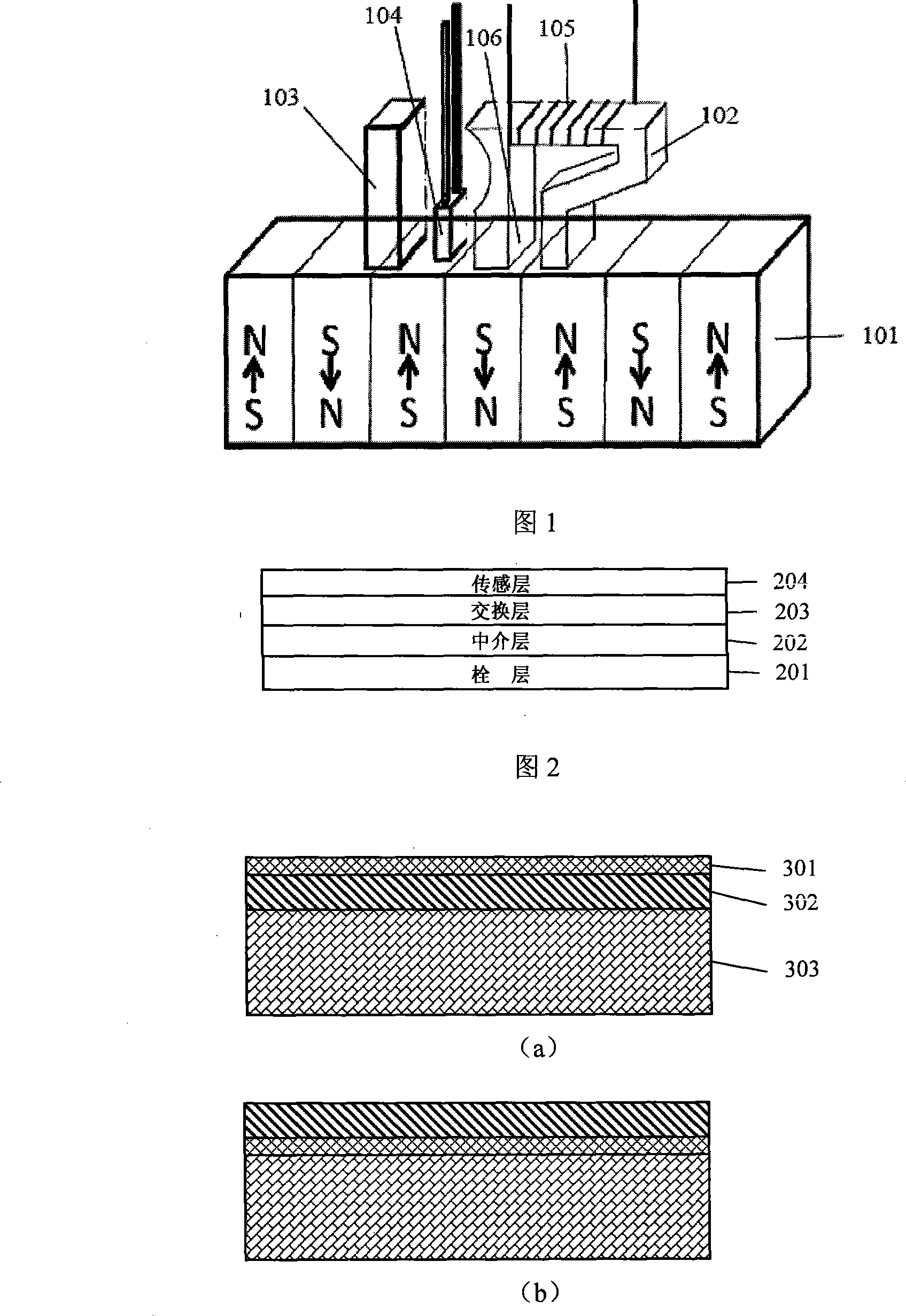
Poly iron performance composed film reading magnetic head based on magnetoelectric effect
A technology of composite thin film and magnetoelectric effect, applied in the direction of magnetic head and magnetic recording head using thin film, can solve the problems of complex structure, high energy consumption, external bias magnetic field, etc., and achieve the effect of simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
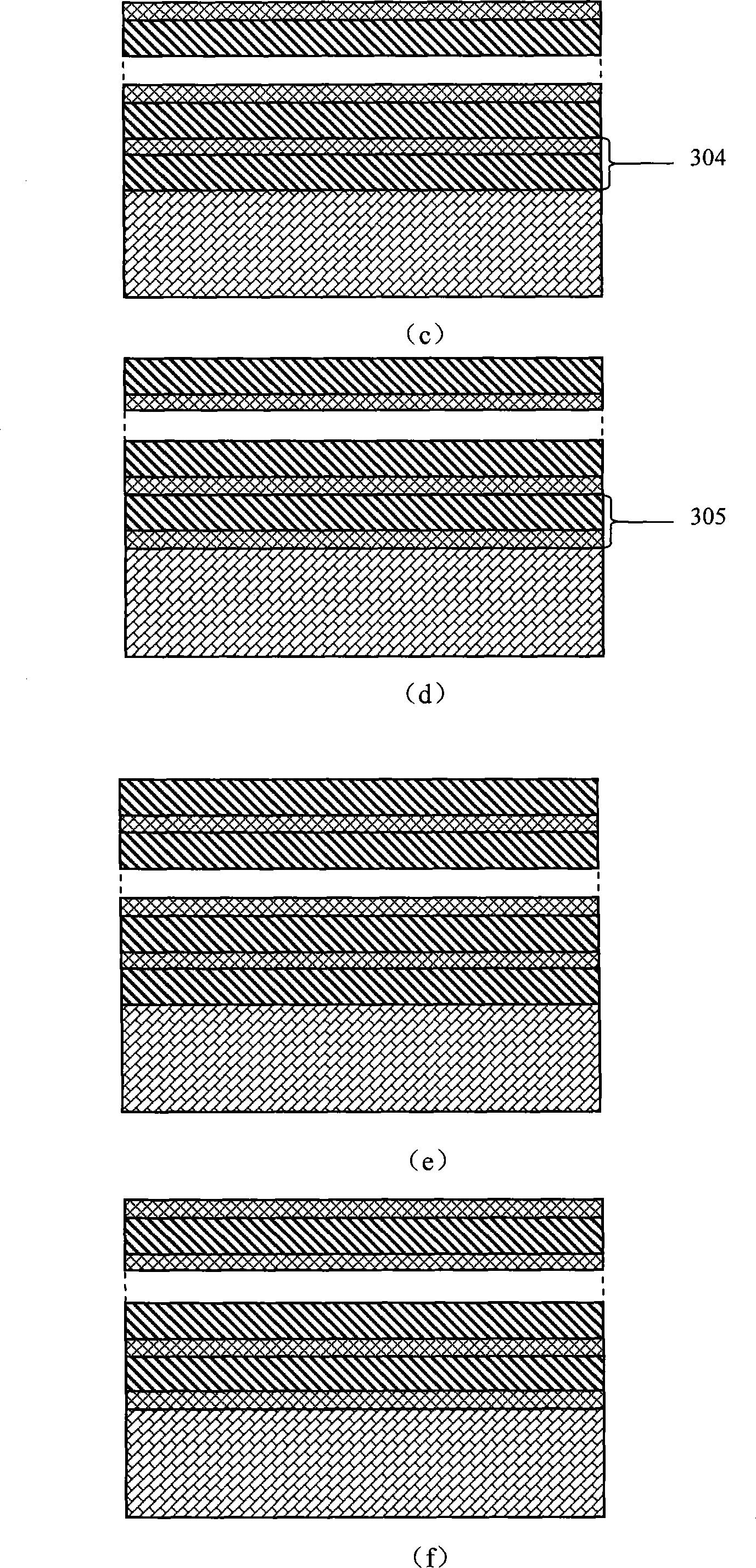
[0045] Using the method of pulsed laser deposition, strontium titanate (SrTiO 3 ) on the substrate to deposit a multiferroic composite thin film, and the first layer to deposit barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ), the second layer deposits nickel ferrite (NiFe 2 o 4 ), forming the structure shown in Figure 3(a). Barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ) layer thickness of 110nm, nickel ferrite (NiFe 2 o 4 ) layer thickness is 40nm. In the perturbed magnetic field δH ac When the frequency is 1000Hz, the magnetoelectric response δV varies with the perturbation magnetic field δH ac The variation of the amplitude is as Image 6 Shown by α E =δV / (δH ac t) (t is the film thickness) calculates that the in-plane magnetoelectric conversion coefficient of the multiferroic composite film read head is 39.2mV / cm Oe, and the out-of-plane magnetoelectric conversion coefficient is 43.9mV / cm Oe.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Using the method of pulsed laser deposition, strontium titanate (SrTiO 3 ) on the substrate to deposit a multiferroic composite film, the first layer deposits nickel ferrite (NiFe 2 o 4 ), the second layer deposits barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ), forming the structure shown in Figure 3(b). Nickel Ferrite (NiFe 2 o 4 ) layer thickness of 40nm, barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ) layer thickness is 75nm. In the perturbed magnetic field δH ac When the frequency is 1000Hz, the magnetoelectric response δV varies with the perturbation magnetic field δH ac The variation of the amplitude is as Figure 7 Shown by α E =δV / (δH ac t) (t is the film thickness) calculates that the in-plane magnetoelectric conversion coefficient of the multiferroic composite film read head is 4.9mV / cm Oe, and the out-of-plane magnetoelectric conversion coefficient is 5.3mV / cm Oe.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Using the method of pulsed laser deposition, strontium titanate (SrTiO 3 ) on the substrate to deposit a multiferroic composite thin film, and the first layer to deposit barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ), the second layer deposits nickel ferrite (NiFe 2 o 4 ), forming the structure shown in Figure 3(a). Barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ) layer thickness of 100nm, nickel ferrite (NiFe 2 o 4 ) layer thickness is 30nm. In the perturbed magnetic field δH ac When the frequency is 1000Hz, the magnetoelectric response δV varies with the perturbation magnetic field δH ac The variation of the amplitude is as Figure 8 Shown by α E =δV / (δH ac t) (t is the film thickness) calculates that the in-plane magnetoelectric conversion coefficient of the multiferroic composite film read head is 44mV / cm Oe, and the out-of-plane magnetoelectric conversion coefficient is 79mV / cm Oe.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com