Fault code storage management method for automobile active stabilization control system
A stability control and fault code technology, applied in the field of vehicle driving safety management system, can solve problems such as unfavorable fault repair and timely elimination of safety hazards, inability to store fault diagnosis result history records, and less information provided by accident repair, etc., to achieve the calculation cycle Short, simple algorithm, and the effect of improving reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
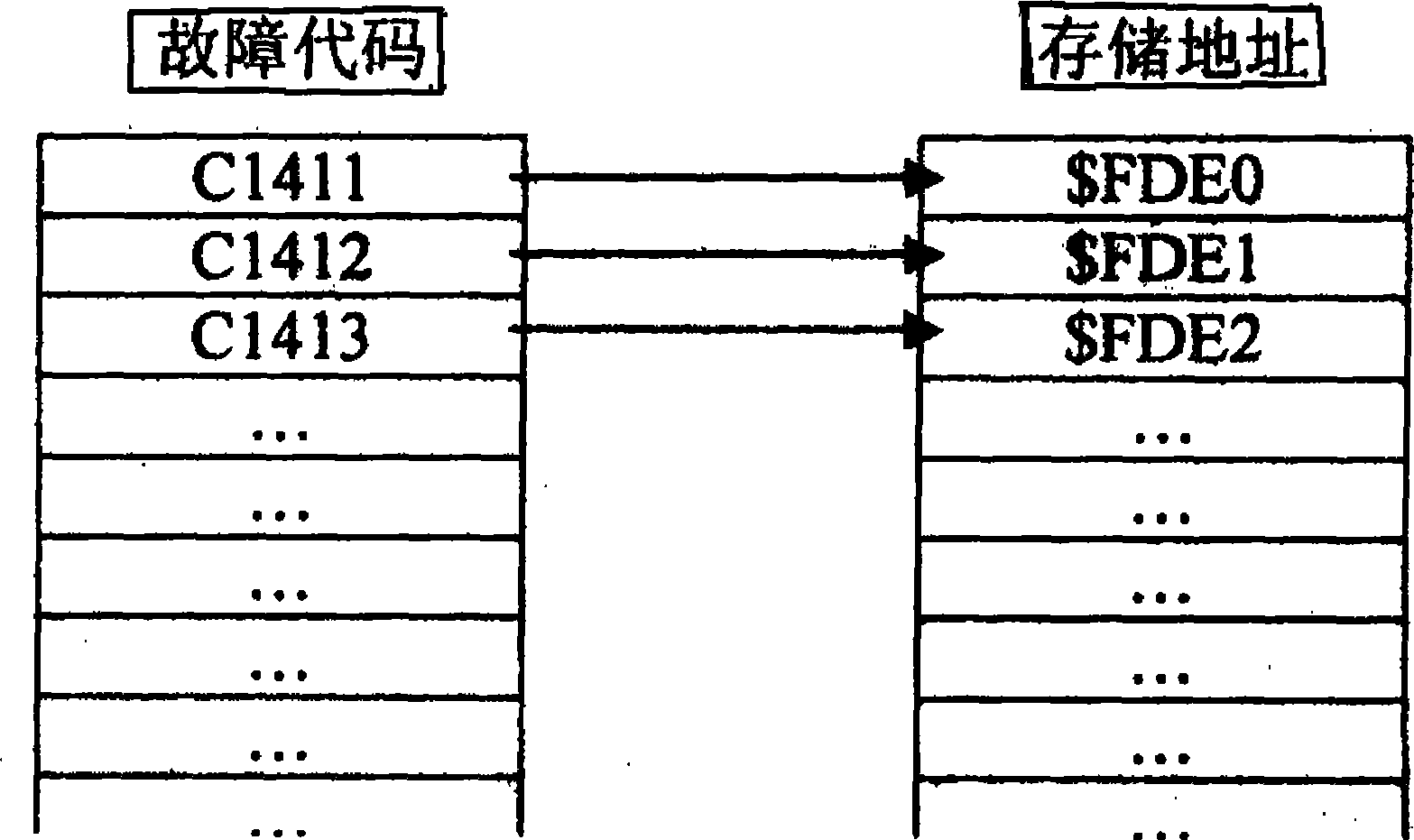
[0012] The ESP fault diagnosis system first determines the fault type of the diagnosed fault, and defines its fault code according to the fault type; the fault code corresponds to the address of a byte in the specified storage unit, that is, each fault in the ESP fault diagnosis system The codes all correspond to a designated storage unit address, which is beneficial to simplify the control program algorithm, code storage, transmission and reading. figure 1 As shown, an example is given to illustrate the correspondence between fault codes and storage addresses. For example, the storage address corresponding to fault code C1411 is $FDE0; the storage address corresponding to C1412 is $FDE1; the storage address corresponding to C1413 is $FDE2;
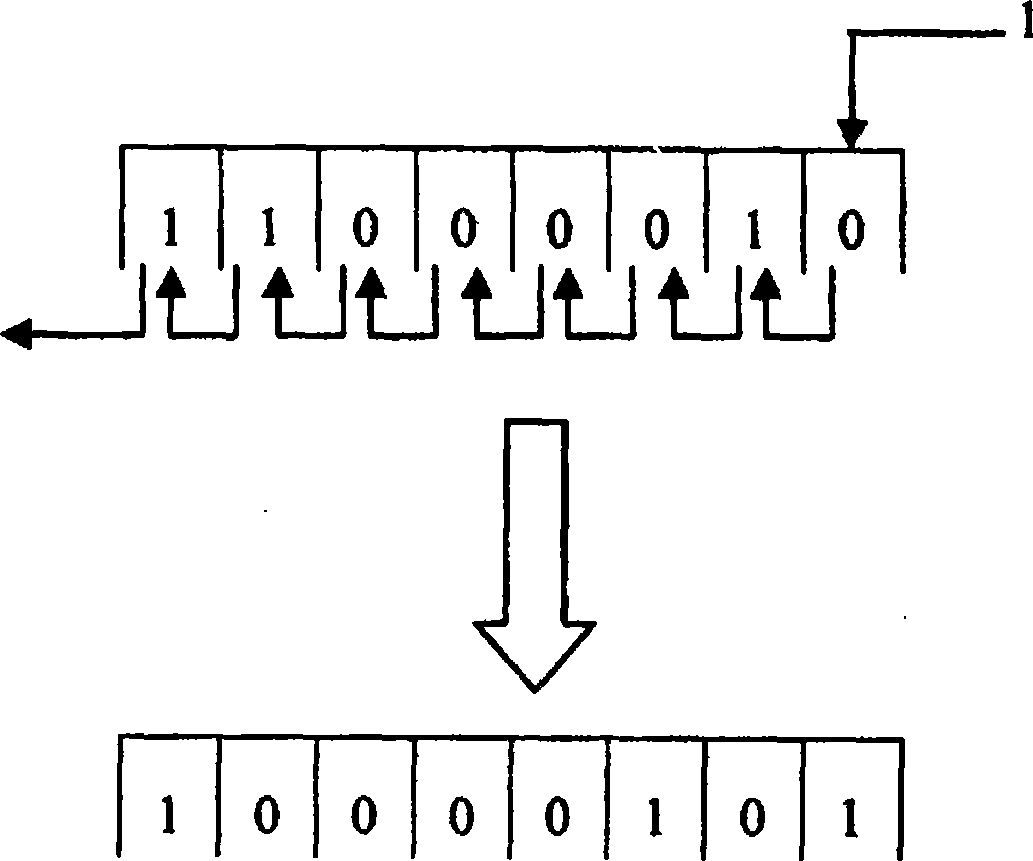
[0013] figure 2 As shown, it is an example of storing fault codes by bits. For the storage unit address corresponding to a t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com