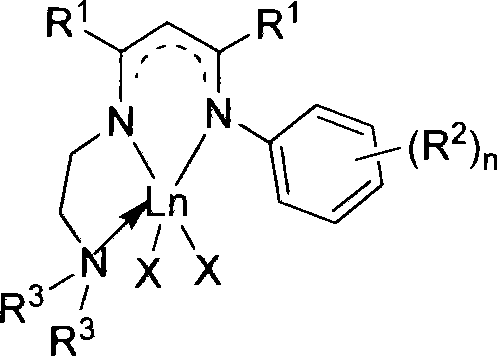
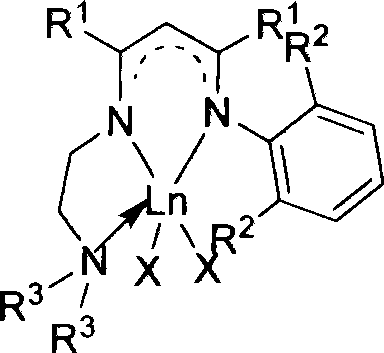
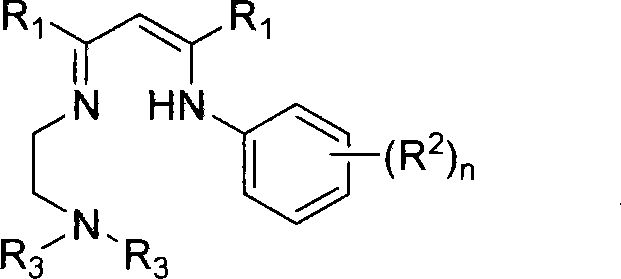
Nitrogen-containing ligand rare earth catalyst and application thereof in polyester synthesis
A technology of rare earth complexes and ligands, applied in the field of novel tridentate nitrogen ligands and rare earth complexes thereof, can solve the problems of materials not having biodegradation characteristics and environmental pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037]Dissolve 8.20 g of 2-(2,6-diisopropylanilino)-2-penten-4-one, 2.79 g of N,N-dimethylethylenediamine and 50 mg of p-toluenesulfonic acid in 30 mL of benzene , heated to reflux for water separation for 24 hours, removed the solvent in vacuo, and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 7.02 g of yellow oily tridentate nitrogen ligand L1 with a yield of 67%. by 1 HNMR, 13 CNMR, mass spectrometry and elemental analysis characterized the structure of the ligands. Anal.Calcd.for C 21 h 35 N 3 : C, 76.54; H, 10.71; N, 12.75. Found: C, 76.65; H, 10.86; N, 12.76. 1 H NMR (300MHz, C 6 D. 6 , 25°C): δ (ppm) 11.04 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.24-7.14 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 4.71 (s, 1H, MeC (N) CH), 3.20 (sp, 3 J HH = 6.9Hz, 2H, ArCHMe 2 ), 2.97(t, 3 J HH = 6.3Hz, 2H, NCH 2 ), 2.18(t, 3 J HH = 6.3Hz, 2H, NCH 2 ), 1.95 (s, 6H, NMe 2 ), 1.69(s, 3H, MeC(NHAr)), 1.66(s, 3H, MeC(NCH 2 CH 2 NMe 2 )), 1.27(t, 3 J HH = 7.8Hz, 12H, ArCHMe 2 ). 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 , 25°C): δ(ppm) 1...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Dissolve 5.79 g of 2-(2,6-diisopropylanilino)-2-penten-4-one, 2.59 g of N,N-diethylethylenediamine and 50 mg of p-toluenesulfonic acid in 30 mL of toluene , heated to reflux for water separation for 24 hours, removed the solvent in vacuo, and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 4.51 g of yellow oily tridentate nitrogen ligand L2 with a yield of 56%. by 1 HNMR, 13 CNMR, mass spectrometry and elemental analysis characterized the structure of the ligands. C 23 h 39 N 3 Elemental analysis data: Calculated value C, 77.26; H, 10.99; N, 11.75. Measured value: C, 77.45; H, 10.95; N, 11.64. 1 H NMR (300MHz, C 6 D. 6 , 25°C): δ (ppm) 10.95 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.23-7.13 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 4.72 (s, 1H, MeC (N) CH), 3.21 (sp, 3 J HH = 6.9Hz, 2H, ArCHMe 2 ), 2.99 (q, 2H, NCH 2 ), 2.38(t, 3 J HH = 6.9Hz, 2H, NCH 2 ), 2.30(q, 4H, N(CH 2 CH 3 ) 2 ), 1.70(s, 6H, MeC(NHAr) and MeC(NCH 2 CH 2 NET 2 )), 1.28(d, 3 J HH = 6.9Hz, 6H, ArCHMe 2 ), 1.24(d, 3 J HH = 6.2Hz, ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Dissolve 5.01 g of 2-(2,6-diisopropylanilino)-2-penten-4-one, 2.47 g of N-(2-aminoethyl)piperidine and 50 mg of p-toluenesulfonic acid in 25 mL of toluene , heated to reflux for water separation for 24 hours, removed the solvent in vacuo, and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 4.19 g of yellow oily tridentate nitrogen ligand L3 with a yield of 59%. by 1 HNMR, 13 CNMR, mass spectrometry and elemental analysis characterized the structure of the ligands. C 24 h 39 N 3 Elemental analysis data: Calculated: C, 77.99; H, 10.64; N, 11.37. Found: C, 78.01; H, 10.46; N, 10.93. 1 H NMR (300MHz, C 6 D. 6, 25°C): δ (ppm) 11.01 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.24-7.16 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 4.71 (s, 1H, MeC (N) CH), 3.20 (sp, 3 J HH = 6.9Hz, 2H, ArCHMe 2 ), 3.03(t, 3 J HH = 6.9Hz, 2H, NCH 2 ), 2.27(t, 3 J HH =6.6Hz, 2H, NCH 2 ), 2.19(m, 4H, N(CH 2 CH 2 ) 2 CH 2 ), 1.69(s, 3H, MeC(NHAr)), 1.67(s, 3H, MeC(NCH 2 CH 2 NC 5 h 10 )), 1.39(m, 4H, N(CH 2 CH 2 ) 2 CH 2 ), 1.29(d,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com