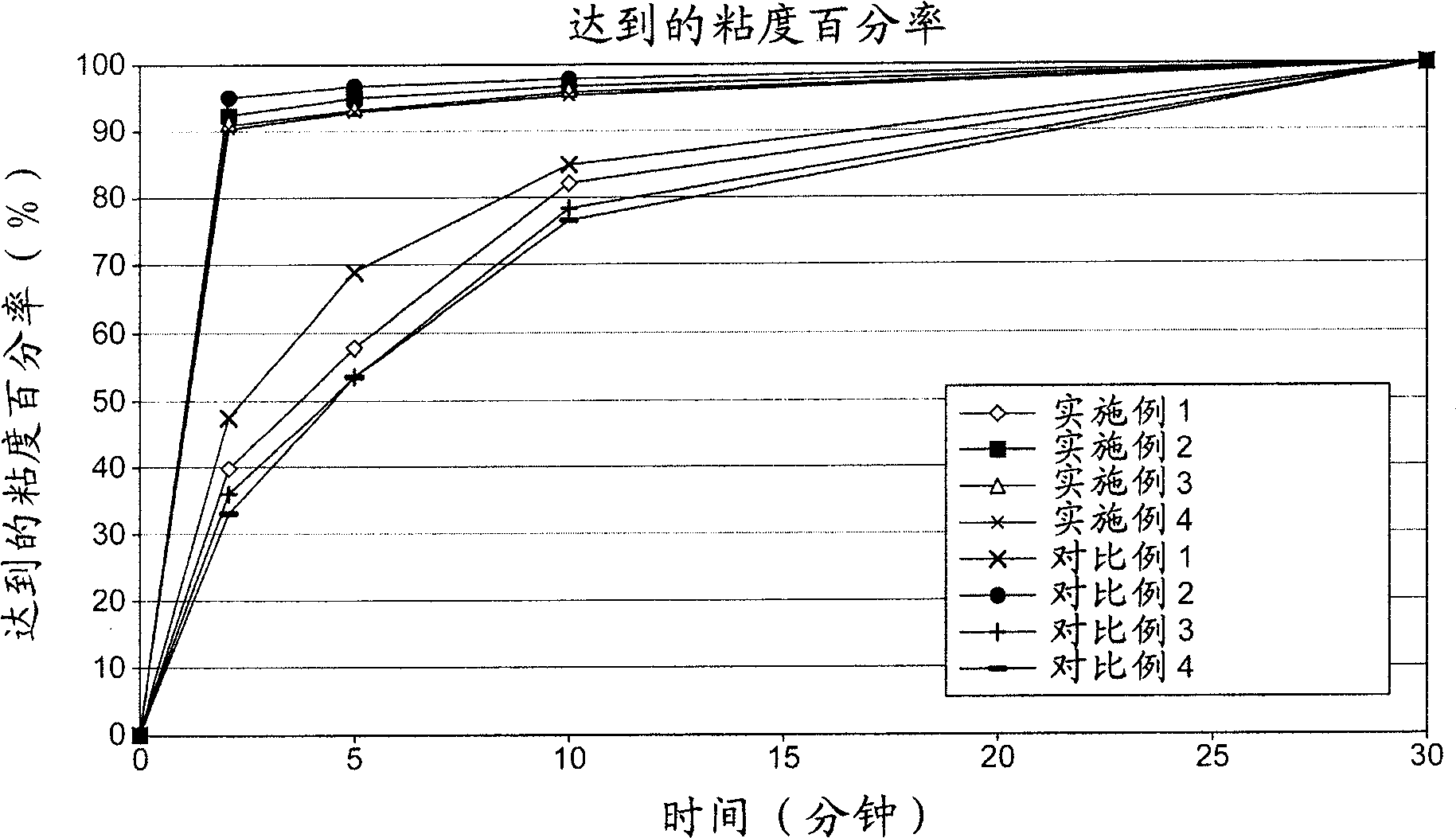
Thickening composition improved in viscosity development
A composition, technology of xanthan gum, applied in the direction of application, food science, food preparation, etc., can solve problems such as clumps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032]
[0033] A potassium chloride solution was prepared by stirring and dissolving potassium chloride (5 g) in 50° C. ion-exchanged water (95 g).
[0034]
[0035] Xanthan gum (100 g) was kept fluid and sprayed with potassium chloride solution (50 g). A xanthan gum composition (94.3 g) was obtained by fluid-drying the granules obtained after spraying was completed. The composition was filled in a 100 ml capacity container to the 100 ml position, and the weight of the filled particles was measured. The weight of the pellets was 41 g, and the bulk specific gravity thereof was 0.41 g / ml. Further, by vibrating the obtained pellets (20 g) for 30 seconds on a Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) 150 mm inner diameter 60-mesh sieve (Octagon 200, produced by (K K) Iida Seisakusho; vibration width 2-3 mm, 3600 vibrations / minute) To determine the degree of binding of the particles, the result was that 2.04 g of 20 g of powder passed through 60 mesh, and the percentage of xanthan ...
Embodiment 2
[0037]
[0038] A sodium chloride solution was prepared by stirring and dissolving sodium chloride (5 g) in 50° C. ion-exchanged water (95 g).
[0039]
[0040] Xanthan gum (100 g) was kept fluid and sprayed with sodium chloride solution (50 g). A xanthan gum composition (93.4 g) was obtained by fluid-drying the granules obtained after spraying was completed. The composition was filled in a 100 ml capacity container to the 100 ml position, and the weight of the filled particles was measured. The pellets weighed 46 g and had a bulk specific gravity of 0.46 g / ml. Furthermore, the degree of binding of the obtained granules (20 g) was determined in a similar manner to Example 1, and it was found that 2.26 g of 20 g of powder passed through 60 mesh, and the percentage of xanthan gum having a low degree of sodium chloride binding was 11.3% by weight. The remaining 88.7% by weight was confirmed to be bound. On the other hand, the sodium contents in the granules after fluidized...
Embodiment 3
[0042]
[0043] A calcium lactate solution was prepared by stirring and dissolving calcium lactate (5 g) in 50° C. ion-exchanged water (95 g).
[0044]
[0045] Xanthan gum (100 g) was kept fluid and sprayed with calcium lactate solution (50 g). A xanthan gum composition (92.8 g) was obtained by fluid-drying the granules obtained after spraying was completed. The composition was filled in a 100 ml capacity container to the 100 ml position, and the weight of the filled particles was measured. The pellets weighed 48 g and had a bulk specific gravity of 0.48 g / ml. Furthermore, the degree of binding of the obtained granules (20 g) was determined in a similar manner to Example 1, and it was found that 2.45 g of 20 g of powder passed through 60 mesh, and the percentage of xanthan gum having a low degree of calcium lactate binding was 12.3% by weight. The remaining 87.7% by weight was confirmed to be bound. On the other hand, the calcium content in the granules after fluidized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com