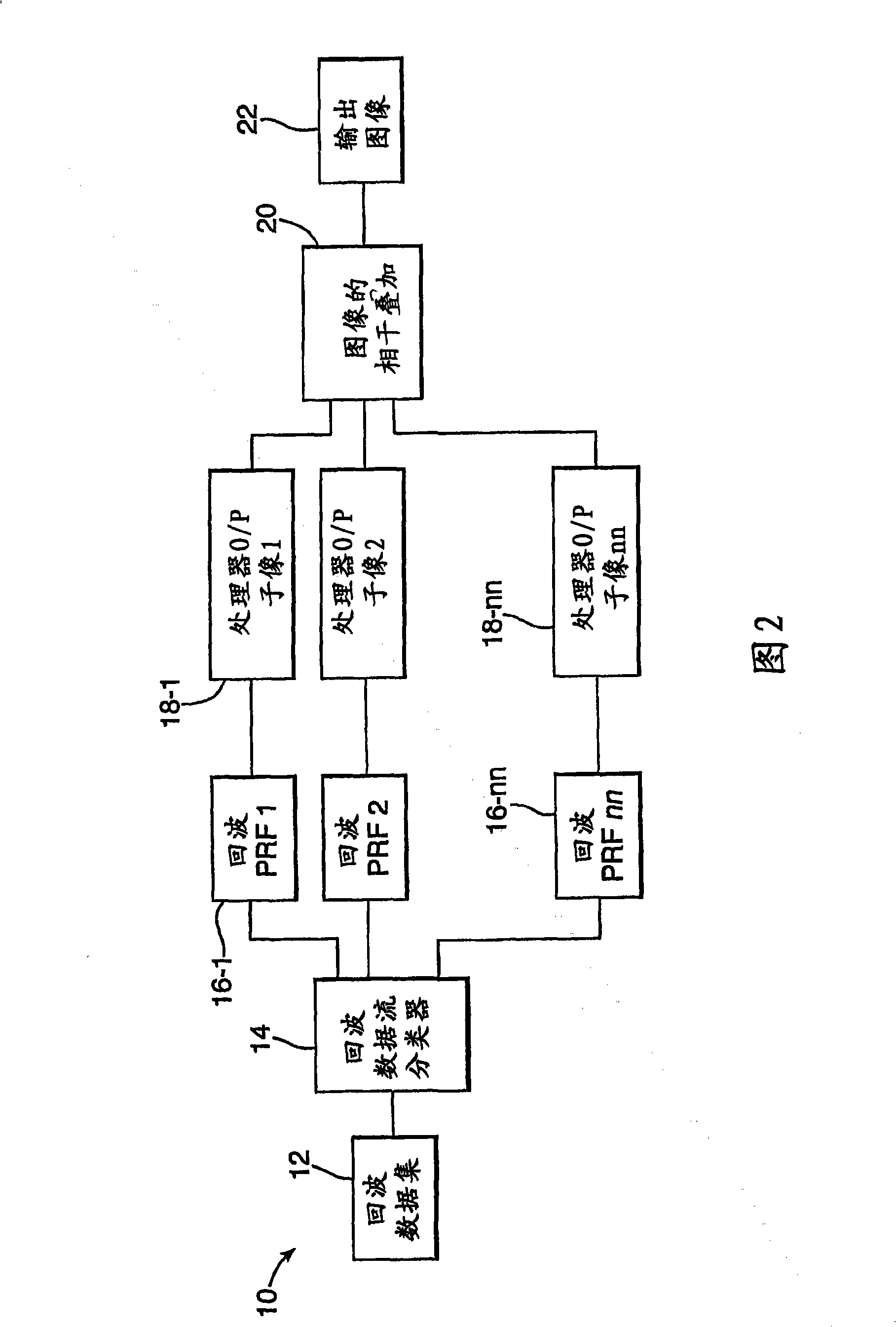
Synthetic aperture radar
A synthetic aperture radar, radar technology, applied in the direction of reflection/re-radiation of radio waves, utilization of re-radiation, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as increasing signal processing overhead and introducing blind spots.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
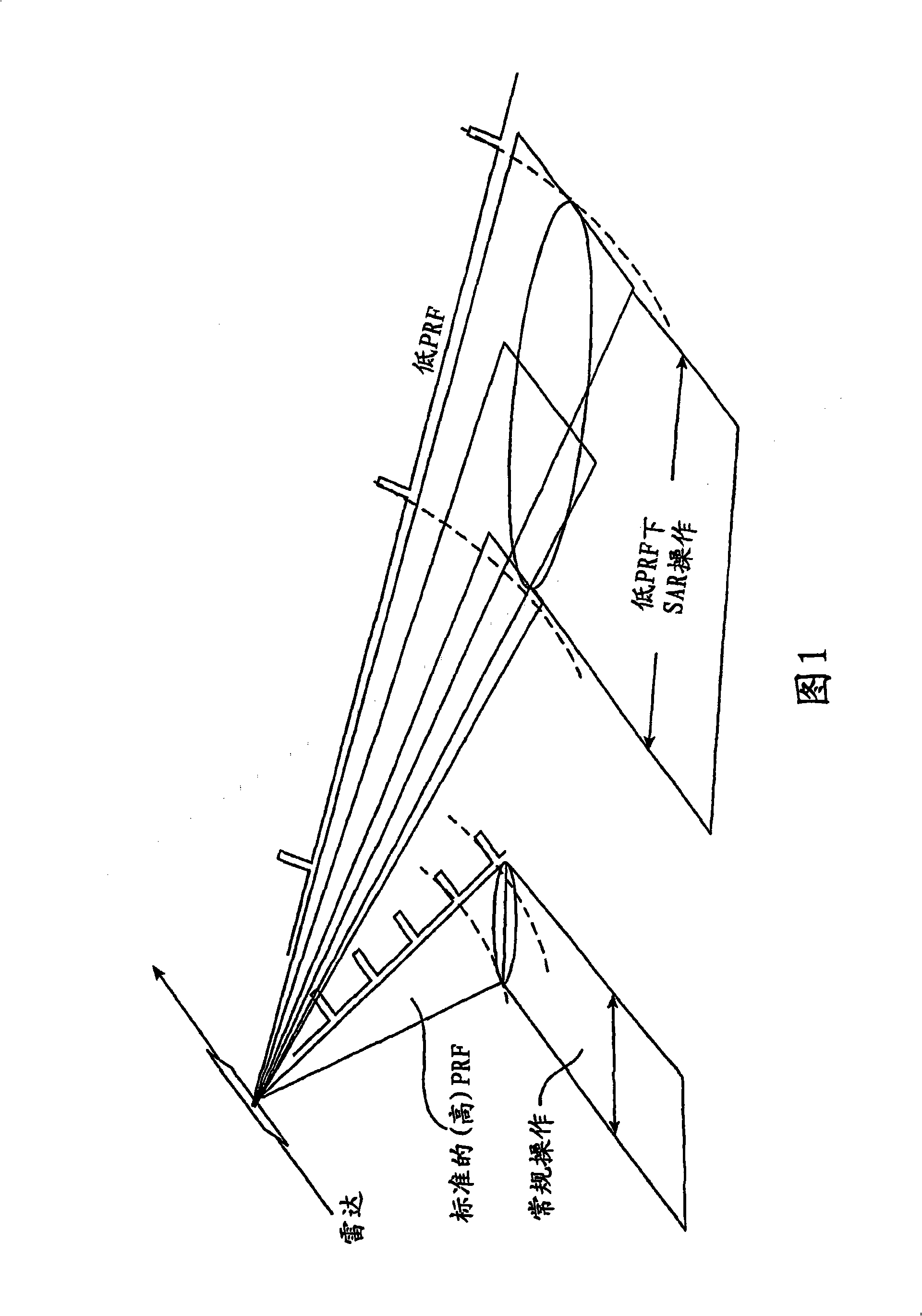
[0029] Low PRF mode situations are uncommon in the context of SAR work, given their tolerance to highly ambiguous azimuth impulse response functions. This will lead to the introduction of highly cluttered echo signals in targets containing resolution cells.
[0030] When operating in this mode, the form of the azimuth impulse response function is significantly different from what is conveniently referred to as "conventional" SAR operation. Here, during a given observation sequence, the radar operates in the usual high PRF mode associated with the normal SAR mode, and the azimuth impulse response function is pre-occupied by a single main lobe surrounded by side lobes of small amplitude. When operating in these "regular" modes, the grating lobes are still present, but with very small amplitudes.
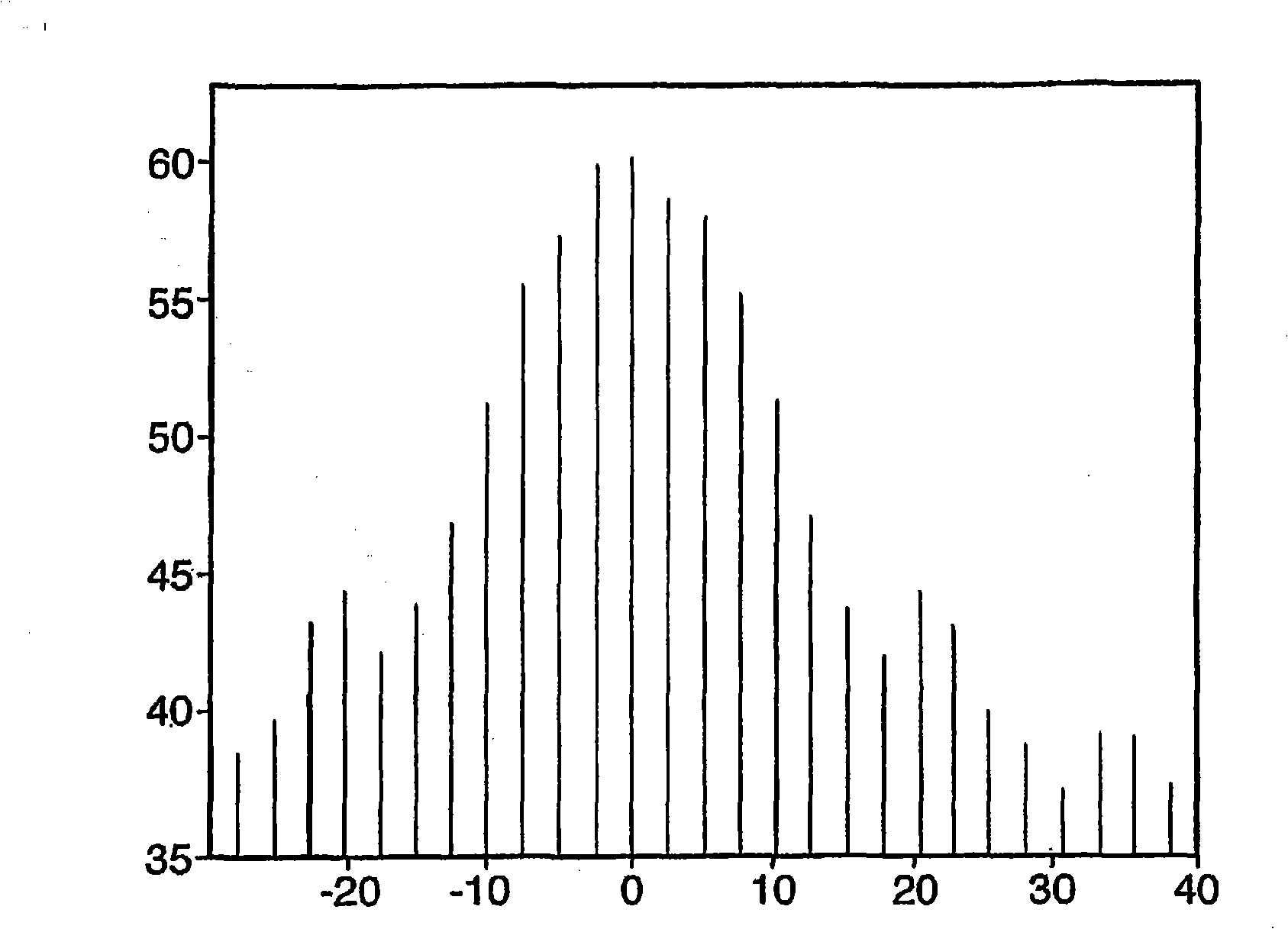
[0031] Azimuth IRF in low PRF mode
[0032] A typical azimuthal IRF profile when operating in low PRF mode is image 3 shown. In this grating lobe array, the main lobe is desired...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com