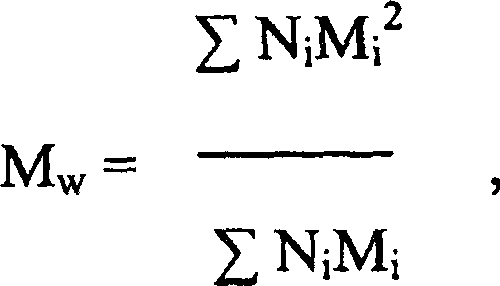Long-chain inulin
A technology of inulin and average polymerization degree, which is applied in food preparation, food science, application, etc., can solve the problems of interfering with the use of coarse inulin, and achieve a strong beneficial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
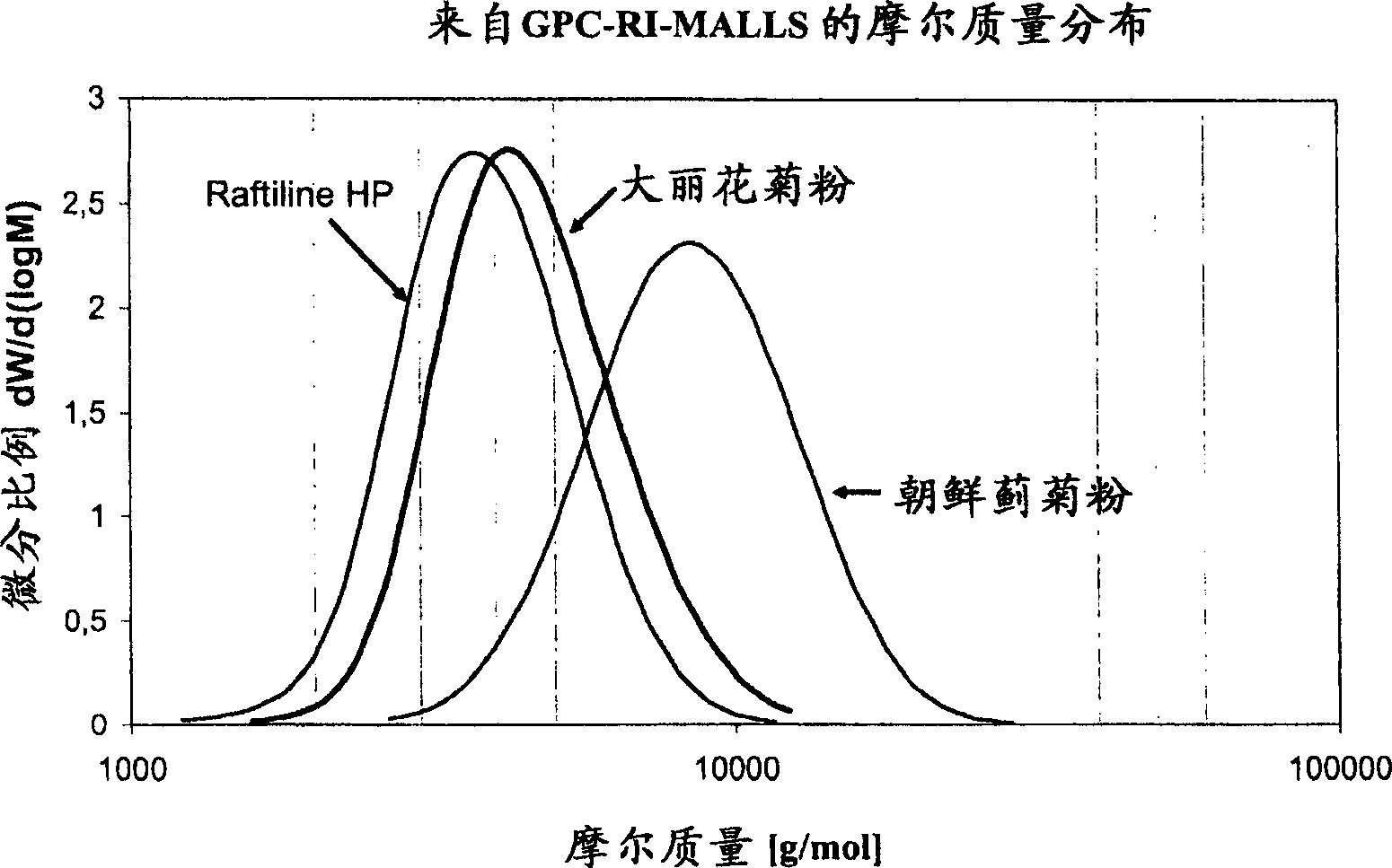
[0293] Example 1: Characterization of inulin from artichoke root
[0294] 1. Cultivating Artichoke Plants
[0295] Variations of the artichoke plant Nun9444 (also known as N9444) grow in neighboring areas of Valencia, Spain. Seeds were sown in June in 104 notched seedling boxes (8 x 13 holes, 4 x 4 cm) in a mesh plant house. Plants were grown for six weeks in seedling boxes. Planted in the field at a density of 10,000 plants / ha in early August. Harvest the whole plant in July of the following year. The roots are separated from the aboveground parts, and the attached soil is washed off by hand in water (under pressure). The roots were shaded and dried on a fixture for 3 days. It was then transported from Spain to Germany, unrefrigerated. Roots were stored at -80°C prior to inulin extraction.
[0296] 2. Preparation of inulin from the root of the artichoke
[0297] For the inulin preparation, the root of the artichoke Madrigal (said Nun 9444) var. was thawed at room temp...
Embodiment 2
[0322] Example 2: Characterization of Inulin Paste
[0323] 1. Determination of the stability of inulin paste
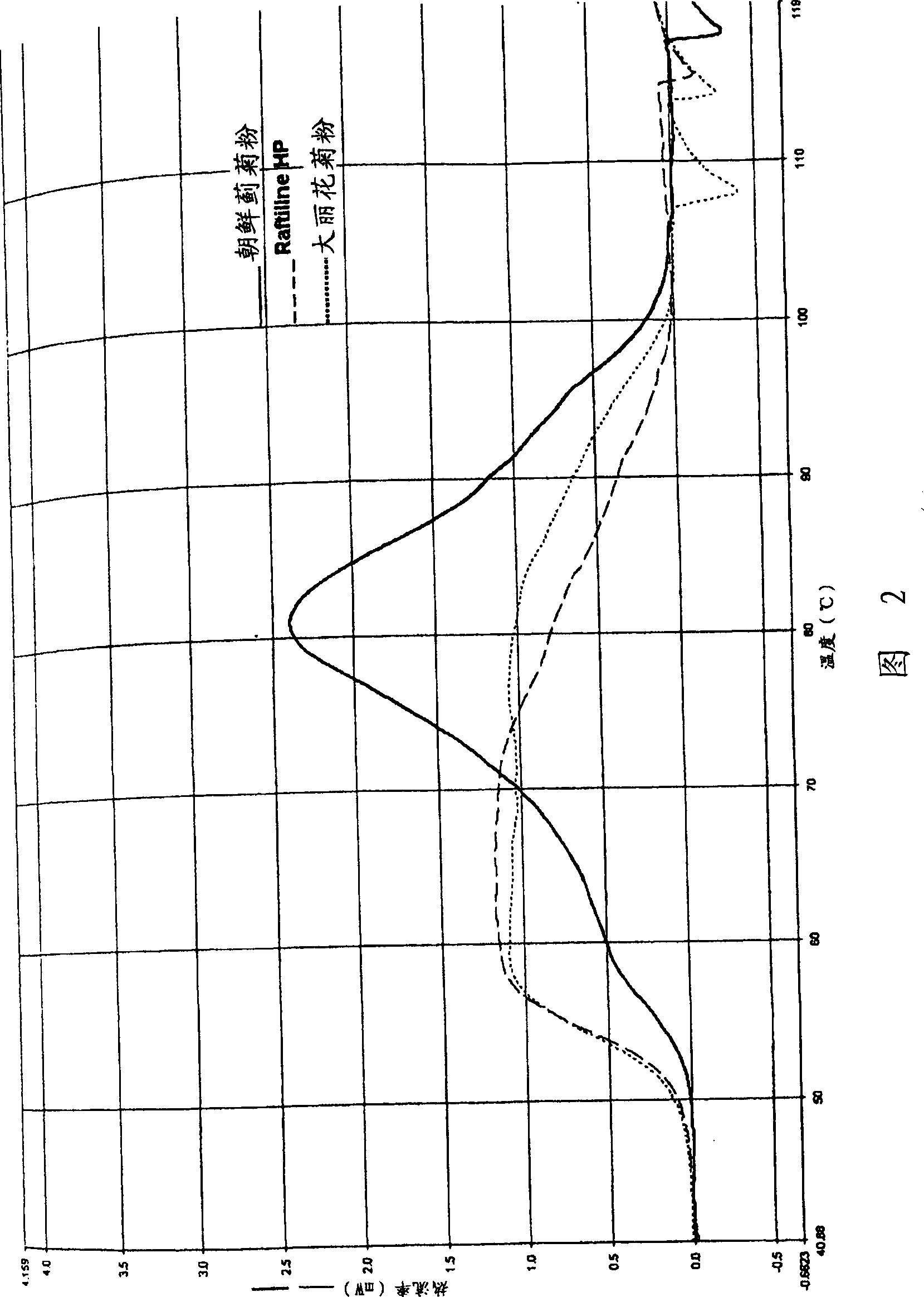
[0324] Analysis of the stability of inulin pastes (protocol: see Methods) showed that the stability behavior of artichoke inulin was significantly altered compared to inulin from chicory (Raftiline HP) and dahlia (see Table 4). At the shear rates used here, artichoke inulin exhibited the highest stability, exceeding 90% of the initial value. Analysis of the viscosity stability of inulin pastes in acidic media (acid stability) also showed that artichoke inulin exhibited minimal changes after 2 weeks of storage compared to the initial value after 24 hours, with only an increase in viscosity 6.7%. In contrast, the viscosity of dahlia inulin pastes increased by more than 15% in acidic media, and by more than 32% for Raftiline HP. This post-thickening is undesirable in many applications in the food sector. The melting temperature of artichoke inulin paste is 73°C, whi...
Embodiment 3
[0331] Example 3: Viscosity, Gelation Behavior, Solubility
[0332] a) viscosity
[0333] Table 6: Comparison of the dynamic viscosity of chicory and artichoke inulin in water as a function of concentration (T=90°C)
[0334]
[0335] As can be seen from the above table, up to a concentration of 22.5%, both inulins exhibit a very low viscosity at 90°C (water = 1 mPas). The inventive inulin started to become viscous when the concentration reached 25% (w / v), while Raftiline HP remained very water-like at 30%. At 30%, the inventive inulin exhibited an unexpectedly high viscosity.
[0336] b) gelation behavior
[0337] Two types of analyzes were performed on the gelation behavior of inulin after thermal solubilization. Inulins are those described in Table 2 and Example 2. First, different concentrations of artichoke inulin (invention), Raftiline HP and dahlia inulin were heated to 90°C and then cooled at room temperature for 20 hours. The gel formed exhibits particle-t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight average molar mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com