Method of deriving progenitor cell line
A progenitor cell line, cell line technology, applied in embryonic cells, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problems of harmful effects and inefficiency of tissue repair and regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0115] It is believed that the methods described herein enable the preparation of progenitor cells, which are of course differentiated using methods known in the art. Thus, any use of differentiated cells will apply equally to those progenitor cells from which they were derived.
[0116] The progenitor cells and combinations prepared by the method described herein can be used for the treatment of diseases, or for preparing pharmaceutical compositions for treating diseases. The disease can include diseases treated by regenerative therapies, including heart failure, bone marrow disease, skin disease, burns, and degenerative diseases such as diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and cancer.
[0117] We thus disclose a method of disease treatment comprising (a) providing embryonic stem (ES); (b) constructing a progenitor cell line from the embryonic stem cell, wherein the progenitor cell line is selected based on its ability to self-renew; (c ) optionally obtaining ...
Embodiment
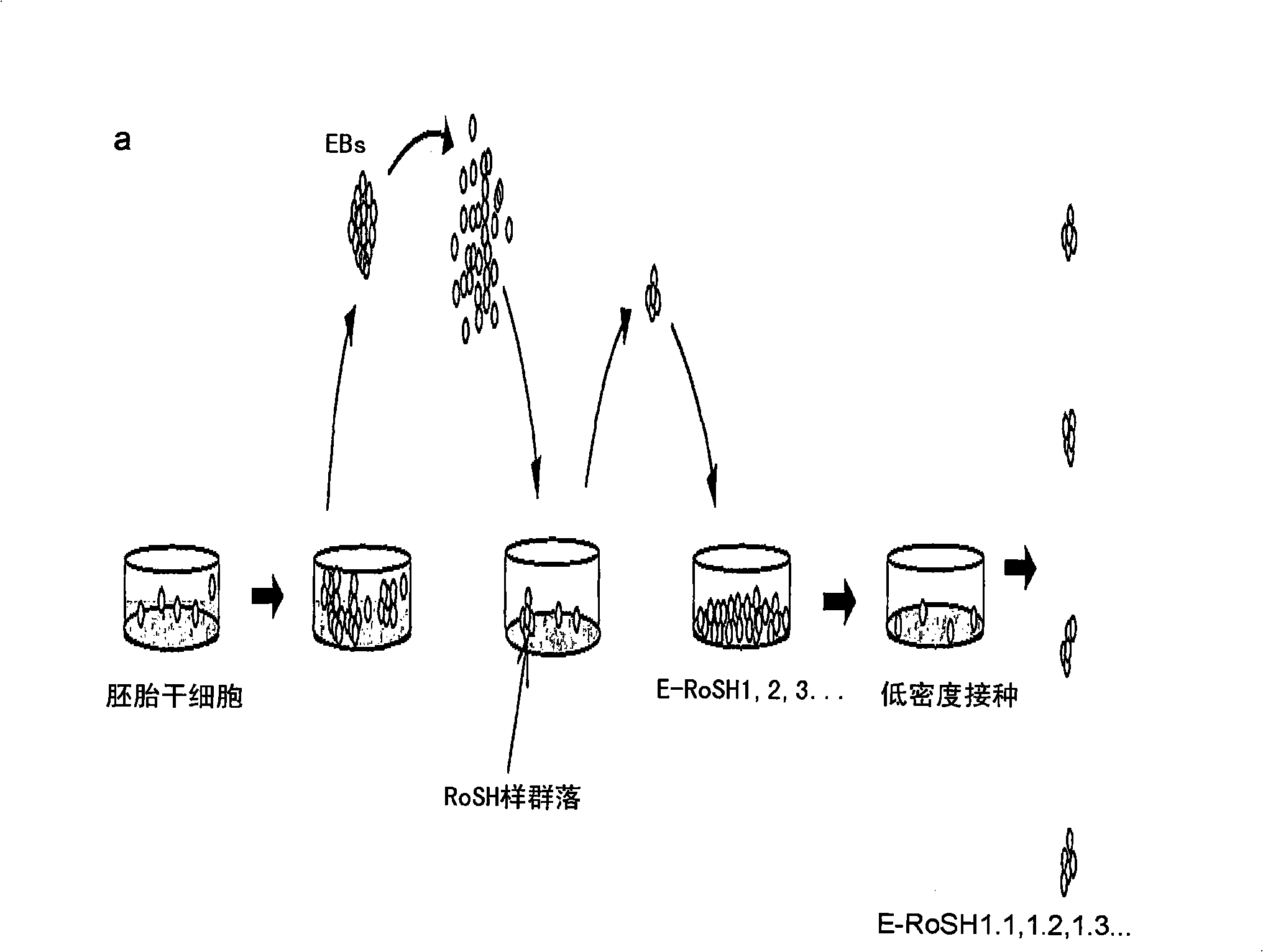
[0211] Example 1. Method: Obtaining E-RoSH cell lines
[0212] Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) were induced to differentiate into embryoid bodies (Ebs) using the methylcellulose-based method described by Lim et al., Blood. 1997; 90: 1291-1299.
[0213] Harvest the embryoid bodies of 3-6 days, separate them into a single cell suspension by collagenase digestion (see Robertson EJ, ed. Teratocarcinomas and embryonic stem cells: apractical approach. Oxford: IRL Press Limited; 1987: 71-112) and Take 1-5×10 5 Cells / 10cm feeder layer culture plate density for planting. After about 1 week, the expressing cells differentiated into a complex mixture of various cell types.
[0214] Rapidly dividing cell clones resembling embryonic-derived RoSH cells were picked and expanded sequentially in 48-well plates, 24-well plates, 6-well plates, and subsequently in 10 cm plates. The cultures of the individual clones were sequentially named E-RoSH1, 2, 3..., and each culture was constructed in this ...
Embodiment 4
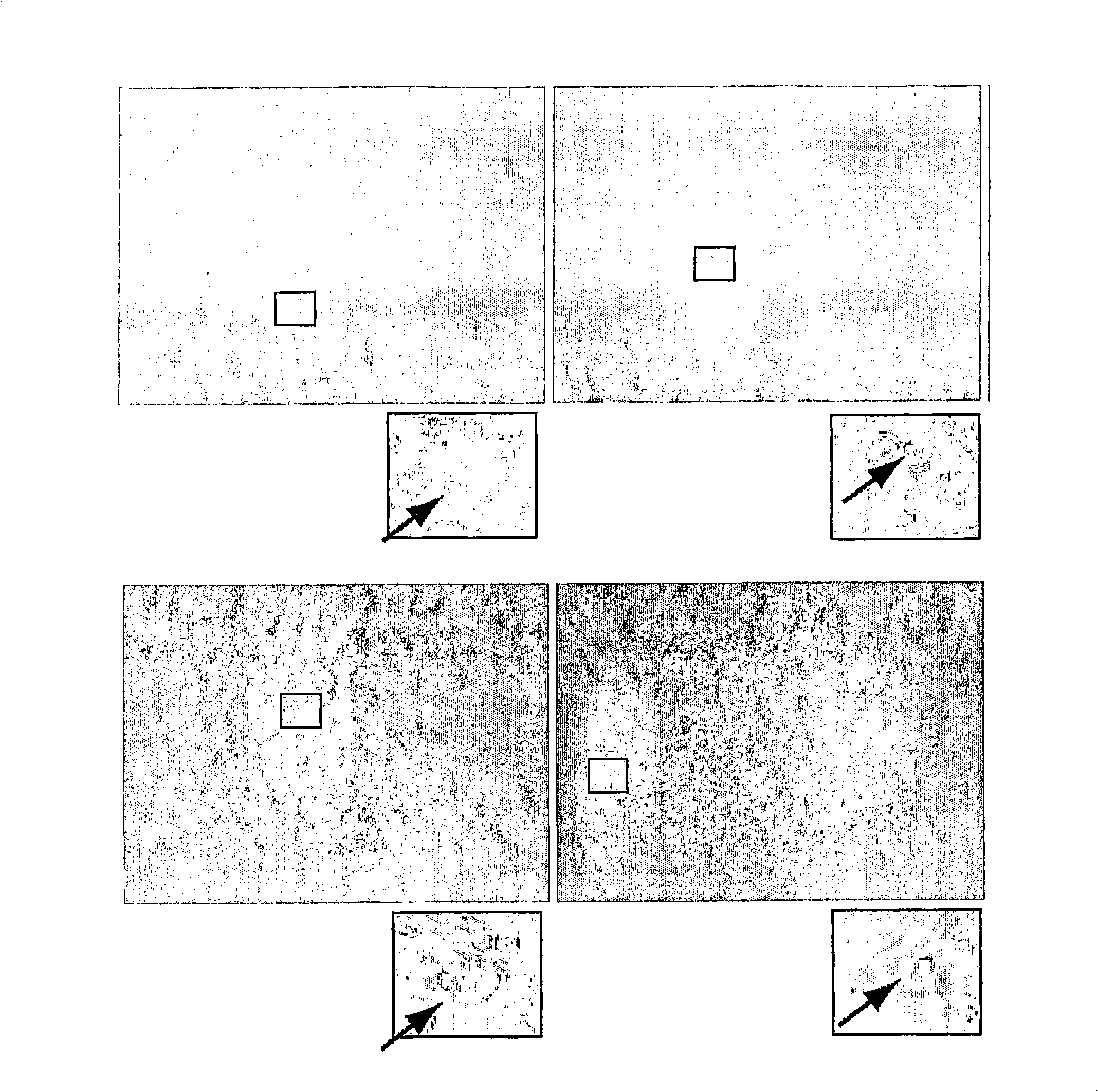
[0225] Example 4. Methods: In Vitro Endothelial Differentiation
[0226] Endothelial differentiation of acetylated LDL extracted from differentiated E-RoSH cells and E-RoSH cells was performed as described above (Yin et al, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004; 24:691-696).
[0227] E-RoSH vascular structures differentiated in vitro were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4 μm, and vWF was stained with rabbit polyclonal antibody and Envision+System-peroxidase (DakoCytomaton, Gostrup, Denmark). Sections were counterstained with Mayer's hematoxylin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com