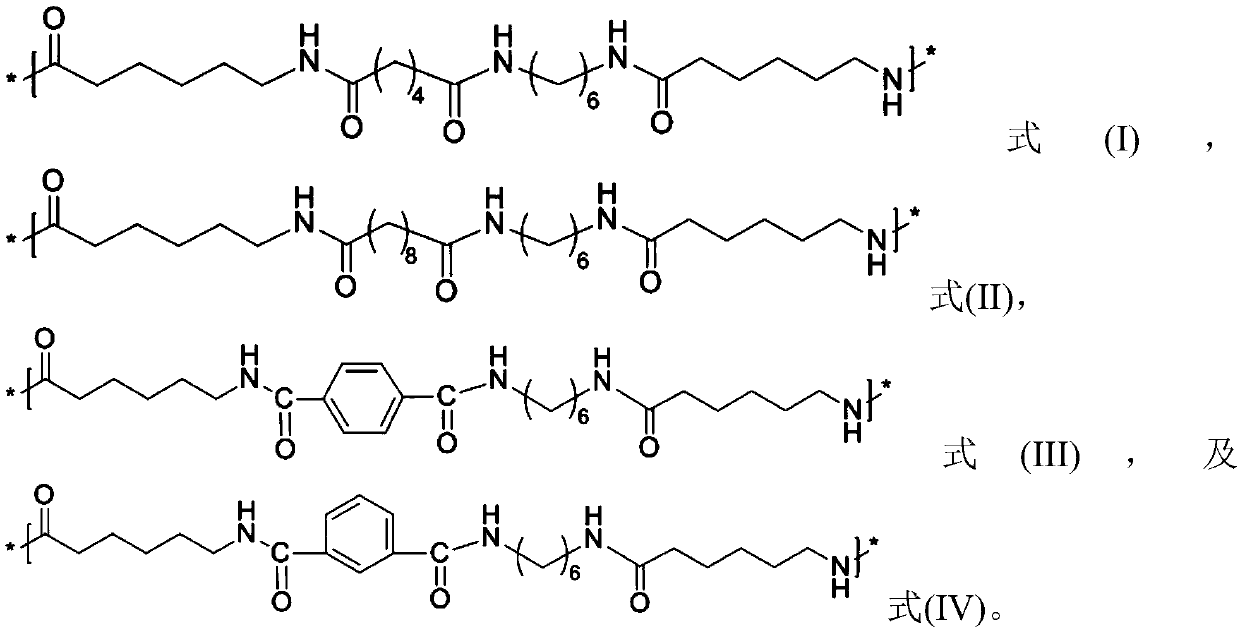
Nylon fiber and manufacturing method of nylon
A nylon fiber and fiber technology, which is applied in the direction of single-component copolyamide rayon, can solve the problems of limiting the applicability of nylon fibers, unable to meet the needs of products, and high melting point, so as to increase the glass transition temperature and improve the spinning. Processing workability and the effect of improving fiber strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0029] Experimental example 1: Synthesis of nylon and testing its properties
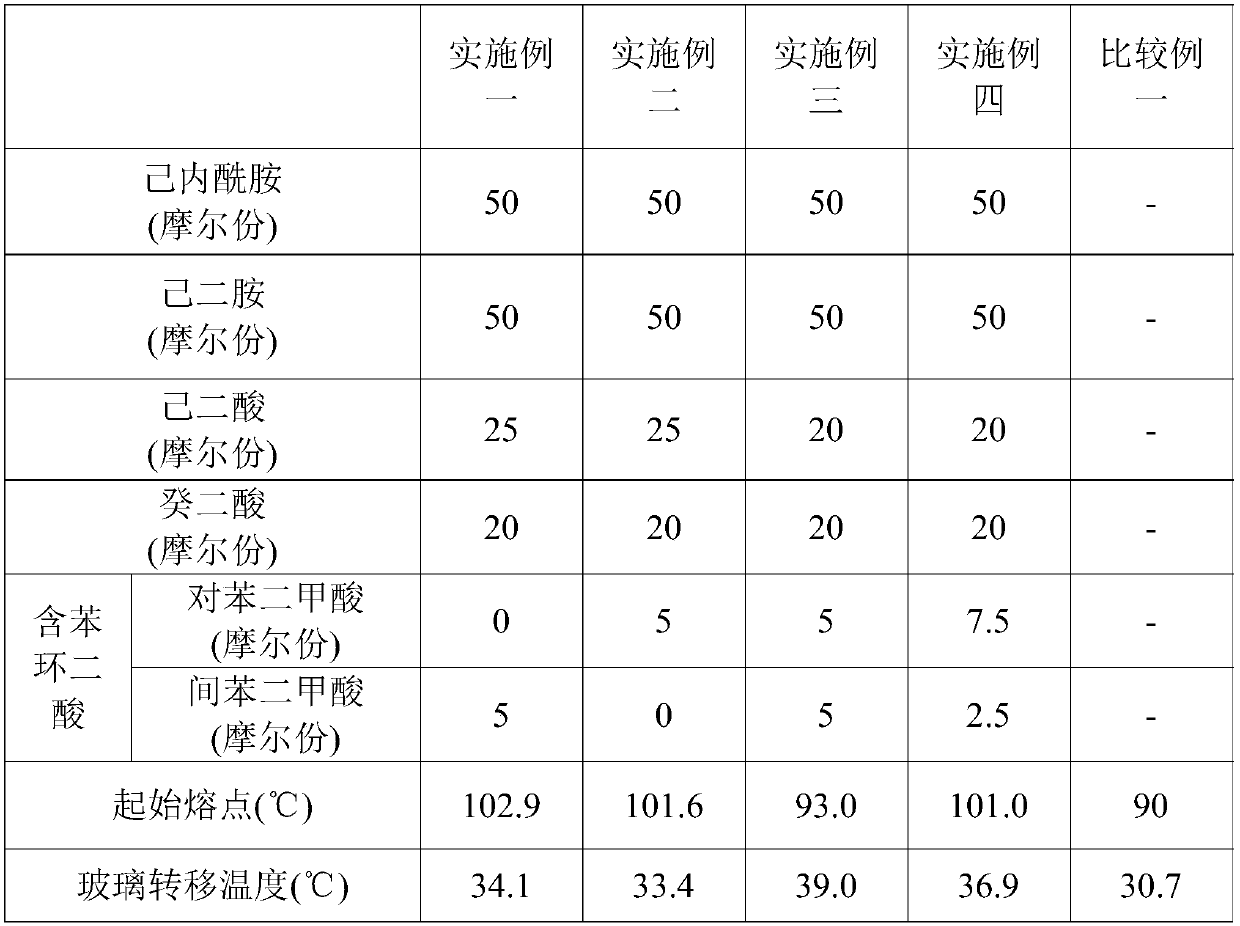
[0030] In this experimental example, 45 molar parts to 55 molar parts of caprolactam, 45 molar parts to 55 molar parts of hexamethylenediamine, 15 molar parts to 30 molar parts of adipic acid, 15 molar parts to 25 molar parts of decane Acid and 2 to 15 moles of benzene ring diacids are copolymerized to form nylon. In Examples 1 to 4, different combinations of reactants and different molar ratios of the reactants were selected for property testing. Comparative Example 1 is commercially available nylon with a low melting point. Please refer to Table 1 below for the initial melting points and glass transition temperatures of the reactants used in the examples and comparative examples and the products formed.
[0031] Table I
[0032]
[0033] In this experimental example, the properties of the products of Examples 1 to 4 and Comparative Example 1 were tested by differential scanning calorimetry (...
experiment example 2
[0034] Experimental example 2: rheological experiment
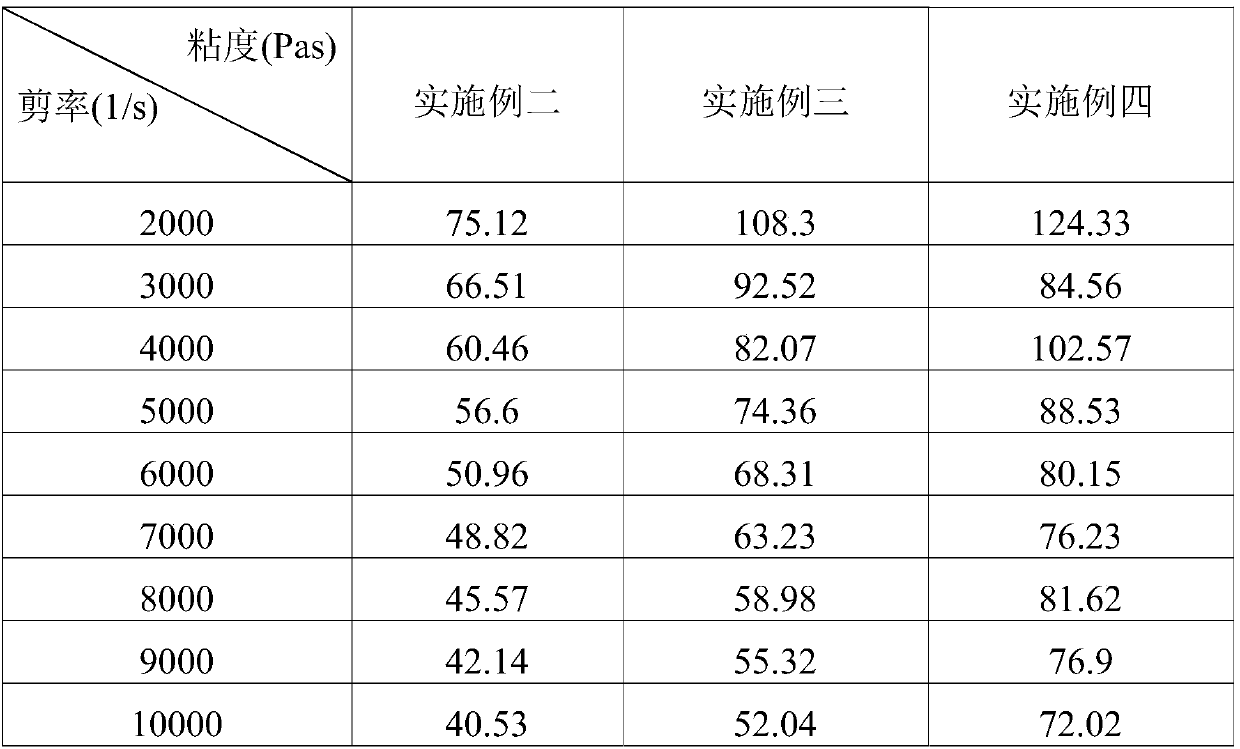
[0035] In this experimental example, the products of Example 2, Example 3 and Example 4 were analyzed by rheological experiments at a temperature of 250° C. Observe the viscosity of each product at different shear rates. Please refer to Table 2 below for the experimental results.
[0036] Table II
[0037]
[0038] It can be seen from the above Table 2 that when the shear rate is small, the viscosity of Embodiment 2, Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 4 is relatively large; on the contrary, when the shear rate is large, for example, the shear rate is 6000 to 10000 (1 / s) , Embodiment 2, Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 4 still have a viscosity of at least about 40 to 80 Pas. Since the shear rate usually reaches 6,000 to 10,000 (1 / s) during the spinning process, the above results show that the nylon of the present invention can meet the material requirements for melt spinning.
experiment example 3
[0039] Experimental Example 3: Drying Test
[0040] In this experimental example, common nylon 6 (PA6) and the products of Examples 1 to 4 were analyzed by dry test. Please refer to Table 3 below for the experimental results.
[0041] Table three
[0042]
[0043] Before nylon molding, it is usually necessary to dry the nylon particles to a moisture content of less than 0.1%, and then proceed to the melt spinning process. Generally, the drying time of the drying procedure is about 12 hours and the drying temperature is about 80°C to 90°C. According to the results in Table 3 above, it shows that the nylon of the present invention can be dried through the normal drying procedure without resetting the parameters of the drying procedure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com