Chemical degumming technique for pineapple leaf fiber
A technology of pineapple leaf fiber and chemical degumming, which is applied in the direction of producing bast fiber by chemical method, can solve the problems of inability to apply production, the fiber is not soft enough, and there is no degumming technology of pineapple leaf fiber, etc., which is beneficial to spinning and fiber fineness. High, consistent effect of fiber molecular length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
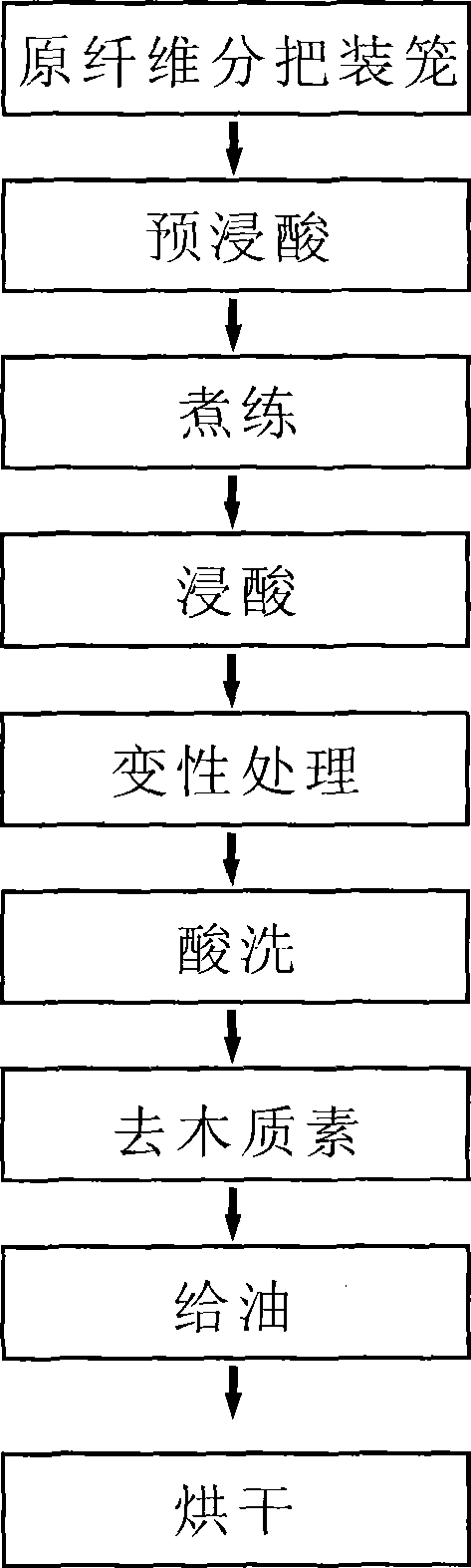
[0025] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of pineapple leaf fiber chemical degumming process is characterized in that adopting the following steps:
[0026] (1) The fibrils are divided into cages, and each cage is filled with 300kg of fibrils;
[0027] (2) Pre-soaking acid: put 300kg of fibrils into H with a concentration of 2.5g / L 2 SO 4 In the solution, the bath ratio is 1:15, soak at room temperature for 40min;
[0028] (2) Scouring: Put the fibrils into 4500kg of mixed solution, keep the pressure at 0.1MPa, and hold the pressure for 4 hours. The mixed solution is prepared by mixing liquid caustic soda with a concentration of 30%, trisodium phosphate and water glass. Wherein, the content of liquid caustic soda is 10g / L, the content of trisodium phosphate is 0.4g / L, and the content of water glass is 2g / L;
[0029] (3) Washing: rinse the scorched fiber with clear water until the pH value is 7;
[0030] (4) pickling: the fibrils are put into H2 with a concentration of 2.5g / L...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) The fibrils are divided into cages, and each cage is filled with 300kg of fibrils;
[0040] (2) Pre-soaking acid: put 300kg of fibrils into H at a concentration of 3.0g / L 2 SO 4 In the solution, the bath ratio is 1:16, soak at room temperature for 45min;
[0041] (3) Scouring: Put the fibrils into 4800kg of mixed solution, keep the pressure at 0.13MPa, and hold the pressure for 4.2 hours. The mixed solution is prepared by mixing liquid caustic soda with a concentration of 30%, trisodium phosphate and water glass. Wherein, the content of liquid caustic soda is 11g / L, the content of trisodium phosphate is 0.5g / L, and the content of water glass is 2.3g / L;
[0042] (4) Washing: rinse the scorched fiber with clear water until the pH value is 7;
[0043] (5) pickling: the fibrils are put into H2 with a concentration of 3.0g / L 2 SO 4 In the solution, the bath ratio is 1:16, soak for 20 minutes at room temperature;
[0044] (6) Denaturation: Put the fibrils into 4800...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) The fibrils are divided into cages, and each cage is filled with 300kg of fibrils;
[0053] (2) Pre-soaking acid: put 300kg of fibrils into H with a concentration of 3.5g / L 2 SO 4 In the solution, the bath ratio is 1:17, soak at room temperature for 50min;
[0054] (3) Scouring: Put the fibrils into 5100kg of mixed solution, keep the pressure at 0.15MPa, and hold the pressure for 4.5 hours. The mixed solution is prepared by mixing liquid caustic soda with a concentration of 30%, trisodium phosphate and water glass. Wherein, the content of liquid caustic soda is 12g / L, the content of trisodium phosphate is 0.6g / L, and the content of water glass is 2.5g / L;
[0055] (4) Washing: rinse the scorched fiber with clear water until the pH value is 7;
[0056] (5) pickling: the fibrils are put into H2 with a concentration of 3.5g / L 2 SO 4 In the solution, the bath ratio is 1:17, soak for 20min at room temperature;
[0057] (6) Denaturation: put the fibrils into 5100 kg o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com