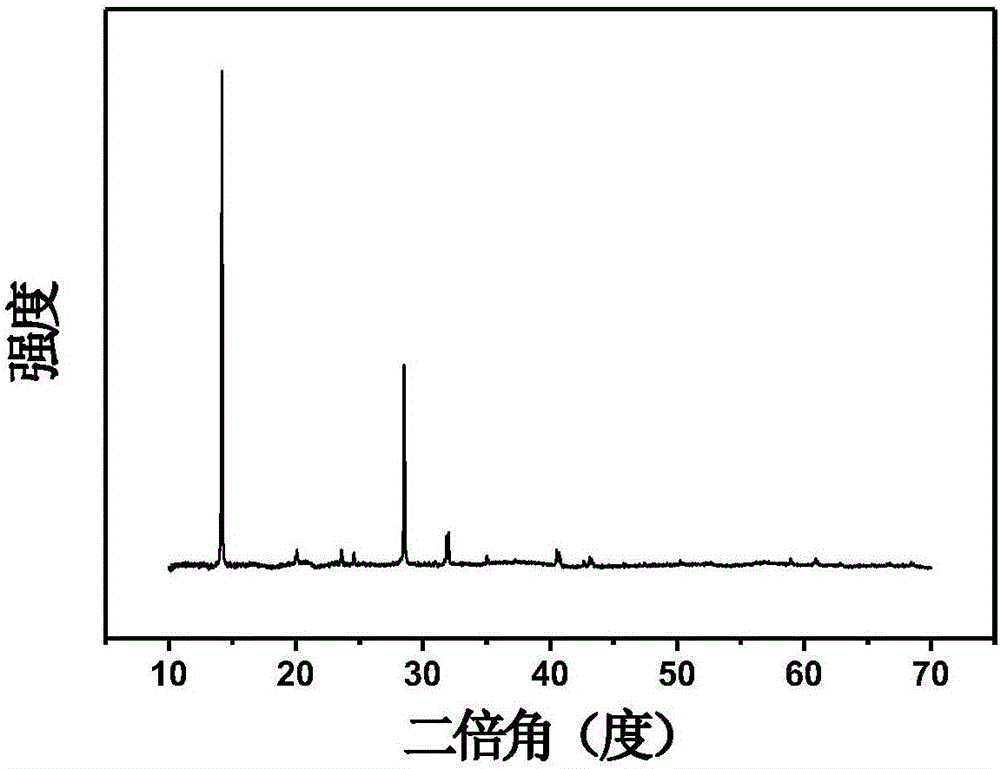
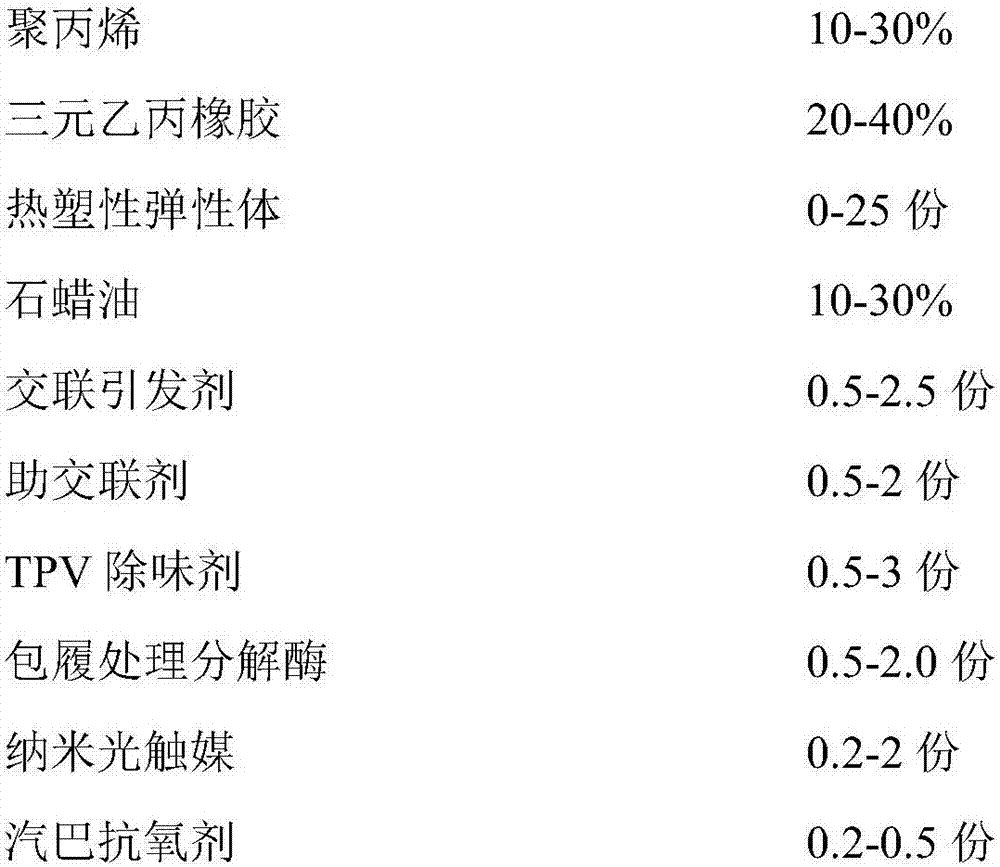
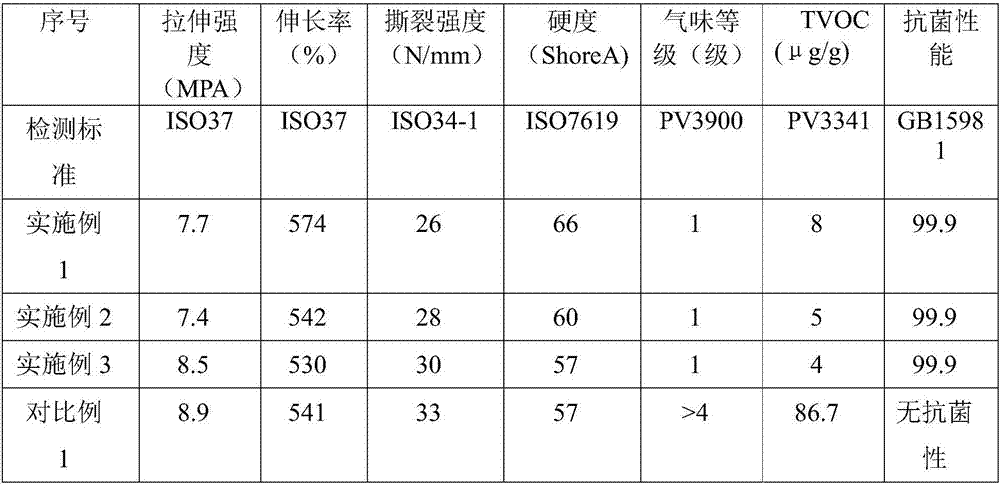
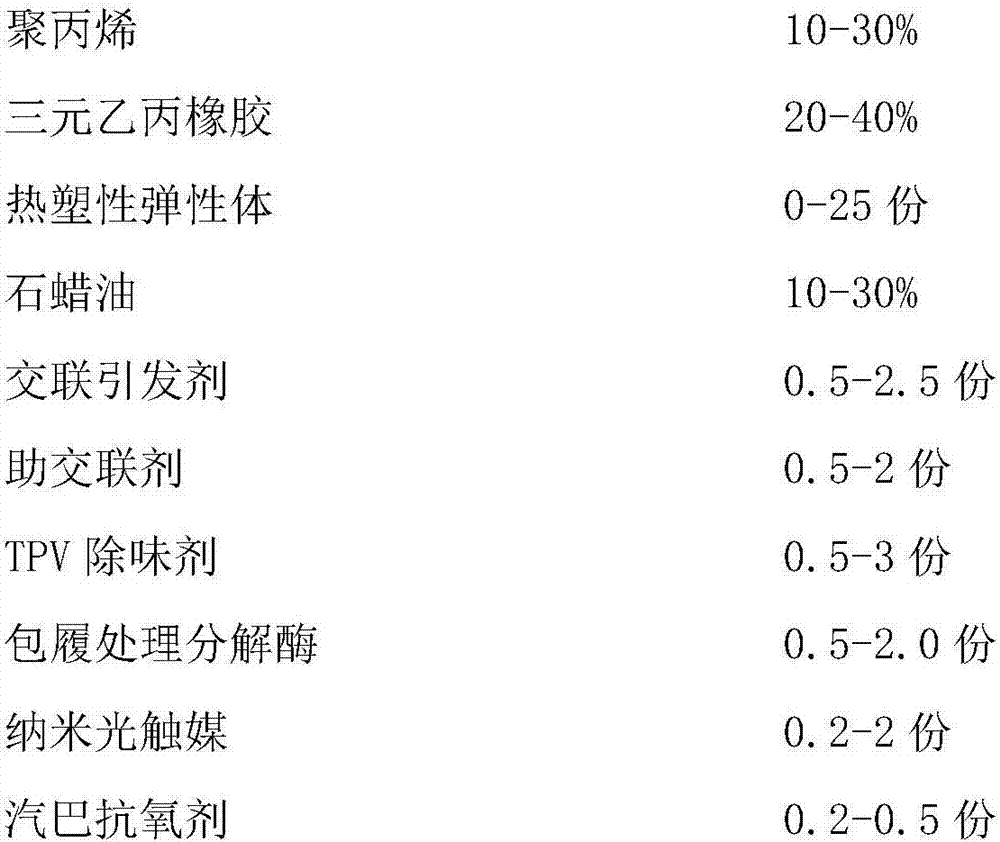
Low-odor TPV material with sterilization function and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a low-odor TPV material with a sterilization function and a preparation method thereof. The TPV material is prepared from polypropylene, ethylene propylene diene terpolymer, thermoplastic elastomer, paraffin oil, cross-linking agent, TPV deodorant, coating lytic enzyme, nano photocatalyst, and antioxidant according to parts by weight. The TPV deodorant eliminates low molecular weight volatile matters in TPV, and releases low boiling point additive in melting and mixing of materials, is similar to and compatible with small molecules with odor, and can extract the small molecular substances with odor in the TPV material, and then the extracted small molecular substances with odor are taken away by a vacuum pumping method, so that a low-odor TPV material is obtained; and the coating lytic enzyme and nano photocatalyst decompose trace low volatility harmful gas generated by a material shaping part and low volatility harmful gas generated by surrounding environment of the part into harmless carbon dioxide and water, so that the TPV material has powerful functions of sterilizing, deodorizing, resisting mildew, resisting stain and self-cleaning, and purifying air.
Owner:DONGGUAN JISU PLASTIC TECH
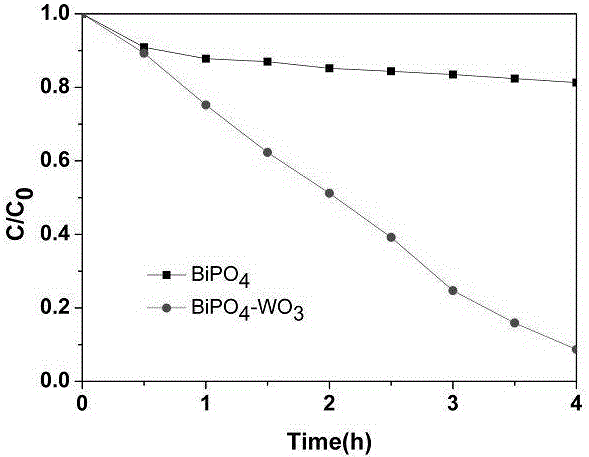
BiPO4-WO3 composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105854912AExtended Spectral Response RangeImprove solar utilizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsCentrifugationSodium tungstate dihydrate
The invention discloses a BiPO4-WO3 composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of inorganic environment-friendly photocatalysis materials. According to the technical scheme, the preparation method of the BiPO4-WO3 composite photocatalyst comprises the steps that 1, sodium tungstate and sodium chloride are added into deionized water according to the molar ratio of 1:1, the pH value of the mixed solution is adjusted with hydrochloric acid to range from 0.5 to 1 and transferred into a hydrothermal reaction still, the hydrothermal reaction still is placed in a microwave digestion instrument, a microwave reaction is carried out for 10 min to 30 min at the temperature of 180 DEG C, cooling, washing and drying are carried out after the reaction is finished, and WO3 powder is obtained; 2, a bismuth nitrate water solution is prepared, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and the WO3 powder are added to form a mixed solution; 3, the mixed solution obtained in the step 2 is stirred for 1 h at room temperature and then transferred into the hydrothermal reaction still, the hydrothermal reaction still is placed in the microwave digestion instrument, a microwave reaction is carried out for 10 min to 30 min at the temperature of 180 DEG C, centrifugation, washing and drying are carried out after the reaction is finished, and the BiPO4-WO3 composite photocatalyst is prepared. According to the prepared BiPO4-WO3 composite photocatalyst, the utilization rate of sunlight and photocatalytic activity are effectively increased.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing N-doped nano flower-shaped TiO2 photocatalysis material by taking carbonized lotus leaf as substrate
ActiveCN108435226AExtended Spectral Response RangeHigh catalytic activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsTetraOrder structure
The invention discloses a method for preparing a N-doped nano flower-shaped TiO2 photocatalysis material by taking carbonized lotus leaf as a substrate. The method is characterized in that tetra-n-butyl titanate is loaded at the carbonized lotus leaf, and an obtained product is subjected to calcining to prepare the TiO2 microcrystal-loaded carbonized lotus leaf substrate; in-situ growth of a TiO2crystal layer is carried out at the TiO2 microcrystal-loaded carbonized lotus leaf substrate, and the nano flower-shaped TiO2 photocatalysis material at the carbonized lotus leaf is prepared; N dopingtreatment is carried out on the nano flower-shaped TiO2 photocatalysis material at the carbonized lotus leaf, and the N-doped nano flower-shaped TiO2 photocatalysis material is obtained. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, and easy large-scale production, the prepared catalysis material prevents characteristics of ordered structure and morphology fixing, and hasthe advantages of wide spectrum response scope and high photocatalytic activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Conjugated fluorene polymer, preparing method thereof and solar cell device
InactiveUS20120312374A1Good optical stabilityImprove thermal stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceSpectral response
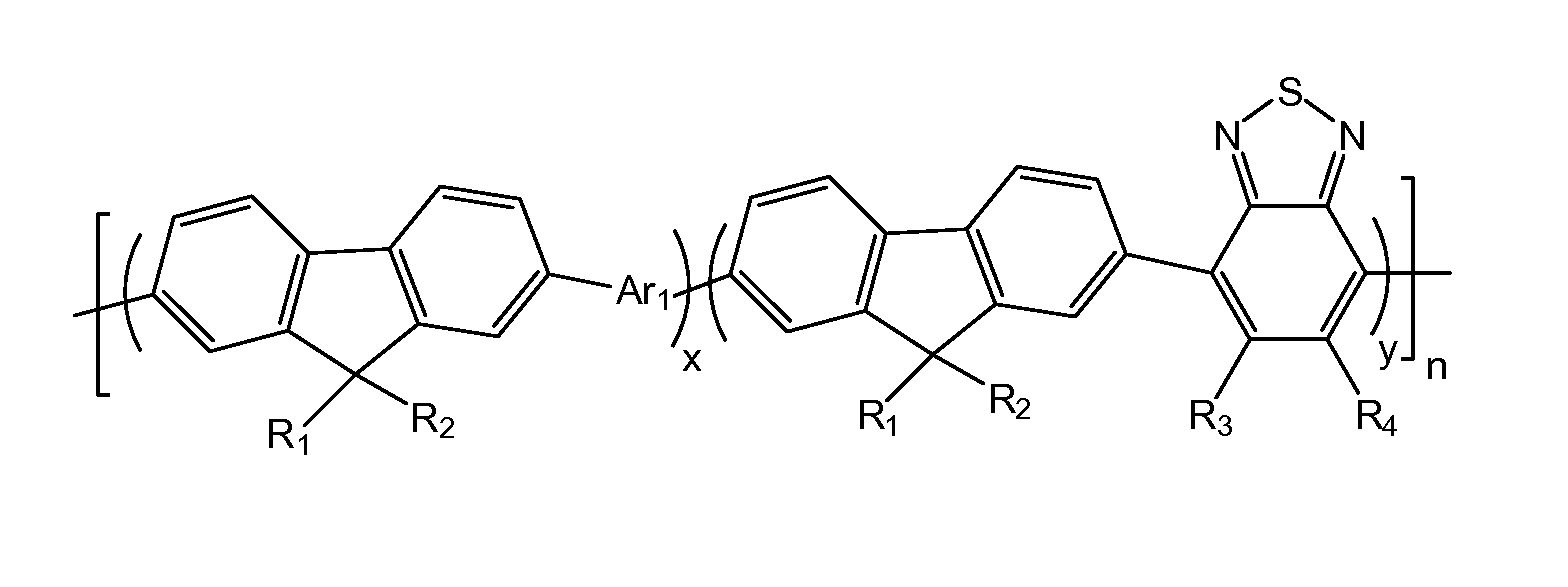
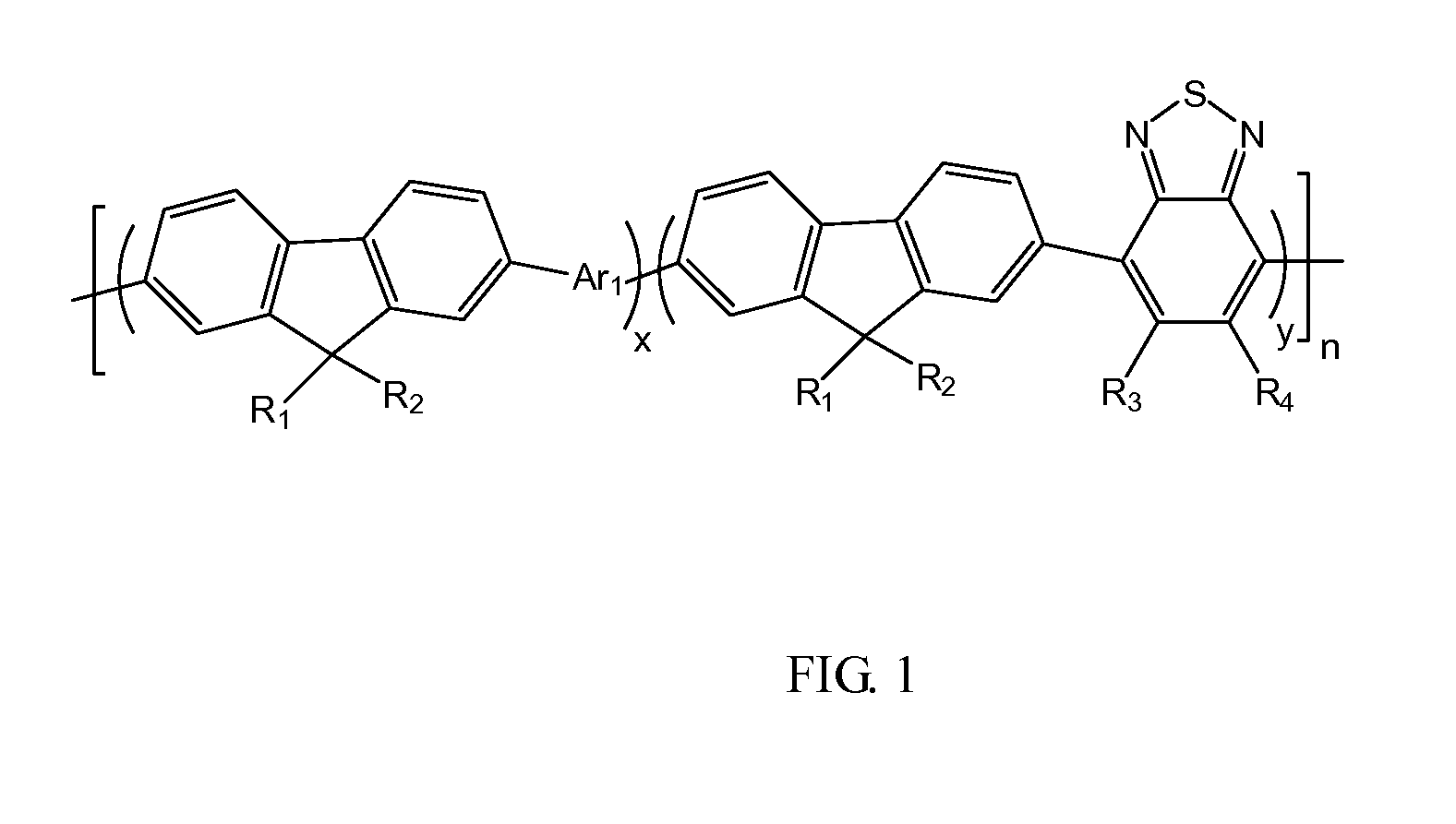
A conjugated fluorene polymer is provided, which is defined by structure formula (1), wherein: R1, R2, R3, R4 represent H or C1-C20 alkyl, x+y=1, x≠0, y≠0, n is a natural number between 1-1000, Ar1 is a group containing thiophene. A preparation method for the conjugated fluorene polymer and a solar cell device containing the conjugated fluorene polymer are also provided. Due to fluorene or its derivatives and conjugated structure, the conjugated fluorene polymer exhibits an excellent light stability and thermal stability. In addition, since thiophene and benzothiadiazole groups are introduced into the main chain of the polymer, the spectral response range of the polymer is broadened.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD
Porphyrin copolymer containing benzothiadiazole unit, its preparation method and application
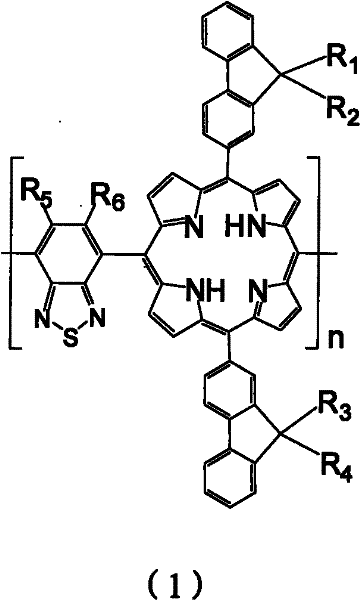
InactiveCN102206328ALower energy gapBandgap narrowingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectral responsePorphyrin
The invention relates to the field of organic material technology, and provides a porphyrin copolymer containing benzothiadiazole unit, which is a copolymer expressed in a structural formula (1). Wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 are selected from alkyl of C1 to C32; n is an integer of 1 to 200. The invention also provides a method for preparing the porphyrin copolymer containing benzothiadiazole unit and an application. The porphyrin copolymer containing benzothiadiazole unit has excellent light stability and heat stability due to a fluorenes porphyrin structure and benzothiadiazole unit. And the benzothiadiazole unit is introduced in the polymer for widening a spectral response range of the polymer.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Preparation method for graphite phase carbon nitride/high bismuth oxyiodide heterojunction with up-conversion characteristics and product thereof, and application of product
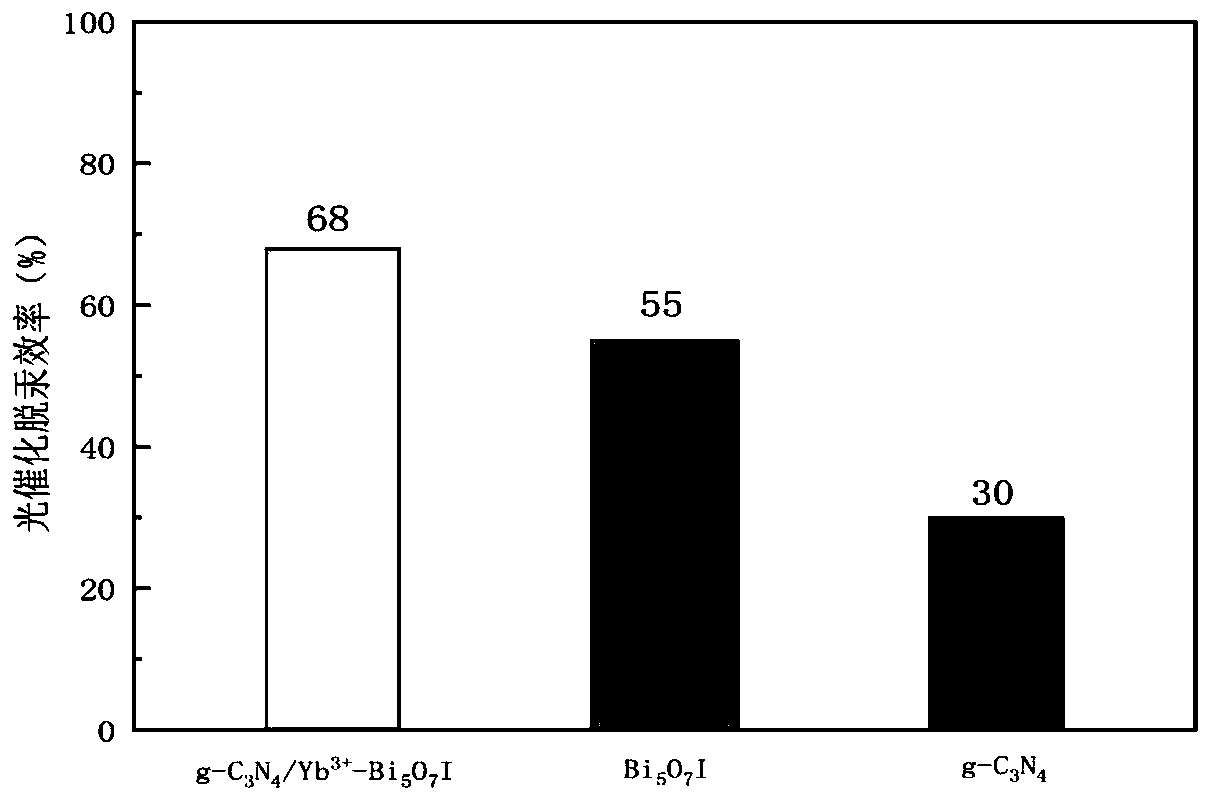
PendingCN111250142AExcellent electron-hole separation abilityExtended Spectral Response RangePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSpectral responsePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphite phase carbon nitride / high bismuth oxyiodide heterojunction with up-conversion characteristics and a product thereof, and application of the product. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively dispersing Bi(NO<3>)<3>.5H<2>O, Re(NO<3>)<3>, g-C<3>N<4> and KI into ethylene glycol, carrying out ultrasonic treatment, andrespectively marking the formed solutions as a solution A, a solution B, a solution C and a solution D; adding the solution B into the solution A, carrying out stirring, then adding the solution C, conducting stirring, finally adding the solution D, and conducting uniform stirring to obtain a mixed solution; subjecting the obtained mixed solution to a reaction for 10-12 hours at a temperature of 150-160 DEG C, and drying the obtained product to obtain a precursor g-C<3>N<4> / Re<3+>-BiOI; and calcining the precursor g-C<3>N<4> / Re<3+>-BiOI for 2 to 3 h at a temperature of 450 to 480 DEG C so as to obtain a product g-C<3>N<4> / Re<3+>-Bi<5>O<7>I. The graphite phase carbon nitride / high bismuth oxyiodide heterojunction with the up-conversion characteristics is prepared through two steps includinga solvothermal method and a calcining method, has excellent electron hole separation capability and a large spectral response range, and is wide in application range.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Near-infrared wide-spectrum metal complex dye and preparation method thereof
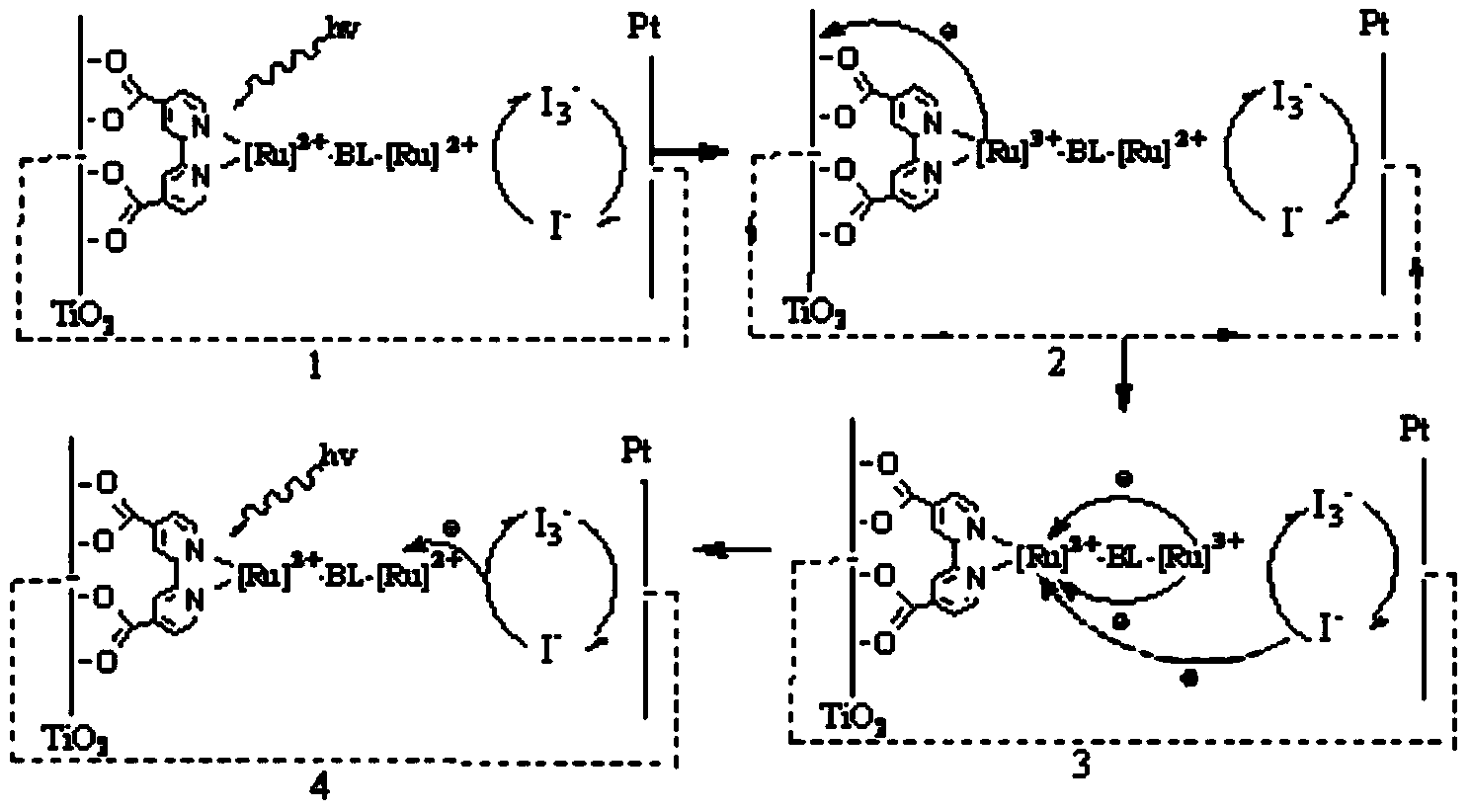
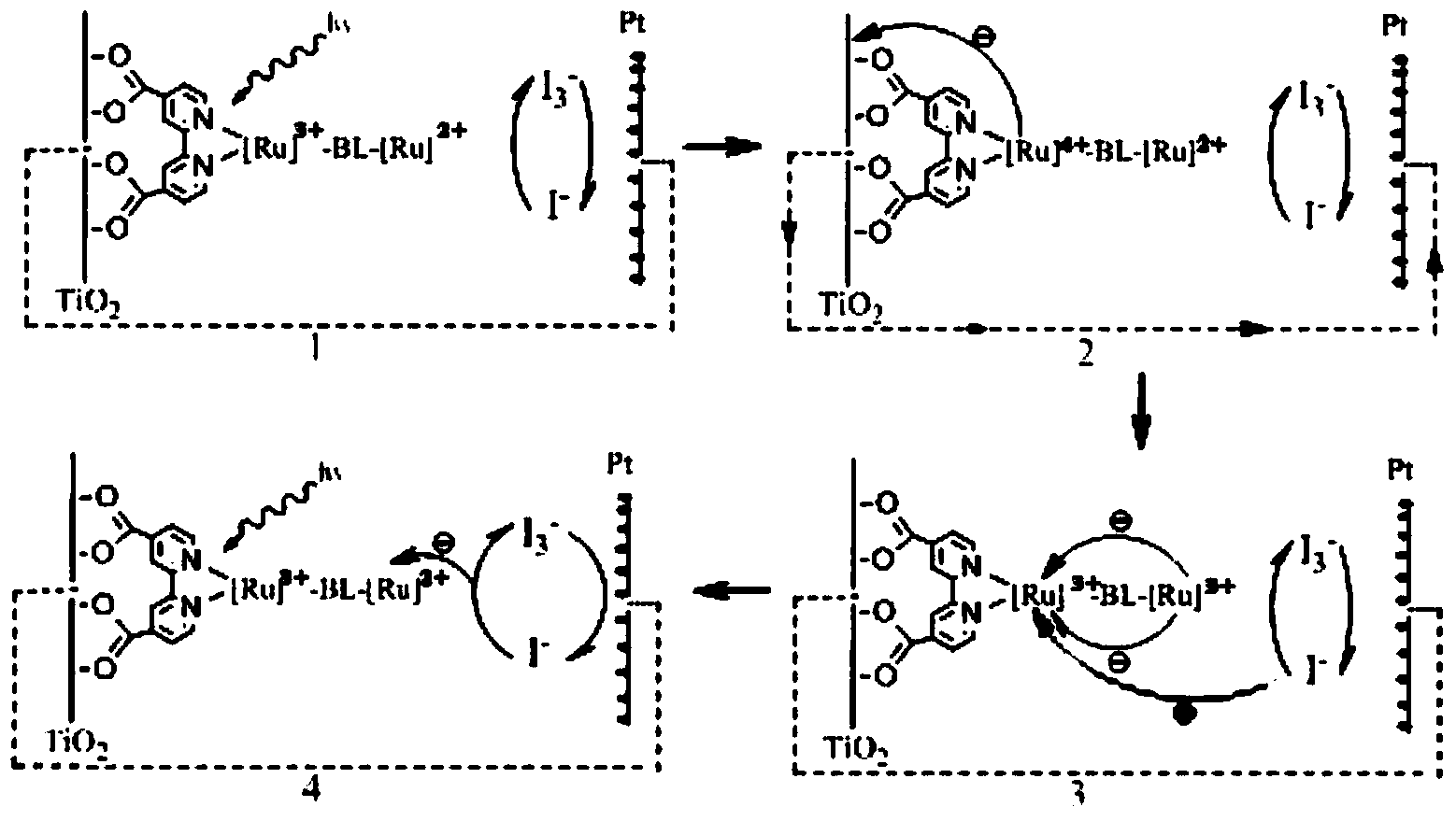
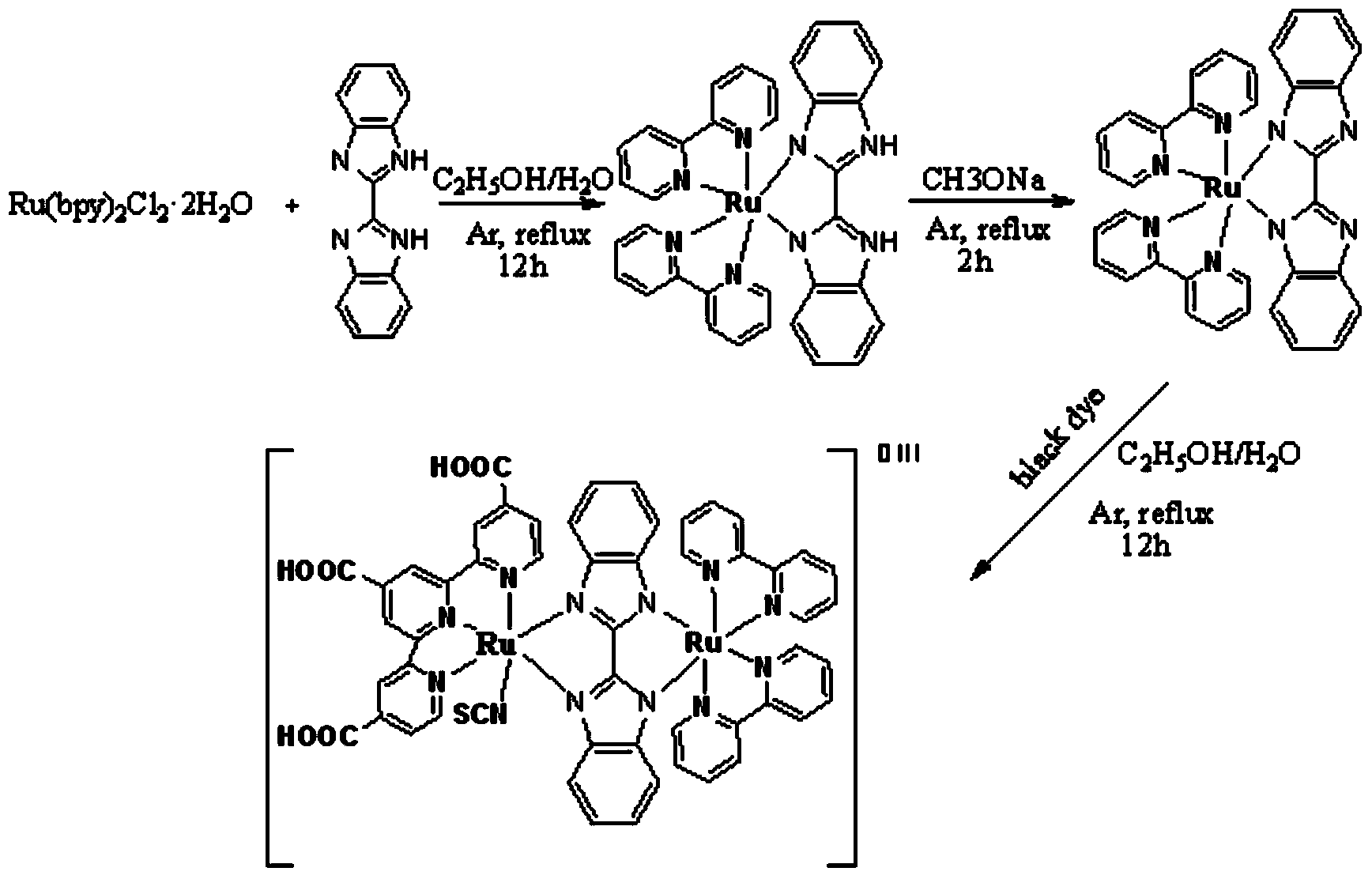
InactiveCN103952009AExtended Spectral Response RangeImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesAzo dyesSpectral responseStructural formula
The invention discloses a near-infrared wide-spectrum metal complex dye. The structural formula of dye molecules is [M<m+>-BL-M<n+>], wherein a metal ion M forms a metal building block with surrounding ligands; BL is a bridging ligand; a delocalized pai orbit is formed between the metal building block and the bridging ligand; the bridging ligand has good conjugation performance and electronic conductivity; the charge distribution of the dye molecules is completely delocalized; when the metal building block receives energy stimulation, a strong valence state transition effect is generated in the dye molecules, and can be used for broadening the absorption range of a dye spectrum and ensuring that an absorption spectrum is red-shifted to a near-infrared area. The near-infrared wide-spectrum metal complex dye disclosed by the invention can be applied to dye-sensitized solar cells, and can be used for increasing the spectral response range of the sensitized solar cells, thus improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of cells.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS +1
Organic photoelectric material containing nitrogen thiophene, manufacturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN102191036AExtended Spectral Response RangeWide spectral response rangeOrganic chemistryFinal product manufactureTerthiopheneChemical compound
The invention relates to the organic material technology field. An organic photoelectric material containing nitrogen thiophene is provided, and comprises a compound expressed by structural formula (1), wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are same or different alkyls expressed as H or C1-C20; m and n stand for same or different integers between 0-10. The invention also provides a manufacturing method and application of the organic photoelectric material containing nitrogen thiophene. Because of possessing thiophene ring and cyan, the organic photoelectric material containing nitrogen thiophene has wide spectrum response, good heat stability and environmental stability. Synthetic route in manufacturing method of the organic photoelectric material containing nitrogen thiophene is simple, thereby manufacturing cost is low and application prospect is wide.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102190680AExtended Spectral Response RangeImprove photoelectric performanceGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsLaser active region structureSpectral responseStructural formula
The invention relates to the technical field of organic materials, and provides a silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material, which comprises compounds shown as a structural formula (1). In the formula, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are same or different, and refer to H or C1-C20 alkyl; and m and n are same or different and refer to an integer from 0 to 10. The invention also provides a manufacturing method for the silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material and application of the silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material. The silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material has thiophene ring and cyan, so the silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material has wider spectral response and higher thermal stability and environmental stability. The manufacturing method for the condensed ring thiophene organic photoelectric material has the advantages of simple synthetic route, low manufacturing cost and wide application prospect.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Spectrum detector based on high electron mobility transistor and preparation method thereof
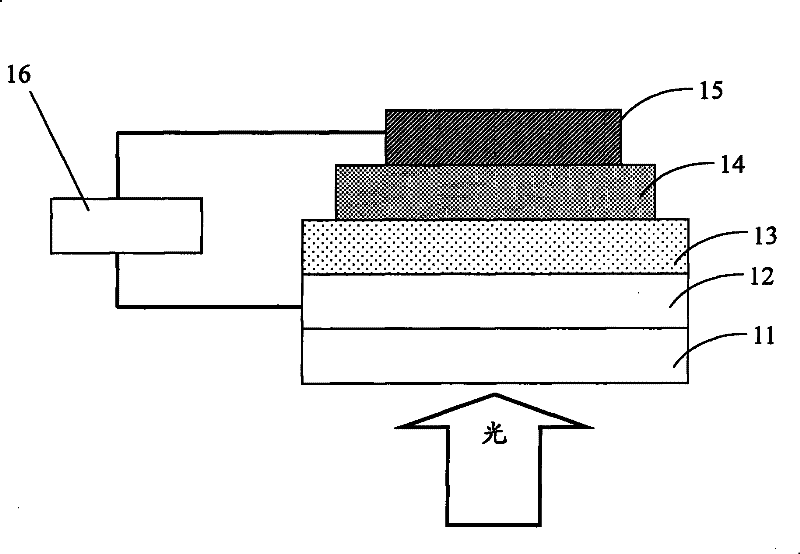
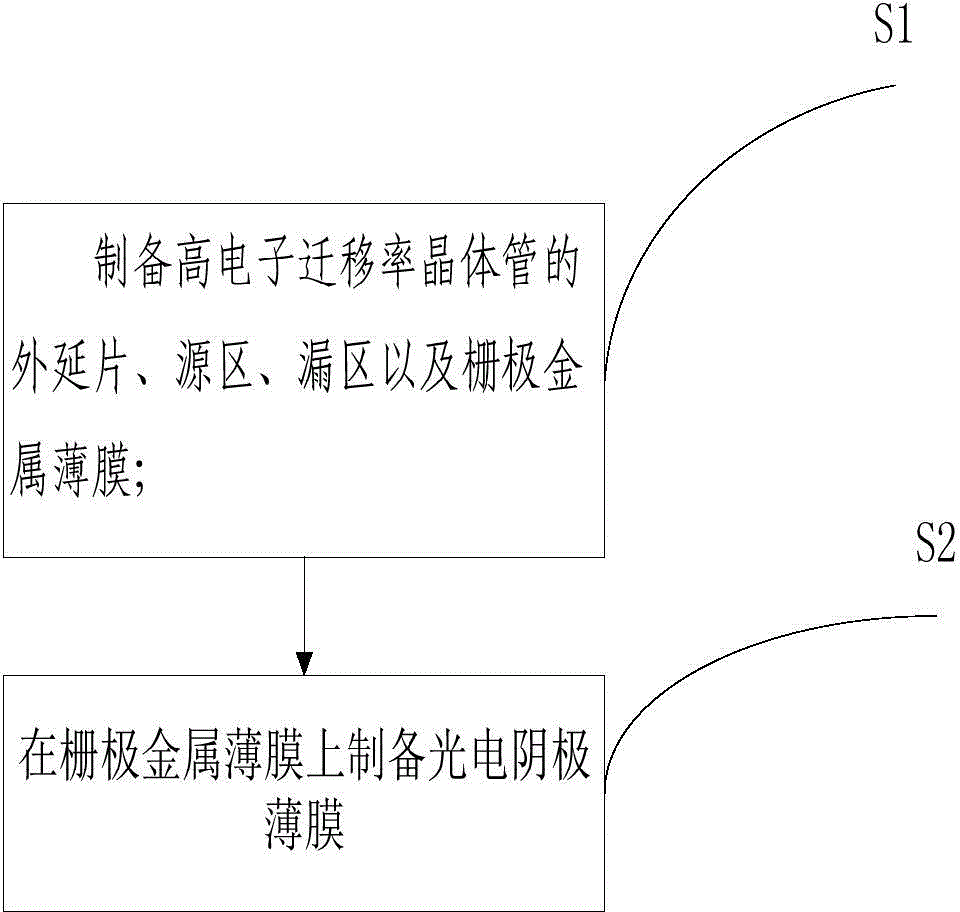
ActiveCN104900745AReduce dependenceHigh sensitivityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesOptical radiationPhotocathode
The invention relates to a spectrum detector based on a high electron mobility transistor and the preparation method thereof. A photoelectric cathode film layer is arranged on a grid metallic film of the high electron mobility transistor. During spectrum detection, light radiates on the photoelectric cathode film, so that external photoeffect occurs on the photoelectric cathode film. The charge distribution on the surface of the photoelectric cathode film changes, the grid voltage changes, so that the two-dimensional electron gas generated or density in the high electron mobility transistor change. The channel current in the high electron mobility transistor changes accordingly, and the light wave signals are converted into electric signals to detect optical radiation in a highly sensitive means.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Alpha-indium selenide two-dimensional photoelectric detector based on transparent electrode
PendingCN112071940ASmall sizeIncrease the photoelectric response rangeSemiconductor devicesIndiumPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an alpha-indium selenide two-dimensional photoelectric detector based on a transparent electrode, which comprises an alpha indium selenide two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor layer, a hafnium oxide dielectric layer and a doped silicon substrate which are sequentially distributed from top to bottom, the alpha-indium selenide two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor layer is provided with the transparent electrode, and the detector is small in size and low in cost. Photoelectric responsivity is high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
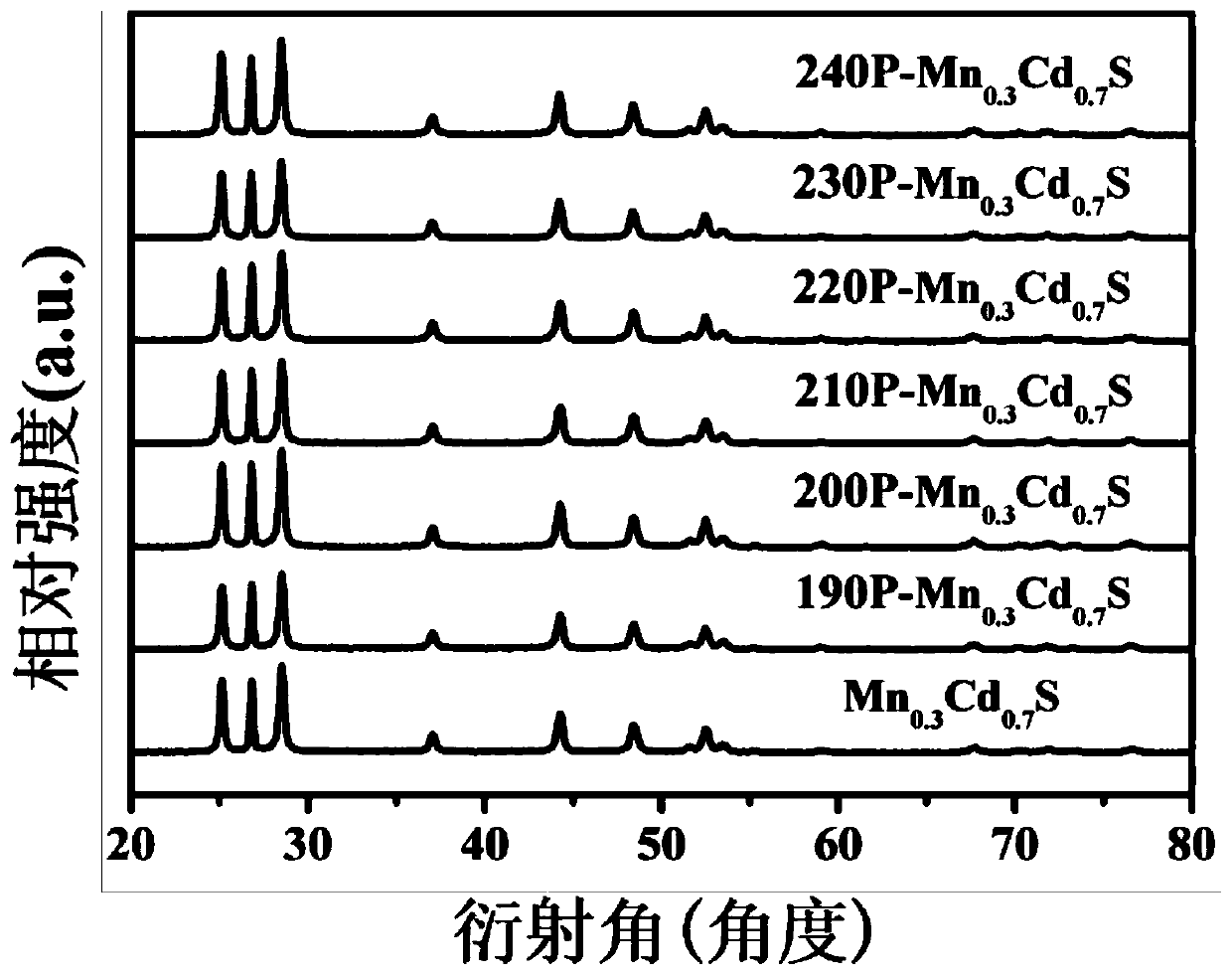
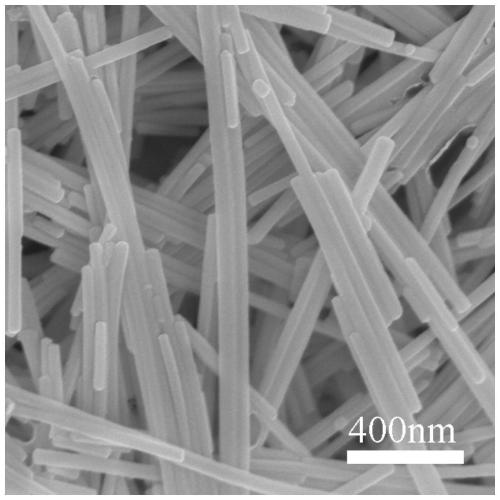
Phosphorus-doped Mn0.3Cd0.7S nanorod photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111085228AEasy transferEasy to separatePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionPtru catalystSulfide compound
The invention discloses a phosphorus-doped Mn0.3Cd0.7S nanorod photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a phosphorus source with Mn0.3Cd0.7S, carrying out ball milling, and calcining the material at 200-400 DEG C for 1-3 hours under the protection of an inert atmosphere; cooling the material to room temperature, and washing, filtering and drying the cooled material to obtain the phosphorus-doped Mn0.3Cd0.7S nanorod photocatalyst. The prepared composite photocatalyst is of a rod-like structure, has a large length-diameter ratio, is beneficial to transfer and separation of photon-generated carriers, can significantly improve the problem of serious photo-corrosion phenomenon of sulfide catalysts, and shows a high photocatalytic hydrogen production rate. In addition, the raw materials used in the preparation method of the catalyst are cheap and easy to obtain, and the method is easy and convenient to operate, mild in reaction condition and easy to implement.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
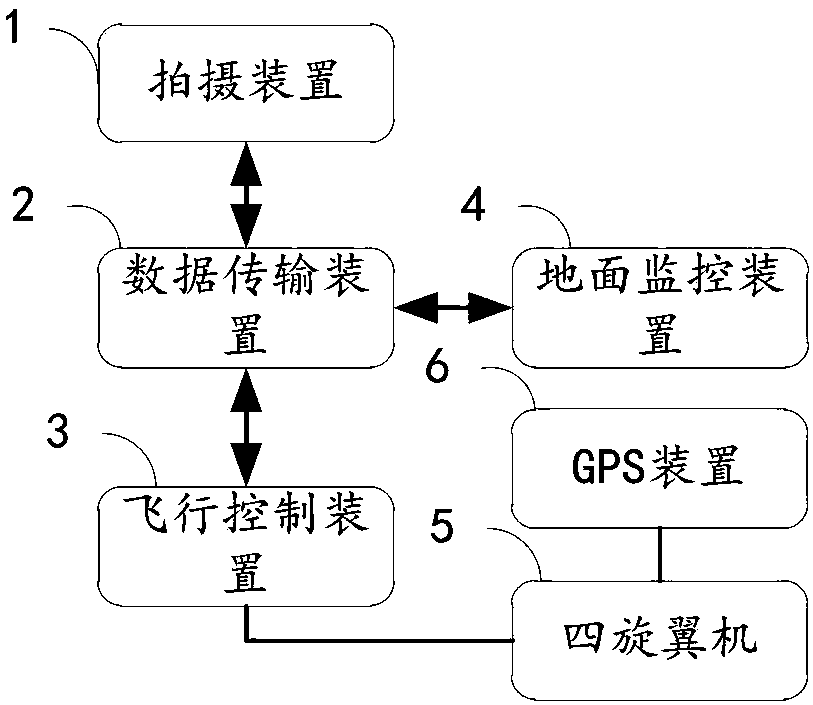
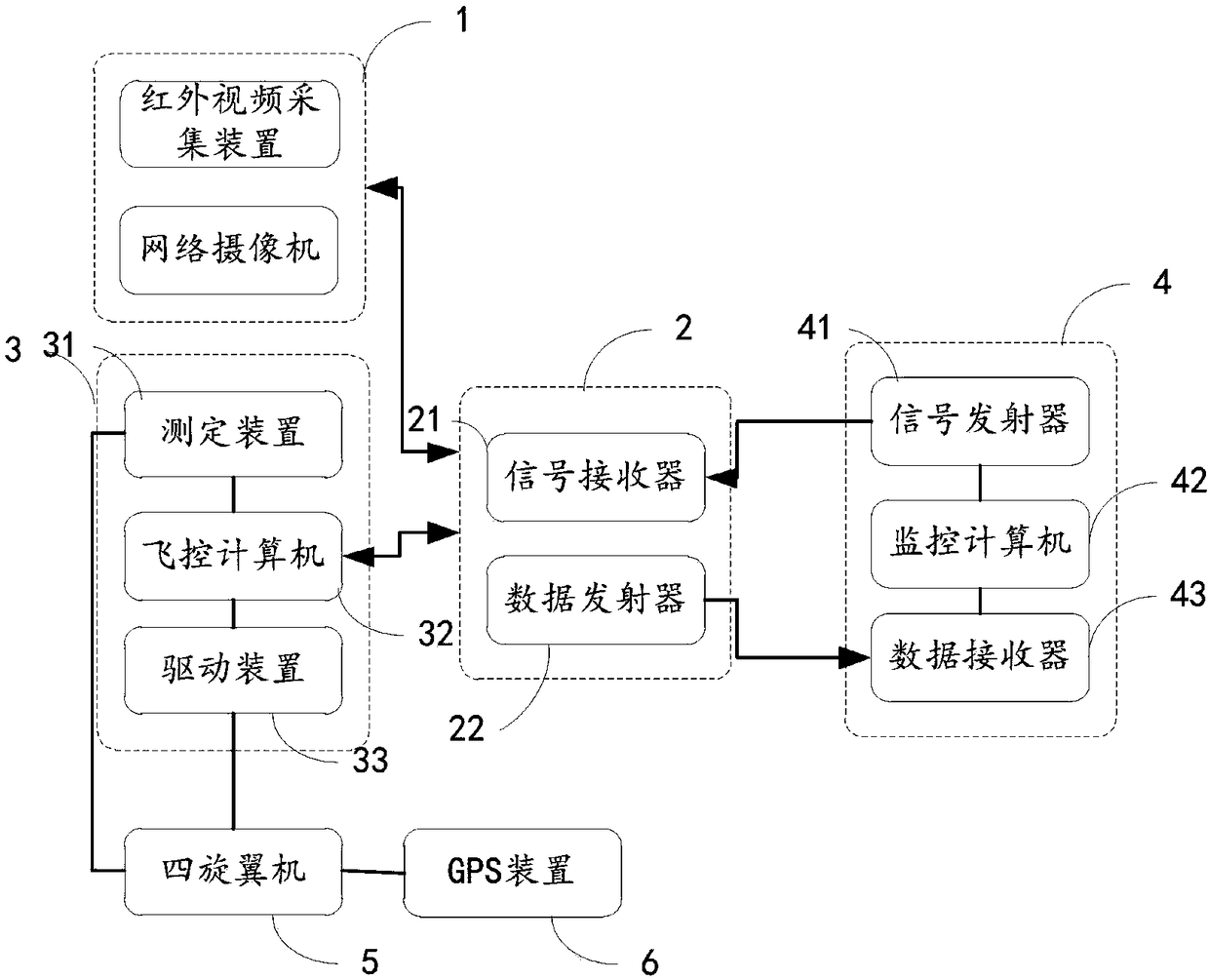
Image acquisition and monitoring device for quadrotor
PendingCN108243328AFlexible controlReduce volumeClosed circuit television systemsAttitude controlEngineeringData transmission
The invention relates to an image acquisition and monitoring device for a quadrotor, which is applicable to a quadrotor. The device comprises a shooting device, a data transmission device, a flight control device and a GPS device arranged on the quadrotor and connected sequentially, and a ground monitoring device wirelessly connected with the data transmission device, wherein the shooting device is used for carrying out image shooting and infrared video shooting under control of the ground monitoring device; the GPS device is used for positioning the quadrotor; and the shooting device comprises a network camera and an infrared video acquisition device. Flexible control on the quadrotor can be realized through the ground monitoring device, an accurate and clear image can be acquired, and real-time, on-site, flexible and all-round agricultural information image monitoring can thus be realized.
Owner:HUBEI ENG UNIV
Visual monitoring management system for substation
PendingCN114069845AAccurate and fast diagnosis of faultsRelieve pressureCircuit arrangementsAlarmsVisual monitoringElectric machine
The invention provides a substation visual monitoring management system, and relates to the substation matching technical field. The system comprises a console and a stand column; the top surface of the console is provided with an unmanned aerial vehicle, the console is in signal connection with the unmanned aerial vehicle, the top end of the stand column is fixedly provided with a cableway, the surface of the cableway is provided with a monitoring device, and the monitoring device comprises a mounting plate; a sliding sleeve is fixed to the bottom face of the mounting plate, the sliding sleeve is movably connected with the cableway, a rotating motor is fixed to the top face of the mounting plate, a roller is fixed to the output end of the rotating motor, the roller penetrates through the mounting plate and is movably connected with the cableway, and when a fault is found, in order to determine and position the fault, the console controls the unmanned aerial vehicle to inspect and shoot the fault position shot by the monitoring device, so that the monitoring management system of the substation is more accurate and rapid in fault diagnosis.
Owner:PANJIN POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +1
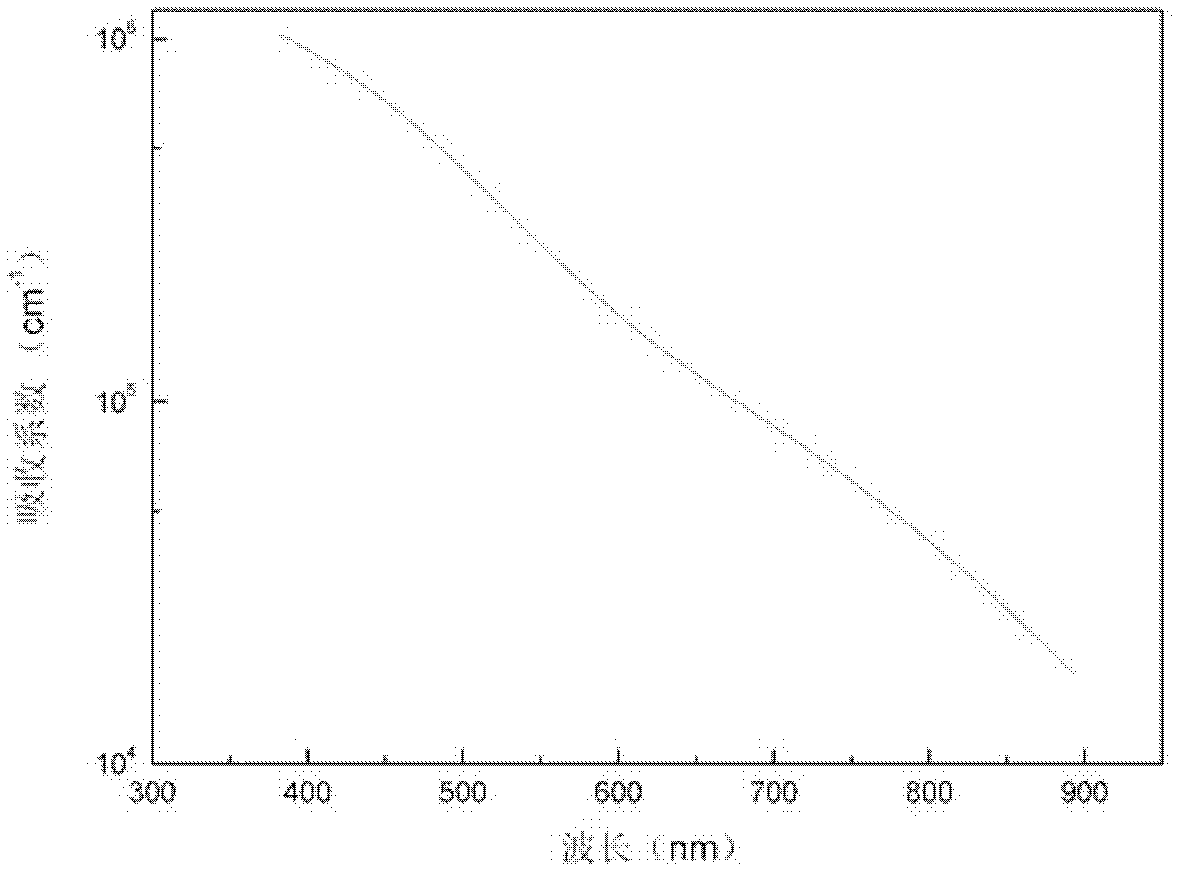
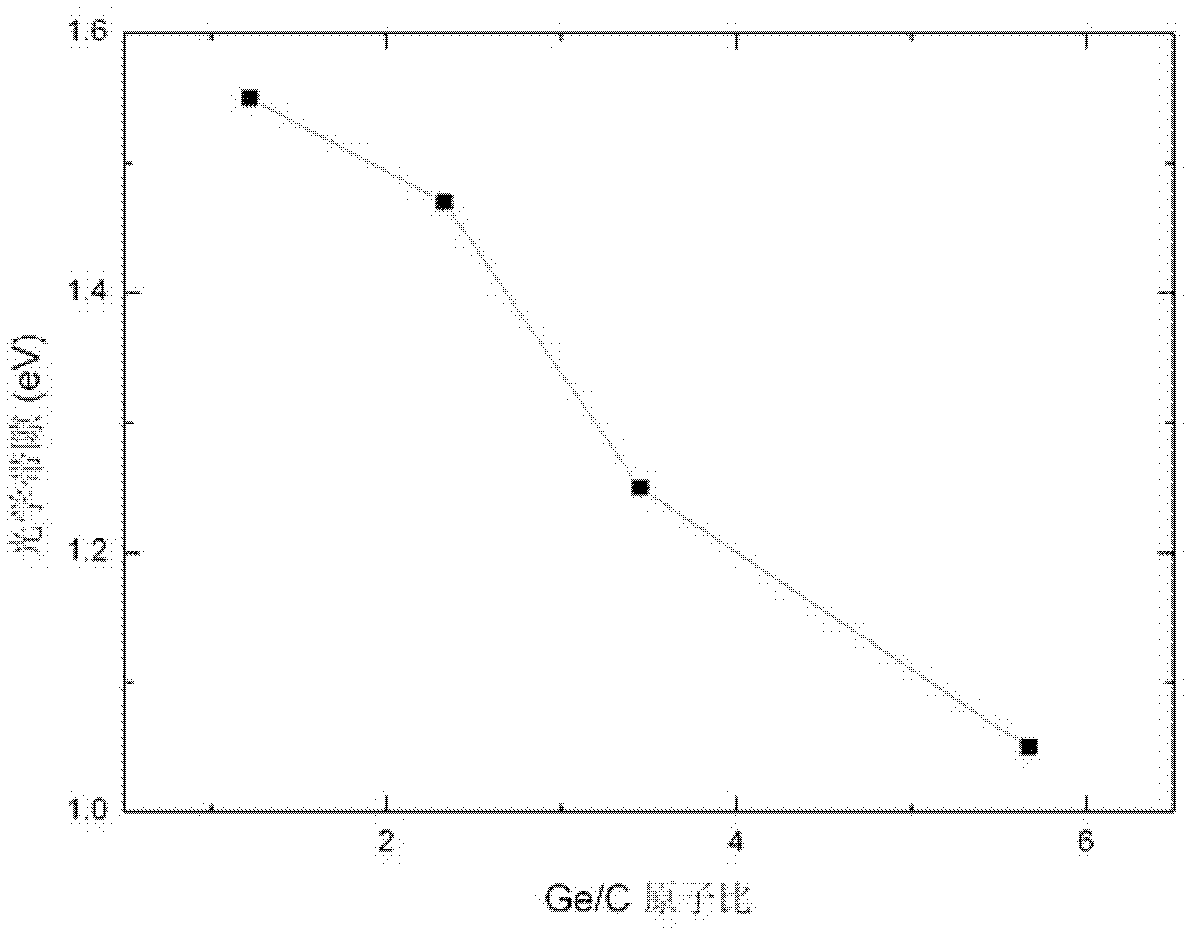
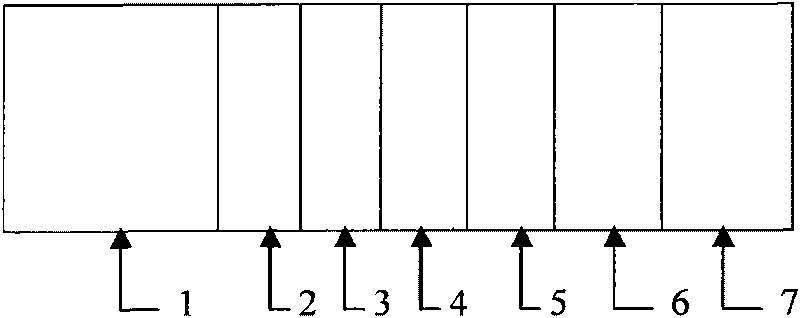
Solar cell with carbon germanium thin film as intrinsic layer and preparation method thereof
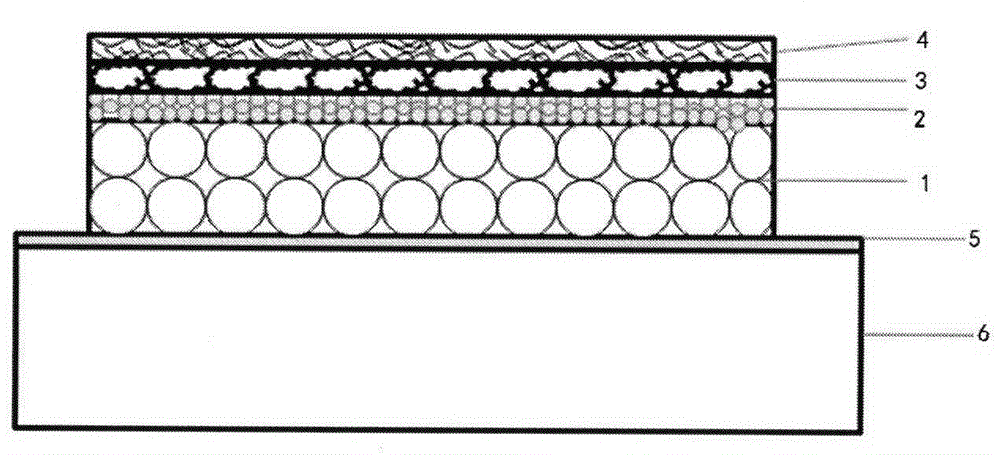
InactiveCN102280514ANovel structureSimple preparation processFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationTransformation efficiencyAmorphous silicon
The invention discloses a method for preparing a solar cell with a carbon germanium thin film serving as an intrinsic layer, and relates to a solar cell and a method for preparing the solar cell. The invention aims to solve the problem that the traditional solar cell which takes an amorphous silicon material as the intrinsic layer has wide band gap and small absorption coefficient. The solar cell comprises a transparent substrate (1), a transparent conductive thin film (2), a P-type window layer (3), an intrinsic layer and an N-type layer (5). The method comprises the following steps of: plating the transparent conductive thin film (2) on the transparent substrate (1); plating the P-type window layer (3) on the transparent conductive thin film (2); cleaning, heating, preserving heat, introducing argon, backwashing and cleaning; preparing the intrinsic layer (4); and preparing the N-type layer (5) to complete the preparation of the solar cell with the carbon germanium thin film serving as the intrinsic layer. The solar cell disclosed by the invention is novel in structure, simple in preparation and easy to operate; the carbon germanium thin film serves as the intrinsic layer, has the advantages of narrow band gap and high optical absorption, and can improve the photoelectric transformation efficiency. The invention is applied to the field of solar cells.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
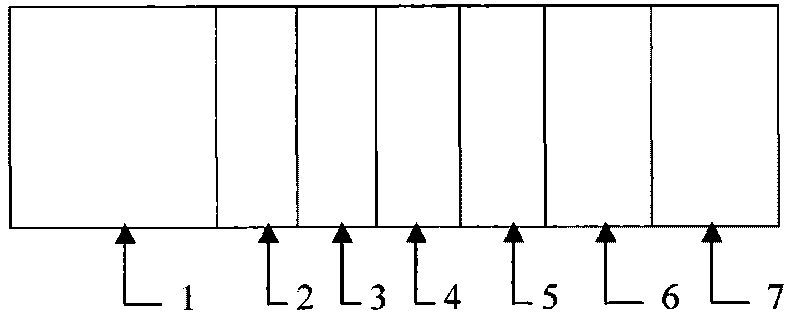
Silicon-based thin film solar cell with microcrystalline silicon-germanium thin film as intrinsic layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101752435ANovel structureExtended Spectral Response RangeFinal product manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingFilm materialReaction chamber
The invention discloses a silicon-based thin film solar cell with a microcrystalline silicon-germanium thin film as an intrinsic layer, which comprises a transparent substrate, a transparent conductive thin film, a P-shaped window layer, an intrinsic layer I, an N+ layer, a back reflection electrode and a metal electrode, wherein the intrinsic layer is the microcrystalline silicon-germanium thin film. The preparation method of the microcrystalline silicon-germanium thin film comprises the following steps of: (1) placing a glass substrate with the transparent conductive film into a vacuum chamber, wherein the base vacuum is higher than 2*10-4Pa; and (2) under the condition of introducing reactant gas silane, germane, fluorogermanate and hydrogen in a reaction chamber, precipitating the microcrystalline silicon-germanium thin film. The invention has the advantages that the silicon-based thin film cell has novel structure, the prepared microcrystalline silicon-germanium thin film material has the advantages of narrow band gap, low defect, high photosensitivity, simple process, easy operation, and low manufacturing cost, and the silicon-based thin film cell adopting the material can improve the spectral response range, stability and conversion efficiency.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method and device for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater
ActiveCN111252846BLarge specific surface areaImprove photocatalytic efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPtru catalystPhotocatalytic degradation
The invention provides a method and a device for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater, belonging to the technical field of organic pollutant treatment. The method firstly introduces nitrogen element into titanium dioxide crystal lattice in the form of replacing nitrogen or interstitial nitrogen to obtain doped N Then, electrospinning was used to obtain the zinc source precursor sol, and the titanium dioxide was grown on the spool of the nano-zinc oxide electrospinning film in an orderly manner by the hydrothermal method to obtain the zinc oxide / titanium dioxide composite thin film catalyst. Hydrogen peroxide has a synergistic effect and has efficient catalytic ability to a variety of organic pollutants. The method has mild reaction conditions and high degradation efficiency. After 2 hours of reaction, the degradation rate can reach more than 95%. The device effectively solves the problem of difficult separation of the photocatalyst through the spirally coiled reaction tank body and the photocatalytic light source vertically inserted in the middle of the reaction tank body, and can prolong the service life of the catalyst membrane layer.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Erbium-mono-doped C12A7 up-conversion material-doped dye-sensitized photoanode and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107633949AExtended Spectral Response RangeImprove battery efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesLuminescent compositionsDye-sensitized solar cellSunlight
The invention belongs to the technical field of new energy materials and discloses an erbium-mono-doped C12A7 up-conversion material-doped dye-sensitized photoanode and a preparation method and application thereof. C12A7:Er is applied to a dye-sensitized solar cell for the first time. According to the method, mixed paste of the C12A7:Er and P25 coats conductive glass by adopting a draw-off methodto prepare a photoanode, and the dye-sensitized solar cell is assembled. The cell comprises the photoanode, a platinum counter electrode and an electrolyte. According to the cell, the photoanode is doped with the C12A7:Er, and the sunlight of over 700nm is converted into visible light, so that the spectral response range of the cell is expanded and the efficiency of the cell is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Sound conduction device and wearable equipment with same
ActiveCN107015649AExtended Spectral Response RangeImprove conduction efficiencyVisual indicationInput/output for user-computer interactionSpectral responseEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of communication equipment, and particularly discloses a sound conduction device. The sound conduction device comprises a mounting part, a metal elastic piece, a ceramic piece and a counterweight block, the mounting part comprises a mounting face and a transmission face which are oppositely arranged, the metal elastic piece is mounted on the mounting face, the ceramic piece and the counterweight block are both installed on the metal elastic piece, the counterweight block is located at one side of the ceramic piece, and the transmission face is used for being fitted with the arm of a user to transmit vibration generated by the ceramic piece to the arm of the user. According to the sound conduction device, a mode that the ceramic piece and the counterweight block are arranged on the metal elastic piece is adopted, the counterweight function of the counterweight block can be utilized, the sound spectral response range is increased, the sound conduction efficiency is improved, and therefore the sound effect is improved, and it is ensured that the user has good sound experience. The invention further discloses wearable equipment with the sound conduction device.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIAOTIANCAI TECH CO LTD
Organic dye sensitized solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109036854AReduced band gapImprove photoelectric conversion performanceLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSpectral responseOrganic dye
The invention discloses an organic dye sensitized solar cell, comprising an organic dye sensitized photoanode, a composite counter electrode and a gel electrolyte, and the gel electrolyte is injectedbetween the organic dye sensitized photoanode and the composite counter electrode. Compared with the prior art, in the organic dye sensitized solar cell and the preparation method thereof provided bythe invention, organic dye with a D-pi-A-type structure serving as a sensitizer has a strong electron push-pull system, has a higher molar extinction coefficient and wider spectral response range, a graphene / platinum composite layer and a titanium dioxide reflective layer coated on the counter electrode have strong catalytic performance and electrical conductivity, the sunlight not absorbed by thephotoanode can be reflected back to the photoanode to be subjected to secondary absorption, the usage amount of valuable catalyst is reduced, thereby reducing cost, and the gel electrolyte has relatively high conductivity and electrochemical stability, which can remarkably improve the short circuit current and open circuit voltage of the battery, high light stability and thermal stability are achieved, and the solar cell has broad application prospects.
Owner:NANJING CHUQING ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Splicing structure based on three sCMOS detectors
ActiveCN109108594ASolve the disadvantages of insufficient widthWide spectral response rangeMetal working apparatusSpectral responseImage detection
The invention discloses a splicing structure based on three sCMOS detectors. The three sCMOS detectors are staggered and spliced according to a delta-shaped structure; a first detector above the deltashape is used as a reference, and specifically the row pixel of the first detector is used as a Y-direction reference, and the column pixel is an X-direction reference so as to adjust the position ofthe first detector; the first detector is used as the reference, and the positions of a second detector in the x direction and the y direction at the lower left part of the delta shape are adjusted according to the splicing requirements; the first detector and the second detector are used as references, and according to the splicing requirement, the positions of a third detector in the x direction and the y direction at the right lower part of the delta shape are adjusted; and the three adjusted detectors are fixed to complete the splicing of the three sCMOS detectors. By the splicing structure, the defect that the width of the aspect of image detection is insufficient can be overcome, the field of view is greatly expanded through splicing, and a wide spectral response range, a high spectral response and ultra-low readout noise are achieved.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102190680BWide spectral response rangeExtended Spectral Response RangeGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsLaser active region structureSpectral responseStructural formula
The invention relates to the technical field of organic materials, and provides a silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material, which comprises compounds shown as a structural formula (1). In the formula, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are same or different, and refer to H or C1-C20 alkyl; and m and n are same or different and refer to an integer from 0 to 10. The invention also provides a manufacturing method for the silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material and application of the silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material. The silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material has thiophene ring and cyan, so the silicon-containing thiophene organic photoelectric material has wider spectral response and higher thermal stability and environmental stability. The manufacturing method for the condensed ring thiophene organic photoelectric material has the advantages of simple synthetic route, low manufacturing cost and wide application prospect.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com