Welding joint method of glass optical fibre with different component
A technology of glass optical fiber and optical fiber, which is applied in the coupling direction of optical waveguide, etc., can solve the problems of large loss of optical fiber joints, failure to meet the requirements of use, low strength, etc., and achieve the effect of large tuning range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] Take, but not limited to, the fusion splice between a low melting temperature phosphate glass fiber and a standard silica glass fiber. The thermal performance parameters of phosphate glass fiber and silica fiber are shown in Table 1.
[0014] Table 1
[0015] Glass
Refractive index (n d )
Softening temperature (℃)
Coefficient of thermal expansion (×10 7 / °C)
Single-mode fiber core diameter (μm)
1.5~1.8
350~600
450~700
65~140
5~7
1.45~1.48
1000~1200
1600~1750
5.0~5.8
8~10
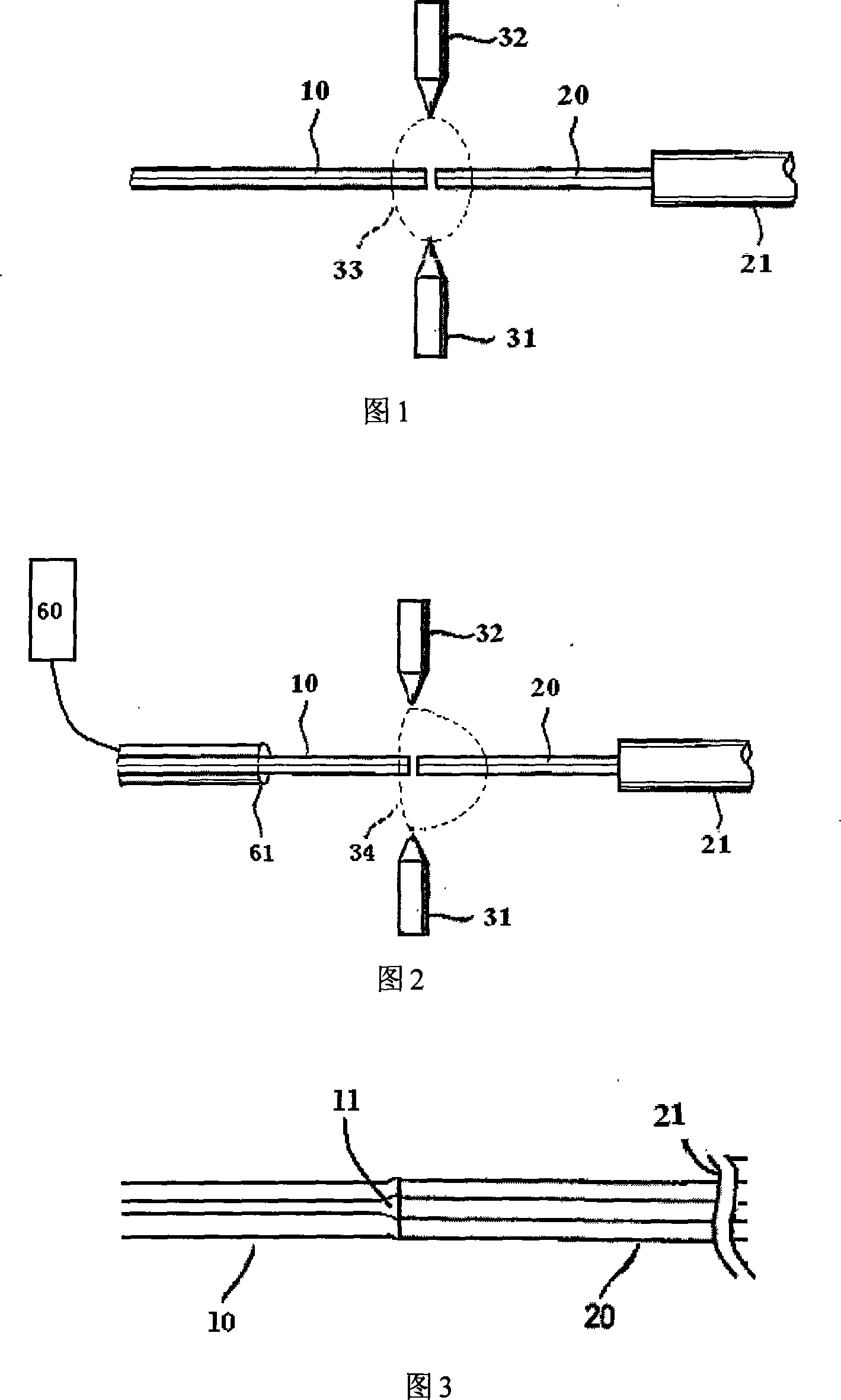
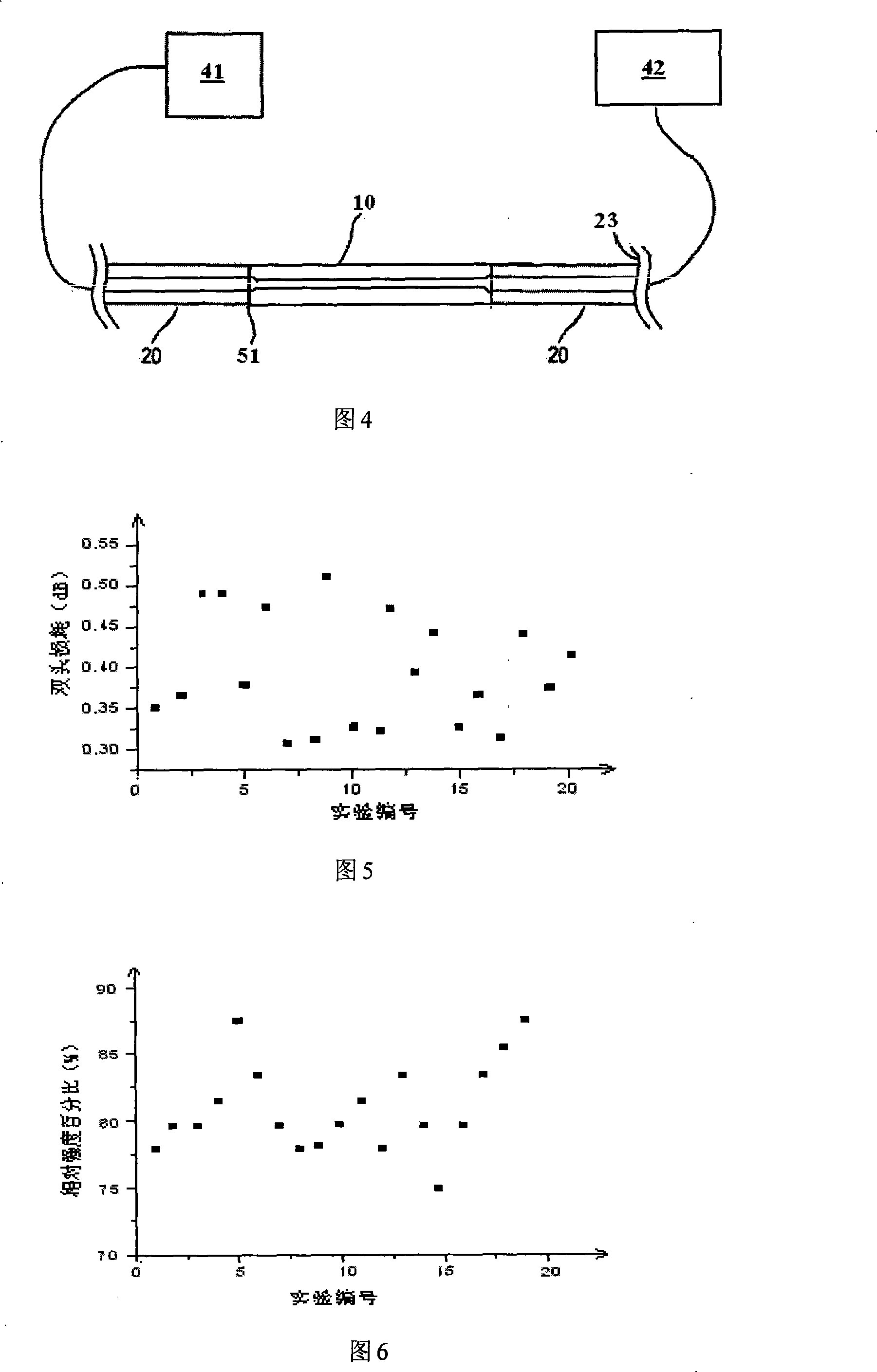
[0016] According to the present invention, an arc blowing heating structure is used to fuse two optical fibers, as shown in FIG. 2 . The quartz optical fiber 21 and the phosphate glass optical fiber 10 with the coating layer stripped are carefully placed in the V-shaped groove of the fusion splicer, and the clamp moving device a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com