Microarray methods
A microarray and subsequence technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, material inspection products, etc., can solve problems such as optimizing hybridization conditions, increasing cross-hybridization and hybridization errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
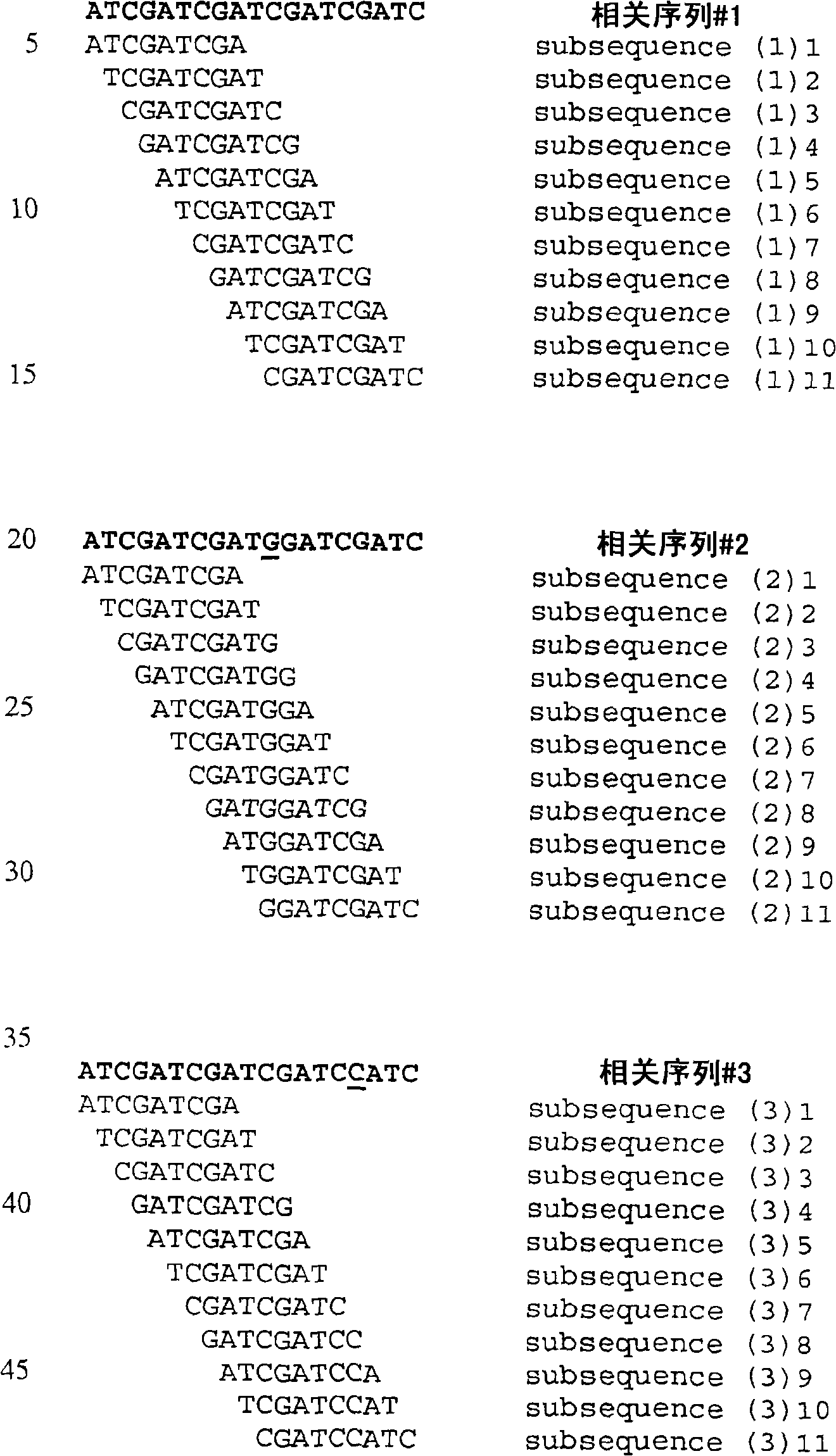
[0017] The present application presents an alternative approach to designing microarray probe sets capable of identifying genetic characteristics (such as single nucleotide polymorphisms; SNPs) or genetic linkage characteristics (such as phenotype) of organisms. This approach differs significantly from the in silico and in vivo methods used by skilled artisans to design probes suitable for screening samples by microarrays. Prior art methods involve detailed consideration of differences in nucleotide sequence, eg, found in alleles of a gene. Once such differences are identified, probes can be designed that specifically hybridize to a target nucleotide sequence within the gene. The hybridization pattern with the probe provides allelic information. This approach poses problems given that the hybridization of the oligonucleotide probe to the target sequence is suboptimal, so only simple Watson-Crick base pairing needs to be considered. Thus, the nucleotide sequence of the probe ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com