Method of detecting genetic mutations
A technology for detecting markers and sequencing primers, which is applied in the field of detecting genetic variants, and can solve the problems of complex samples of small amounts of RNA molecules, difficulty in designing primer sets for pol genes, and inability to use sequences, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0040] Experiment Details
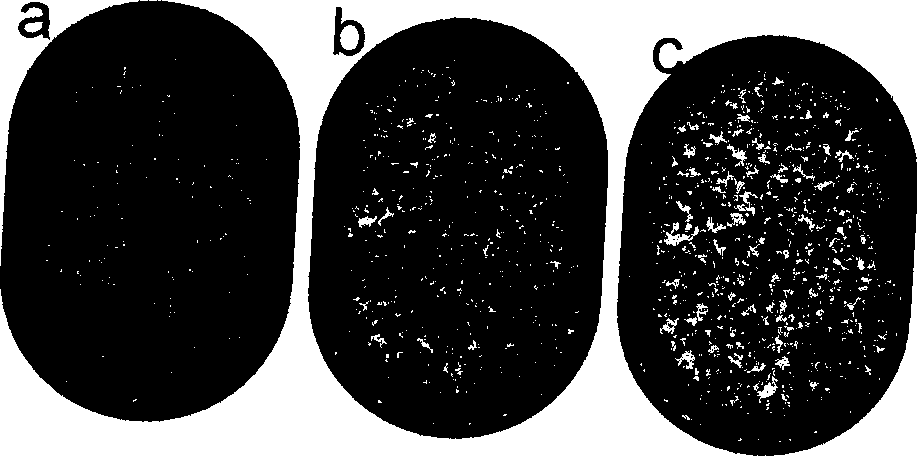
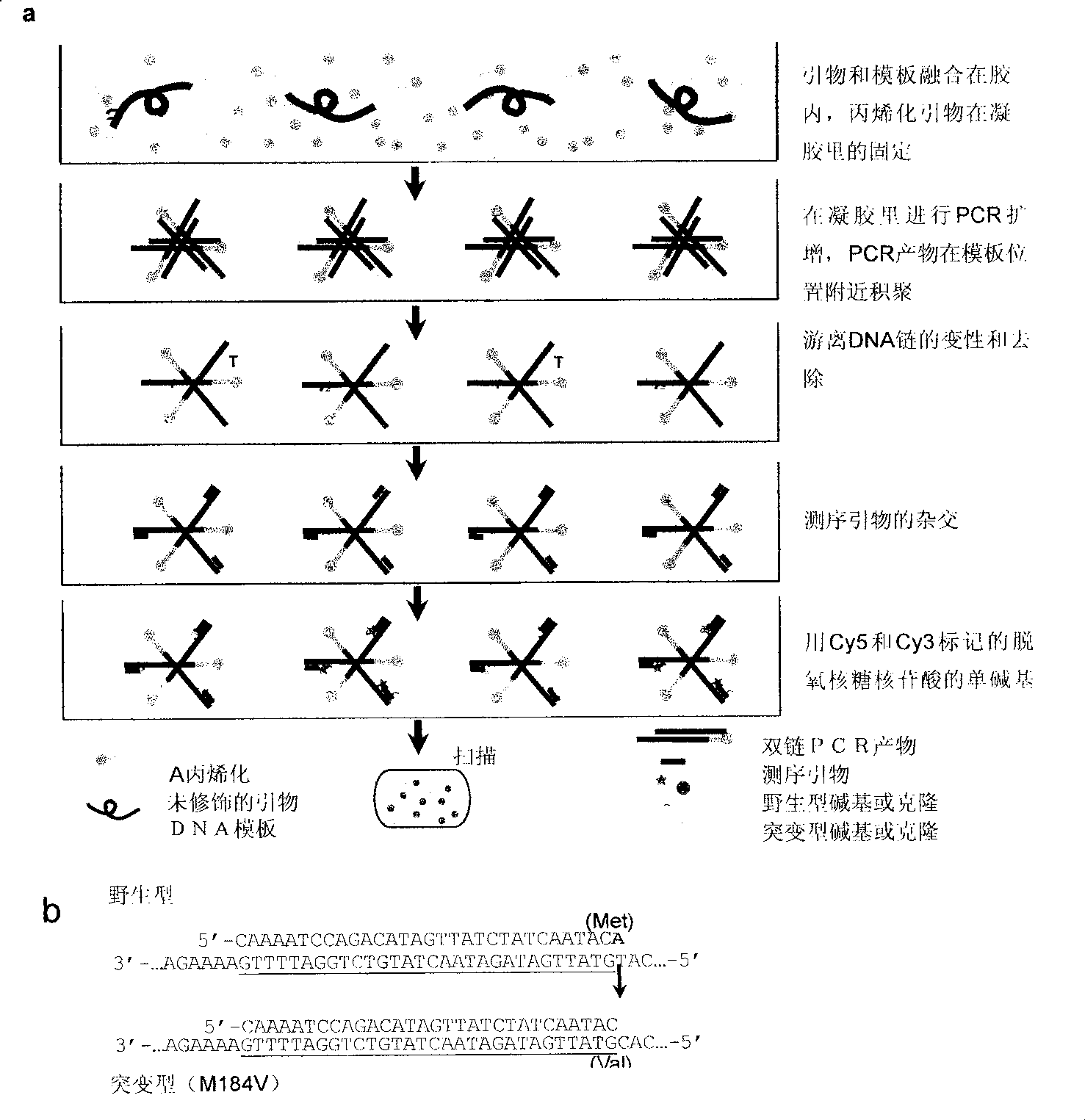
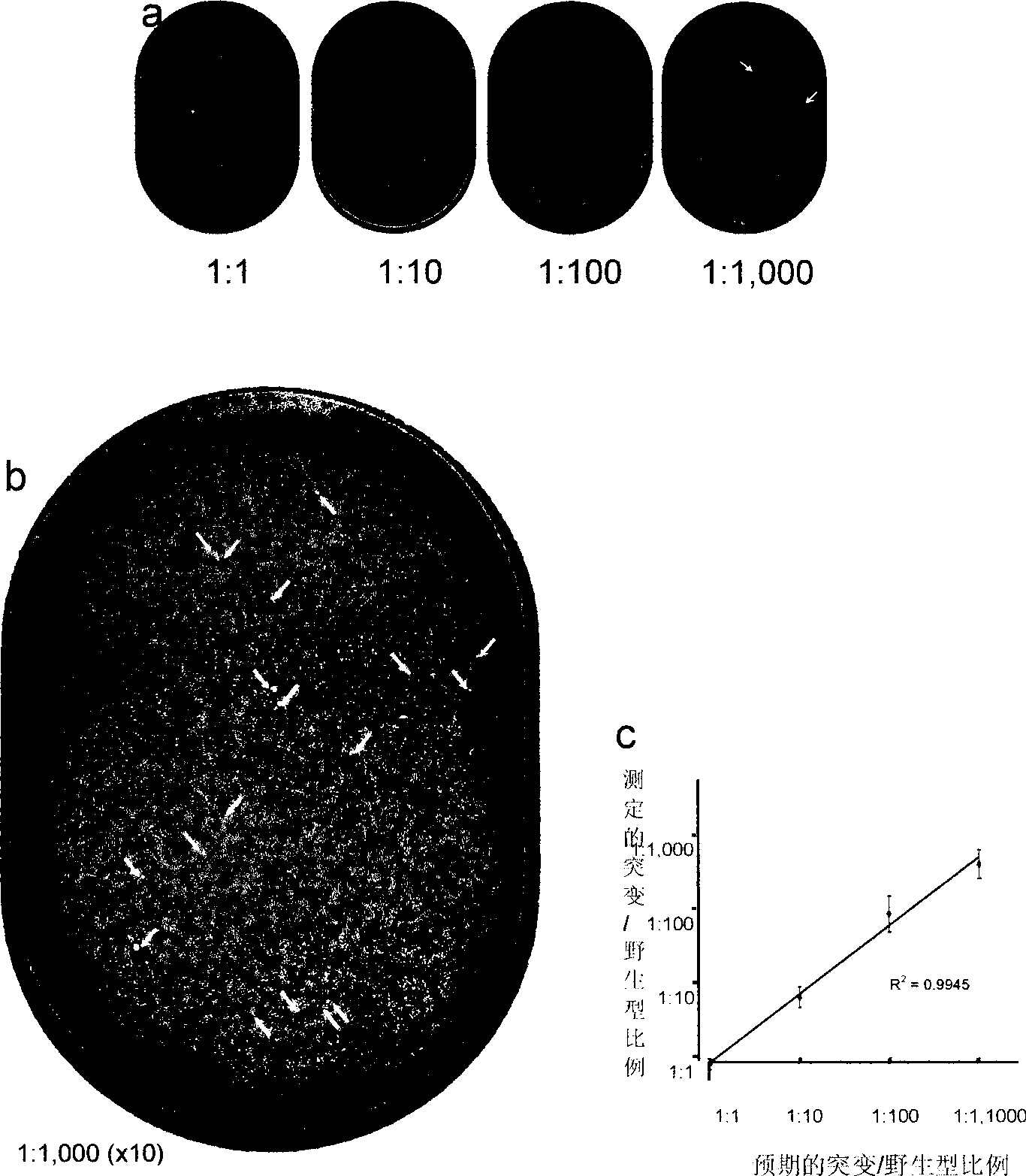
[0041] Preparation of drug-resistant mutant clones. A portion of the pol gene containing the most drug resistance mutation sites was amplified from an almost full-length HIV-1 clone WEAU.A1. By overlapping PCR method, E44D, M90L and M184V mutations were introduced. The wild type (WEAU.wt) and mutant PCR products (WEAU.E44D, WEAU.M90L and WEAU.M184M) were then cloned directly into the pSTBBlue vector (Novagen, Madison, WI). These drug resistance mutations were confirmed by sequencing. For tracer experiments, mutant and wild-type clones were used in different ratios (higher than 10 4 ) for mixing. The concentration of plasmid DNA was determined by NanoDrop spectrophotometer, and the number of molecules in each DNA sample was calculated based on DNA concentration and plasmid length (bp).
[0042] Slide handling. Teflon-coated glass slides (Eriescientific, Portsmouth, NH) were exposed to UV light in a PCR hood (PCR hood) for 15 minutes, followed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com