Automatic gain control for a wireless receiver
A technology of gain value and equipment, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as increased cost and complex design of wireless receivers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The word "exemplary" is used herein to mean "serving as an example, instance, or illustration." Any embodiment or design described herein as "exemplary" is not necessarily to be construed as preferred or advantageous over other embodiments or designs.
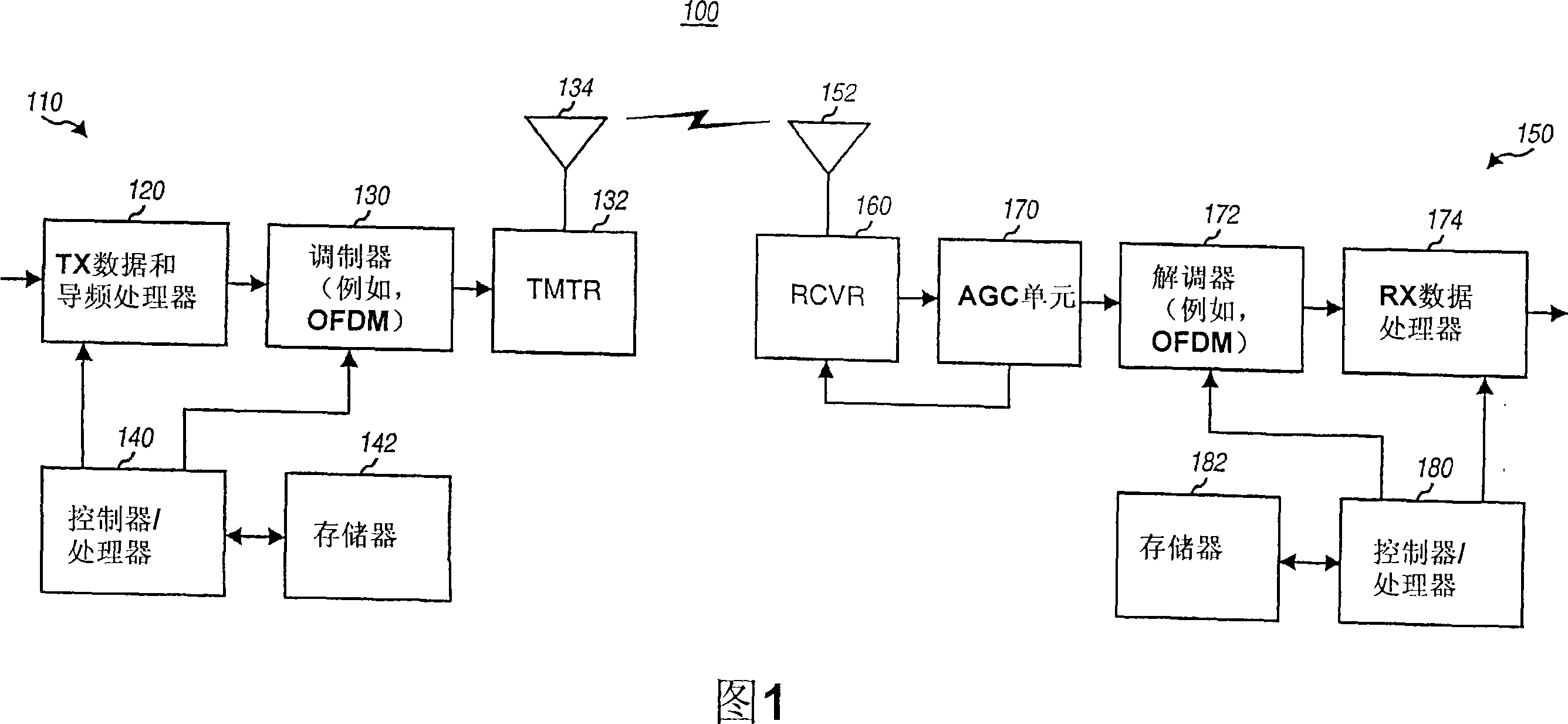
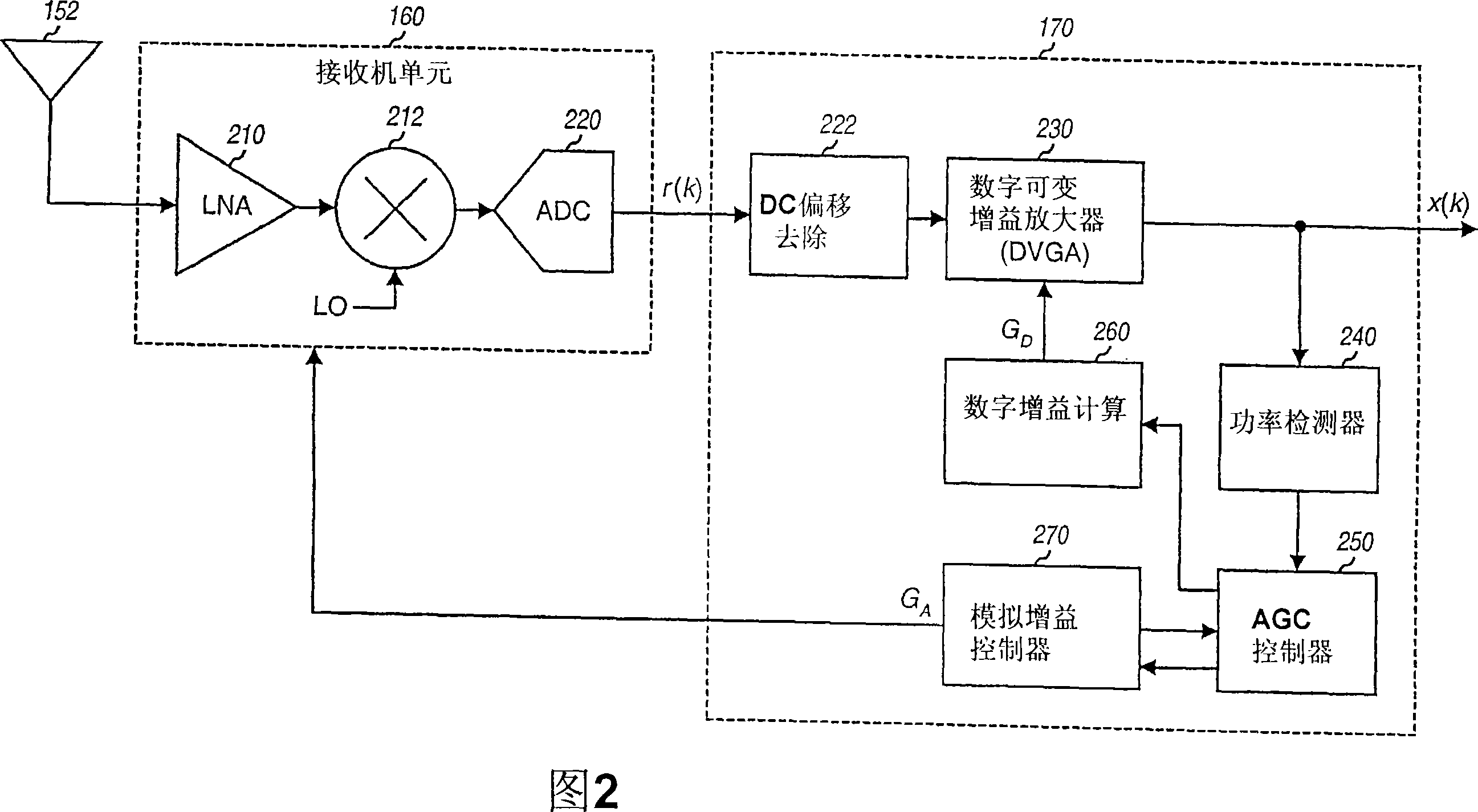
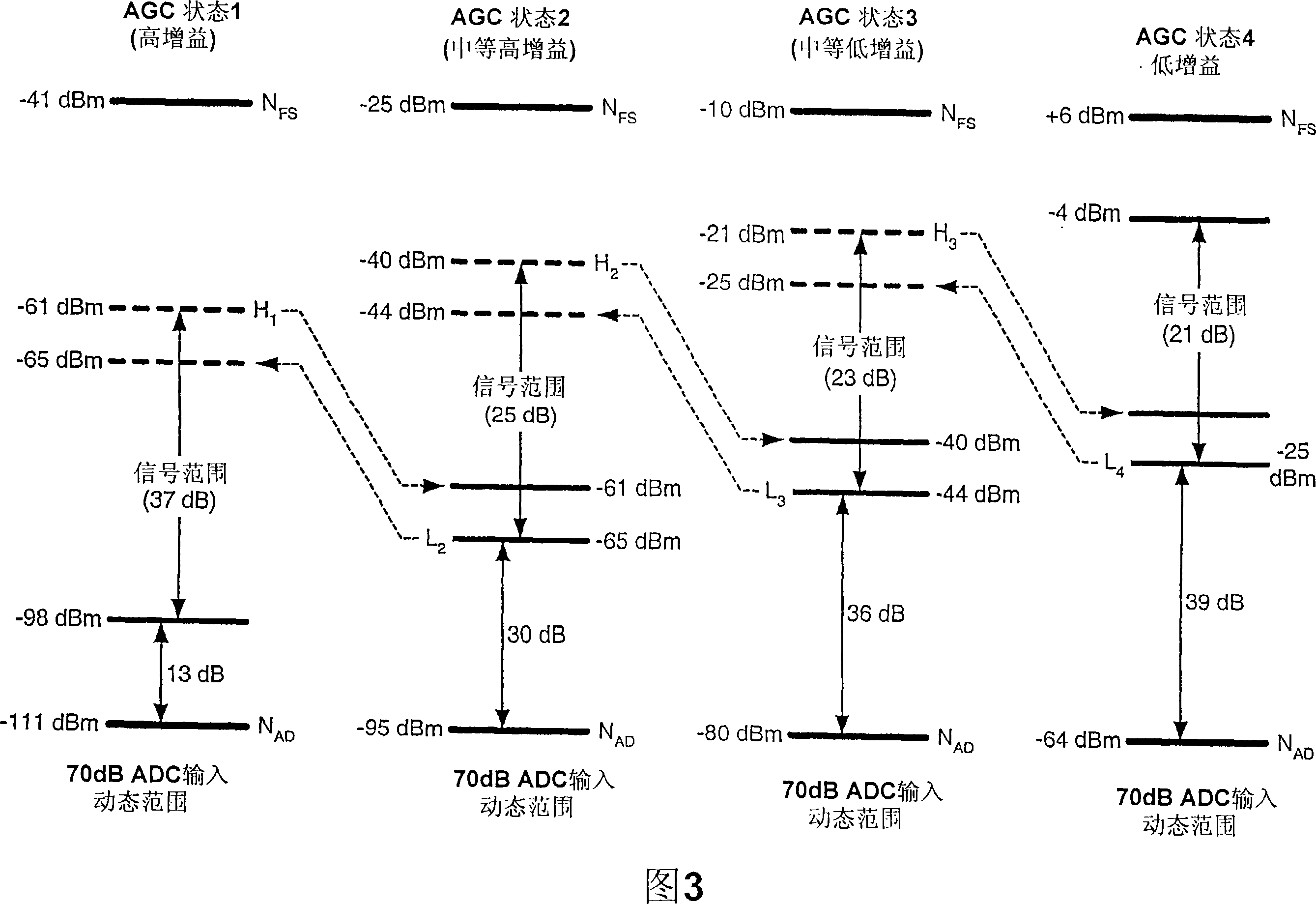
[0025] The AGC techniques described herein may be used in a variety of wireless communication systems such as cellular systems, broadcast systems, wireless local area network (WLAN) systems, and the like. The cellular system can be a Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) system, a Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) system, a Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) system, an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) system, a Signal Carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) ) system, etc. The broadcasting system may be a MediaFLO system, a digital video broadcasting (DVB-H) system, an integrated services digital broadcasting (ISDB-T) system for terrestrial television broadcasting, etc. The WLAN system may be an IEEE 802.11...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com