Vertical type wind energy machine with rotary vanes with a plurality of cambered surfaces
A wind energy machine and leaf vertical technology, applied in the field of multi-arc rotary blade vertical wind energy machine, can solve the problems of difficult installation and maintenance, large floor space, low conversion efficiency, etc., and achieve high installation height, installation and maintenance Convenience and low conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
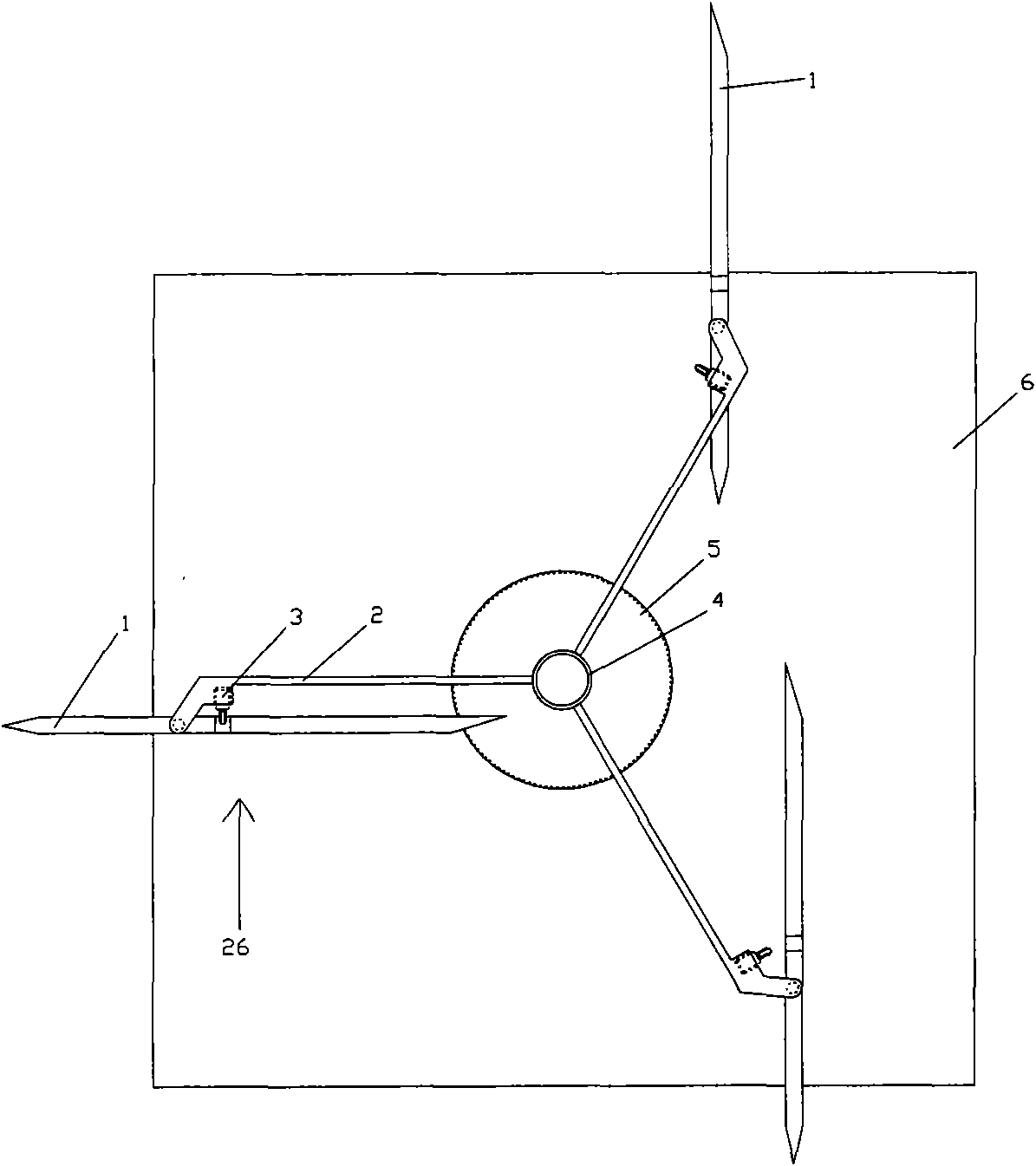
[0020] figure 1 It is a top view of a multi-arc rotary vane vertical wind energy machine: consisting of (1), multi-arc rotating blades, (2), a shaft beam, (3), a buffer protector, (4), a drive shaft, (5), Power output gear, (6), base composition.
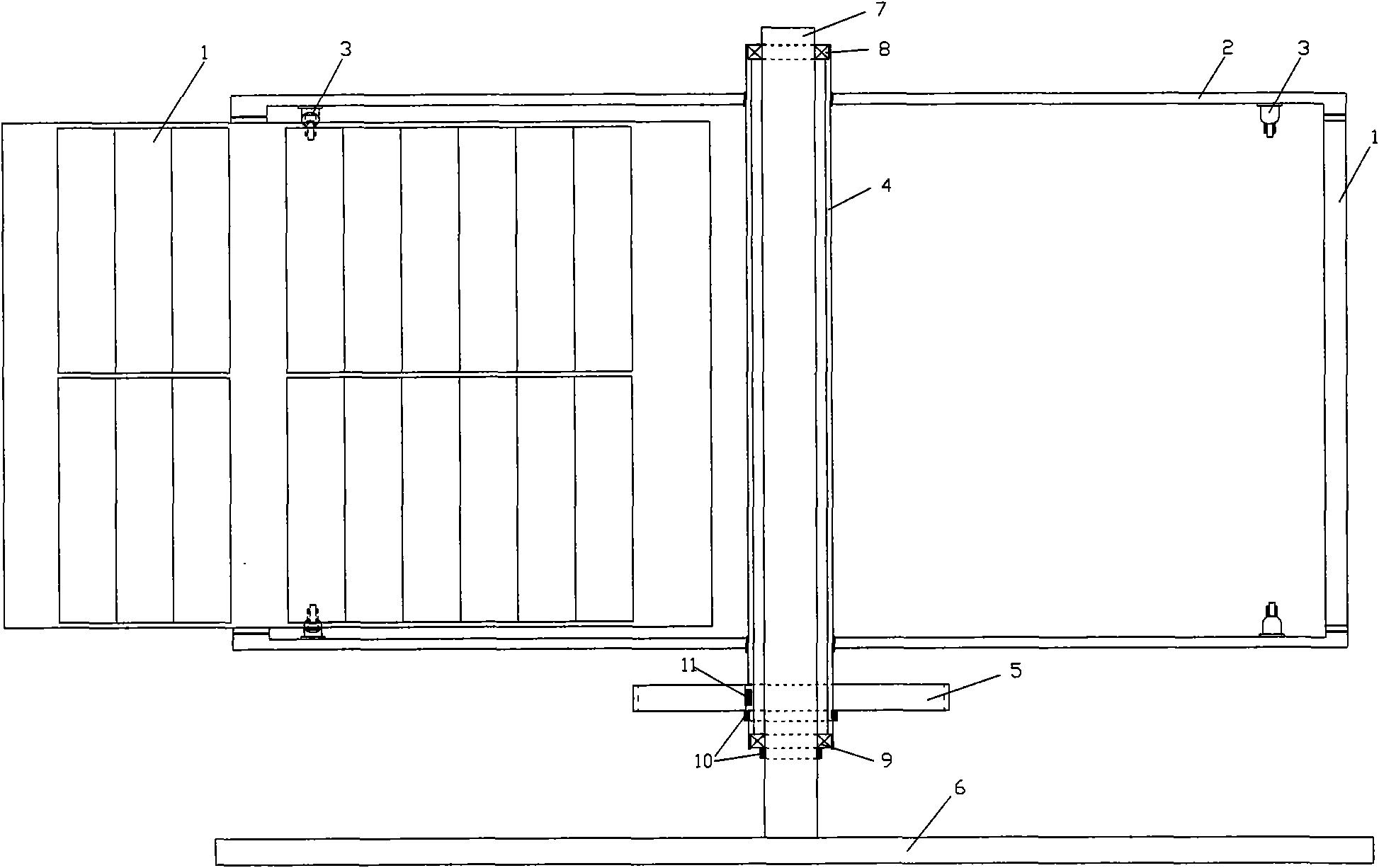
[0021] figure 2 It is the longitudinal section structural diagram of multi-arc rotary blade vertical wind energy machine: in the figure, (1), multi-arc rotating blade, (2), rotating shaft beam, (3), buffer protector, (4), transmission shaft , formed the rotor part, (6), the base, (7), and the vertical shaft formed the frame part, after installing (8), roller bearing, (9), tapered roller bearing, (10), retaining ring, (11 ), key, (5), and the power output gear form a multi-arc rotary vane vertical wind energy machine.
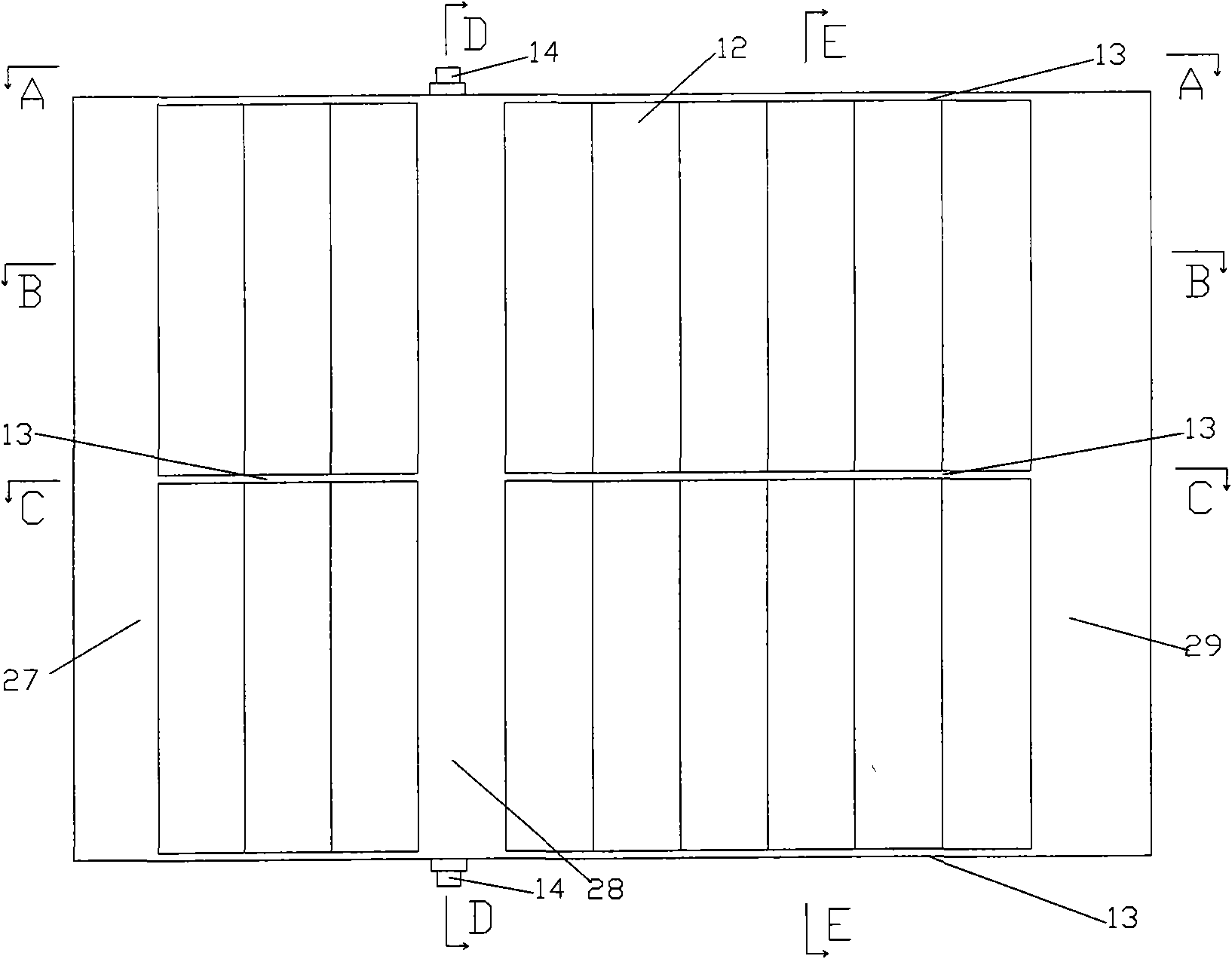
[0022] image 3 It is the plan view of multi-arc rotating blade: by (12), arc surface, (13), transverse rib, (14), blade shaft head, (27), front post, (28), middle post, (29) , The rear column is made of light, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com