Cuneiform honeycomb I-profile component
A wedge-shaped honeycomb and I-beam technology, which is applied to truss-type structures, joists, girders, etc., can solve the problems that the strength of all components cannot be fully utilized, the layout of dense pipelines is complicated, and the average stress level is low, so as to save steel consumption, Reasonable material distribution and large bearing capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
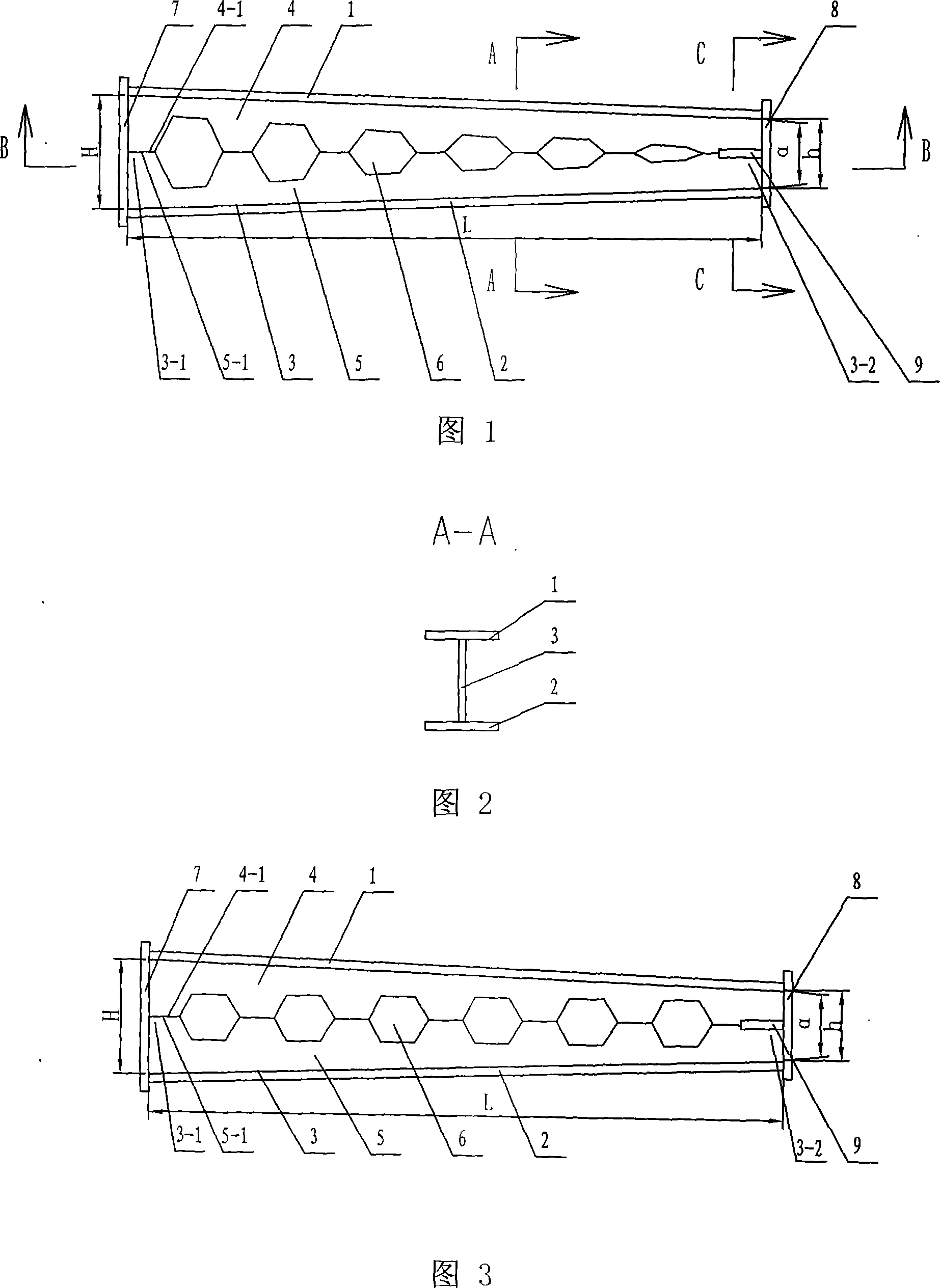
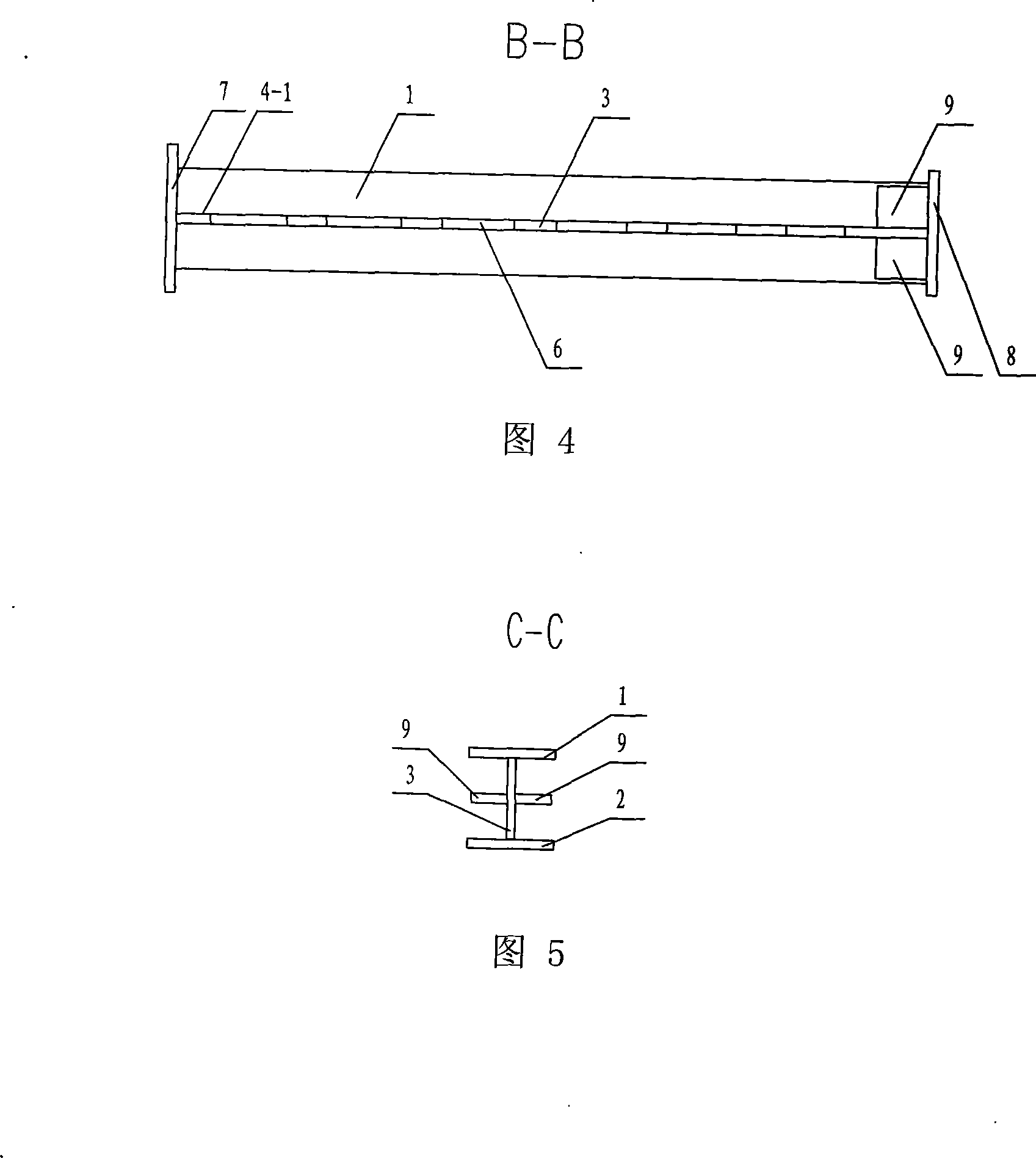
[0007] Specific embodiment 1: This embodiment is described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 3. This embodiment is composed of a section steel upper flange 1, a section steel lower flange 2 and an I-shaped steel web 3. The upper part of the I-shaped steel web 3 is The upper flange 1 of the shaped steel is fixed on the end surface, and the lower flange 2 of the shaped steel is fixed on the lower end surface of the I-shaped steel web 3, and the wedge rate formed by the upper end surface and the lower end surface of the I-shaped steel web 3 is α , the I-shaped steel web 3 is composed of an upper toothed web 4 and a lower toothed web 5, the tooth tip 4-1 of the upper toothed web 4 and the tooth tip 5 of the lower toothed web 5 -1 is fixedly connected, and the tooth tips 4-1 of the upper tooth-shaped web 4 and the tooth tips 5-1 of the lower tooth-shaped web 5 form honeycomb holes 6. The manufacturing method of this embodiment adopts the secondary cutting technology for the prototype st...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0008] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is described in conjunction with Fig. 1, the honeycomb hole 6 that the tooth tip 4-1 of the upper tooth-shaped web 4 of this embodiment and the tooth tip 5-1 of lower tooth-shaped web 5 of this embodiment form is from the worker. The hole that becomes smaller successively from the big wedge head 3-1 of the I-beam web 3 to the small wedge 3-2 of the I-beam web 3. The component stress is more reasonable, and the section height change is close to the bending moment diagram under load. Other compositions and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0009] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment is described in conjunction with FIG. 3 . The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the tooth tips 4-1 of the upper toothed web 4 and the teeth of the lower toothed web 5 The honeycomb holes 6 formed by the tip 5-1 are holes of equal size. The cutting route is simple and the processing and molding are simple. Other compositions and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com