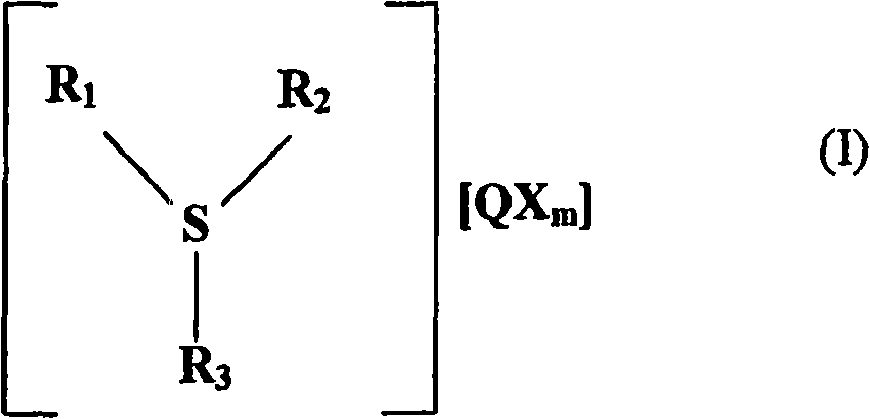
Antimony-free photocurable resin composition and three dimensional article
A technology for products and compositions, applied in the field of low-viscosity photocurable compositions, capable of solving problems such as instability of antimony hexafluoride salt, increased resin viscosity, unusable antimony resin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A
[0148]A general procedure for preparing three-dimensional articles using a stereolithographic apparatus is as follows. The photocurable composition was placed at about 30°C in a barrel designed for stereolithography equipment. The surface of the composition is irradiated with a UV / VIS light source, either all of it or according to a predetermined pattern, so that a layer of desired thickness is cured and set in the irradiated areas. New layers are irradiated either over the entire surface or in a predetermined pattern. The freshly cured layer adheres to the underlying cured layer. The layer forming step and the irradiation step are repeated until a green mold of multiple cured layers is made.
[0149] A "green mold" is a three-dimensional article initially formed by a stereolithographic process of layering and photocuring, where typically the layers are not fully cured. This allows the connected layers to be better connected by bonding together upon further curing. "Wet st...
Embodiment B
[0195] Tables BII-BV list the components of each of the photocurable compositions labeled Examples B2, B3, B5-B26 and Comparative Examples B1 and B4. The numbers in Tables B II to B V represent the weight percent of each component, based on the total weight of the photocurable composition. Table BVI provides identifying information for the trade names of the components of Tables BII-BV.
[0196] Form B II
[0197] components
[0198] Form B III
[0199] components
[0200] Form B IV
[0201] components
[0202] Form B V
[0203] components
[0204] Table BVI
[0205] components
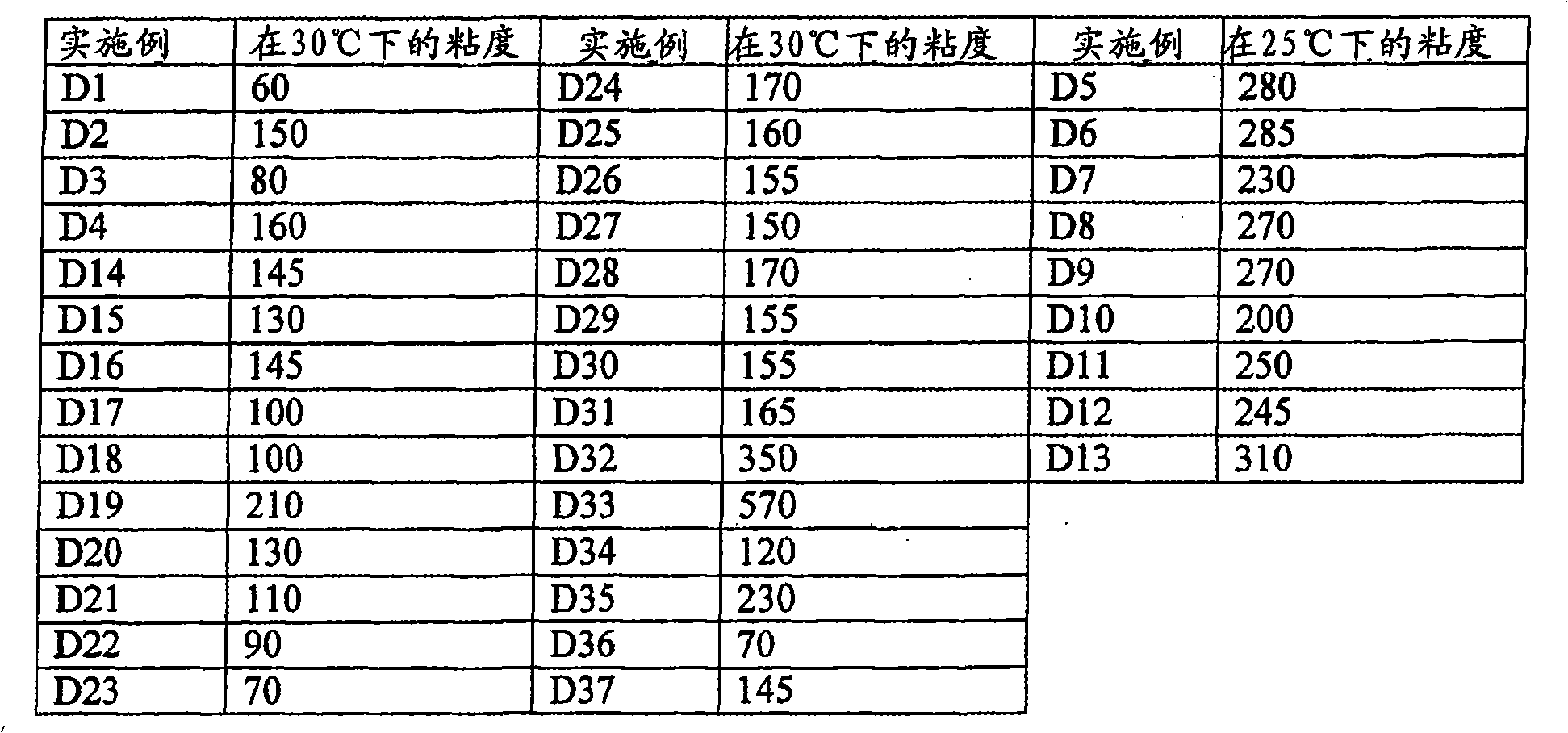
[0206] The viscosity of several photocurable compositions was measured at 25°C or 30°C using a Brookfield viscometer, and the results are shown in Table B VII.
[0207] Form B VII
[0208] photocurable composition
[0209] Test models were then made from the photocurable composition on a 3D Systems SLA 350 or 7000 stereolithography mach...
Embodiment C
[0233] Table C II lists the components of a photocurable composition according to the invention and labeled Example C1. The numbers in Table CII represent the weight percent of each component, based on the total weight of the photocurable composition. Table CIII provides identifying information for the trade names of the components of Table CII.
[0234] Table C II
[0235] components
[0236] Form C III
[0237] components
[0238] The viscosity of this photocurable composition and a commercially available acrylate-containing photocurable composition (hereinafter referred to as "Comparative Example C") was measured at 30° C. using a Brookfield viscometer. Test models of the photocurable compositions of Example C1 and Comparative Example C were subsequently made on a SLA 7000 stereolithography machine. Before the mechanical test, the test model was conditioned at 23°C and 50% RH for 3-5 days.
[0239] The photosensitivity of the photocurable composition...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com