Chinese syntax parsing method with merged semantic information
A technology of syntactic analysis and semantic information, which is applied in the fields of instruments, computing, and electronic digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as whether the description of language phenomena is accurate, data is sparse, etc., and achieve the effects of performance improvement, efficiency and accuracy improvement, and performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
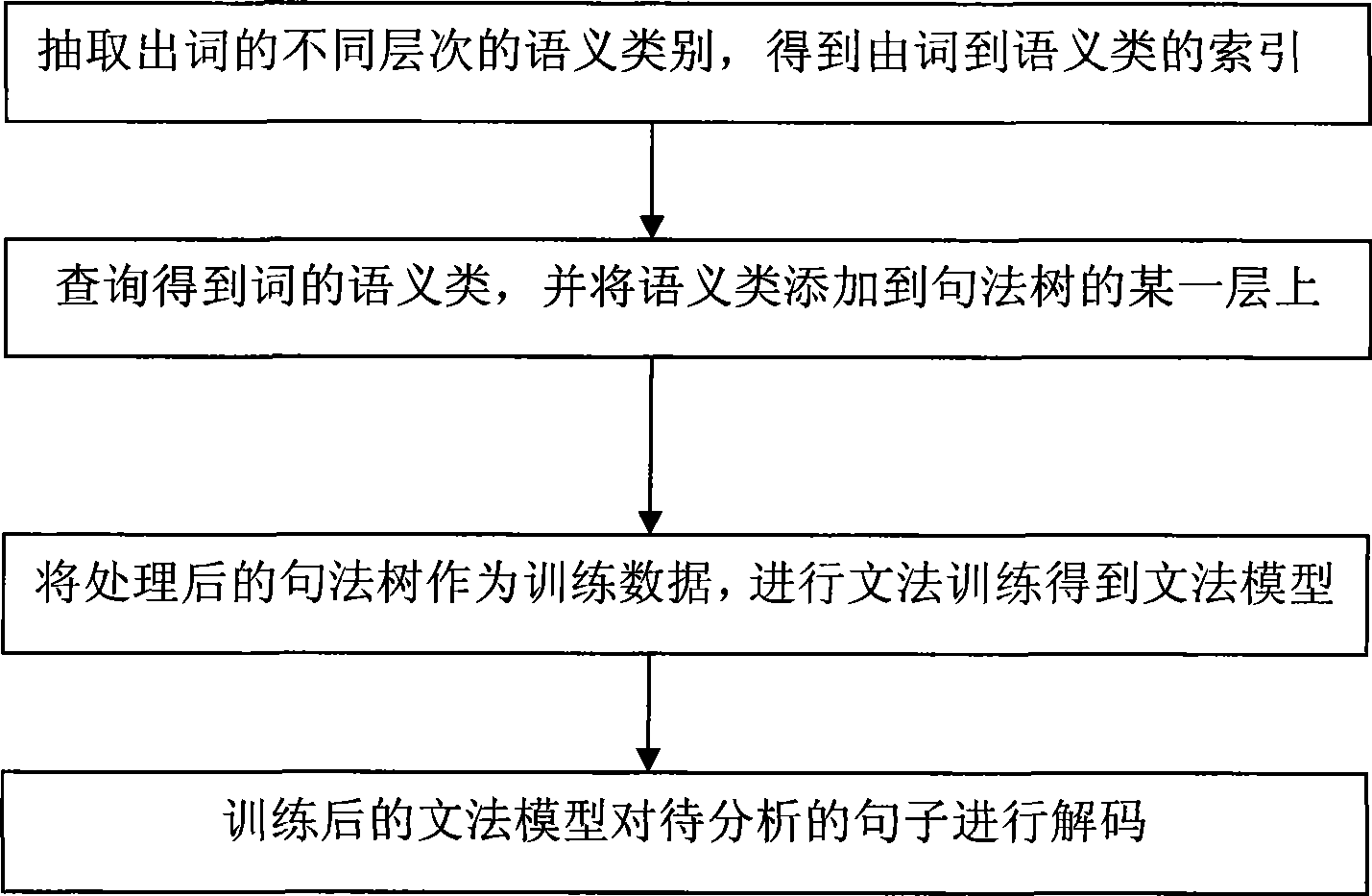
[0031] Describe the specific embodiment of the present invention in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the method flowchart of the present invention is as follows image 3 shown.
[0032] 1. Build a word-semantic index
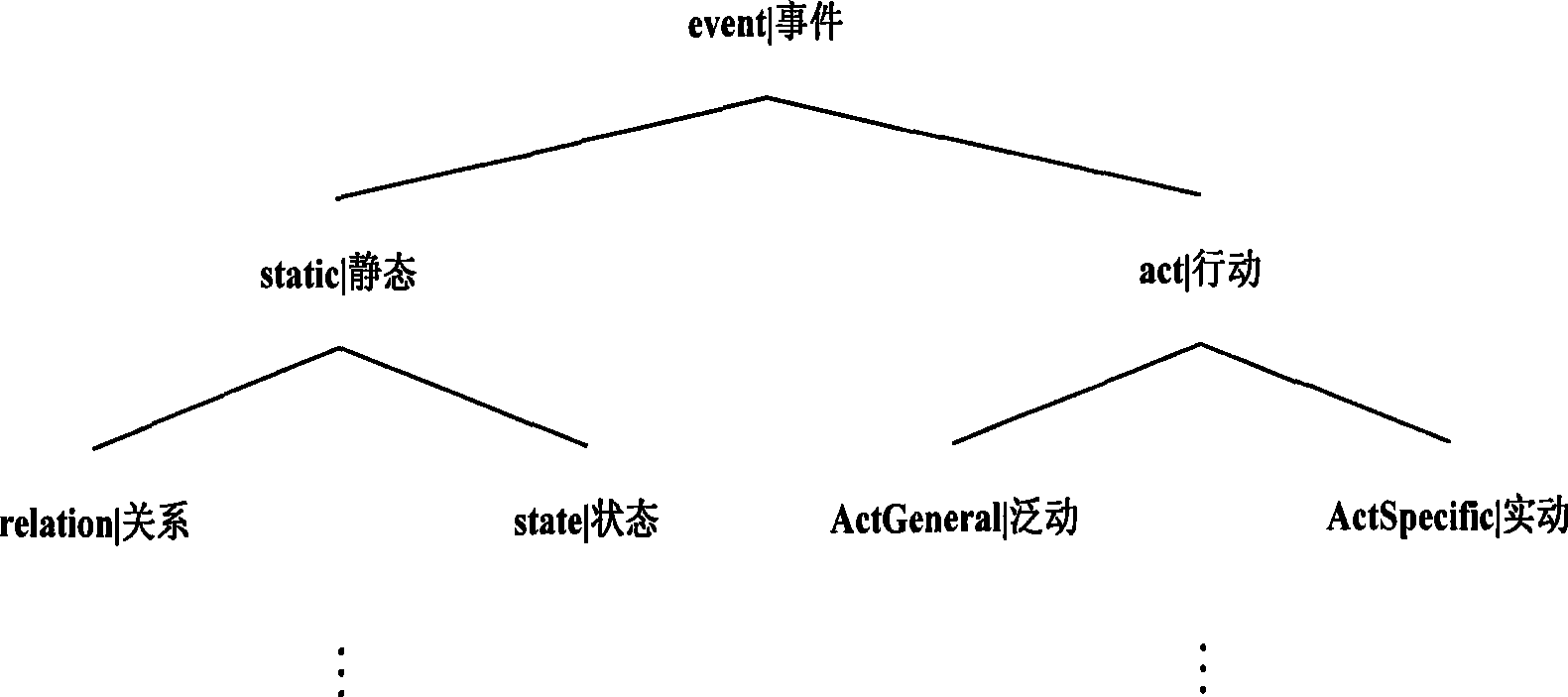
[0033] According to the hyponym relationship between sememes defined in HowNet, the semantic classes of different layers from coarse to fine are extracted, and correspond to each word, so as to construct the index from word to semantic class. The words here are accompanied by part-of-speech information.
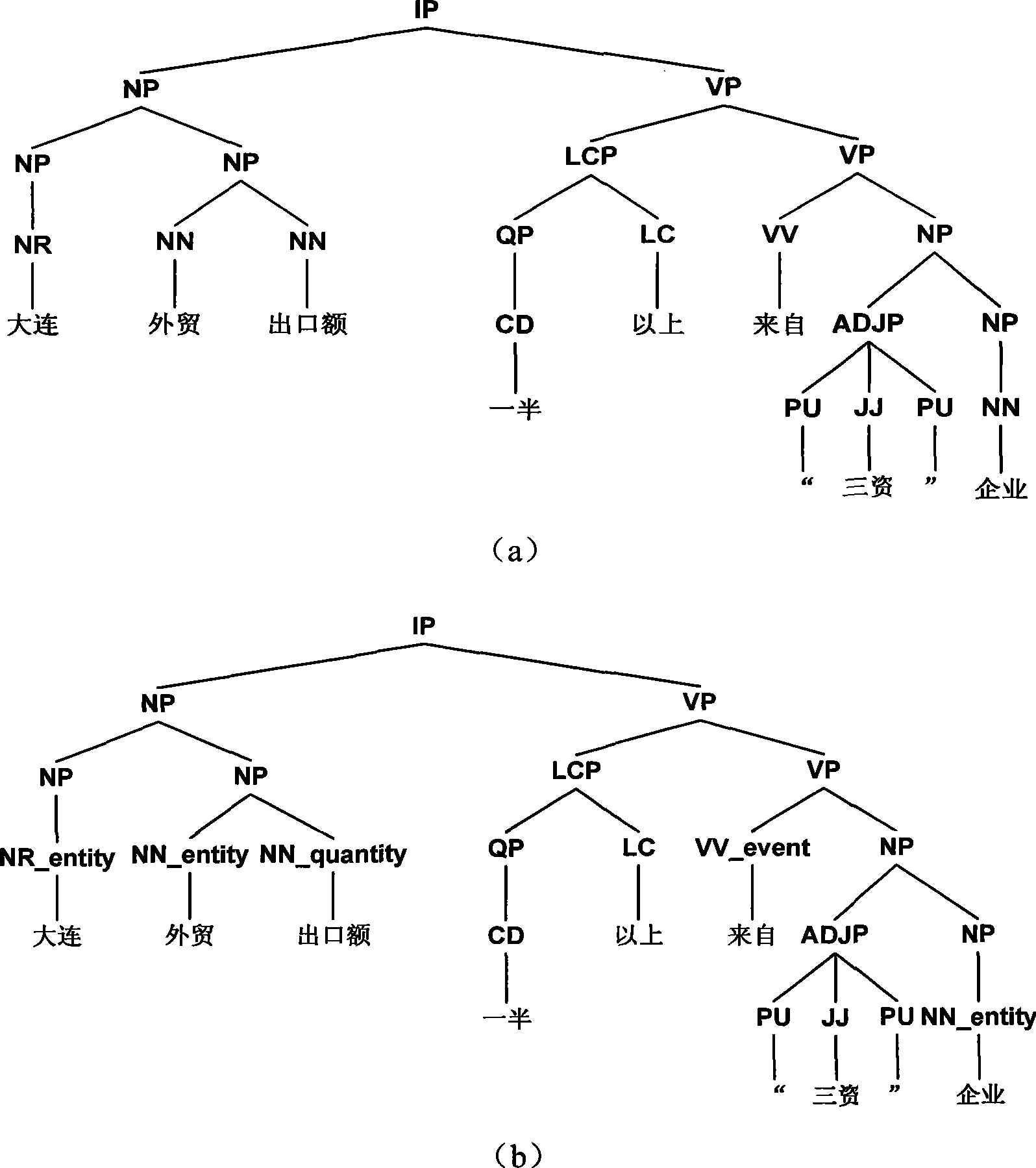
[0034] 2. Add semantic class information to the original tree bank
[0035] For the original tree bank, the semantic class information is obtained by using word and part of speech as the key value, and then the semantic class information is attached to the part of speech (pre-terminal) level to realize the refinement of the part of speech layer tag. Such parts of speech contain semantic information.
[0036] Some words may have multipl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com