Wheeltrack magnetic levitation universal technology
A technology of magnetic levitation and magnetic levitation trains, which is applied to tracks, roads, buildings, etc., can solve problems such as unreliable reliability, long construction time, and land consumption, and achieve the effects of ensuring driving safety, shortening construction time, and saving construction land
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
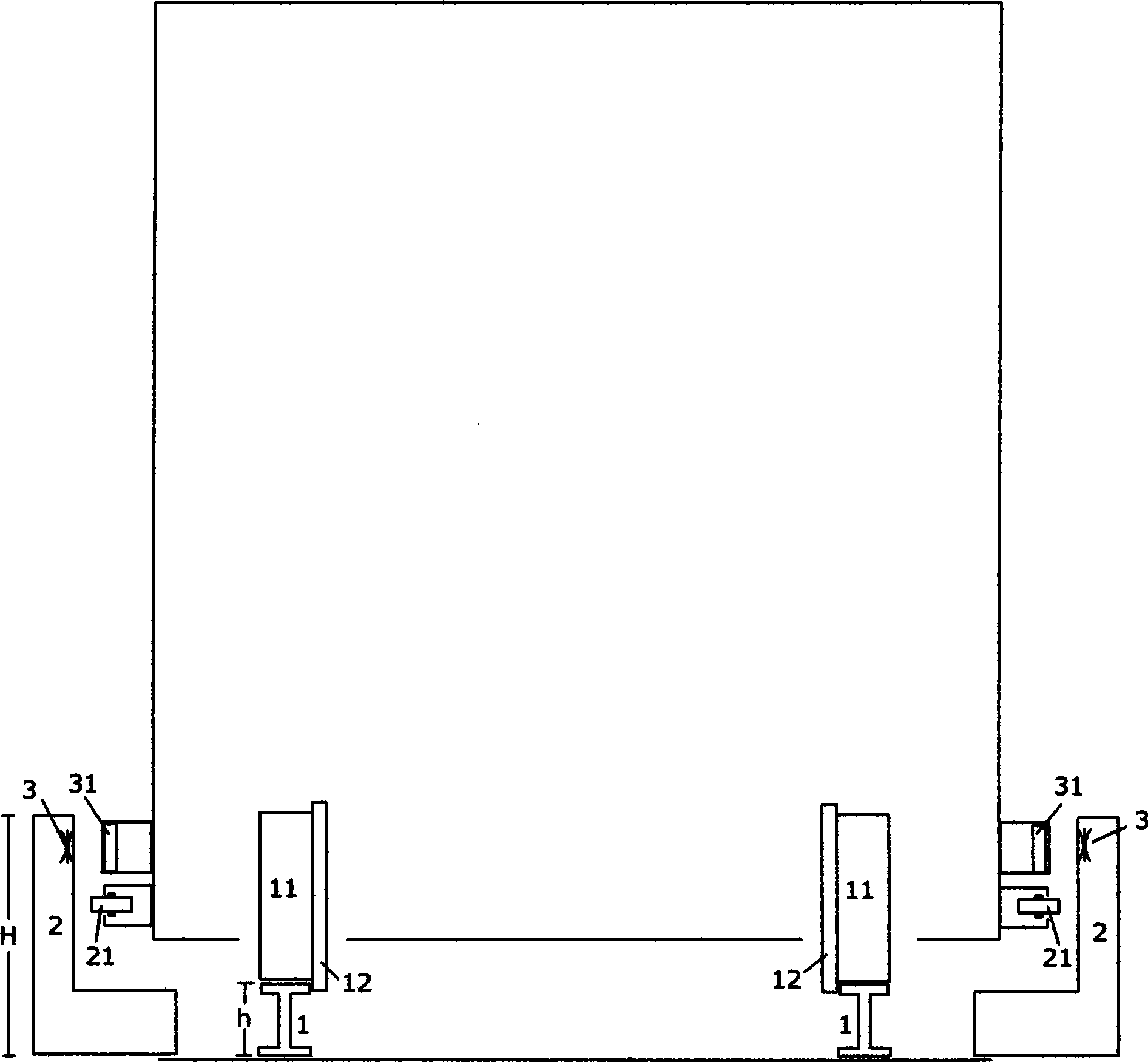
[0075] Figure 1A A cross-sectional view of a wheel-rail track with side rails and long stator windings and the corresponding wheel-rail train. Two parallel steel rails 1 are laid in the wheel-rail track, and a side rail 2 is arranged on the outside of the two steel rails 1. The inner wall of the side rail 2 is basically parallel to the steel rail 1, and the height H of the side rail 2 is greater than the height of the steel rail. h. The long stator winding 3 of the linear motor is installed and fixed on the side rail 2 and kept basically parallel to the rail 1 , and the long stator winding 3 is on the common plane of the two rails 1 .
[0076] The short rotor magnetic group 31 installed and fixed on the wheel-rail train and the long stator winding 3 installed and fixed on the side rail 2 correspond to each other and do not touch each other. The components that can be used for the short rotor magnetic group 31 include permanent magnets and normal wires. A coil electromagnet a...
Embodiment 2
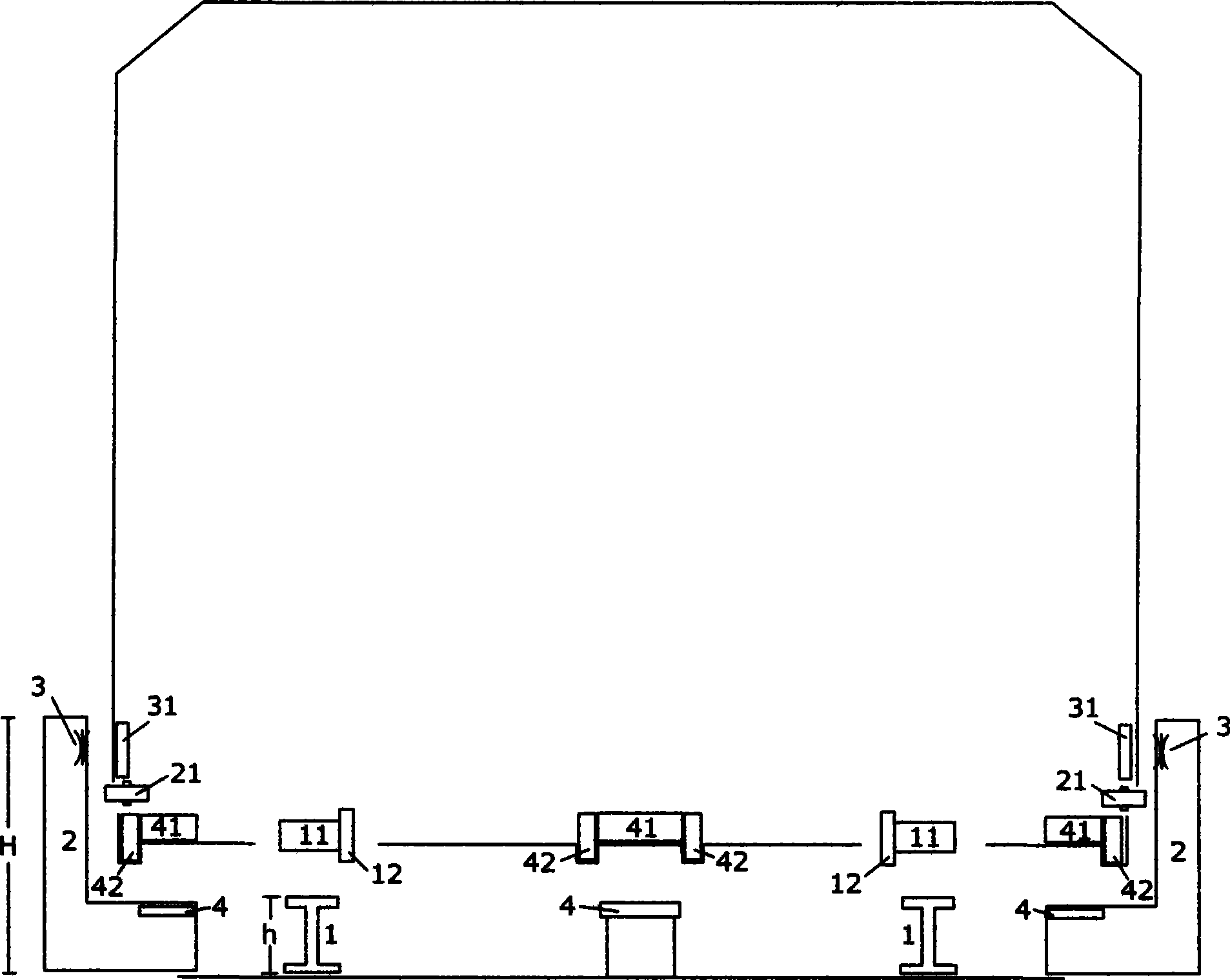
[0082] Figure 2A It is a sectional view of a wheel-rail maglev dual-purpose track and a corresponding maglev train. Two parallel steel rails 1 are laid in the wheel-rail magnetic levitation dual-purpose track shown in Figure 2, and side rails 2 are arranged on the outer sides of the two steel rails 1. The height H of 2 is greater than the height h of the rail. The long stator winding is inside the ferromagnetic track. The ferromagnetic track is made of steel, iron, nickel, cobalt or its alloy materials. The long stator winding and the ferromagnetic track together form the suspension drive track 5, and the suspension drive track 5 is located on two steel rails 1 On the common plane, the suspension drive track 5 and the steel rail 1 are basically kept parallel to each other, and the suspension drive track 5 is installed and fixed on the side rail and is located between the suspension guide drive magnetic group A 51 and the suspension guide drive magnetic group B 52 .
[0083...
Embodiment 3
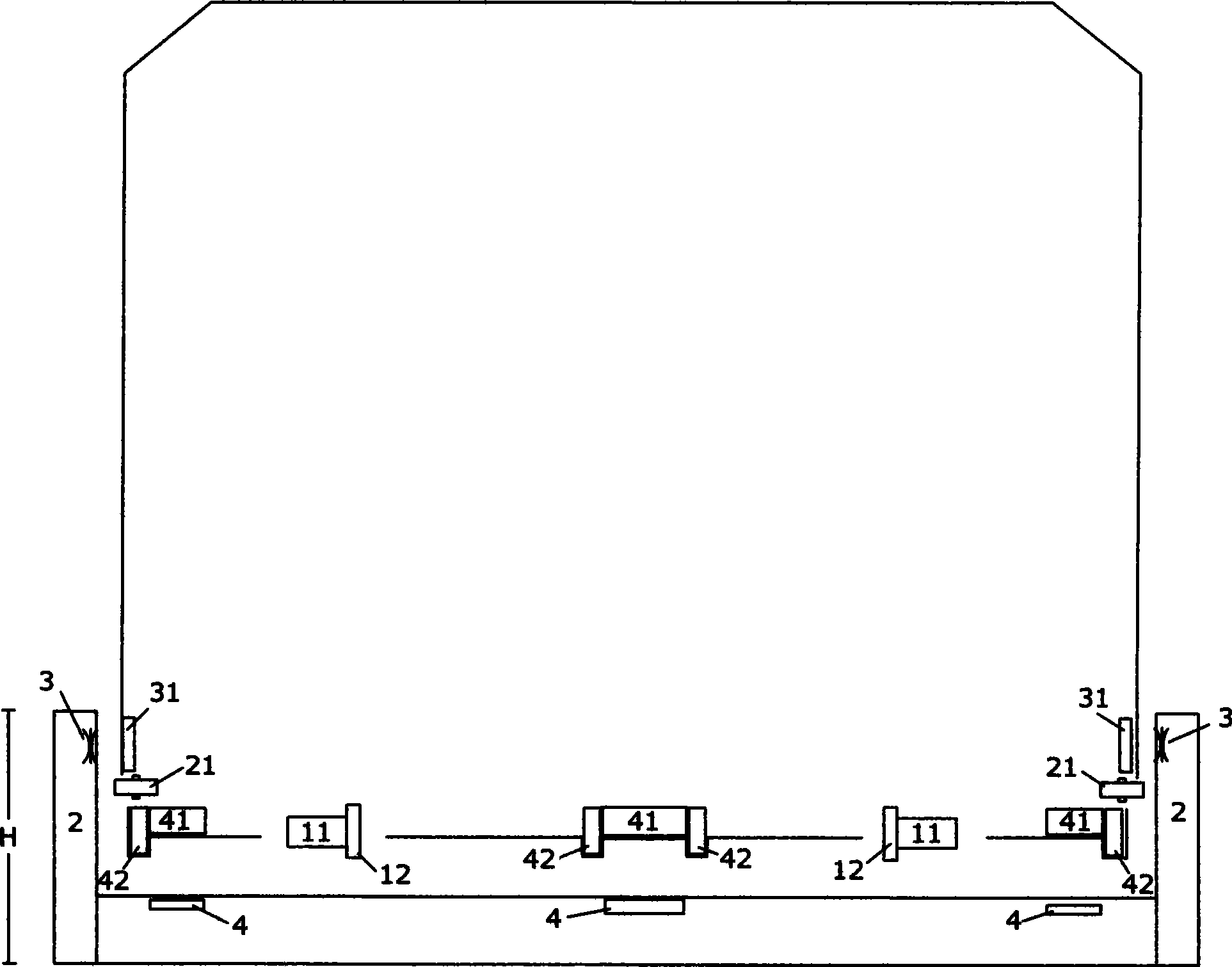
[0086] image 3 It is a sectional view of a wheel-rail maglev dual-purpose track and a corresponding maglev train. Two parallel steel rails 1 are laid in the wheel-rail track, and a side rail 2 is arranged on the outside of the two steel rails 1. The inner wall of the side rail 2 is basically parallel to the steel rail 1, and the height H of the side rail 2 is greater than the height of the steel rail. h. The long stator winding is inside the ferromagnetic track. The ferromagnetic track is made of steel, iron, nickel, cobalt or its alloy materials. The long stator winding and the ferromagnetic track together form the suspension driving track 6. The suspension driving track 6 is located on two steel rails 1 On the common plane, the suspension driving track 6 and the steel rail 1 are basically kept parallel to each other, and the suspension driving track 6 is installed and fixed on the side rail 2 . The guide track 7 installed on the side rail is basically parallel to the rail...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com